What You'll Learn
Get a strong foundation in Java programming, object-oriented concepts, and database handling through the Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Training.
Learn front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern frameworks such as Angular and React for building interactive web interfaces.
Master backend development using Spring, Spring Boot, and REST APIs to create robust and scalable applications.
Gain practical experience in integrating databases, performing CRUD operations, and managing server-side logic efficiently.
Work on real-time projects, debugging, deployment, and version control to prepare for professional development roles.
Earn a professional certification in the Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Course to boost career opportunities in IT companies.
Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Objectives
- High demand for full-stack developers across IT, software, and startup sectors.
- Opportunities in cloud computing, microservices, and enterprise application development.
- Growth in AI, data-driven web applications, and remote software development roles.
- Core Java and Object-Oriented Programming
- Frontend: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Angular/React
- Backend: Spring, Spring Boot, REST APIs
- Database: MySQL, MongoDB
- Tools: Git, Maven, Docker
- IT Services and Software Development Companies
- E-commerce and Retail Tech
- FinTech and Banking Software
- Startups and Product-based Companies
- End-to-end skill development in full-stack technologies
- Hands-on project experience
- Improved employability in IT and software sectors
- Professional certification for career credibility
Request more informations
WhatsApp (For Call & Chat):
+91 76691 00251
Java Full Stack Developer Masters ProgramBenefits
The Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Course provides learners hands-on experience with frontend and backend development through real-time Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Projects. With expert guidance, students master frameworks, databases, and deployment workflows using comprehensive Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Course Materials. This Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Course With Placement and Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Certification Course prepares learners for IT roles with practical skills and industry-ready expertise.
- Designation
-
Annual SalaryHiring Companies
About Java Full Stack Developer Certification Training
The Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Training offers complete guidance in building and deploying web applications using modern Java technologies. Learners gain practical exposure through live Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Projects and real-time Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Internship, while utilizing comprehensive Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Course Materials. This program equips students with industry-ready skills for successful careers in IT and software development.
Skills You Will Gain
- Core Java
- Spring Boot Frameworks
- REST APIs Development
- Frontend
- Database
- Version Control
- DevOps Practices
- Debugging
12+ Java Full Stack Developer Tools
Online Classroom Batches Preferred
No Interest Financing start at ₹ 5000 / month
Corporate Training
- Customized Learning
- Enterprise Grade Learning Management System (LMS)
- 24x7 Support
- Enterprise Grade Reporting
Not Just Studying
We’re Doing Much More!
Empowering Learning Through Real Experiences and Innovation










Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Course Curriculam
Trainers Profile
Syllabus for Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Download syllabus
- Introduction to Java programming
- Data types, variables, and operators
- Object-Oriented Programming principles
- Exception handling and debugging techniques
- Collections framework
