- Financial Performance – A Complete Tutorial
- How Six Sigma Principles Can Progress Your Productivity – Tutorial
- Google Analytics Pro Tutorial | Fast Track your Career
- Activity-Based Costing Tutorial | Know about Definition, Process, & Example
- Create a workbook in Excel Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Excel ROUNDUP Formula Tutorial | Learn with Functions & Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Tutorial | Learn In 1 Day
- SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- IBM SPSS Statistics Tutorial: Getting Started with SPSS
- SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [Updated]
- SAP FIORI Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Introduction to Business Analytics with R Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Tableau Desktop Tutorial | Step by Step resource guide to learn Tableau
- Implementing SAP BW on SAP HANA | A Complete Guide
- SAP HANA Administration | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau API Tutorial | Get Started with Tools, REST Basics
- SAP FICO ( Financial Accounting and Controlling ) Tutorial | Complete Guide
- Alteryx Tutorial | Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- Getting started with Amazon Athena Tutorial – Serverless Interactive | The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction to Looker Tutorial – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Sitecore Tutorials | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE |Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Adobe Analytics Tutorial – The Ultimate Student Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- Pentaho Tutorial – Best Resources To Learn in 1 Day | CHECK OUT
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Spotfire Tutorial for Beginners | Quickstart – MUST- READ
- JasperReports Tutorial: Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Charts and Tables – Qlikview Tutorial – Complete Guide
- TIBCO Business Works | Tutorial for Beginners – Learn From Home
- Cognos TM1 Tutorial : Learn Cognos from Experts
- Kibana
- Power BI Desktop Tutorial
- Tableau Tutorial
- SSAS Tutorial
- Creating Tableau Dashboards
- MDX Tutorial
- Tableau Cheat Sheet
- Analytics Tutorial
- Lean Maturity Matrix Tutorial
- MS Excel Tutorial
- Business Analysis Certification Levels & Their Requirements Tutorial
- Solution Assessment and Validation Tutorial
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Enterprise Analysis Tutorial
- Create Charts and Objects in Excel 2013 Tutorial
- Msbi Tutorial
- MicroStrategy Tutorial
- Advanced SAS Tutorial
- OBIEE Tutorial
- Tableau Server Tutorial
- OBIA Tutorial
- Business Analyst Tutorial
- Cognos Tutorial
- Qlik Sense Tutorial
- SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
- SAS Tutorial
- PowerApps Tutorial
- Financial Performance – A Complete Tutorial
- How Six Sigma Principles Can Progress Your Productivity – Tutorial
- Google Analytics Pro Tutorial | Fast Track your Career
- Activity-Based Costing Tutorial | Know about Definition, Process, & Example
- Create a workbook in Excel Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Excel ROUNDUP Formula Tutorial | Learn with Functions & Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Tutorial | Learn In 1 Day
- SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- IBM SPSS Statistics Tutorial: Getting Started with SPSS
- SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [Updated]
- SAP FIORI Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Introduction to Business Analytics with R Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Tableau Desktop Tutorial | Step by Step resource guide to learn Tableau
- Implementing SAP BW on SAP HANA | A Complete Guide
- SAP HANA Administration | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau API Tutorial | Get Started with Tools, REST Basics
- SAP FICO ( Financial Accounting and Controlling ) Tutorial | Complete Guide
- Alteryx Tutorial | Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- Getting started with Amazon Athena Tutorial – Serverless Interactive | The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction to Looker Tutorial – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Sitecore Tutorials | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE |Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Adobe Analytics Tutorial – The Ultimate Student Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- Pentaho Tutorial – Best Resources To Learn in 1 Day | CHECK OUT
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Spotfire Tutorial for Beginners | Quickstart – MUST- READ
- JasperReports Tutorial: Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Charts and Tables – Qlikview Tutorial – Complete Guide
- TIBCO Business Works | Tutorial for Beginners – Learn From Home
- Cognos TM1 Tutorial : Learn Cognos from Experts
- Kibana
- Power BI Desktop Tutorial
- Tableau Tutorial
- SSAS Tutorial
- Creating Tableau Dashboards
- MDX Tutorial
- Tableau Cheat Sheet
- Analytics Tutorial
- Lean Maturity Matrix Tutorial
- MS Excel Tutorial
- Business Analysis Certification Levels & Their Requirements Tutorial
- Solution Assessment and Validation Tutorial
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Enterprise Analysis Tutorial
- Create Charts and Objects in Excel 2013 Tutorial
- Msbi Tutorial
- MicroStrategy Tutorial
- Advanced SAS Tutorial
- OBIEE Tutorial
- Tableau Server Tutorial
- OBIA Tutorial
- Business Analyst Tutorial
- Cognos Tutorial
- Qlik Sense Tutorial
- SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
- SAS Tutorial
- PowerApps Tutorial

SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
Last updated on 11th Aug 2022, Blog, Business Analytics, Tutorials
What is SAP?
