- Understanding Agile Methodologies and Principles | A Complete Tutorial
- What is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)? | Learn Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Traditional Project Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Complete Guide [STEP-IN]
- Total Productive Maintenance Tutorial | Get an Overview
- Virtual Team Tutorial – Learn Origin, Definition and its Scope
- The Rule of Seven in Project Management – Tutorial
- Make or Buy Decision – A Derivative Tutorial for Beginners
- What is Halo Effect? | Learn More through Tutorial
- Balanced Score Card Tutorial | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Supply Chain Management? | Tutorial with Examples
- Succession Planning Tutorial | A Complete Guide with Definitions
- What is Structured Brainstorming? | Quickstart & Learn the Tutorial
- Stress Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- What is a Statement of Work? | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Stakeholder Management? – The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- How to Create a Staffing Management Plan? | Learn from Tutorial
- What is Resource Leveling? | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Requirements Collection Tutorial: Gather Project Needs
- What Is a RACI Chart? | Learn with Example & Definitions
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control: Tutorial with Definitions & Differences
- Project Workforce Management Tutorial | A Definitive Guide
- Project Time Management Tutorial: Strategies, Tips & Tools
- Project Management Success Criteria Tutorial | Understand and Know More
- Identify Risk Categories in Project Management | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Project Records Management Tutorial | Quickstart -MUST READ
- Project Quality Plan (PQP) Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Project Portfolio Management | A Defined Tutorial for Beginners
- Goals of a Project Manager Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Project Management Triangle Tutorial: What It Is and How to Use
- Project Management Tools Tutorial | Learn Tools & Techniques
- What is PMO (project management office)? | A Complete Tutorial from Scratch
- Project Management Lessons | Learn in 1 Day [ STEP-IN ]
- What is a Project Kickoff Meeting? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Project Cost Management Tutorial | Steps, Basics, and Benefits
- Types of Contracts in Project Management | Learn with Examples
- Project Activity Diagram | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- What is Project Procurement Management? | Tutorial Explained
- Procurement Documents Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Process-Based Project Management Tutorial: A Beginner’s Guide
- What Is PRINCE2 Project Management? | A Definitive Tutorial for Beginners
- Effective Presentation Skills – Learn More through Tutorial
- Powerful Leadership Skills Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- PERT Estimation Technique Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Pareto Chart Tool Tutorial | Learn Analysis, Diagram
- Organizational Structure Tutorial: Definition and Types
- Negotiation Skills for Project Management | Learn from the Basics
- Monte Carlo Analysis in Project Management Tutorial | A Perfect Guide to Refer
- Effective Management Styles Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Management by Objectives (MBO) Tutorial | Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Leads, Lags & Float – Understand the Difference through Tutorial
- What is Knowledge Management? – Tutorial Explained
- What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT)? | Know More through Tutorial
- Gantt Chart Tool Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Extreme Project Management Tutorial – Methodology & Examples
- Introduction for Event Chain Methodology Tutorial | Guide For Beginners
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | A Complete Tutorial for Beginners
- What Is Design of Experiments (DOE)? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Decision Making Tutorial – Know about Meaning, Nature, Characteristics
- Critical Path Method Tutorial | How to use CPM for project management
- What is Critical Chain Project Management? | A Complete Tutorial
- What is Conflict Management? | Learn the Definition, styles, strategies through Tutorial
- Effective Communication Skills Tutorial – Definitions and Examples
- Communication Models Tutorial – Project Management
- Methods of Communication Tutorial | A Complete Learning Path
