- Financial Performance – A Complete Tutorial
- How Six Sigma Principles Can Progress Your Productivity – Tutorial
- Google Analytics Pro Tutorial | Fast Track your Career
- Activity-Based Costing Tutorial | Know about Definition, Process, & Example
- Create a workbook in Excel Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Excel ROUNDUP Formula Tutorial | Learn with Functions & Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Tutorial | Learn In 1 Day
- SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- IBM SPSS Statistics Tutorial: Getting Started with SPSS
- SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [Updated]
- SAP FIORI Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Introduction to Business Analytics with R Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Tableau Desktop Tutorial | Step by Step resource guide to learn Tableau
- Implementing SAP BW on SAP HANA | A Complete Guide
- SAP HANA Administration | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau API Tutorial | Get Started with Tools, REST Basics
- SAP FICO ( Financial Accounting and Controlling ) Tutorial | Complete Guide
- Alteryx Tutorial | Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- Getting started with Amazon Athena Tutorial – Serverless Interactive | The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction to Looker Tutorial – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Sitecore Tutorials | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE |Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Adobe Analytics Tutorial – The Ultimate Student Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- Pentaho Tutorial – Best Resources To Learn in 1 Day | CHECK OUT
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Spotfire Tutorial for Beginners | Quickstart – MUST- READ
- JasperReports Tutorial: Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Charts and Tables – Qlikview Tutorial – Complete Guide
- TIBCO Business Works | Tutorial for Beginners – Learn From Home
- Cognos TM1 Tutorial : Learn Cognos from Experts
- Kibana
- Power BI Desktop Tutorial
- Tableau Tutorial
- SSAS Tutorial
- Creating Tableau Dashboards
- MDX Tutorial
- Tableau Cheat Sheet
- Analytics Tutorial
- Lean Maturity Matrix Tutorial
- MS Excel Tutorial
- Business Analysis Certification Levels & Their Requirements Tutorial
- Solution Assessment and Validation Tutorial
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Enterprise Analysis Tutorial
- Create Charts and Objects in Excel 2013 Tutorial
- Msbi Tutorial
- MicroStrategy Tutorial
- Advanced SAS Tutorial
- OBIEE Tutorial
- Tableau Server Tutorial
- OBIA Tutorial
- Business Analyst Tutorial
- Cognos Tutorial
- Qlik Sense Tutorial
- SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
- SAS Tutorial
- PowerApps Tutorial
- Financial Performance – A Complete Tutorial
- How Six Sigma Principles Can Progress Your Productivity – Tutorial
- Google Analytics Pro Tutorial | Fast Track your Career
- Activity-Based Costing Tutorial | Know about Definition, Process, & Example
- Create a workbook in Excel Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Excel ROUNDUP Formula Tutorial | Learn with Functions & Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Tutorial | Learn In 1 Day
- SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- IBM SPSS Statistics Tutorial: Getting Started with SPSS
- SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [Updated]
- SAP FIORI Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Introduction to Business Analytics with R Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Tableau Desktop Tutorial | Step by Step resource guide to learn Tableau
- Implementing SAP BW on SAP HANA | A Complete Guide
- SAP HANA Administration | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau API Tutorial | Get Started with Tools, REST Basics
- SAP FICO ( Financial Accounting and Controlling ) Tutorial | Complete Guide
- Alteryx Tutorial | Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- Getting started with Amazon Athena Tutorial – Serverless Interactive | The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction to Looker Tutorial – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Sitecore Tutorials | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE |Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Adobe Analytics Tutorial – The Ultimate Student Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- Pentaho Tutorial – Best Resources To Learn in 1 Day | CHECK OUT
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Spotfire Tutorial for Beginners | Quickstart – MUST- READ
- JasperReports Tutorial: Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Charts and Tables – Qlikview Tutorial – Complete Guide
- TIBCO Business Works | Tutorial for Beginners – Learn From Home
- Cognos TM1 Tutorial : Learn Cognos from Experts
- Kibana
- Power BI Desktop Tutorial
- Tableau Tutorial
- SSAS Tutorial
- Creating Tableau Dashboards
- MDX Tutorial
- Tableau Cheat Sheet
- Analytics Tutorial
- Lean Maturity Matrix Tutorial
- MS Excel Tutorial
- Business Analysis Certification Levels & Their Requirements Tutorial
- Solution Assessment and Validation Tutorial
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Enterprise Analysis Tutorial
- Create Charts and Objects in Excel 2013 Tutorial
- Msbi Tutorial
- MicroStrategy Tutorial
- Advanced SAS Tutorial
- OBIEE Tutorial
- Tableau Server Tutorial
- OBIA Tutorial
- Business Analyst Tutorial
- Cognos Tutorial
- Qlik Sense Tutorial
- SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
- SAS Tutorial
- PowerApps Tutorial

SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
Last updated on 11th Aug 2022, Blog, Business Analytics, Tutorials
Introduction to SAP security :
SAP Security is required to protect SAP Systems and Critical Information from Communication Security and protecting standard users and other best practices should be followed in maintaining SAP Environment.
