What You'll Learn
This course introduces of fundamentals of cybersecurity making it ideal for absolute beginners.
Learn the core principles of securing digital systems, including threat detection, encryption, and risk management.
Cyber Security Online Course Gain an understanding of key security domains such as network security of data protection and access control.
Gain hands-on experience in ethical hacking, vulnerability scanning and incident handling.
Progress from fundamental security principles to advanced cybersecurity measures employed in actual applications.
Discover Cyber Security Online Training with guidance from experts and industry-based projects to enhance your skills.
Cyber Security Course Objectives
- Increased demand for cybersecurity experts across industries
- Growth cloud security and AI-driven security solution
- Rising need ethical hacker and penetration testers
- Expansion threat intelligence and risk management practices
- Greater focus on compliance with global security regulation
- Introduction Cyber Security and Threat Landscape
- Network Security and Firewalls
- Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing
- Security Operations and SIEM Tools
- Banking and Financial Services
- Information Technology
- Government
- Telecommunications
- Energy and Utilities
- Recognition as a certified cybersecurity professional
- Increased job opportunities in IT security ethical hacking, and risk management
- Hands-on experience in cybersecurity tools and threat analysis
Request more informations
WhatsApp (For Call & Chat):
+91 89259 58912
Cyber Security Course Benefits
The Cyber Security Certification Course covers threat detection, risk management and encryption techniques. Gain hands-on experience through a Cyber Security Internship while mastering network security. Get Cyber Security Placement Support and explore high-demand careers with competitive salaries. Contact us for cybersecurity course fees and start your journey today.
- Designation
-
Annual SalaryHiring Companies
About Your Cyber Security Certification Training
Our Cyber Security Online Training offers an affordable path to mastering cybersecurity fundamentals, threat detection, risk management, and encryption techniques we provide lucrative career opportunities and guaranteed placement support To Gain an hands-on experience by working on real-world cybersecurity projects an ensuring you develop practical skills to excel in the industry Start your journey today and build a successful career in Cyber Security Internship!
Top Skills You Will Gain
- Network Security
- Risk Management
- Threat Intelligence
- Cryptography Techniques
- Incident Response
- Security Auditing
- Malware Analysis
- Penetration Testing
- Cloud Security
12+ Cyber Security Tools
Online Classroom Batches Preferred
No Interest Financing start at ₹ 5000 / month
Self Paced Training
- 50+ Hours High-quality Video
- 28+ Downloadable Resource
- Lifetime Access and 24×7 Support
- Access on Your Computer or Mobile
- Get Certificate on Course Completion
- 3+ Projects
Corporate Training
- Customized Learning
- Enterprise Grade Learning Management System (LMS)
- 24x7 Support
- Enterprise Grade Reporting
Not Just Studying
We’re Doing Much More!
Empowering Learning Through Real Experiences and Innovation










Cyber Security Course Curriculum
Trainers Profile
At Learnovita, our Cyber Security training is led by certified experts with real-world experience in ethical hacking, network security, and threat management Learn from professionals who have worked with top global companies, handling complex security challenges Get hands-on training with an cybersecurity course material and industry-relevant insight build successful.
