- Understanding Agile Methodologies and Principles | A Complete Tutorial
- What is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)? | Learn Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Traditional Project Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Complete Guide [STEP-IN]
- Total Productive Maintenance Tutorial | Get an Overview
- Virtual Team Tutorial – Learn Origin, Definition and its Scope
- The Rule of Seven in Project Management – Tutorial
- Make or Buy Decision – A Derivative Tutorial for Beginners
- What is Halo Effect? | Learn More through Tutorial
- Balanced Score Card Tutorial | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Supply Chain Management? | Tutorial with Examples
- Succession Planning Tutorial | A Complete Guide with Definitions
- What is Structured Brainstorming? | Quickstart & Learn the Tutorial
- Stress Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- What is a Statement of Work? | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Stakeholder Management? – The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- How to Create a Staffing Management Plan? | Learn from Tutorial
- What is Resource Leveling? | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Requirements Collection Tutorial: Gather Project Needs
- What Is a RACI Chart? | Learn with Example & Definitions
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control: Tutorial with Definitions & Differences
- Project Workforce Management Tutorial | A Definitive Guide
- Project Time Management Tutorial: Strategies, Tips & Tools
- Project Management Success Criteria Tutorial | Understand and Know More
- Identify Risk Categories in Project Management | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Project Records Management Tutorial | Quickstart -MUST READ
- Project Quality Plan (PQP) Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Project Portfolio Management | A Defined Tutorial for Beginners
- Goals of a Project Manager Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Project Management Triangle Tutorial: What It Is and How to Use
- Project Management Tools Tutorial | Learn Tools & Techniques
- What is PMO (project management office)? | A Complete Tutorial from Scratch
- Project Management Lessons | Learn in 1 Day [ STEP-IN ]
- What is a Project Kickoff Meeting? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Project Cost Management Tutorial | Steps, Basics, and Benefits
- Types of Contracts in Project Management | Learn with Examples
- Project Activity Diagram | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- What is Project Procurement Management? | Tutorial Explained
- Procurement Documents Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Process-Based Project Management Tutorial: A Beginner’s Guide
- What Is PRINCE2 Project Management? | A Definitive Tutorial for Beginners
- Effective Presentation Skills – Learn More through Tutorial
- Powerful Leadership Skills Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- PERT Estimation Technique Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Pareto Chart Tool Tutorial | Learn Analysis, Diagram
- Organizational Structure Tutorial: Definition and Types
- Negotiation Skills for Project Management | Learn from the Basics
- Monte Carlo Analysis in Project Management Tutorial | A Perfect Guide to Refer
- Effective Management Styles Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Management by Objectives (MBO) Tutorial | Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Leads, Lags & Float – Understand the Difference through Tutorial
- What is Knowledge Management? – Tutorial Explained
- What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT)? | Know More through Tutorial
- Gantt Chart Tool Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Extreme Project Management Tutorial – Methodology & Examples
- Introduction for Event Chain Methodology Tutorial | Guide For Beginners
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | A Complete Tutorial for Beginners
- What Is Design of Experiments (DOE)? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Decision Making Tutorial – Know about Meaning, Nature, Characteristics
- Critical Path Method Tutorial | How to use CPM for project management
- What is Critical Chain Project Management? | A Complete Tutorial
- What is Conflict Management? | Learn the Definition, styles, strategies through Tutorial
- Effective Communication Skills Tutorial – Definitions and Examples
- Communication Models Tutorial – Project Management
- Methods of Communication Tutorial | A Complete Learning Path
- Communication Management Tutorial | Know more about Plans & Process
- What are Communication Channels? | Learn Now Tutorial
- Communication Blocker Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Cause and Effect Diagrams Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- What is Benchmarking? | Technical & Competitive Tutorial
- Seven Processes of Prince2 Tutorial | Everything you Need to Know
- Design Thinking Tutorial – Quick Guide For Beginners