- Communication Management Tutorial | Know more about Plans & Process
- What are Communication Channels? | Learn Now Tutorial
- Communication Blocker Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Cause and Effect Diagrams Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- What is Benchmarking? | Technical & Competitive Tutorial
- Seven Processes of Prince2 Tutorial | Everything you Need to Know
- Design Thinking Tutorial – Quick Guide For Beginners
- What is Performance Testing | A Complete Testing Guide With Real-Time Examples Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Agile Scrum Tutorial
- PMI-RMP Plan Risk Management Tutorial
- Designing the Blueprint Delivery Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Program Benefits Management Tutorial
- Continuous Improvement – Agile Value Stream Mapping
- Program Organization Tutorial
- Risk and Issue Management Tutorial
- Project Integration Management Tutorial
- Planning and Control Tutorial
- Program Management Principles Tutorial
- program strategy Alignment Tutorial
- PMP Tutorial
- Program Governance Tutorial
- Program Life Cycle Management Tutorial
- PMP Exam Preparation Tutorial
- PMI-PgMP Tutorial
- Agile Methodologies and Frameworks- Kanban and Lean Management Tutorial
- JIRA Tutorial
- Primavera P6 Tutorial
- Understanding Agile Methodologies and Principles | A Complete Tutorial
- What is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)? | Learn Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Traditional Project Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Complete Guide [STEP-IN]
- Total Productive Maintenance Tutorial | Get an Overview
- Virtual Team Tutorial – Learn Origin, Definition and its Scope
- The Rule of Seven in Project Management – Tutorial
- Make or Buy Decision – A Derivative Tutorial for Beginners
- What is Halo Effect? | Learn More through Tutorial
- Balanced Score Card Tutorial | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Supply Chain Management? | Tutorial with Examples
- Succession Planning Tutorial | A Complete Guide with Definitions
- What is Structured Brainstorming? | Quickstart & Learn the Tutorial
- Stress Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- What is a Statement of Work? | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Stakeholder Management? – The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- How to Create a Staffing Management Plan? | Learn from Tutorial
- What is Resource Leveling? | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Requirements Collection Tutorial: Gather Project Needs
- What Is a RACI Chart? | Learn with Example & Definitions
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control: Tutorial with Definitions & Differences
- Project Workforce Management Tutorial | A Definitive Guide
- Project Time Management Tutorial: Strategies, Tips & Tools
- Project Management Success Criteria Tutorial | Understand and Know More
- Identify Risk Categories in Project Management | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Project Records Management Tutorial | Quickstart -MUST READ
- Project Quality Plan (PQP) Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Project Portfolio Management | A Defined Tutorial for Beginners
- Goals of a Project Manager Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Project Management Triangle Tutorial: What It Is and How to Use
- Project Management Tools Tutorial | Learn Tools & Techniques
- What is PMO (project management office)? | A Complete Tutorial from Scratch
- Project Management Lessons | Learn in 1 Day [ STEP-IN ]
- What is a Project Kickoff Meeting? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Project Cost Management Tutorial | Steps, Basics, and Benefits
- Types of Contracts in Project Management | Learn with Examples
- Project Activity Diagram | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- What is Project Procurement Management? | Tutorial Explained
- Procurement Documents Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Process-Based Project Management Tutorial: A Beginner’s Guide
- What Is PRINCE2 Project Management? | A Definitive Tutorial for Beginners
- Effective Presentation Skills – Learn More through Tutorial
- Powerful Leadership Skills Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- PERT Estimation Technique Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Pareto Chart Tool Tutorial | Learn Analysis, Diagram
- Organizational Structure Tutorial: Definition and Types
- Negotiation Skills for Project Management | Learn from the Basics
