
SAP MM (Material Management) Tutorial | A Complete Guide
Last updated on 09th Aug 2022, Blog, Tutorials
This SAP MM in simple method to implement a SAP MM module step by step with a real time project scenarios and problems
SAP MM stand for the Material Management, it is one of the important module of SAP logistics that deals with a procurement, vendor master data and material resources of the company.
In SAP, MM module records all the transactions that are related to goods or materials on the regular basis.
SAP MM module helps to implement the supply chain management (SCM) in a organization and enables that to control the inventory management, forecast customer demand and updated on all the transactions of the supply chain.
MM module can be integrated with different modules of SAP such as Production planning(SAP PP), Financial Accounting and controlling (SAP FICO), Quality Management(SAP QM), Warehouse Management(SAP WM), Sales and Distribution(SAP SD), etc.
The integration of SAP MM with the other modules enables are the replication of transactions that are processed in other SAP modules to MM module.
Organizational Structure of SAP MM
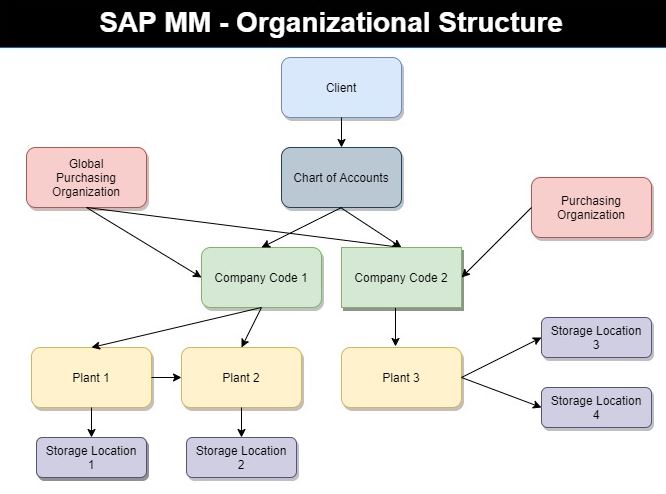
The important organizational elements of the material management are
- 1. Client
- 2. Company Code
- 3. Plant
- 4. Purchase Organization
- 5. Storage Location
- 6. Purchasing Group
Client:
It is a highest level of organizational unit that contains set of tables, master data, etc.
In real-time SAP basis are consultant made new SAP clients other than existing clients.
Company Code:
Company code is a separate legal entity or separate accounting the department of the organization.
All the financial statements are like profit and loss account, business Balance sheets, etc.. are prepared at a company code level.
Plant:
Plant is a location where the logistics are activities such as production, services and maintenance facilities are to be performed.
Purchasing Organization:
Purchase Organization is a physical organizational unit which is responsible for a procurement of goods and services for the organization from a vendors.
Storage Location:
Storage location is the sub division of the plant where the materials are to be maintained and saved.
Purchasing Group:
It is a group of the persons or employees who are responsible with the materials that are being purchased in an organization.
Purchase groups are assigned to be a respective material master.
SAP MM – Procurement Process
Every organization acquired a material or services to finish its business needs.
The process of buying a materials and obtaining the services from vendors or dealers is called a procurement.
Procurement be done in such a way that materials are ordered in correct quantity, with a proper value at a proper time.
It is subdivided into below parts
- Basic Procurement
- Special Procurement
Basic Procurement
Basic procurement is a process of acquiring goods or services in the right quantity, at the right price, and at the right time.
However it is critical to keep a right balance between a quantity, price, and time.
Consider the following example
Organizations try and maintain inventory levels at a minimum, due to the prices associated with high levels of an inventory; at the same time, it can be find to stop production due to the shortage of raw materials.
Getting the minimum price for the product or service is often necessary, however it is equally important to keep a balance between the product availability, quality, and vendor (seller) relations.
Procurement Lifecycle
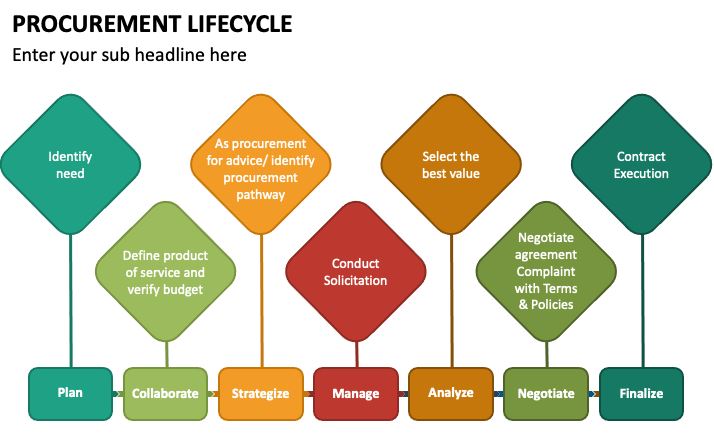
Procurement in most modern organizations that follow some sequential steps which are explained below
Requirement and Information Gathering
Procurement process starts with the gathering data about a product and its quantity.
Then for the required products and services, it is need to look for suppliers who can satisfy the needs.
Supplier Contact
After collecting the requirements, one looks for the suppliers who can fulfill these requirements.
Based on that, quotation requests or data requests are sent to the suppliers or they are contacted to directly.
Background Review
Once the supplier is known, the product/service quality is verified, and any necessities for the services such as installation, warranty, and maintenance parameters are investigated.
Some samples of the products can be obtained for a quality examination.
Negotiation
Some negotiations are with the suppliers is made regarding the price, availability, and delivery schedule of the products/services.
Thereafter, a contract is signed that is a binding legal document between the supplier and an ordering party.