SAP is an ERP programme and stands for systems, applications, and products in data processing. SAP software offers real time integration with internal systems and external systems. So the executed data can be shared across the organization. SAP R/3 system split the SAP modules into functional modules and technical modules. The important functional modules of SAP are FICO, MM, SD, HR, CRM, PP, Payroll, etc and the most important technical modules are HANA, Security, ABAP, BI/BW, etc.
SAP – Modules:
SAP solutions include a number of functional modules, which encourage transactions to execute key business processes, they are :
- Financial Accounting (FI)
- Financial Supply Chain Management (FSCM)
- Controlling (CO)
- Materials Management (MM)
- Sales and Distribution (SD)
- Logistics Execution (LE)
- Production Planning (PP)
- Quality Management (QM)
- Plant Maintenance (PM)
- Project System (PS)
- Human Resources (HR)
Finance and Controlling (FICO)
SAP FICO is a combination of two ERP modules, that is Finance Accounting (FI) and Controlling (CO). Under Finance in SAP and at an enterprise level, the following modules are take part −
- FI − Finance
- CO − Controlling
- IM − Investment Management
- TR − Treasury
- EC − Enterprise Controlling
SAP FI(Financial Accounting)
SAP FI(Financial Accounting) is accountable for tracing the flow of financial information across the organization in a controlled manner and integrating all the information for effective strategic decision-making.
Activities Involved in SAP FI:- Creation of Organizational Structure (Explain Company, Company Codes, business Areas, Functional Areas, Credit Control, Assignment of Company Codes to Credit Controls)
- Financial Accounting Global Settings (Maintain of Fiscal Year, Posting Periods, Explaining Document types, posting keys, Number ranges for documents)
- General Ledger Accounting (Creation of Chart of Accounts, Account groups, Explaining data transfer rules, creation of General Ledger Account)
- Tax Configuration and House of Banks Creation and Maintenance.
- Account Payables (Creation of Vendor Master data and vendor-related finance attributes are account groups and payment terms)
- Account Receivables (Creation of Customer Master data and customer-related finance attributes are account groups and payment terms
- Asset Accounting)
- Integration with SD & MM.
SAP CO (Controlling)
SAP CO (Controlling) module facilitates coordinating, screening, and optimizing all the processes in an organization. It controls the business flow in an enterprise.
This module helps to analyze the actual figures with the planned data and in planning business strategies.
Two kinds of elements are maintain in CO −
- Cost elements
- Revenue elements
These elements are saved in the FI module.
Activities Involved in SAP CO:- Cost Element Accounting (Overview of the costs and income that occur in an organization).
- Cost Center Accounting.
- Activity-Based-Accounting (Analyses cross-departmental business processes).
- Internal Orders.
- Product Cost Controlling (Estimate the costs that occur during the manufacture of a product or provision of a service).
- Profitability Analysis (Analyzes the gain or loss of an organization by individual market segments),
- Profit Center Accounting (calculate the profit or loss of individual, independent areas within an organization).
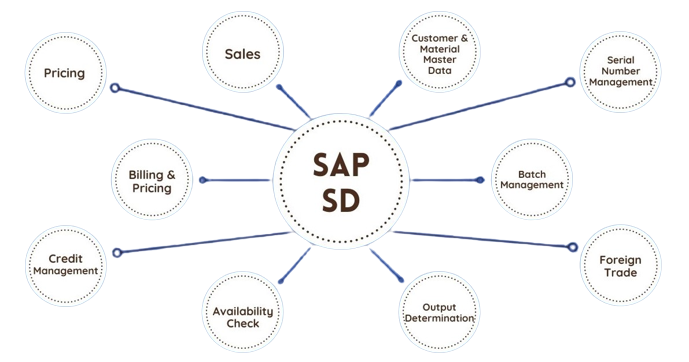
Sales & Distribution Management (SD):
It ranks among the most crucial SAP modules. It has a high level of integration difficulty. SAP SD is used by organizations to encourage sales and distribution activities of products and services, starting from enquiry to order and then ending with delivery.
SAP SD can screen a plethora of activities that take place in an organization such as products enquiries, quotation (pre-sales activities), placing order, pricing, scheduling deliveries (sales activity), picking, packing, goods issue, shipment of products to customers, delivery of products and invoices.
In all these, multiple modules are involved such as FI (Finance Accounting), CO (Controlling), MM (Material Management), PP (Production Planning), LE (Logistics Execution), etc., which shows the difficulty of the integration involved.