Syllabus for Cyber Security Online Training Download syllabus
- Basics of Cyber Security and its Importance
- Types of Cyber Threats and Attacks
- Cyber Security Terminologies
- Security Policies and Governance
- Cyber Laws and Compliance
- Basics of Networking and Protocols
- Firewalls, IDS, and IPS Concepts
- Virtual Private Networks
- Network Security
- Wireless Network Security
- Introduction to Ethical Hacking
- Phases of Penetration Testing
- Footprinting and Reconnaissance
- Scanning and Enumeration Techniques
- Exploitation and Gaining Access
- SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting
- Security Misconfigurations
- Broken Authentication and Session Management
- Secure Web Application Development
- Fundamentals of Cryptography
- Encryption and Decryption Methods
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Hashing Algorithms and Digital Signatures
- Secure Data Transmission Techniques
- Types of Malware: Virus, Ransomware, Trojans
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Solutions
- Sandboxing and Malware Detection Techniques
- Behavioral and Signature-Based Analysis
- Preventive Measures Against Malware Attacks
- Authentication and Authorization Concepts
- Multi-Factor Authentication
- Role-Based Access Control
- Privileged Access Management
- Identity Federation and Single Sign-On
- Cloud Security Fundamentals
- Secure Cloud Architecture
- Identity and Access Control in the Cloud
- Cloud Threats and Risk Management
- Security Controls in AWS, Azure, and GCP
- Understanding Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)
- Risk Assessment and Management Frameworks
- Threat Modeling Techniques
- Incident Detection and Mitigation Strategies
- Cybersecurity Compliance and Regulations
- Introduction to Security Operations Center (SOC)
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Log Analysis and Monitoring
- Threat Hunting Techniques
- Incident Handling and Response
Request more informations
WhatsApp (For Call & Chat):
+91 89259 58912
Industry Projects
Exam & Cyber Security Certification
- Basic understanding computer network and operating system
- Familiarity with network security cloud computing or scripting language
- Knowledge of IT infrastructure and cyber threat is beneficial
- No prior experience in cyber security required but technical background.
- Cyber Security Analyst
- Penetration Tester
- Network Security Engineer
- Cloud Security Engineer
- Risk and Compliance Analyst

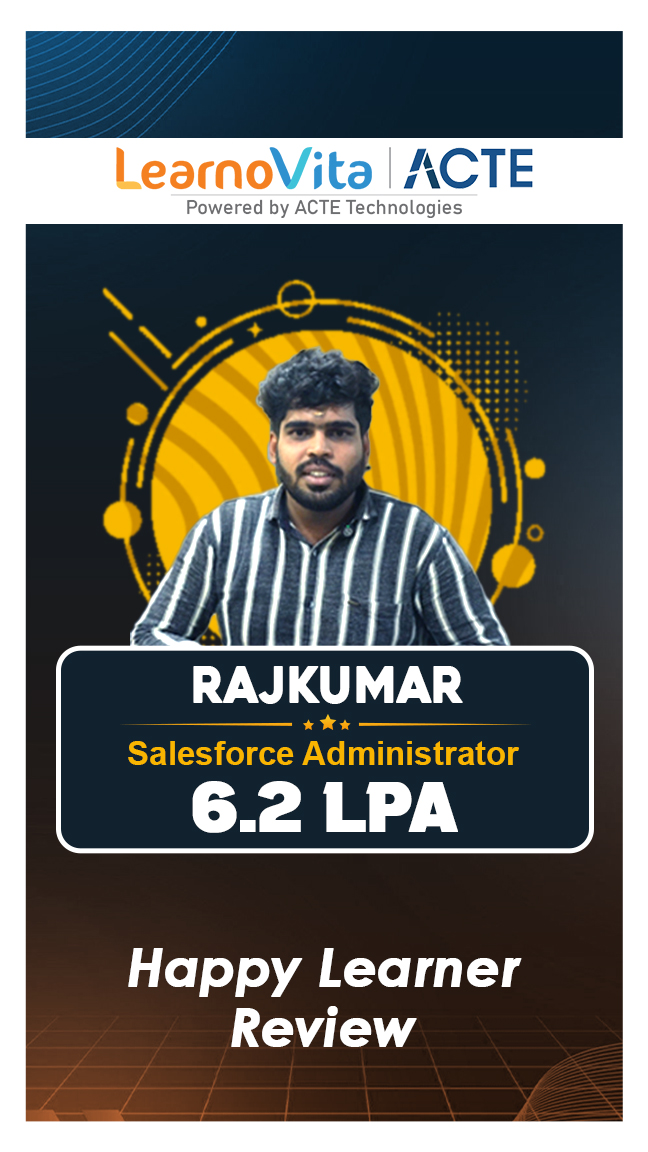
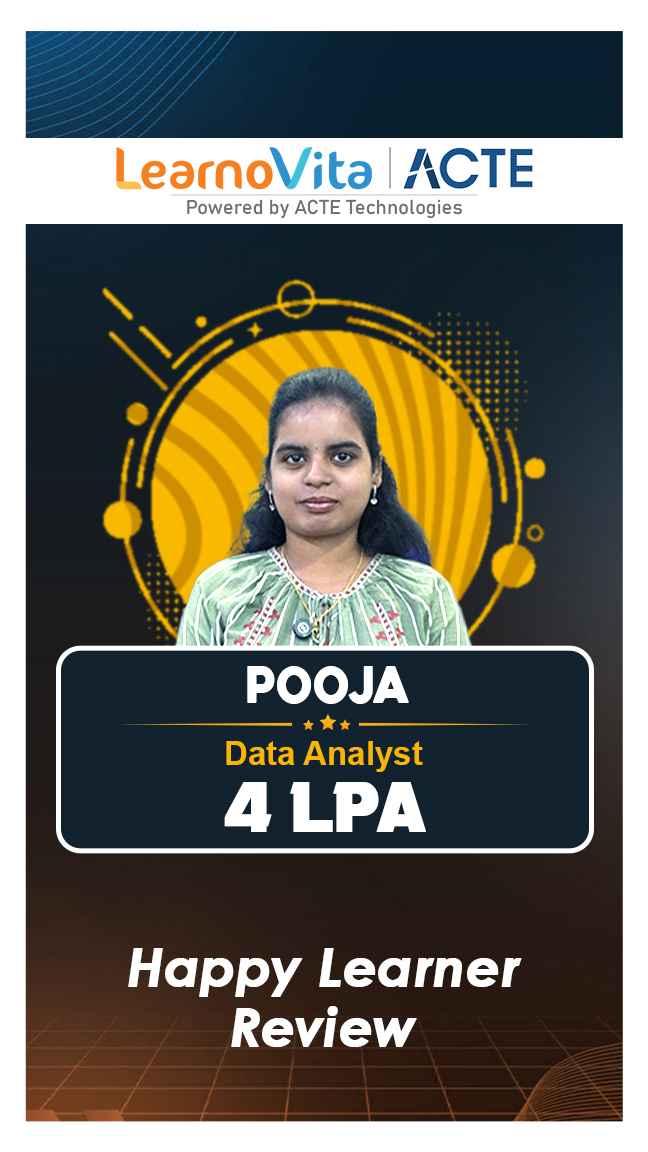
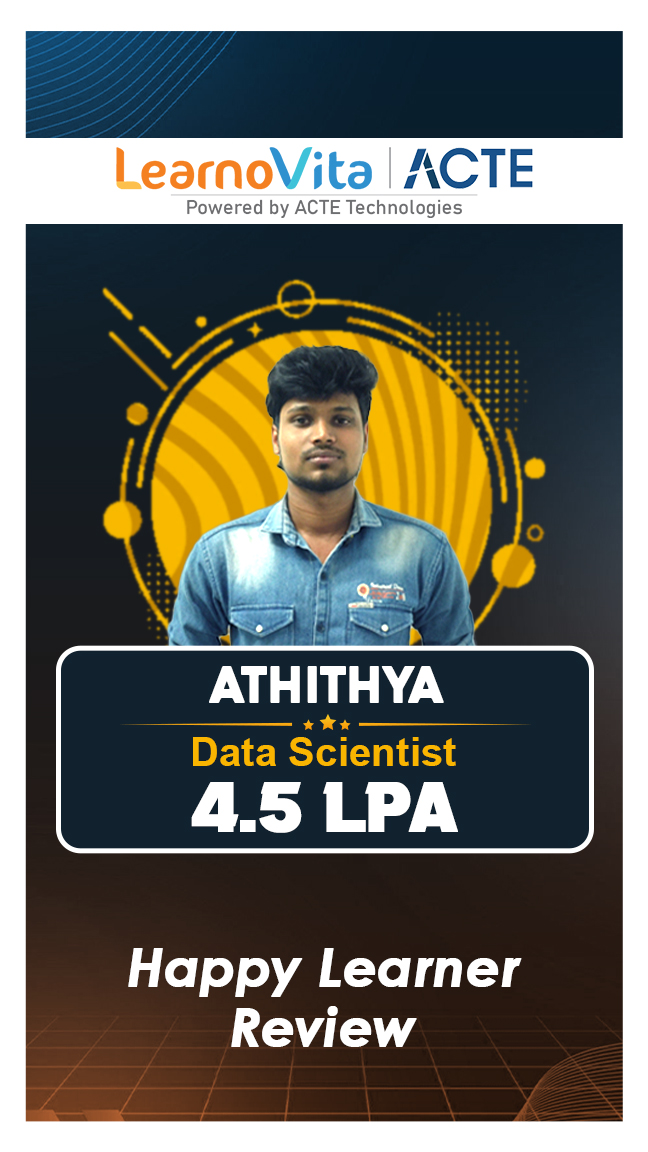
Our learners
transformed their careers

A majority of our alumni
fast-tracked into managerial careers.
