
Inheritance in Java
Last updated on 22nd Sep 2020, Artciles, Blog
The process by which one class acquires the properties(data members) and functionalities(methods) of another class is called inheritance. The aim of inheritance is to provide the reusability of code so that a class has to write only the unique features and rest of the common properties and functionalities can be extended from the other class.
Child Class:
The class that extends the features of another class is known as child class, subclass or derived class.
Parent Class:
The class whose properties and functionalities are used(inherited) by another class is known as parent class, super class or Base class.
Syntax: Inheritance in Java
To inherit a class we use an extended keyword. Here class XYZ is child class and class ABC is parent class. The class XYZ is inheriting the properties and methods of ABC class.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
class XYZ extends ABC
{
}
Example
In this example, we have a base class Teacher and a sub class PhysicsTeacher. Since class PhysicsTeacher extends the designation and college properties and work() method from base class, we need not to declare these properties and methods in subclass.
Here we have collegeName, designation and work() method which are common to all the teachers so we have declared them in the base class, this way the child classes like MathTeacher, MusicTeacher and PhysicsTeacher do not need to write this code and can be used directly from base class.
-
class Teacher {
String designation = “Teacher”;
String collegeName = “ABC”;
void does(){
System.out.println(“Teaching”);
}
}
public class PhysicsTeacher extends Teacher{
String mainSubject = “Physics”;
public static void main(String args[]){
PhysicsTeacher obj = new PhysicsTeacher();
System.out.println(obj.collegeName);
System.out.println(obj.designation);
System.out.println(obj.mainSubject);
obj.does();
}
}
Output:
ABC
Teacher
Physics
Teaching
Based on the above example we can say that PhysicsTeacher IS-A Teacher. This means that a child class has an IS-A relationship with the parent class. This is inheritance is known as IS-A relationship between child and parent class
Types of Inheritance
Single Inheritance in Java
Single Inheritance is the simple inheritance of all, When a class extends another class(Only one class) then we call it Single inheritance. The below diagram represents the single inheritance in java where Class B extends only one class Class A.
Here Class B will be the Sub class and Class A will be one and only Super Class.
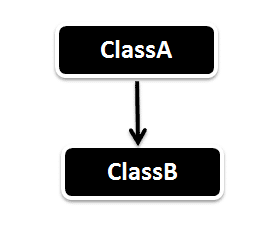
Single Inheritance Example
-
public class ClassA
{
public void dispA()
{
System.out.println(“disp() method of ClassA”);
}
}
public class ClassB extends ClassA
{
public void dispB()
{
System.out.println(“disp() method of ClassB”);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
//Assigning ClassB object to ClassB reference
ClassB b = new ClassB();
//call dispA() method of ClassA
b.dispA();
//call dispB() method of ClassB
b.dispB();
}
}
Output :
disp() method of ClassA
disp() method of ClassB
Multiple Inheritance in Java
Multiple Inheritance is nothing but one class extending more than one class. Multiple Inheritance is basically not supported by many Object Oriented Programming languages such as Java, Small Talk, C# etc.. (C++ Supports Multiple Inheritance). As the Child class has to manage the dependency of more than one Parent class. But you can achieve multiple inheritance in Java using Interfaces.
Multilevel Inheritance in Java
In Multilevel Inheritance a derived class will be inheriting a parent class and as well as the derived class act as the parent class to other class. As seen in the below diagram. ClassB inherits the property of ClassA and again ClassB act as a parent for ClassC. In Short ClassA parent for ClassB and ClassB parent for ClassC.
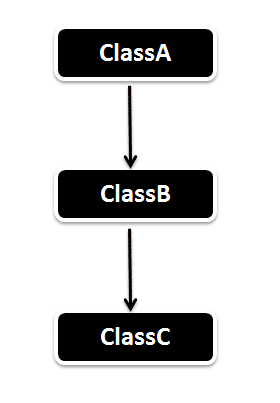
MultiLevel Inheritance Example
-
public class ClassA
{
public void dispA()
{
System.out.println(“disp() method of ClassA”);
}
}
public class ClassB extends ClassA
{
public void dispB()
{
System.out.println(“disp() method of ClassB”);
}
}
public class ClassC extends ClassB
{
public void dispC()
{
System.out.println(“disp() method of ClassC”);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
//Assigning ClassC object to ClassC reference
ClassC c = new ClassC();
//call dispA() method of ClassA
c.dispA();
//call dispB() method of ClassB
c.dispB();
//call dispC() method of ClassC
c.dispC();
}
}
Output :
disp() method of ClassA
disp() method of ClassB
disp() method of ClassC
Hierarchical Inheritance in Java
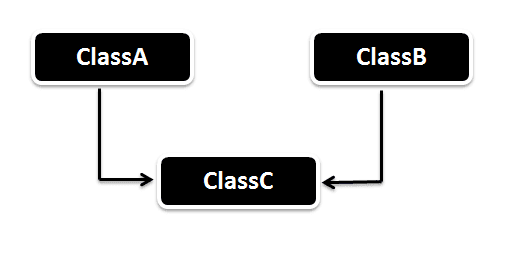
In Hierarchical inheritance one parent class will be inherited by many sub classes. As per the below example ClassA will be inherited by ClassB, ClassC and ClassD. ClassA will be acting as a parent class for ClassB, ClassC and ClassD.
