- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Project Management Process ? : A Complete Guide
- What is Lean Management? : A Complete Guide
- What is ITIL ? Know about the Framework
- What is Six Sigma?| Know the tools used
- What is Kanban Training?|Know more about it
- Project Management Tools and Techniques : A Complete Guide
- What is Project Management? Everything You need to Know | Salary for the role
- Srum Org Certification? All you need to know about it
- MS Project Certification | All you need to know
- What is Project Manager? Know about the salary
- Six Sigma Certification Cost | Know all details about it
- Difference Between PMO and Project Manager? | Expert’s Top Picks
- What are Project Management Tools | Its Techniques | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Agile |Its Methodology and Types | How to Implement [ OverView ]
- What is a Product Roadmap? | How to Create one | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Scrum vs Kanban | Agile at Scale | New Agile BenchMark
- How to Effectively Manage Stakeholders | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Experts Top Picks
- What is Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) | The Leading Framework For Business Agility | Everything You Need to Know
- How to Become a Project Manager | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- Time Management Tools to Help You Succeed as a Professional | Expert’s Top Picks
- Top 10 Tips for Agile Sprint Planning To Implement Efficient Marketing | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is ICP-ACC (ICAgile Certified Agile Coaching)? | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices [ OverView ]
- How To Run An Effective Agile Retrospective-Agile management | Everything You Need to Know
- What Skills Does One Acquire After The PMP Certification?
- A Definitive Guide: Most Effective and Proven Time Management Techniques [ OverView ]
- What Gaps I Filled After CSM Certification For my Scrum Project? [ OverView ]
- How to Create A Plan And Manage Your Projects Better?: Step-By-Step Process [ OverView ]
- What is User Story Mapping? : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is Design Thinking ? : Benefits and Special Features | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What is the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is Sprint Planning ? | A Definitive Guide | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and How Does It Help in Equipment Effectiveness [ OverView ]
- What are Agile Metrics ? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Agile Marketing and Why Do You Need It | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Why is Retrospection Needed? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Developing Project Schedule : Role of Float, Leads, and Lags [ OverView ]
- Project Life Cycle vs Product Life Cycle | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Projects in Business Environments | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Business Agility ? and Why is it Important ? Expert’s Top Picks
- The Most Important Benefits of Blended Learning | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- Can Business Analyst be a Project Manager? : Expert’s Top Picks
- Why A PMO Is Second In Line To A Project Manager ? | Expert’s Top Picks
- Devops vs Waterfall | A Definitive Guide and Which Should You Learn?
- Jira vs Trello | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Key Values and Principles Behind the Agile Manifesto | A Definitive Guide
- What are Scrum Ceremonies : The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Business Analyst vs Financial Analyst | Know Their Differences and Which Role is Better ?
- Learn Burndown Charts With Jira : Comprehensive Guide [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What Is Scrum XP? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Phases of Project Management | Step-By-Step Process | Expert’s Top Picks
- Project Manager Salary in India – How much does a PM earn? [ Job & Future ]
- Why Do Scrum Masters Get Paid so Much? [For Freshers and Experience]
- What Best Describes a Scrum Team? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- JIRA vs TFS | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Anti-patterns of a Scrum Master : Step-By-Step Process
- SCM Tools and Frameworks | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Stages of Team Development | Everything You Need to Know
- Project Management Consultant : Job Description, Skills Required | Everything You Need to Know
- CSM vs PSM : Difference You Should Know
- Top Characteristics of a Project Manager : Expert’s Top Picks
- Roles And Responsibilities Of A Product Owner : Everything You Need to Know
- Common Project Risks and How to Tackle Them | Expert’s Top Picks
- Benefits of Having Shorter Sprints in Agile – Everything You Need to Know
- Group Discussion Tips | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- PMP Certification Cost : All you need to know
- DMAIC Process and Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Agile Scrum Vs Kanban | Know the difference
- Deming vs Juran vs Crosby
- What is Project Scope Management and Why It’s Important?
- The Basic Principles of Project Management
- Top PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2020
- Risk Management Strategies
- Roles and Responsibilities of A Scrum Master
- ROM Estimate Vs Definitive Estimate
- Guidelines for Creating and Maintaining a WBS Dictionary
- How to Become a Certified ScrumMaster?