- Monte Carlo Analysis in Project Management Tutorial | A Perfect Guide to Refer
- Effective Management Styles Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Management by Objectives (MBO) Tutorial | Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Leads, Lags & Float – Understand the Difference through Tutorial
- What is Knowledge Management? – Tutorial Explained
- What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT)? | Know More through Tutorial
- Gantt Chart Tool Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Extreme Project Management Tutorial – Methodology & Examples
- Introduction for Event Chain Methodology Tutorial | Guide For Beginners
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | A Complete Tutorial for Beginners
- What Is Design of Experiments (DOE)? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Decision Making Tutorial – Know about Meaning, Nature, Characteristics
- Critical Path Method Tutorial | How to use CPM for project management
- What is Critical Chain Project Management? | A Complete Tutorial
- What is Conflict Management? | Learn the Definition, styles, strategies through Tutorial
- Effective Communication Skills Tutorial – Definitions and Examples
- Communication Models Tutorial – Project Management
- Methods of Communication Tutorial | A Complete Learning Path
- Communication Management Tutorial | Know more about Plans & Process
- What are Communication Channels? | Learn Now Tutorial
- Communication Blocker Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Cause and Effect Diagrams Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- What is Benchmarking? | Technical & Competitive Tutorial
- Seven Processes of Prince2 Tutorial | Everything you Need to Know
- Design Thinking Tutorial – Quick Guide For Beginners
- What is Performance Testing | A Complete Testing Guide With Real-Time Examples Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Agile Scrum Tutorial
- PMI-RMP Plan Risk Management Tutorial
- Designing the Blueprint Delivery Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Program Benefits Management Tutorial
- Continuous Improvement – Agile Value Stream Mapping
- Program Organization Tutorial
- Risk and Issue Management Tutorial
- Project Integration Management Tutorial
- Planning and Control Tutorial
- Program Management Principles Tutorial
- program strategy Alignment Tutorial
- PMP Tutorial
- Program Governance Tutorial
- Program Life Cycle Management Tutorial
- PMP Exam Preparation Tutorial
- PMI-PgMP Tutorial
- Agile Methodologies and Frameworks- Kanban and Lean Management Tutorial
- JIRA Tutorial
- Primavera P6 Tutorial
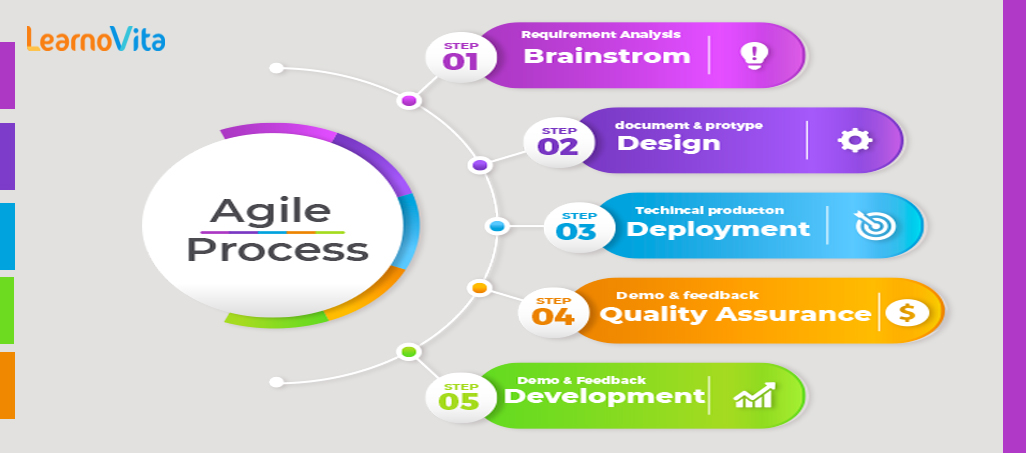
Understanding Agile Methodologies and Principles | A Complete Tutorial
Last updated on 24th Aug 2022, Blog, Project Management, Tutorials
Agile
Most of the days, each term agile and scrummage square measures are used interchangeably however there’s a crucial distinction between the 2.
Agile is outlined because the complete set of ways that square measure supports principles or values expressed within the Agile declaration because of the cross-functionality of groups, collaboration, or self-organization etc.
Scrum
Scrum could be a framework for project management that emphasizes cooperation, answerability and repetitive progress toward a well-defined goal.
The framework begins with an easy premise: begin with what may be seen or famous. The 3 pillars of scrummage square measure transparency, review and adaptation.
Scrum method
A scrummage method is distinguished from different agile processes by specific ideas and practices, divided into the 3 classes of Roles, Artifacts, and Time Boxes. These and different terms utilized in scrummage square measure outlined below.
Scrum is most frequently accustomed to manage advanced package and merchandise development, victimization, repetitive and progressive practices. scrummage considerably will increase productivity and reduce time to edges relative to classic “waterfall” processes.
scrummage processes alter organizations to regulate swimmingly to rapidly-changing needs, and manufacture a product that meets evolving business goals. Associate in Nursing agile scrummage method edges the organization by serving to it to
- Increase the standard of the deliverables
- Cope higher with modification (and expect the changes)
- Provide higher estimates whereas defrayment less time making them
- Be a lot of up to the mark of the project schedule and state
Scrum method Work
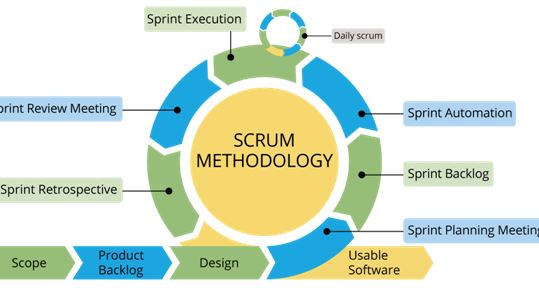
The image below roughly outlines how a sprint in scrummage works.