Get inspired by their progress in the Career Growth Report.
Our Student Successful Story
How are the Cyber Security Course with LearnoVita Different?
Feature
LearnoVita
Other Institutes
Affordable Fees
Competitive Pricing With Flexible Payment Options.
Higher Cyber Security Fees With Limited Payment Options.
Live Class From ( Industry Expert)
Well Experienced Trainer From a Relevant Field With Practical Cyber Security Training
Theoretical Class With Limited Practical
Updated Syllabus
Updated and Industry-relevant Cyber Security Course Curriculum With Hands-on Learning.
Outdated Curriculum With Limited Practical Training.
Hands-on projects
Real-world Cyber Security Project With Live Case Studies and Collaboration With Companies.
Basic Projects With Limited Real-world Application.
Certification
Industry-recognized Cyber Security Certifications With Global Validity.
Basic Cyber Security Certifications With Limited Recognition.
Placement Support
Strong Placement Support With Tie-ups With Top Companies and Mock Interviews.
Basic Placement Support
Industry Partnerships
Strong Ties With Top Tech Companies for Internships and Placements
No Partnerships, Limited Opportunities
Batch Size
Small Batch Sizes for Personalized Attention.
Large Batch Sizes With Limited Individual Focus.
Additional Features
Lifetime Access to Cyber Security Course Materials, Alumni Network, and Hackathons.
No Additional Features or Perks.
Training Support
Dedicated Mentors, 24/7 Doubt Resolution, and Personalized Guidance.
Limited Mentor Support and No After-hours Assistance.
Cyber Security Course FAQ's
- LearnoVita is dedicated to assisting job seekers in seeking, connecting, and achieving success, while also ensuring employers are delighted with the ideal candidates.
- Upon successful completion of a career course with LearnoVita, you may qualify for job placement assistance. We offer 100% placement assistance and maintain strong relationships with over 650 top MNCs.
- Our Placement Cell aids students in securing interviews with major companies such as Oracle, HP, Wipro, Accenture, Google, IBM, Tech Mahindra, Amazon, CTS, TCS, Sports One , Infosys, MindTree, and MPhasis, among others.
- LearnoVita has a legendary reputation for placing students, as evidenced by our Placed Students' List on our website. Last year alone, over 5400 students were placed in India and globally.
- We conduct development sessions, including mock interviews and presentation skills training, to prepare students for challenging interview situations with confidence. With an 85% placement record, our Placement Cell continues to support you until you secure a position with a better MNC.
- Please visit your student's portal for free access to job openings, study materials, videos, recorded sections, and top MNC interview questions.

- Build a Powerful Resume for Career Success
- Get Trainer Tips to Clear Interviews
- Practice with Experts: Mock Interviews for Success
- Crack Interviews & Land Your Dream Job



 Fees Starts From
Fees Starts From



















 Regular 1:1 Mentorship From Industry Experts
Regular 1:1 Mentorship From Industry Experts