- Top Professional Skills for 2020
- Fast Tracking Vs Crashing
- PMP Vs PRINCE2 Vs CAPM
- PMP Earned Value Management (EVM) And Formulas
- What is Certified Scrum Professional (CSM)?
- Top Leadership Theories Every Manager Should Know
- What is Deliverables in Project Management?
- How To Prepare For TOEFL
- History and evolution of the PMP Certification
- What Is Float In Microsoft Project?
- Rules to set you up for success in project
- What is Scrum Project Management?
- What Is Estimating Activity Duration in Project Management?
- What Are The PMP Terminologies Relating To Cost Knowledge Area?
- What is Project Scope Management processes?
- What Are The Types of Organization In PMP?
- Books to Beat the Scrum Master Certification
- Agile Coach Vs Agile Consultant
- What is the cost of quality in project management?
- Signs Your Career May Be Stagnation and Tips to Overcome Downturn
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) Certification
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification
- What is schedule Activity in project management?
- Why Do We Need a Project Charter?
- PMP Certification Exam Preparation Mind Map
- Why Quality Professionals Should Use Infographics In Project Management?
- Role of Earned Value Technique in Project Management
- What is Project Quality Management?
- Tools and Techniques to Estimate Project Cost
- What is a Project Charter And Project Scope in Project Management?
- Why Should You Conduct Project Status Meetings with Your Team?
- The 7 R’s of Change Management
- What Are The Categories and sources of risk in your project?
- What Is a Network Diagram in Project Management?
- What are The Types of Contracts In PMP?
- Residual Risk Vs Secondary Risk
- Impact of the stakeholders on the projects
- Effort Vs Duration Vs Elapsed Time
- Agile vs Scrum
- What Is Six Sigma Quality Assurance?
- How to Close a Project?
- What Qualifications Do You Need to be a Project Manager?
- Project Management Vs General Operations Management
- Enterprise Environmental Factors & Organizational Process Assets
- What is a project manager?
- Important Questions for PMP Certification Exam
- How is the PMP Exam changing, in 2015 & 2020?
- How To Renew Your PMP Certification?
- The Importance of Having Project Acceptance Criteria in Your Projects
- Tips for PMP Exam Preparation
- What is requirement traceability matrix RTM in Project Management?
- Poor Performance Appraisal? Here are the tips to turn any negative feedback into positive.
- How to build a successful Career in Agile and Scrum?
- Importance of Tuckman ladder model in HR management
- How To Apply For The PMP® Exam In Easy Steps
- How to Write a Six Sigma Problem Statement
- What is a lessons learned document in PMI?
- Perform Quality Assurance Vs Perform Quality Control
- How to Improve Quality Management Consistently?
- Interactive Vs Push Vs Pull Communication
- what is risk management?
- Key Appraisal Questions to Prepare For
- What are the MSP Certifications?
- What Is A Six Sigma Control Plan?
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel?
- Agile Prioritization Techniques
- Tips to Help Millennials Climb the Corporate Ladder
- What is an Issue Log?
- Advantages of PMP over MBA
- Top Successful Project Estimation Techniques
- PMP Examination Preparation – ITTO’s
- Employee Training Rewards That Actually Improve Learning
- Lean principles
- What Does It Take to Become a Successful Agile Coach
- Projects VS Programs
- The Role of Six Sigma in Manufacturing
- The Top Formulas to Memorize Before Your PMP Exam
- Roadmap to CSM (Certified Scrum Master) Certification
- What are Some Qualities of a Good Manager and Good Leader?
- How to Handle Project Monitoring and Controlling Processes?
- Top Free Agile Tools For Any Project Manager
- Risk Assessment in Project Management
- The Concept of Zero Defects in Quality Management
- The Importance of Work Packages in Project Scope Management
- How to Get Project Management Experience for PMP Certification
- Different Ways to Calculate the Estimate at Completion (EAC)
- What Is a ScrumMaster?
- What is Risk Register?
- Agile Certifications
- Top-down Approach Vs Bottom-up Approach
- Leadership Vs Management
- What is Feasibility Study and Its Importance in Project Management?
- What Is a Project Management Plan?
- The Professional Advantages of the CAPM Certification
- PRINCE2 Vs PMP
- Rita Mulcahy’s PMP Prep and PMBOK® Guide
- What is Project Cycle Management?
- What is Project and Process Metrics?
- PMBOK® Sixth Edition is Here! What Project Managers Should Know?