- Generics and annotations
- Java I/O and File Handling
- Multithreading and concurrency
- HTML5 structure and semantic tags
- CSS3 styling and layouts
- Responsive design techniques
- Flexbox and Grid systems
- JavaScript fundamentals and syntax
- DOM manipulation and events
- ES6 features and functions
- Asynchronous programming (Promises, Async/Await)
- Introduction to Angular/React frameworks
- Components, modules, and props
- Data binding and state management
- Routing and frontend navigation
- Introduction to Spring framework
- Dependency injection and configuration
- REST API creation using Spring Boot
- Handling requests and responses
- Introduction to MySQL and MongoDB
- Writing queries and managing tables
- CRUD operations and relationships
- Connecting databases with Java applications
- Introduction to Git and GitHub
- Commit, push, pull, and branch management
- Resolving merge conflicts
- Collaboration workflow techniques
- Introduction to Maven and Gradle
- Managing dependencies
- Packaging Java applications
- Deployment basics for web applications
- Introduction to Docker for containerization
- Jenkins for CI/CD basics
- Postman for API testing
- Unit testing and debugging tools
Request more informations
WhatsApp (For Call & Chat):
+91 76691 00251
Industry Projects
Exam & Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Certification
- Basic understanding of programming concepts or computer fundamentals
- Familiarity with HTML, CSS, or any programming language (optional)
- Willingness to learn both frontend and backend technologies
- Full Stack Developer
- Backend Java Developer
- Frontend Developer (Java/Angular/React)
- Software Engineer – Full Stack

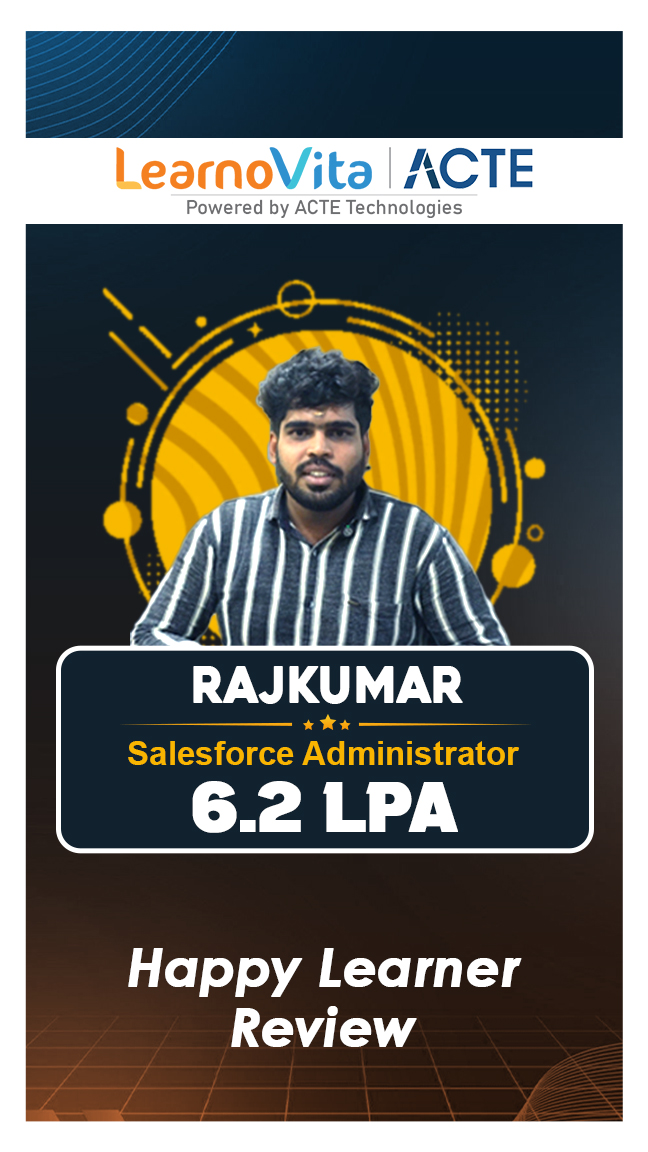
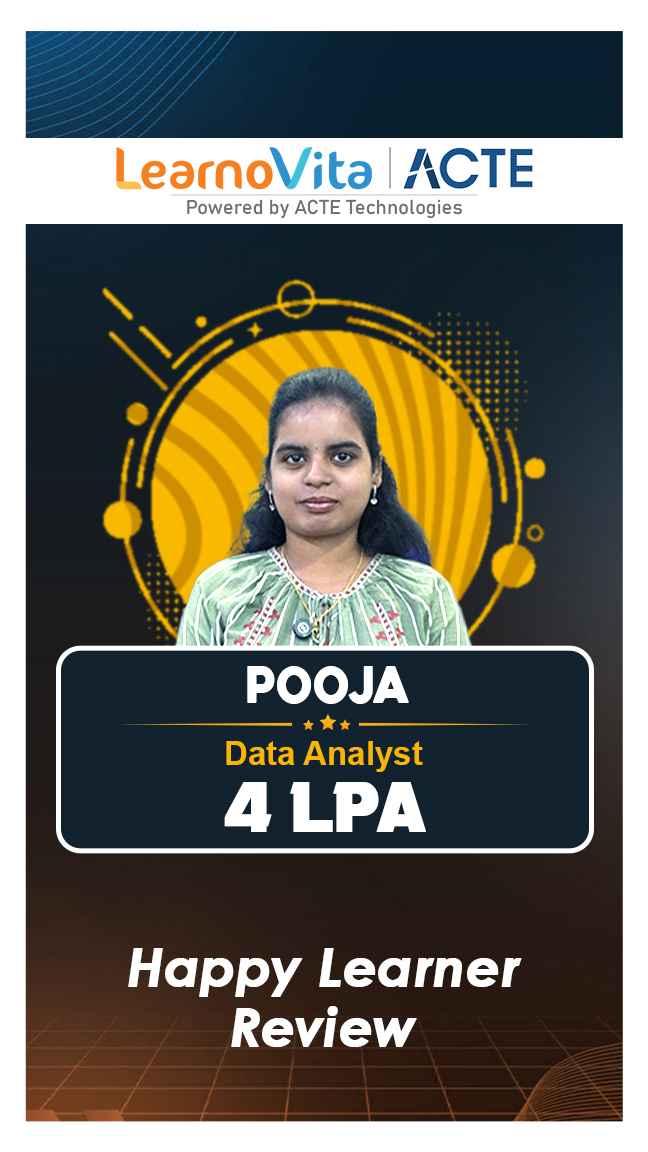
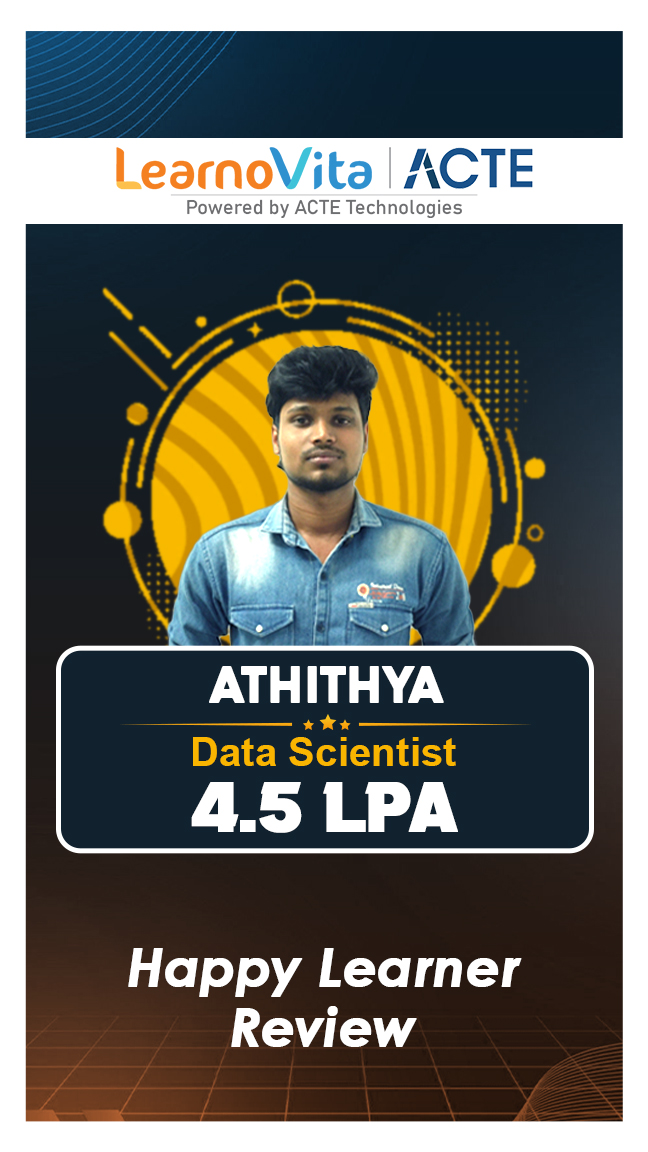
Our learners
transformed their careers

A majority of our alumni
fast-tracked into managerial careers.
Get inspired by their progress in the Career Growth Report.