Step1: scrummage method begins with a product owner. Product Owner creates a product backlog, an inventory of tasks and needs the ultimate product desires. The vital half is that product backlog should be prioritized.
Step2: The scrummage team gets along for sprint designing, that is once the team decides along what to figure on initially from the merchandise backlog. This set of things from the merchandise backlog becomes the sprint backlog.
Step3: Throughout the sprint, the team meets to speak about progress and problems, this meeting is named the daily scrummage. It’s overseen by the scrummage master World Health Organization ensures that each one the team members follow scrum’s theories, rules, and practices.
Step4: At the top of the sprint, the sprint review meeting is organized by the merchandise owner. Throughout the meeting, the event team demonstrates what they completed since the last sprint. Then the merchandise owner offers info regarding what’s remaining on the merchandise backlog and calculable time to complete the project if required.
Step5: When the sprint review, the scrummage team gathers-up in a sprint retrospective meeting, wherever, the team discusses what went well, what didn’t and if they may have done higher. could be a school limitation is holding them back or a team member is full with tasks. The team decides the way to fix these issues and creates a thought for enhancements to be enacted throughout consecutive sprints.
Step6: The cycle repeats for the remaining tasks within the product backlog. This goes on till either of the below-mentioned things happen:
The point in time has been reached
The budget is exhausted
The product owner is happy with the ultimate product
So, in an exceedingly large shell, however, the scrummage Framework is employed to provide an operating piece of the merchandise when each sprint. To conclude, scrummage could be a versatile approach of operating in an exceedingly chop-chop dynamic world. With Scrum, you’re not making a lot of work for yourself; you’re being a lot economical together with your time and work.
Agile method
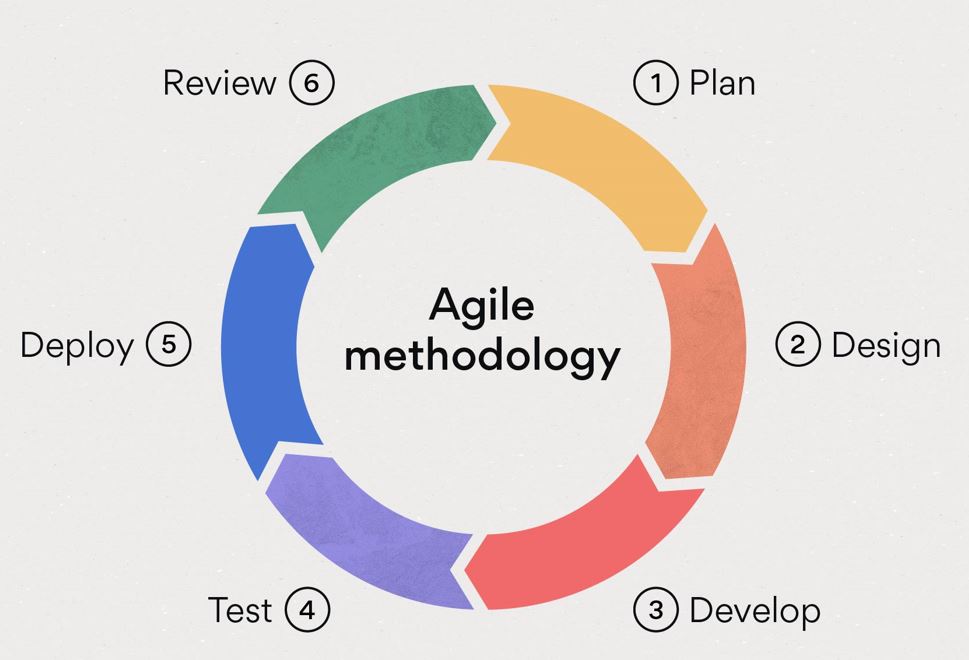
The vital principle or best followed in the start is Transparency. The team leader ought to perceive that everybody is functioning for the corporate and equally answerable for the progress and achievements accomplished. That’s why keeping a lot of information clear is vital for advanced code.
