
SAP SD (Sales & Distribution) Training Tutorial | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day
Last updated on 10th Aug 2022, Blog, Supply chain management, Tutorials
SAP Sales and Distribution is one of the key components of the SAP ERP system and is used to keep shipping, billing, selling and transportation of products and services in the organization.
SAP Sales and Distribution module is a part of SAP Logistics module that keep customer relationship starting from raising a quotation to sales order and billing of the product or service.
This module is closely integrated with other modules like SAP Material Management and also PP.
Key Components in SAP SD
The key components are in SAP Sales and Distribution module :
- Customer and Vendor Master Data
- Sales Support
- Shipping of Material
- Sales Activities
- Billing related
- Transportation of products
- Credit Management
- Contract Handling and Management
- Foreign Trade
- Information System
SAP Sales and Distribution Cycle
SAP SD – Organizational Structure
SAP provides more components to finish SAP Sales and Distribution organizational structure like Sales Areas, Distribution Channels, Divisions, etc. The SAP SD organization structure majorly consists of 2 steps
- Creation of Organization an elements in SAP system, and
- second is to link every element as per requirement.
On top of this organization structure in the SD module, sales organization is at more level and is responsible for distribution of goods and services.
SAP recommends to maintain the number of sales organization in an organizational structure to be minimum. This will help in create the reporting process simple and ideally it should have a single sales organization.
The next level is distribution channel, which tells the medium by which the products and services are distributed by the organization to its end users.
Division is the organizational structure, which represents a product or service line in a unique organization.
A sales area is known as entity, which is required to process an order to a company.
It comprises of sales organization, distribution channel and division.
In SAP SD organizational structure, every sales organization is assigned to a company code.
Then the distribution channel and divisions are assigned to sales an organization and all of these comprise to made a sales area.
In the first step of an SD organizational structure, sales organization is assigned to the company code and then is to explain a distribution channel and then division to a sales organization.
The below diagram shows the organizational structure of a Sales and Distribution module.
Material management
Material Management is one of the key modules in SAP ERP System and covered the day to day business operations related to an inventory and procurement.
This module is closely integrated with the other modules of R/3 systems like Finance Accounting and Controlling, Sales and Distribution, Quality Management, Product Planning.
Integration with Sales and Distribution SD Module
Consider an example of creating a sales order in SAP SD, it involved copying the details of items from the Material Management.
Availability check of the item and price details are also taken from a MM, but this can be controlled ina SD module.
To made inbound and outbound delivery of goods for a sales order, shipping details, loading point etc. also comes from a Material Master.
The item that is placed using a Sales order must be extended to the sales area of the organization to sales order/customer, otherwise it not be possible to transact with this material.
Finance and Accounting
- SAP FI stands for Financial Accounting and it is one of the more important modules of SAP ERP.
- It is used to save the financial data of an organization.
- SAP FI helps to analyse the financial condition of a company in a market.
- It can integrate with the other SAP modules such as SD, PP, SAP MM, SAP SCM etc.
- SAP SD – Create Partner Function
- Partner function allows to identify which functions a partner has to perform in any of business process.
- Consider a simplest case, where all the customer functions are performed by a partner customer.
- As these are mandatory functions, they have to be explained as obligatory functions in a SD system.
- These functions are categorized as per partner type in Sales and also Distribution system.
The below partner kinds are Customer, Vendor, Personnel, Contact Person and common partner functions as per these partner types are
Partner Type Customer
- Sold-To-Party
- Ship-To –Party
- Bill-To-Party
- Payer
SAP SD – Defining a Sales Document
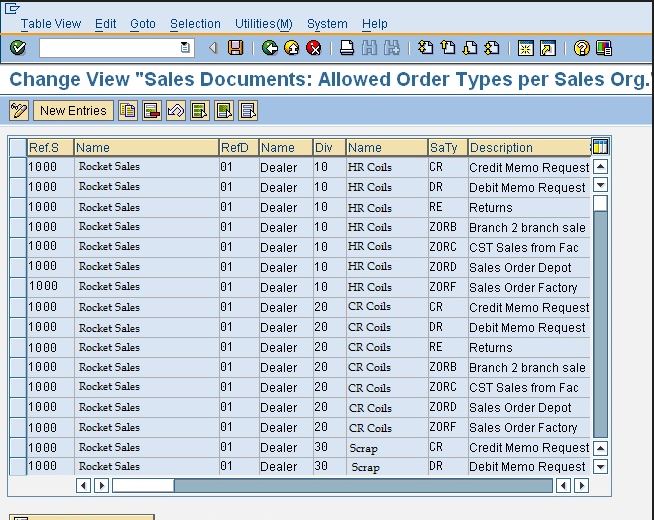
There are various types of sales documents that can be explained in a SAP system. These include
- Credit Memo
- Debit Memo
- Standard Order
- Delivery Returns, etc.
SAP SD – Special Business Process
In SAP Sales and Distribution module, along with the processing of normal sales orders, that can also made special business processes like configurable products, items manufactured on order, etc.
Consignments Processing
Consignments are known as products, which are owned by the company and are located at the client location
- It is not need for the customer to pay for these goods, until they are moved from the consignment stock.
- The customers can return the products in a consignment stock, which are not required.
Key Features of Consignment Stock
- The goods in a consignment stock can be an accessed by a customer at any time.
- Consignment goods are stored by a customers at the warehouse.
- Customer has to only pay for goods, which are eliminate from the stock and only for the quantity taken.