Our Student Successful Story
How are the Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Course Training Course with LearnoVita Different?
Feature
LearnoVita
Other Institutes
Affordable Fees
Competitive Pricing With Flexible Payment Options.
Higher Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Course Training Course Fees With Limited Payment Options.
Live Class From ( Industry Expert)
Well Experienced Trainer From a Relevant Field With Practical Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Course Training Training
Theoretical Class With Limited Practical
Updated Syllabus
Updated and Industry-relevant Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Course Training Course Curriculum With Hands-on Learning.
Outdated Curriculum With Limited Practical Training.
Hands-on projects
Real-world Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Course Training Course Project With Live Case Studies and Collaboration With Companies.
Basic Projects With Limited Real-world Application.
Certification
Industry-recognized Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Course Training Certifications With Global Validity.
Basic Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Course Training Course Certifications With Limited Recognition.
Placement Support
Strong Placement Support With Tie-ups With Top Companies and Mock Interviews.
Basic Placement Support
Industry Partnerships
Strong Ties With Top Tech Companies for Internships and Placements
No Partnerships, Limited Opportunities
Batch Size
Small Batch Sizes for Personalized Attention.
Large Batch Sizes With Limited Individual Focus.
Additional Features
Lifetime Access to Java Full Stack Developer Masters Program Online Course Training Course Materials, Alumni Network, and Hackathons.
No Additional Features or Perks.
Training Support
Dedicated Mentors, 24/7 Doubt Resolution, and Personalized Guidance.
Limited Mentor Support and No After-hours Assistance.
Android App Developer Course FAQ's
- LearnoVita will assist the job seekers to Seek, Connect & Succeed and delight the employers with the perfect candidates.
- On Successfully Completing a Career Course with LearnoVita, you Could be Eligible for Job Placement Assistance.
- 100% Placement Assistance* - We have strong relationship with over 650+ Top MNCs, When a student completes his/ her course successfully, LearnoVita Placement Cell helps him/ her interview with Major Companies like Oracle, HP, Wipro, Accenture, Google, IBM, Tech Mahindra, Amazon, CTS, TCS, HCL, Infosys, MindTree and MPhasis etc...
- LearnoVita is the Legend in offering placement to the students. Please visit our Placed Students's List on our website.
- More than 5400+ students placed in last year in India & Globally.
- LearnoVita Conducts development sessions including mock interviews, presentation skills to prepare students to face a challenging interview situation with ease.
- 85% percent placement record
- Our Placement Cell support you till you get placed in better MNC
- Please Visit Your Student's Portal | Here FREE Lifetime Online Student Portal help you to access the Job Openings, Study Materials, Videos, Recorded Section & Top MNC interview Questions
- LearnoVita Certification is Accredited by all major Global Companies around the World.
- LearnoVita is the unique Authorized Oracle Partner, Authorized Microsoft Partner, Authorized Pearson Vue Exam Center, Authorized PSI Exam Center, Authorized Partner Of AWS.
- Also, LearnoVita Technical Experts Help's People Who Want to Clear the National Authorized Certificate in Specialized IT Domain.
- LearnoVita is offering you the most updated, relevant, and high-value real-world projects as part of the training program.
- All training comes with multiple projects that thoroughly test your skills, learning, and practical knowledge, making you completely industry-ready.
- You will work on highly exciting projects in the domains of high technology, ecommerce, marketing, sales, networking, banking, insurance, etc.
- After completing the projects successfully, your skills will be equal to 6 months of rigorous industry experience.
- We will reschedule the classes as per your convenience within the stipulated course duration with all such possibilities.
- View the class presentation and recordings that are available for online viewing.
- You can attend the missed session, in any other live batch.

- Build a Powerful Resume for Career Success
- Get Trainer Tips to Clear Interviews
- Practice with Experts: Mock Interviews for Success
- Crack Interviews & Land Your Dream Job



 Fees Starts From
Fees Starts From



















 Regular 1:1 Mentorship From Industry Experts
Regular 1:1 Mentorship From Industry Experts