- What is Performance Testing | A Complete Testing Guide With Real-Time Examples Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Agile Scrum Tutorial
- PMI-RMP Plan Risk Management Tutorial
- Designing the Blueprint Delivery Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Program Benefits Management Tutorial
- Continuous Improvement – Agile Value Stream Mapping
- Program Organization Tutorial
- Risk and Issue Management Tutorial
- Project Integration Management Tutorial
- Planning and Control Tutorial
- Program Management Principles Tutorial
- program strategy Alignment Tutorial
- PMP Tutorial
- Program Governance Tutorial
- Program Life Cycle Management Tutorial
- PMP Exam Preparation Tutorial
- PMI-PgMP Tutorial
- Agile Methodologies and Frameworks- Kanban and Lean Management Tutorial
- JIRA Tutorial
- Primavera P6 Tutorial
- Understanding Agile Methodologies and Principles | A Complete Tutorial
- What is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)? | Learn Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Traditional Project Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Complete Guide [STEP-IN]
- Total Productive Maintenance Tutorial | Get an Overview
- Virtual Team Tutorial – Learn Origin, Definition and its Scope
- The Rule of Seven in Project Management – Tutorial
- Make or Buy Decision – A Derivative Tutorial for Beginners
- What is Halo Effect? | Learn More through Tutorial
- Balanced Score Card Tutorial | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Supply Chain Management? | Tutorial with Examples
- Succession Planning Tutorial | A Complete Guide with Definitions
- What is Structured Brainstorming? | Quickstart & Learn the Tutorial
- Stress Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- What is a Statement of Work? | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Stakeholder Management? – The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- How to Create a Staffing Management Plan? | Learn from Tutorial
- What is Resource Leveling? | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Requirements Collection Tutorial: Gather Project Needs
- What Is a RACI Chart? | Learn with Example & Definitions
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control: Tutorial with Definitions & Differences
- Project Workforce Management Tutorial | A Definitive Guide
- Project Time Management Tutorial: Strategies, Tips & Tools
- Project Management Success Criteria Tutorial | Understand and Know More
- Identify Risk Categories in Project Management | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Project Records Management Tutorial | Quickstart -MUST READ
- Project Quality Plan (PQP) Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Project Portfolio Management | A Defined Tutorial for Beginners
- Goals of a Project Manager Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Project Management Triangle Tutorial: What It Is and How to Use
- Project Management Tools Tutorial | Learn Tools & Techniques
- What is PMO (project management office)? | A Complete Tutorial from Scratch
- Project Management Lessons | Learn in 1 Day [ STEP-IN ]
- What is a Project Kickoff Meeting? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Project Cost Management Tutorial | Steps, Basics, and Benefits
- Types of Contracts in Project Management | Learn with Examples
- Project Activity Diagram | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- What is Project Procurement Management? | Tutorial Explained
- Procurement Documents Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Process-Based Project Management Tutorial: A Beginner’s Guide
- What Is PRINCE2 Project Management? | A Definitive Tutorial for Beginners
- Effective Presentation Skills – Learn More through Tutorial
- Powerful Leadership Skills Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- PERT Estimation Technique Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Pareto Chart Tool Tutorial | Learn Analysis, Diagram
- Organizational Structure Tutorial: Definition and Types
- Negotiation Skills for Project Management | Learn from the Basics
- Monte Carlo Analysis in Project Management Tutorial | A Perfect Guide to Refer
- Effective Management Styles Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Management by Objectives (MBO) Tutorial | Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Leads, Lags & Float – Understand the Difference through Tutorial
- What is Knowledge Management? – Tutorial Explained
- What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT)? | Know More through Tutorial
- Gantt Chart Tool Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Extreme Project Management Tutorial – Methodology & Examples
- Introduction for Event Chain Methodology Tutorial | Guide For Beginners
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | A Complete Tutorial for Beginners
- What Is Design of Experiments (DOE)? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Decision Making Tutorial – Know about Meaning, Nature, Characteristics