Activities Involved in SAP SD:- Setting up Enterprise Structure (formation of new firm, company codes, sales structure, distribution routes, divisions, business region, plants, sales area, maintaining sales offices, storage site) (formation of new firm, company codes, sales organization, distribution routes, divisions, business region, plants, sales area, maintaining sales offices, storage site).
- Assigning Enterprise Units (Assignment of single components created in the above activities with each other according to design like company code to company, sales organization to company code, distribution channel to sales organization, etc.)
- Explaining Pricing Components (Explaining condition tables, condition types, condition sequences). (Explaining condition tables, condition types, condition sequences)..
- Setting up sales document kinds, invoice types, and tax-related components.
- Setting up Customer master data records and settings.
Material Management (MM)
It deals with transportation of goods by other modules including logistics, supply chain management, sales and delivery, warehouse management, manufacturing and planning.
Logistic Execution (LE):
Logistic Execution can be splitted into two sub-modules, i.e., shipment of goods (purchase to procurement process) and warehouse management (storage of goods).
These two modules work in tandem with production and planning, material management, and sales and distribution.
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
This module deals with the effective and efficient transition of products and services between an enterprise and its suppliers.
The major process covered in this section is procurement of products like direct materials, indirect materials, and services.
This module can efficiently integrate with the planning, accounting, and inventory system.
End-to-End Procurement Cycle:
Procurement process with SAP Enterprise Buyer comprises of the following important steps −
- Shopping Carts
- Approval of Shopping Cart
- Sourcing of Requirements
- Purchase Orders
- Purchase Order Approval
- Confirm Goods/Services
- Confirmation Approval
- Process Invoice
- Invoice Approval
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
CRM offers end-to-end customer related processes. CRM is designed to centralize the data relating to all the customers associated with an organization. It helps an organization −
- Manage its sales, services, and build marketing strategies according to the market demand and customer data analysis.
- Remain focused on its customers and by information analysis, help the business to know more about its customers.
- Increase sales and services and build better relationships with customers.
Human Resource (HR):
The most important objective of master data administration in Human Resources is to enter employee-related information for administrative, time-recording, and payroll purposes. A new employee can be hired without using the Recruitment. Instead can hire anyone by running a personnel action in Personnel Administration, thereby creating the necessary data for the employee to be hired. Employee data must be maintained.
After an employee is hired, circumstances can always arise which necessitate either the entry of new data or the editing of current data. For instance −
- An employee moving to his or her new address must be saved in the system.
- An employee receives a compensation increase at the beginning of the year. For the applicable date, the new wage must be set aside.
- An employee changes jobs within the organization. His or her organizational assignment, working time, and salary also to be changed.
- Data can be saved for the past, present, or future.
- It comprises the major areas of functionality known as sub-modules.
- It is a true demo of the strength of the SAP product in Enterprise Resource Planning.
- The HR system has more strong integration points (where data is passed back and forth without human intervention) with about all of the other SAP modules.
- There is very tight integration among the HR sub-modules.
- The above illustration highlights some of the basic SAP HR terms as are:
- Business trip management
- Recruitment
- Payroll
- Personal development
- Organizational Management
- Time Management
- Workforce Planning
- ESS
- MSS
- Training and event management
- CATS
- Benefits
- Compensation management
- Personal Administration

SAP – Security:
There are three points ensure security −:
Confidentiality − Unauthorized disclosure of information.
Integrity − Unauthorized changes of data.
Availability − Denial of service (a lack of availability of computer resources) (a lack of availability of computing resources).
In the SAP runtime environment, both application security and illegal system access to SAP must be regulated. The user accounts mentioned for users in the SAP runtime environment are protected by roles that give authorizations to them.
SAP authorizations control access to transactions or what can be performed within a specific business process step by −
- Maintaining unauthorized persons out of the system.
- Maintaining people out of places where they should not be.
- Safeguarding the data from damage or loss.
Safeguards:
To avoid threats, a sound and robust system implements safeguards like access control, firewall, encryption, O/S hardening, digital certificate, security
Classification of Security:
Security can be classified into three categories −
Organizational Security − Related to an organization.
Physical − Relating to the physical assets.
Technical − Relating to technical threats. This is also divided into four types −
- Program-level security
- O/S-level security
- Database security
- Network
Different Layers of Security:
- Authentication − Only legitimate users are able to access the system.
- Authorization − Users only able to perform their designated tasks.
- Integrity − Data integrity requires to be granted at all times.
- Privacy − security of data against unauthorized access.
- Obligation − Ensuring liability and legal obligation towards stakeholders and shareholders including the validation.