The major element of Framework for transparency is the start Board. This can be the place wherever you’ll manage backlogs, or tasks effectively and check the progress of the present Sprint along. Start Boards are straightforward to know like sticky notes wherever charts or different chase options are for every task.
The main objective here is to ascertain every task is visible fully to the users. The team members will see the work themselves and begin on a constant basis. there’s no reason that they ought to return to the project manager all the time for work. once tasks ar printed intimately properly before you assign them, work will be completed abundant quicker than your expectations.
Important components or individuals of the start Methodology
To understand the start topic fully, you must understand the individuals and a part of the Framework well. The most effective half is that you just don’t like any special expertise or certification to start out. There’s a requirement for organizing your thoughts and your backlogs. allow us to break down the components that build start happen:
Scrum Framework starts with the merchandise Owner and he’s the one who expresses the most effective interests of users and he has the authority to choose what ought to be the ultimate product.
The product owner takes care of the Backlog that involves tasks or needs for the ultimate product wants. This can be a crucial half and BACKLOG ought to be prioritized with wisdom here. This can be the task of a product owner solely. Next vital half is the Sprint that’s represented because of the preset framework serving to the team to complete a collection of tasks from the Backlog. Every task is to line some deadlines supporting the length or efforts.
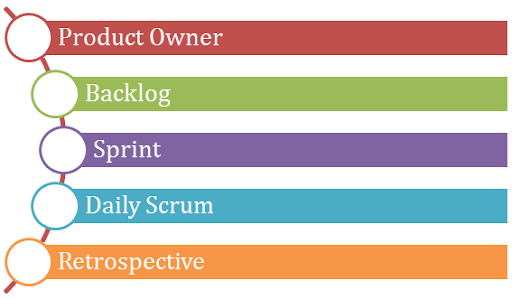
Teams work along nearly daily to satisfy up the deadlines to feature the progress standing within the Daily star. For a couple of individuals, it’s named because of the daily stand-ups too.
For each Sprint, there’s else one Retrospective or {we can|we will|We are able to} say Review in straightforward words wherever the work of the team is reviewed well and potential ways in which are mentioned to create necessary enhancements within the next Sprint.
Events in beginning
In explicit, there are four events that you simply can encounter throughout the beginning method. However, before we have a tendency to proceed from now on, you ought to remember what sprint is.
Sprint – A beginning sprint primarily may be such that a period of time throughout that a beginning Team produces a product. It forces prioritization, demonstrates progress, avoids unessential perfections, motivates closure, improves certainty and improves the come of investment.
The four events or ceremonies of beginning Framework are:
Scrum Artifacts
Artifacts are simply physical records that give project details once developing a product. beginning Artifacts include: Product Backlog
It is a straightforward document that outlines the list of tasks and each demand that the ultimate product wants. it’s perpetually evolving and isn’t complete. The merchandise Owner manages the merchandise Backlog, as well as however it’s created, offered to the beginning team, its content, and the way it’s ordered, everything.
The Product Owner and therefore the remainder of the beginning team work along to review the merchandise Backlog and build changes as and once necessary. for every item within the product backlog, you ought to add some extra data like:
- Description
- Order supported priority
- Estimate
- Value to the business
- Sprint Backlog
It is the list of all things from the merchandise backlog that require to be worked on throughout a sprint. Team members sign in for tasks supporting their skills and priorities. It’s a period of time image of the work that the team presently plans to finish throughout the sprint. Here are some small print regarding sprint backlog:
The sprint backlog is dynamic in nature as a result of every beginning sprint has perennial changes to achieve the goal
It is the end result of sprint designing meeting sessions
The development team owns the sprint backlog and divides tasks in step with their skills
It is a extremely visible, period of time image of the work that the event Team plans to accomplish Product Increment
The most vital object is the product improvement, or in alternative words, the addition of product work completed throughout a Sprint, combined with all work completed throughout previous sprints.
The important purpose is that the increment should be in usable condition in spite of whether or not the merchandise Owner decides to unleash it.
Role
The scrummage Team consists of 3 roles, specifically a ScrumMaster, a Product Owner, and therefore the Team.
ScrumMaster
The scrummageMaster (sometimes written as the Scrum Master, though the official term has no house once “Scrum”) is the keeper of the scrummage method. He/she is accountable for making the method run swimmingly removing obstacles that impact productivity organizing and facilitating the essential conferences
Product Owner
The Product Owner is chargeable for increasing the worth of the merchandise and therefore the work of the Team. however this can be done across organizations, scrummage groups, and people.