- CAPM Certification
- Top Project Selection Methods for Project Managers
- Free Float Vs Total Float
- What is Critical Chain Project Management?
- How to Build a Career in Project Management?
- Scrum Master or Product Owner: What Suits You Better?
- Project Documentation and its Importance
- What is Performance Reporting in the Project Management?
- Top Highest Paying Tech Jobs in India
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Project Management Process ? : A Complete Guide
- What is Lean Management? : A Complete Guide
- What is ITIL ? Know about the Framework
- What is Six Sigma?| Know the tools used
- What is Kanban Training?|Know more about it
- Project Management Tools and Techniques : A Complete Guide
- What is Project Management? Everything You need to Know | Salary for the role
- Srum Org Certification? All you need to know about it
- MS Project Certification | All you need to know
- What is Project Manager? Know about the salary
- Six Sigma Certification Cost | Know all details about it
- Difference Between PMO and Project Manager? | Expert’s Top Picks
- What are Project Management Tools | Its Techniques | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Agile |Its Methodology and Types | How to Implement [ OverView ]
- What is a Product Roadmap? | How to Create one | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Scrum vs Kanban | Agile at Scale | New Agile BenchMark
- How to Effectively Manage Stakeholders | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Experts Top Picks
- What is Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) | The Leading Framework For Business Agility | Everything You Need to Know
- How to Become a Project Manager | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- Time Management Tools to Help You Succeed as a Professional | Expert’s Top Picks
- Top 10 Tips for Agile Sprint Planning To Implement Efficient Marketing | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is ICP-ACC (ICAgile Certified Agile Coaching)? | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices [ OverView ]
- How To Run An Effective Agile Retrospective-Agile management | Everything You Need to Know
- What Skills Does One Acquire After The PMP Certification?
- A Definitive Guide: Most Effective and Proven Time Management Techniques [ OverView ]
- What Gaps I Filled After CSM Certification For my Scrum Project? [ OverView ]
- How to Create A Plan And Manage Your Projects Better?: Step-By-Step Process [ OverView ]
- What is User Story Mapping? : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is Design Thinking ? : Benefits and Special Features | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What is the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is Sprint Planning ? | A Definitive Guide | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and How Does It Help in Equipment Effectiveness [ OverView ]
- What are Agile Metrics ? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Agile Marketing and Why Do You Need It | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Why is Retrospection Needed? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Developing Project Schedule : Role of Float, Leads, and Lags [ OverView ]
- Project Life Cycle vs Product Life Cycle | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Projects in Business Environments | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Business Agility ? and Why is it Important ? Expert’s Top Picks
- The Most Important Benefits of Blended Learning | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- Can Business Analyst be a Project Manager? : Expert’s Top Picks
- Why A PMO Is Second In Line To A Project Manager ? | Expert’s Top Picks
- Devops vs Waterfall | A Definitive Guide and Which Should You Learn?
- Jira vs Trello | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Key Values and Principles Behind the Agile Manifesto | A Definitive Guide
- What are Scrum Ceremonies : The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Business Analyst vs Financial Analyst | Know Their Differences and Which Role is Better ?
- Learn Burndown Charts With Jira : Comprehensive Guide [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What Is Scrum XP? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Phases of Project Management | Step-By-Step Process | Expert’s Top Picks
- Project Manager Salary in India – How much does a PM earn? [ Job & Future ]
- Why Do Scrum Masters Get Paid so Much? [For Freshers and Experience]
- What Best Describes a Scrum Team? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- JIRA vs TFS | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Anti-patterns of a Scrum Master : Step-By-Step Process
- SCM Tools and Frameworks | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Stages of Team Development | Everything You Need to Know
- Project Management Consultant : Job Description, Skills Required | Everything You Need to Know
- CSM vs PSM : Difference You Should Know
- Top Characteristics of a Project Manager : Expert’s Top Picks
- Roles And Responsibilities Of A Product Owner : Everything You Need to Know
- Common Project Risks and How to Tackle Them | Expert’s Top Picks
- Benefits of Having Shorter Sprints in Agile – Everything You Need to Know
- Group Discussion Tips | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- PMP Certification Cost : All you need to know
- DMAIC Process and Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Agile Scrum Vs Kanban | Know the difference
- Deming vs Juran vs Crosby
- What is Project Scope Management and Why It’s Important?