- Critical Path Method Tutorial | How to use CPM for project management
- What is Critical Chain Project Management? | A Complete Tutorial
- What is Conflict Management? | Learn the Definition, styles, strategies through Tutorial
- Effective Communication Skills Tutorial – Definitions and Examples
- Communication Models Tutorial – Project Management
- Methods of Communication Tutorial | A Complete Learning Path
- Communication Management Tutorial | Know more about Plans & Process
- What are Communication Channels? | Learn Now Tutorial
- Communication Blocker Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Cause and Effect Diagrams Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- What is Benchmarking? | Technical & Competitive Tutorial
- Seven Processes of Prince2 Tutorial | Everything you Need to Know
- Design Thinking Tutorial – Quick Guide For Beginners
- What is Performance Testing | A Complete Testing Guide With Real-Time Examples Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Agile Scrum Tutorial
- PMI-RMP Plan Risk Management Tutorial
- Designing the Blueprint Delivery Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Program Benefits Management Tutorial
- Continuous Improvement – Agile Value Stream Mapping
- Program Organization Tutorial
- Risk and Issue Management Tutorial
- Project Integration Management Tutorial
- Planning and Control Tutorial
- Program Management Principles Tutorial
- program strategy Alignment Tutorial
- PMP Tutorial
- Program Governance Tutorial
- Program Life Cycle Management Tutorial
- PMP Exam Preparation Tutorial
- PMI-PgMP Tutorial
- Agile Methodologies and Frameworks- Kanban and Lean Management Tutorial
- JIRA Tutorial
- Primavera P6 Tutorial

Project Time Management Tutorial: Strategies, Tips & Tools
Last updated on 24th Aug 2022, Blog, Project Management, Tutorials
Project Management Knowledge Areas
The project management knowledge areas are important to know about effective project management. Whether a project manager studying for the Project Management Professional (PMP), freshening up the knowledge, or just looking to streamline and understand the project management knowledge.Below each of the 10 knowledge areas of project management at a more level along with a few of the process groups or action items associated with each of them.
1. Project Integration Management:
PM activities from project initiation to closure.It helps to link the processes and tasks together. This generates a single, coherent project lifecycle.
Project Integration Management covers the following:
- Project Charter Development to start the project and explain the project stakeholders.
- Project Management Plan Development outlines how to maintain the project to get results.
- Directing and Management of Project Work focuses on a production and release of a project’s deliverables.
- Project Knowledge Management is about knowledge acquisition and also sharing. It’s especially important if team works in international or a cross-functional teams. This way team members built knowledge and share it with their colleagues, improving project quality.
- Ensuring that it complete on time without exceeding its budget.
- Monitoring and Controlling the Project Work involves project performance monitoring, estimation of achieved results, identification of the possible project challenges, and changes.
- Performance of Integrated Change Control if the project needs changing administrative parts, such as a project sponsor or reviewing the project documentation, then it involved integrated change control tasks.
- Closure of the Project or Phase covers tasks or objectives that are required to close the project or its phases.
2. Project Scope Management:
Project Scope Management explains the scope of work to finish during the project. It’s essential as it sets boundaries to the amount of work that can be included in a one project. This eliminates the possibility of more work being added on without authorization. Also, it helps to avoid going over budget.
It included the following processes:
- Scope Management planning involves the generation of the scope management plan. It’s usually included in a project management plan.
- Requirements Collection involves collecting detailed requirements to explain the deliverable features and project stakeholders’ requirements for a project management process.
- Scope Definition is about the preparation of a detailed description of a project scope. It helps to uncover the hidden risks and other problems. The project scope should be built up gradually and become a more precise with every iteration.
- WBS Creation. WBS stands for a Work Breakdown Structure. It involved the graphical breakdown of the project into components. These components represent the scope of work an arranged hierarchically.
- Scope Validation is about approving and accepting a released for project deliverables by project stakeholders.
- Scope Control is a revision of scope statements to ensure that the project work was finished within the set requirements.