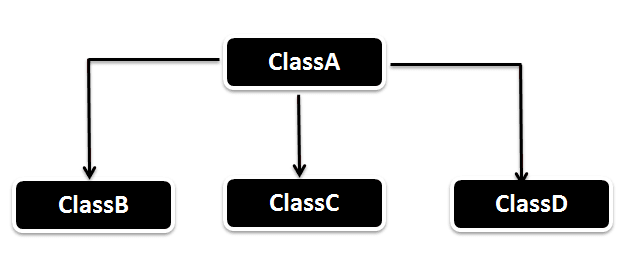
Hierarchical Inheritance Example
public class ClassA
{
public void dispA()
{
System.out.println(“disp() method of ClassA”);
}
}
public class ClassB extends ClassA
{
public void dispB()
{
System.out.println(“disp() method of ClassB”);
}
}
public class ClassC extends ClassA
{
public void dispC()
{
System.out.println(“disp() method of ClassC”);
}
}
public class ClassD extends ClassA
{
public void dispD()
{
System.out.println(“disp() method of ClassD”);
}
}
public class HierarchicalInheritanceTest
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//Assigning ClassB object to ClassB reference
ClassB b = new ClassB();
//call dispB() method of ClassB
b.dispB();
//call dispA() method of ClassA
b.dispA();
//Assigning ClassC object to ClassC reference
ClassC c = new ClassC();
//call dispC() method of ClassC
c.dispC();
//call dispA() method of ClassA
c.dispA();
//Assigning ClassD object to ClassD reference
ClassD d = new ClassD();
//call dispD() method of ClassD
d.dispD();
//call dispA() method of ClassA
d.dispA();
}
}
Output :
disp() method of ClassB
disp() method of ClassA
disp() method of ClassC
disp() method of ClassA
disp() method of ClassD
disp() method of ClassA
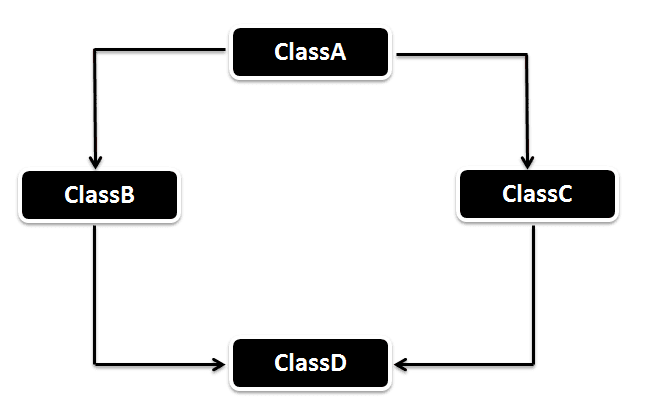
Hybrid Inheritance in Java
Hybrid Inheritance is the combination of both Single and Multiple Inheritance. Again Hybrid inheritance is also not directly supported in Java only through the interface we can achieve this. Flow diagram of the Hybrid inheritance will look like below. As you can ClassA will be acting as the Parent class for ClassB & ClassC and ClassB & ClassC will be acting as Parent for ClassD.
This is a guide to Inheritance in Java. Here we discuss the importance and different types of inheritance in java along with syntax, examples and code implementation.
Are you looking training with Right Jobs?
Contact Us- The Most Popular Java Applications Used World-wide
- Resources To Help You Learn Java Programming
- Top Skills that Boosts Java Developer Salaries
- Java Interview Questions and Answers
- JAVA Tutorial
Related Articles
Popular Courses
- Python Online Training
11025 Learners - C And C Plus Plus Online Training
12022 Learners - Dot Net Training
11141 Learners
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- Difference between Data Lake vs Data Warehouse: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- What does the Yield keyword do and How to use Yield in python ? [ OverView ]
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know