About SAP security :
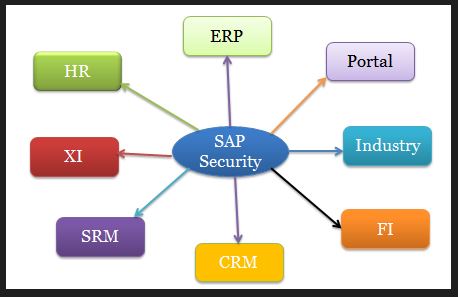
In a SAP Distributed Environment, there is always a need to protect critical Provisioning shouldn`t permit unauthorized access to the system and there is a need to manage and review the profile policies and system security policies in SAP environment.
Methods of SAP security :
- The Most common type of authentication in a SAP system is by using the username and The SAP administrator creates a login user ID.
- There is a need for a secure authentication mechanism with username and password that explains a password policy that prevents users from setting passwords that are simply predictable.
- SAP provides a variety of default parameters that need to be set to define password rules, password lengths, password complexity, default password changes, and more.
- SAP system user management tool: Numerous user management options are available through the SAP NetWeaver system. Some of the most popular tools for managing users include: User administration for ABAP application servers (transaction code: SU01).
- can update users in ABAP using transaction code SU01 in User Management.
Importance of SAP security :
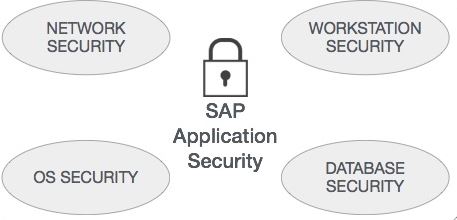
- They are Protect key components when in use Started implementation of security measures the system.
- Network security consists of management Network topology, network isolation, Network service and protocol restrictions, Domain concept development.
- Network security should match the security Requirements.
- The ever-increasing number of mobiles Devices and Internet accessibility.
- It is recommended to configure the network to enable it Internal network segments within an infrastructure internal zone similar to Scheme require different levels of approval to reflect different levels of access.
Functions of SAP security :
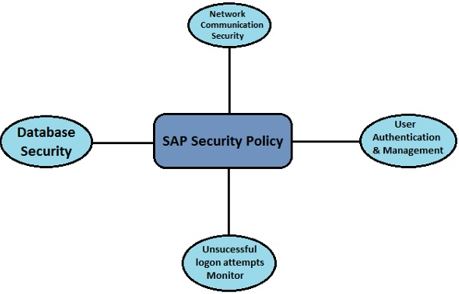
For screening and recording safety-related data events.Backup and emergency procedures You must set up a disaster recovery and backup mechanism in order to do this.Use quickly in an emergency. It should address the following emergency scenarios are:
- Failure of an single server.
- Failure of an single database.
- Compromise of SAP solution.
- Failure of the transport system (ABAP).
- Explain the processes and people responsible.
- Conduct regular emergency drills and adjusting the processes accordingly.
- Create and change emergency users.
- Gather required logs and data.
- Explain the rules and triggers for identification and classification of incidents.
- Explain implementation of corrections and recovery measures.
- Prepare technical and nontechnical follow on activities and improvements A material aspect of emergency planning is the data backup of the SAP software systems.
Features of SAP security :
- SAP Security Optimization Services Media Library.
- Security Baseline Template.
- Secure Operations Map.
- Security White Papers.
- SAP Security Optimization.
- Security guides for SAP Solutions.
- SAP HANA Security Checklists and Recommendations.
- SAP EarlyWatch Alert.
Uses of SAP security :
- Use SAP GUI. SAP EP controls all access to applications.
- That is Called human integration SAP EP is based on the SAP Web ASJ2EE.
- This is the SAP application server that creates the SAP Enterprise Portal with other knowledge management software components, Union Server and Connector Framework.
- The portal server includes the portal runtime, which is the portal runtime environment.
- It is properly prepared for the front end of the page (PRT), containing application information partially returned by backend apps (like XML) (web browser). builder.
- Users are given access to various materials in iView.
- iView Portal services include services for preserving iView content. User administration through the user management engine is also crucial. The smallest unit for separating and organizing a portal page.
- Another service manages the connection of single iViews to backend applications via the connector framework.
- URL creation services (e.g. via SAP Internet transactions) Server) for additional significant services, such as portal content, caching services, and portal content processing services.
- The portal can be accessed by the latter Internet service.
- It can also access web services.
- Website content In a directory (PCD), all items are content (eg, all objects). iView, roles, content, programmes, and backend programmes).
- In order to clarify responsibilities and access to certain objects and services, PCD sets up a portal that it may refer to as H. Portal content management employing management tools and the TREX search and categorization engine.
- TREX is a search engine for SAP that indexes on.
- It searches the whole portal’s material, allowing users to look for keywords or logically connected search phrases.
- Users can save the files and data discovered on the portal for their own knowledge management.
Conclusion :
The User Account API is implemented for maintaining services.Group API can use the Groups API to Make group definitions.Also, at run time can inquire if a user belongs to a particular group.The Role API is used to maintain the role of the portal.Can be used to assign The role of the portal to the user.Connection to UME. This is specifically important when implementing SAPEP. Internet scenario.
For example, can make external users persistent in the portal database and internal users in the LDAP directory.This categorisation may also be carried out based on user characteristics.For example, can store the portal role assignments to the users in the portal database.The corresponding master data can be saved in the LDAP directory.Managers can manage more LDAP directories at the same time.Therefore, users can be distributed across various storage systems.