- The Basic Principles of Project Management
- Top PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2020
- Risk Management Strategies
- Roles and Responsibilities of A Scrum Master
- ROM Estimate Vs Definitive Estimate
- Guidelines for Creating and Maintaining a WBS Dictionary
- How to Become a Certified ScrumMaster?
- Top Professional Skills for 2020
- Fast Tracking Vs Crashing
- PMP Vs PRINCE2 Vs CAPM
- PMP Earned Value Management (EVM) And Formulas
- What is Certified Scrum Professional (CSM)?
- Top Leadership Theories Every Manager Should Know
- What is Deliverables in Project Management?
- How To Prepare For TOEFL
- History and evolution of the PMP Certification
- What Is Float In Microsoft Project?
- Rules to set you up for success in project
- What is Scrum Project Management?
- What Is Estimating Activity Duration in Project Management?
- What Are The PMP Terminologies Relating To Cost Knowledge Area?
- What is Project Scope Management processes?
- What Are The Types of Organization In PMP?
- Books to Beat the Scrum Master Certification
- Agile Coach Vs Agile Consultant
- What is the cost of quality in project management?
- Signs Your Career May Be Stagnation and Tips to Overcome Downturn
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) Certification
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification
- What is schedule Activity in project management?
- Why Do We Need a Project Charter?
- PMP Certification Exam Preparation Mind Map
- Why Quality Professionals Should Use Infographics In Project Management?
- Role of Earned Value Technique in Project Management
- What is Project Quality Management?
- Tools and Techniques to Estimate Project Cost
- What is a Project Charter And Project Scope in Project Management?
- Why Should You Conduct Project Status Meetings with Your Team?
- The 7 R’s of Change Management
- What Are The Categories and sources of risk in your project?
- What Is a Network Diagram in Project Management?
- What are The Types of Contracts In PMP?
- Residual Risk Vs Secondary Risk
- Impact of the stakeholders on the projects
- Effort Vs Duration Vs Elapsed Time
- Agile vs Scrum
- What Is Six Sigma Quality Assurance?
- How to Close a Project?
- What Qualifications Do You Need to be a Project Manager?
- Project Management Vs General Operations Management
- Enterprise Environmental Factors & Organizational Process Assets
- What is a project manager?
- Important Questions for PMP Certification Exam
- How is the PMP Exam changing, in 2015 & 2020?
- How To Renew Your PMP Certification?
- The Importance of Having Project Acceptance Criteria in Your Projects
- Tips for PMP Exam Preparation
- What is requirement traceability matrix RTM in Project Management?
- Poor Performance Appraisal? Here are the tips to turn any negative feedback into positive.
- How to build a successful Career in Agile and Scrum?
- Importance of Tuckman ladder model in HR management
- How To Apply For The PMP® Exam In Easy Steps
- How to Write a Six Sigma Problem Statement
- What is a lessons learned document in PMI?
- Perform Quality Assurance Vs Perform Quality Control
- How to Improve Quality Management Consistently?
- Interactive Vs Push Vs Pull Communication
- what is risk management?
- Key Appraisal Questions to Prepare For
- What are the MSP Certifications?
- What Is A Six Sigma Control Plan?
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel?
- Agile Prioritization Techniques
- Tips to Help Millennials Climb the Corporate Ladder
- What is an Issue Log?
- Advantages of PMP over MBA
- Top Successful Project Estimation Techniques
- PMP Examination Preparation – ITTO’s
- Employee Training Rewards That Actually Improve Learning
- Lean principles
- What Does It Take to Become a Successful Agile Coach
- Projects VS Programs
- The Role of Six Sigma in Manufacturing
- The Top Formulas to Memorize Before Your PMP Exam
- Roadmap to CSM (Certified Scrum Master) Certification
- What are Some Qualities of a Good Manager and Good Leader?
- How to Handle Project Monitoring and Controlling Processes?
- Top Free Agile Tools For Any Project Manager
- Risk Assessment in Project Management
- The Concept of Zero Defects in Quality Management
- The Importance of Work Packages in Project Scope Management
- How to Get Project Management Experience for PMP Certification
- Different Ways to Calculate the Estimate at Completion (EAC)
- What Is a ScrumMaster?
- What is Risk Register?
- Agile Certifications
- Top-down Approach Vs Bottom-up Approach
- Leadership Vs Management
- What is Feasibility Study and Its Importance in Project Management?
- What Is a Project Management Plan?