As the consignment stock is still a part of the company’s valuable stock, so there is a require to manage this in the system.Must manage the consignment stock separately, so that company should be aware, which stock is available at a customer location.This should be managed separately for every customer.
For an organization, consignment stock is keep as a special stock in inventory and this helps to track returnable goods from the customer. Consignment stock management includes 4 key activities in the system, which are
- Creating a Consignment Fill-Up (Stock is fill up at warehouse).
- Creating Consignment Issue (Stock issued from warehouse).
- Creating a Consignment Pick-Up (Stock return to manufacturer).
- Displaying Consignment Returns (Stock return from customer).
SAP SD – Pricing
Pricing in Sales and Distribution is used to explain the calculation of prices for external vendors or customers and cost. This condition is explained as a set of conditions when a price is calculated.
Example
Consider a case when customer orders certain quantity of a product on a particular day.
Different factors like customer, product, order quantity and date tells the final price to that customer.
This information saved in the system as master data in the form of condition records.
There are different pricing elements like prices, surcharges, discounts, and taxes, which are defined in SAP system as condition types.
To keep pricing information for a pricing element in a system, have to create condition records.
Manual Pricing
While processing a sales order,that can also manipulate the pricing at the item as well as the header level.
Manual processing of a price screen is dependent on one condition types.
During a Sales Order processing using a manual processing for a condition type, that can perform the below activities
- Deleting the pricing element.
- Changing a condition amount.
- Entering additional pricing elements.
How to add Pricing elements manually?
If want to add customer discount manually in the pricing screen of the sales order, click on Add line.
In Data screen, can enter an additional conditions like – customer discount in the condition type field.
Enter a percentage range and then press ENTER. can also delete pricing elements in item pricing and header screens.
To do this, select thespecific condition by positioning the cursor and click on a delete line.
Note that all header conditions explained at header level cannot be changed at the item level, and conditions explained at this level cannot be changed at the header level.
Only the Conditions that explain at both header and item conditions can only be edited at both levels.
SAP SD – Delivery Processing
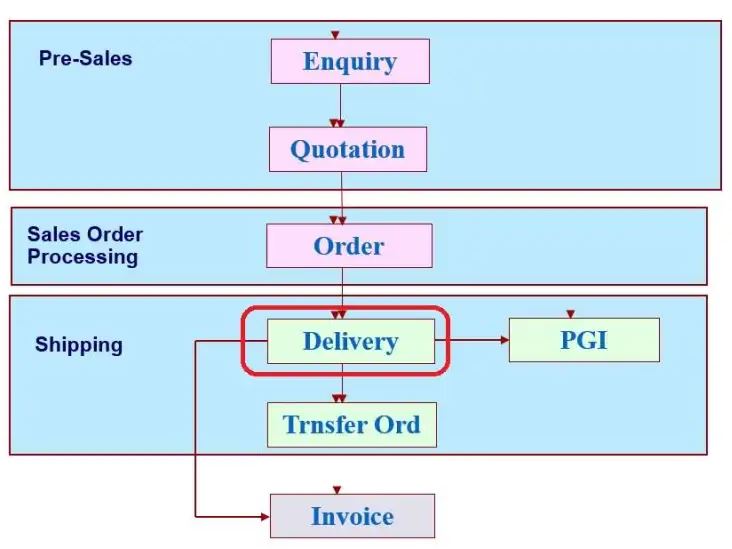
There are differentfunctions in delivery processing like
- Quantity Management and adjustment
- Text Management
- Printing
- Validation
Quantity difference in the inbound delivery for an outbound delivery to post change in the delivery.
Using text management, can made the below changes to the delivery document like
- Display
- Change
- Delete
- Save
If want to create and save new texts for a specific delivery, this can also be done.
Printing is done in EWM to print the delivery notes.
Can create an outbound delivery order or an outbound delivery.
Validation in an EWM is used to checkn the delivery document, if it is finish and can be further processed in the system.
SAP SD – Access Sequence
- This is the search strategy, which is used by the system to found valid data for a specific condition type.
- It tells about the order in which the system searches for the data.
- An access sequence include of one or more access sequences.
- It helps to the system to search first, second and so on until it finds a valid record.
- An access sequence is explained for every condition type where a condition record is created.
Create or maintain an access sequence in customizing
Go to SPRO → IMG → Sales and Distribution → Basic Functions → Pricing → Pricing Control → Define Access Sequences
Determine Pricing by item Category
It is not need that all the items are suitable for pricing or not
If an item is not relevant for a pricing, then line item will be blank for the item.
An Item category is using a control the pricing of an item.
Billing Item Categories
- An item is suitable for a billing?
- Cost of item should be a determined?
- Is it return item?
- Whether it is statistical item?
SAP SD – Item Categories
- An item category is used to explain if an item is suitable for billing or pricing.
- It explain the additional control functions for a sales document.
General Data Control Elements
- An item refers to the material or a text item?
- Whether pricing has to be carried out for the item?
- Are schedule lines allowed for the item?
- When the item has to be considered as finished?
- If an item cannot be fully delivered, a message will appear in a system or not?
- Which partner functions are allowed for the tem?
- Which output is allowed for abusiness transactions?
Shipping Data Control Elements
- Is the volume and weight of an item find?
- Whether this Item is relevant for the delivery or not?
Billing Data Control Elements
- Is an item suitable for a billing?
- Should the cost of an item should be determined?
- Is it return an item?
- Whether it is a statistical item?