The Product Owner is the sole author for managing the merchandise Backlog. Product Backlog management includes
- Expressing Product Backlog things clearly.
- Ordering the merchandise Backlog things to best accomplish goals and missions.
- Optimizing the worth of the work the Team performs.
- Ensuring that the merchandise Backlog is visible, clear, and clear to any or all, and shows what the Team can work on more.
- Ensuring that the Team understands things within the Product Backlog to the extent required.
- The Product Owner might do the on top of work, or have the Team get laid. However, the merchandise owner remains in charge of these tasks.
The merchandise Owner might represent the wishes of a committee within the Product Backlog, however those desirous to amend a Product Backlog item’s priority should address the merchandise Owner.
For the merchandise owner to succeed, the complete organization should respect his or her choices. The merchandise Owner’s choices are a unit visible within the content and ordering of the merchandise Backlog. Nobody is allowed to inform the Team to figure out a special set of necessities, and therefore the Team isn’t allowed to act on what anyone else says. This can be ensured by ScrumMaster.
The Team
The Team is self-organizing and cross-functional. meaning the team includes analysts, designers, developers, testers, etc. as acceptable and as relevant to the project.
Some folks within the trade seek advice from this team as a development team. However, such a reference is resulting in contention that the team will have solely developers and no different roles. it’s a visible understanding that it’s solely a thought. To develop a product, we tend to need all the roles which is the essence of scrummage – the team can perform unitedly.
Cross-functional groups have all competencies required to accomplish the work while not counting on others not a part of the team, and therefore time and energy is saved. The team model in scrummage is meant to optimize flexibility, creativity, and productivity.
Optimal Team size is little enough to stay nimble and huge enough to complete important work among a Sprint. The Team size ought to be unbroken within the range from 5 to 9 folks, if attainable. Fewer than 5 team members decrease interaction and lead to smaller productivity gains. Having over 9 members needs an excessive amount of coordination.
The scrummage team works closely, day to day, to confirm the graceful flow of knowledge and therefore the fast resolution of problems. The scrummage team delivers products iteratively and incrementally, increasing opportunities for feedback. progressive deliveries of a whole product guarantee a doubtless helpful version of the operating product is often out there.
Benefits to the Client
Customers discover that the provider responds to development needs more quickly. Short cycles accelerate the development and delivery of high-value features compared to the lengthier cycles preferred by traditional “waterfall” procedures.
Advantages for Vendors
By concentrating development efforts on high-value features, vendors cut wastage and time-to-market compared to waterfall procedures because of lower overhead and greater efficiency. Increased customer satisfaction leads to higher client retention and more favorable word-of-mouth recommendations.
The Advantages for Development Teams
Team members like working on new projects and prefer to see their effort put to good use. Scrum gives Team members more time to focus on the work they enjoy by minimizing non-productive work (such as drafting specifications or other artifacts that no one uses).
Team members also know their work is valued, because requirements are chosen to maximize value to customers.
Advantages for Product Managers
Product Managers, who often fill the Product Owner function, are in charge of keeping customers happy by ensuring that development activity is in line with their requirements. Scrum facilitates this alignment by offering frequent opportunities to re-prioritize work to guarantee maximum value delivery.
Advantages for Project Managers
When compared to waterfall methods, Project Managers (and others) that play the ScrumMaster role think that planning and tracking are easier and more concrete. The emphasis on task-level tracking, the use of Burndown Charts to highlight daily progress, and the Daily Scrum meetings all work together to provide the Project Manager with constant awareness of the project’s status. This awareness is critical for monitoring the project and identifying and correcting concerns as they arise.
Advantages for PMOs and C-Level Executives
Scrum provides daily visibility into the status of a development project. External stakeholders, including C-level executives and Project Management Office workers, can take use of this insight to plan more efficiently and change their strategy based on more hard data and less guesswork.
Conclusion
The framework’s goal is not to do more work, but to work smarter and achieve more. With the Scrum Framework, you can always finish twice as much work in half the time.
With Scrum, accomplishments are measured based on the job completed rather than the amount of hours worked. You can always spend more time with the people and things you care about this way. It would also result in an ideal life-balance approach.