- The Professional Advantages of the CAPM Certification
- PRINCE2 Vs PMP
- Rita Mulcahy’s PMP Prep and PMBOK® Guide
- What is Project Cycle Management?
- What is Project and Process Metrics?
- PMBOK® Sixth Edition is Here! What Project Managers Should Know?
- CAPM Certification
- Top Project Selection Methods for Project Managers
- Free Float Vs Total Float
- What is Critical Chain Project Management?
- How to Build a Career in Project Management?
- Scrum Master or Product Owner: What Suits You Better?
- Project Documentation and its Importance
- What is Performance Reporting in the Project Management?
- Top Highest Paying Tech Jobs in India

What is Critical Chain Project Management?
Last updated on 29th Sep 2020, Artciles, Blog, Project Management
Scheduling is the process of sequencing all the project activities by assigning each activity a duration in a way so that they are completed in a timely manner. Critical Path Method (CPM) is the most widely adopted method of scheduling.
In spite of preparing an optimized schedule and building adequate buffers into activities, it has been very often found that the projects miss their committed schedule. Schedule overruns have become the norm. As per the latest survey of PMI pulse of the Profession 2017, only 50% of the projects completed on time.
This is when Dr Eliyahu M Goldratt studied the underlying reasons of failing schedule commitments, proposed a different method of scheduling known as Critical Chain Method.
Dr Goldratt studied deeply the reasons of project failure, specially the failure in scheduling point of view. He found that most of the reasons are due to human behaviour and cultural beliefs of people. Below are some of the reasons for project delays.
- Over-estimating
- Overrunning the estimate
- Not passing on time savings
- Path convergence
- Multitasking
- Loss of focus
1. Causes of Over-Estimating:
- Estimate criteria not well-defined
- Level of Accuracy?
- Probability of completion within estimate?
- Contingency included?
- Optimistic? Pessimistic? Most Likely?
- Any instructions about “buffer” or “padding”
- Cultural beliefs
- “PM wants ‘low risk’ estimate”
- Organizational policies
- Rewards for on-time, punishment for late
- Adjustments to schedules
2. Causes of Overrunning the Estimate:
- Tendency to wait until activity is urgent to work on it
- Willingness to accept other high priority work due to belief that contingency is built into estimate
- Typical work pattern of many people
- “Student Syndrome” – Goldratt
- Work expands to fill the time—and “safety time is wasted” (Parkinson’s Law)
- Failure to provide resources when needed
3. Causes of Not Passing on Time Savings:
- Little or no reward for finishing early
- Finish early one time and it’s always expected
- Finish early, get more to do!
- Time & Materials Contracts — early finish = less revenue
- Result:
- Completion is made a lower priority
- Contingency Time that was in the estimate was wasted!
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
4. What is Path Convergence?
- Multiple predecessors merging into a single activity
- What’s the result of Path Convergence?
- The longest delay is passed on to the successor activity
5. Causes of Multitasking:
- Trying to keep everyone busy
- “While waiting, work on something else”
- Many companies encourage extensive multitasking
- Focus on local efficiency could damage overall performance of a system (Sub-optimization)
6.Causes of Loss of Focus:
- Early Start Schedules
- Allow all activity pathways to start at same time
- Can cause PM’s attention to become diffused
- Changing Critical Path during project performance
- Trying to exclusively use Earned Value for project control
- EV does not discriminate between activities of differing importance
- Using Earned Value Action Thresholds that are too tight
- Resulting in too many control actions
Critical Chain Method of Scheduling
A Critical Chain is a resource constrained critical path. Scheduling in the new method is done by keeping the above problems in mind and ensuring that we turn them into an advantage.
In critical chain method,
- The team members are encouraged to make optimistic estimates rather than traditional pessimistic estimates
- Buffers are not kept with individual activities, rather than the collective buffers are built at the end of each path, in this case known as a chain of activities.
- Project Buffer is kept at the end of the Critical Chain (longest chain) and Feeding Buffers are kept at the end of Non-Critical Chains which are feeding into the Critical Chain thus reducing the impact of Path Convergence impacts.
- Buffers are shown as activities which are under the control of the project manager.
- This helps in effective use of buffers and eliminating their unnecessary wastage.
- Resources are not punished if they miss a deadline of an activity, as there are buffer at the end of the chains
- Late Start schedules are used rather than traditional Early Start schedules used in Critical Path Method
- Resources are allocated 100% to avoid multitasking.