A contract will be include all necessary data such as price and quantity of material, delivery date, etc.
Order Fulfillment
Ordered material is shipped, delivered to an ordering party, and the supplier is a paid accordingly.
Training and installation of the product or services may also be included.
Consumption, Maintenance and Disposal
As the products/services are consumed, the performance of the products or services is calculated and any follow-up service support, if required, is analysed.
Contract Renewal
Once the products or services are consumed or the contract expires and require to be renewed, or the product or service is to be re-ordered, the experience with the vendors and service providers are reviewed.
If the products or services are to be re-ordered, the company decided, whether to order from the previous supplier or think about a new suppliers.
Basic Procurement Activities
The following diagram illustrates the flow of basic procurement activities
- Type of Basic Procurement
- There are 2types of basic procurement
- Procurement for Stock vs Consumption
- External vs Internal Procurement
Procurement for Stock vs Consumption
The below points show the difference of Procurement for Stock vs. Consumption
Procurement for Stock
A stock material is a material that is maintain in stock.
These materials are maintain in stock once received from a vendor.
The stock of this material maintains on increasing or decreasing based on the amount of quantity received or issued.
To order a material for stock, the material must have a master record within a system.
Procurement for Direct Consumption
When the procurement is for the direct consumption, i.e., it will be consumed as soon as it is received, the user should denote the consumption purpose.
To order for a material for consumption, the material may have a master record within a system.
External vs Internal Procurement
The below points show the difference of External vs Internal Procurement
External procurement
It is the process of procuring goods or services from the external vendors.
There are three basic forms of external procurement commonly supported by the purchasing component of the IT system.
One-time orders
Are generally used for the material and services that are to be ordered irregularly.
Longer-term contracts with the subsequent issue of release orders
For materials that are being ordered regularly and in high quantities, that can negotiate deal with the vendor (seller) for pricing or conditions & record then in a contract.
In a contract also denote the validity date.
Longer-term scheduling agreements and delivery schedules
If a material is ordered to an everyday basis and is to be delivered according to the exact time schedule, then set up a scheduling agreement.
Internal Procurement
Large corporate organizations own multiple separate businesses or companies.
Internal Procurement is a process of getting the material and services from among identical company.
So, each of these companies keep a complete bookkeeping system with separate Balance, Profit & Loss Statements so that when trade occurs between them it will be recorded.
Special Procurement
Special stocks are the stocks that are managed variously, as these stocks do not belong to the company.
Special stocks are maintain at some particular location.
Special procurement and special stock types are divided into the below categories
Consignment Stocks
Consignment stocks are those material that is available at the store premises, however it still belongs to a vendor (seller) of the material.
If utilize the material from the consignment stocks, then have to pay to the vendor.
Third-party Processing
In third-party processing, a company passes on a sales order to the associate an external vendor (seller) who sends a goods directly to the customer.
The sales order is not processed by a company, but by the vendor (seller).
Third-party items are entered in purchase requisitions, purchase orders, and sales orders.
Pipeline Handling
In pipeline handling, the company required not order or store the material involved.
It is obtainable as and when required by a pipeline (for example, oil or water), or another style of cable .
The material that are consumed is settled with the vendor (seller) on the regular basis.
Returnable Transport Stock
The company orders goods from a vendor (seller).
The goods are delivered with the returnable transport packaging (pallets, containers) that belongs to a vendor (seller) and is saved at the customer premises until they are return it to the company.
Subcontracting
The vendor (the subcontractor) received a components from the ordering party with the help of which it produces a product.
The product is ordered by the company through a purchase order.
The components need by the vendor (seller) to manufacture the ordered product are listed in the purchase order and offered to the subcontractor.
Subcontracting
- Stock Transfer Using Stock Transport Order
- Goods are procured and supplied within the company.
- One plant orders the goods an internally from the another plant (receiving plant/issuing plant).
- The goods are procured with the special type of purchase order – the stock transport order.
- Able to request and monitor the transfer of goods with the stock transport order.
Features of SAP MM

Here are some of the major features of SAP MM:
Handles both the raw material management and an inventory management
Ensures that there is no shortage of the materials in a supply chain
Helps to increase the efficiency of procurement activities
Accelerates productivity while reducing the overall procurement costs
Handles different business aspects like material requirement planning, vendor evaluation, procurement, material
validation, warehouse management and invoice verification
Benefits of SAP MM
With changing customer demands and expectations, the efficiency of the organisation relates to its ability to cater to market demands in a shortest time possible. To ensure that seamless delivery of products, the business is need to maintain the right stock at the right time.
Having an efficient material management process helps to prevent supply gaps and shortages of an inventory and raw materials and increase the supply chain’s efficiency.
SAP MM automates material management and are procurement activities, making the full process more competent.
Here are few of the top benefits of a SAP MM:
Enhances the overall inventory management
Minimises and eliminates an inventory losses
Reduces the time and labour spent on the maintaining inventory
Decreases a material wastage by avoiding the stocking on obsolete or unnecessary products
lowers labour costs and also optimises labour employment
minimises the manufacturing cycle times
Reduces an expenditure on storing the unwanted materials
Improves the product delivery time
Increases the transparency of an inventory management
Are you looking training with Right Jobs?
Contact Us- Windows Azure Interview Questions and Answers
- Salesforce Architecture Tutorial
- Wrapper Class in Salesforce Tutorial
- salesforce lightning
Related Articles
Popular Courses
- VM Ware Training
11025 Learners - Microsoft Dynamics Training
12022 Learners - Siebel Training
11141 Learners
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- Difference between Data Lake vs Data Warehouse: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- What does the Yield keyword do and How to use Yield in python ? [ OverView ]
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know