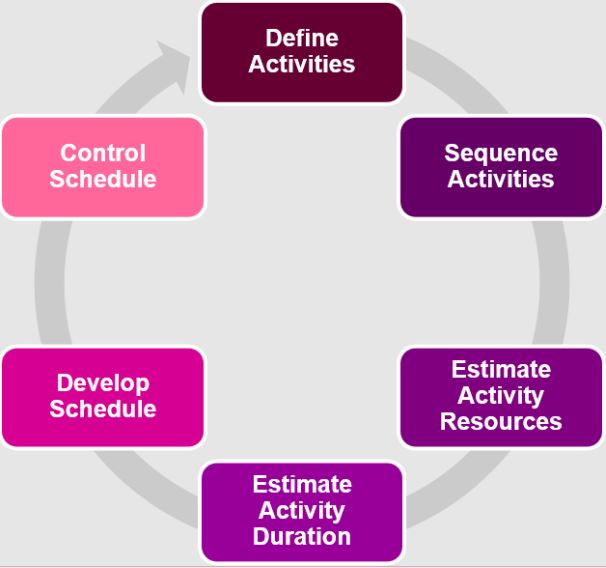
3. Project Schedule Management:
Project schedule management is one of the most sophisticated among all knowledge areas. It need a lot of pre-preparation. A project manager has to explain project tasks first and after generate a schedule where they mark the starting and finishing dates. Moreover, the project plan and timetable often to change. That’s why a project management schedule require frequent revisions and stakeholders’ approval.
Project Schedule Management includes:
- Schedule Management Planning. This activity means that list in the schedule management plan the employee responsible for its execution, how strict it should be, and under a which circumstances can alter it.
- Activities explanation divides a project into a separate tasks. Basically, this activity matches with the generation of WBS.
- Activities Sequence is about ordering the tasks on the timeline. That’s the point where you need to allocate Finish-to-Start (FS), Finish-to-Finish (FF), Start-to-Start (SS), and Start-to-Finish (SF) times.
- Estimation of Activity Durations overlaps with the previous point. At this stage, need to explain the duration of each task.
- Schedule Development stage make a diagram with a critical path. This is the longest way between starting and completing points, a graphical bar chart with activities that have their early starting dates, and the resource usage allocated to every activity. That means you allocate the resources effectively.
- Schedule Control is the calculation of project progress following the schedule. At this stage, can explain if the project goes ahead or is late.
4. Project Cost Management:
Get to know the ins and outs of calculation of the project budget. This knowledge area offers effective estimation techniques that help to explain the sums need to spend on the project. By doing so, ensure that project owners and stakeholders stay satisfied with the amounts they need to spend on product development.
Project Cost Management involves:
- Cost Management Planning is the generation of a plan that find the procedures and methodologies to estimate the project budget. It involved planning, management, expenditure, and control of project costs.
- Costs Estimation includes the processes of the cost estimation. Here include the estimation of labor, materials, and an equipment costs needed.
- Budget finding entails separate budget estimations into a one project budget.
- Costs Control involves analysing how the project budget is spent, and status at a definite time.
5. Project Quality Management:
Project Quality Management heavily depends on the Project Time and Project Cost knowledge areas. The more the time and budget, the better the quality. Therefore, the deliverable quality level should be explained at the stage of project planning and a project manager should specify it in the overall project management plan.
Project Quality Management includes:
- Quality Management Planning. This process involves generating a separate document that includes the specifications that explain the deliverables’ quality.
- Product quality is fundamental to Quality Management. Regular inspection and approval is required.
- Quality Control means that the quality level meets a quality requirements.
6. Project Resource Management:
Project Resource Management included people, equipment, facilities, and others to ensure successful project fulfillment. However, equipment and budgeting play an important role in project performance. The project team is the key factor that often find the time and money spent on a project and influences the deliverable quality level. That’s why it’s particularly important to focus on the team when planning the project resources.
Project Resource Management includes:
- Resource Management Planning involves a document that explains the resources for the project. Usually, this plan is devoted to a human resource management. It find the roles in the project team and role requirements, and how they’re applicable to a project.
- Activity Resource Estimation ensures that have all the resources are available to fulfill the project.
- Resource Acquisition is about an acquiring the needed resources for a project.
- Resource Control is about monitoring and evaluating how the resources are to be spent. It also covers how the team interacts throughout the project.
7. Project Communication Management:
When develop the project plan, need to establish a policy on how the project stakeholders shall communicate during the project execution, and in case of its changing. It’s important to develop a communication rules for stakeholders to get in touch fastly once there appear unforeseen issues. For successful project communication.