A conceptual example of critical chain scheduling using buffers at the end of chain is shown below.
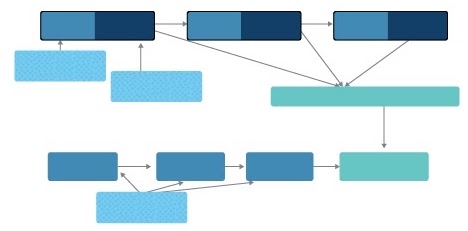
The steps followed are as below:
1. Both pessimistic and optimistic estimates are taken from the team members for each task.
2. In above example, tasks A,B and C have pessimistic estimate of 4 weeks each and an optimistic estimate of 2 weeks each.
3. First a low-risk schedule with pessimistic estimates is built. In this case it comes to 12 weeks.
4. Then the critical chain schedule is prepared by taking the optimistic estimates, which comes to 6 weeks. Then the 2 weeks savings from each task is used as a buffer for the whole chain.
5. Fifty per cent of the 6 weeks, which is 3 weeks, is added as buffer at the end of the chain.
6. The total duration of the chain now comes to 9 weeks with a project buffer of 3 weeks.
7. The resources are encouraged to complete the tasks in the optimistic time. In case someone fails, they are not punished. The project buffer, which is now under the control of project manager, can be responsibly used as the cushion.
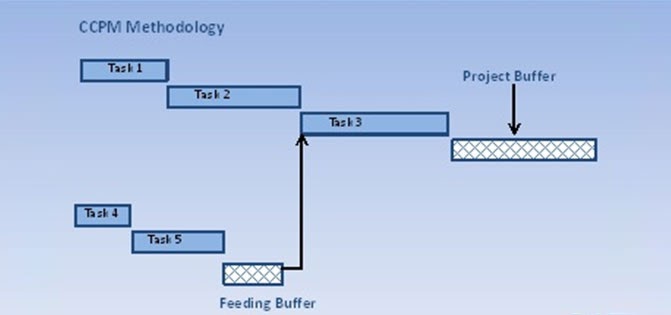
Critical Path Project Management Defines Three Types of Buffers
1.Project Buffer :The total pooled buffer depicted in the image above is referred to as the project buffer.
2.Feeding Buffer :
In a project network, there are path/s which feed into the critical path. The pooled buffer on each such path represents the feeding buffer to the critical path (depicted in the image below), resulting in providing some slack to the critical path.
3.Resource Buffer :
This is a virtual task inserted just before critical chain tasks that require critical resources. This acts as a trigger point for the resource, indicating when the critical path is about to begin.
As the progress of the project is reported, the critical chain is recalculated. In fact, monitoring and controlling of the project primarily focused on the utilization of the buffers. As you can see, the critical chain method considers the basic critical path based project network and schedule to derive a completely new schedule.
The critical path project management methodology is very effective in organizations which do not have evolved project management practices.
However, the methodology does not advocate multi-tasking, and in projects with complex schedule networks, the results of implementing the critical path methodology have proven to be a deterrent to the overall project schedule. In addition, there is no standard method for calculating and optimizing the project buffers. The critical path project management methodology has had a fair amount of success in manufacturing; however, it has not achieved any noteworthy success in the IT industry.
Along similar lines, the event chain methodology of project management focuses on determining the uncertain events and the chain reactions they propagate. It is a method of modeling uncertainties and is based on Monte Carlo analysis, Bayesian Belief Network, and other established simulation methodologies. When they occur, events can cause other events, triggering an event chain, which will effectively alter the course of the project. Events and event chains are identified, and quantitative analysis is performed to determine the extent of the uncertainty and the probable impact of the same on the project. From this exercise, critical event chains are derived, which have the potential to impact the project significantly. Event chain diagrams are visual representations of events, event chains, and their impact.
It is clear that neither the critical path project management methodology nor the event chain methodology can be considered alternatives to the standard methodology for project management as advocated by PMBOK. While the critical path project management methodology can be at best used as a tool for deriving project schedule networks, the event chain methodology for project management can be used as a tool for quantitative risk analysis.
Conclusion:
The Critical Chain Method has practically addressed the challenges in standard scheduling using critical path method. And CCM effectively comes out as a better method and has significantly improved the chances of meeting a schedule deadline. This method is being practiced across organizations, both in projects as well as operation scheduling.