The project manager should perform the below activities:
- Communication Management Planning. The development of this plan involves explaining communication requirements. Including: how often and when to have a meetings, what kind of means a communication to use for daily interaction, communications steps to undertake in case of unforeseen problems.
- Communication Management entails the implementation of the communication management plan.
- Communication Monitoring involves monitoring and revision of how a communication plan is executed.
8. Project Risk Management:
Project risks are often hidden and cannot be seen at a mere glance. That’s why to ensure successful project execution and minimize the unexpected problems, project managers should perform a deep analyze of possible risks.
To estimate project risks successfully, a project manager should carry out the tasks:
- Risk Management Planning involves the generation of a risk management plan that define how to categorize and prioritize possible risks.
- Risks Identification means that a project manager should identify a project risks. They record them for screening and prevention of their occurrence.
- Quantitative Risk Analysis involved estimation risks in numbers and how they influence each project aspect such as budget, team, timelines, and so on.
- Risk Response Implementation is about an executing the steps planned in a risk response planning.
9. Project Procurement Management:
Not every project needs the procurement of outside subcontractors to speed up project development or involve niche specialists. However, if I feel the necessity to add an extra workforce to a project, I need a set of clear steps on how to do it. As a result, there will be less of a chance that either the time or money allotted will be overrun.
This ensures that the project stays contained within its established parameters:
- Procurement Management Planning helps to explain the project needs and sets the parameters for hiring extra specialists.
- Procurement Conducting involves the process of searching and hiring an employee or an outsourcing company. This step also explain under what conditions outsource part of the work and what project requirements the responsible party has to fulfill.
- Procurement Control implies management and screening of contracts and informing the parties in case of the project changes.
10. Project Stakeholder Management:
Stakeholders’ management is a fundamental part of any project. They initiate the project, identify the product needs, model project processes, estimate the project outcomes, and declare a project success. Every stakeholder has a set of functions in a project. Therefore, a project manager should establish their roles and responsibilities. It’s important to set the rules for the stakeholders so that they effectively interact and add value to a successful project development.
That’s why a project manager should perform these activities:
- Stakeholders Identification is one of the first steps done to start a project. Project stakeholders and their roles are usually outlined in one of the first project documents —the stakeholders’ register.
- Stakeholder Engagement Planning is about making a list of stakeholders and estimating their force on a project, their roles, and responsibilities.
- Stakeholder Engagement Management involved the identification and meeting expectations of stakeholders. For example, if they have enough tools to finish parts of the project, what project problems they might face in the future, and others.
- Monitoring the Stakeholder Engagement is about screening if the stakeholders’ needs are met and what they might need in a future.
PMBOK project management knowledge areas sort 49 project processes into logical groups, facilitating their selection for the project. As a project manager, I don’t need to pick up all of them. The number of processes choose depends on the single characteristics of each project. They can be find by the scope of the project, budget, time, resources involved, and other factors. Once decided which project processes that want to include in the project, need to make them work. can do it with PMBOK process groups. They line the processes upon the timeline, making it simpler to understand which process should start, move forward, and finish the project with.
5 PMBOK Process Groups
While knowledge management areas are implemented more theoretically and used to better explain and understand the project management processes, PMBOK process groups outline the practical approach to a project organization. They represent consecutive stages on a timeline project walks through with its development.
PMBOK process groups are work like this:
- At the initiating stage, a project manager drafts a document with the project idea, major objectives, stakeholders, and explains general processes and resources needed to develop the product.
- The planning stage involved detailing parts of the project, establishing milestones and deadlines, investigating stakeholders’ requirements to finish the project, and developing a plan on how to tackle possible risks.
- The execution stage is about bringing all the planned activities to life and working on deliverables.
- At the monitoring and controlling stage, project stakeholders monitor and calculate project outcomes, estimate project risks, and adapt the project plan and its development in line with the stakeholders’ needs and necessities. This stage often overlaps with an execution stage.
- The closing stage is about an evaluation of the final product and the retrospection of a project execution process to improve the future projects of a company.
