- What is Lean?| Everything You Need to Know
- What is SAP Workflow? : A Complete Guide
- Difference between Tableau and Power BI | Benefits and Special Features
- Data Warehouse in Tableau | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Tableau Server?| Everything You Need to Know | A Definitive Guide
- What is Dax in Power BI? | A Comprehensive Guide
- Upgrade in Tableau Desktop and Web Authoring | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is SAP HANA | SAP HANA Database Connection | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- SAP BPC – What is Business Planning and Consolidation? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Root Cause Analysis: Definition, Examples & Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Seven Basic Quality Improvement Ishikawa Tools | Important asset to control quality in your project [OverView]
- What is Power BI | Its Use Cases and Applications | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- How and why to measure and analyze employee productivity | Everything You Need to Know
- Top 10 Employee Retention Strategies | Everything You Need to Know
- What are LookML Projects and the Developer Mode | How to Create LookML Projects?
- What are Slowly Changing Dimension | SCD Types and Implementations | Step-By-Step Process
- What is Pareto Chart and How to Create Pareto Chart | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- What does an Agile Business Analyst do | Required Skills, Roles and Responsibilities [ Job & Future ]
- What is Lean Management? | Role and Concepts of Lean Management | Expert’s Top Picks
- A Definitive Guide of Working Capital Management with Best Practices & REAL-TIME Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Fundamentals | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- Business Analyst : Job Description | All you need to know [ Job & Future ]
- How to create a Splunk Dashboard | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Splunk Logging ? | The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Alteryx vs Tableau | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Predictive Analytics? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- An Overview of SAS Stored Processes | The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- How to Create Conditional Formatting in Cognos Report Studio | A Complete Guide
- Difference between OLTP vs OLAP | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- ECBA vs CCBA vs CBAP | A Complete Guide For Beginners | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Import Custom Geocode Data in Tableau | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- Data Warehouse Tools : Features , Concepts and Architecture
- PGDM vs MBA | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Most Popular Data Visualization Tools | A Complete Beginners Guide | REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau vs Looker : Comparision and Differences | Which Should You Learn?
- Benefits of Employee Satisfaction for the Organization [ Explained ]
- DAX In Power BI – Learn Power BI DAX Basics [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- Power Bi vs Tableau : Comparision and Differences | Which Should You Learn?
- What is Alteryx Tools | Alteryx ETL Tools | Comprehensive Guide
- What is Tableau Prep? : Comprehensive Guide | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- What are Business Intelligence Tools ? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Tableau Aggregate Functions | A Complete Guide with REAL-TIME Examples
- Intervalmatch Function in Qlikview | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- QlikView Circular Reference | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Data Blending in Tableau | A Complete Guide with Best Practices | Free Guide Tutorial [ OverView ]
- Splunk vs ELK | Differences and Which Should You Learn? [ OverView ]
- QlikSense vs QlikView | Differences and What to learn and Why?
- What Is Measurement System Analysis | Required Skills | Everything You Need to Know
- Splunk Timechart | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- What Is Image Processing ? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is a Business Analysis ? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Top Business Analytics Tools | Comprehensive Guide
- Business Analyst Career Path [ Job & Future ]
- Time Series Analysis Tactics | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is Splunk ? Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Which Certification is Right for You: Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma?
- SAS Vs R
- Top Technology Trends for 2020
- Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist
- What are the Essential Skills That You Need to Master in Data Analyst?
- What is Six Sigma?
- Common Cause Variation Vs Special Cause Variation
- Reasons to Get a Six Sigma Certification
- What Is Strategic Enterprise Management and its Components?
- What Are The Benefits Measurement Constrained Optimization Methods?
- What Is the Benefit of Modern Data Warehousing?
- What Is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
- What Is The Purpose and Importance Of Financial Analysis?
- What is Insights-as-a-Service (IaaS)?
- Business Analytics With R Programming Languages
- Where Are The 8 Hidden Wastes?
- What Are Market Structures?
- What is Cost of Quality (COQ)?
- What is Build Verification Testing?
- Quality Improvement in Six Sigma
- What is Process Capability Analysis?
- How To Measure The Effectiveness Of Corporate Training
- SAP Financials And SAP Accounting Modules
- Tips to Learn Tableau
- Why Should I Become a CBAP?
- History And Evolution of Six Sigma
- How to use Control Chart Constants?
- Data Analytics Course For Beginners
- How to Build a Successful Data Analyst Career?
- Data Analytics Vs Business Analytics
- What is SAP Certification?
- Books To Read For a Six Sigma Certification
- Six Sigma Green Belt Salary
- What is the ASAP Methodology?
- Complete list of SAP modules
- What is Lean?| Everything You Need to Know
- What is SAP Workflow? : A Complete Guide
- Difference between Tableau and Power BI | Benefits and Special Features
- Data Warehouse in Tableau | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Tableau Server?| Everything You Need to Know | A Definitive Guide
- What is Dax in Power BI? | A Comprehensive Guide
- Upgrade in Tableau Desktop and Web Authoring | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is SAP HANA | SAP HANA Database Connection | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- SAP BPC – What is Business Planning and Consolidation? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Root Cause Analysis: Definition, Examples & Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Seven Basic Quality Improvement Ishikawa Tools | Important asset to control quality in your project [OverView]
- What is Power BI | Its Use Cases and Applications | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- How and why to measure and analyze employee productivity | Everything You Need to Know
- Top 10 Employee Retention Strategies | Everything You Need to Know
- What are LookML Projects and the Developer Mode | How to Create LookML Projects?
- What are Slowly Changing Dimension | SCD Types and Implementations | Step-By-Step Process
- What is Pareto Chart and How to Create Pareto Chart | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- What does an Agile Business Analyst do | Required Skills, Roles and Responsibilities [ Job & Future ]
- What is Lean Management? | Role and Concepts of Lean Management | Expert’s Top Picks
- A Definitive Guide of Working Capital Management with Best Practices & REAL-TIME Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Fundamentals | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- Business Analyst : Job Description | All you need to know [ Job & Future ]
- How to create a Splunk Dashboard | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Splunk Logging ? | The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Alteryx vs Tableau | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Predictive Analytics? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- An Overview of SAS Stored Processes | The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- How to Create Conditional Formatting in Cognos Report Studio | A Complete Guide
- Difference between OLTP vs OLAP | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- ECBA vs CCBA vs CBAP | A Complete Guide For Beginners | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Import Custom Geocode Data in Tableau | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- Data Warehouse Tools : Features , Concepts and Architecture
- PGDM vs MBA | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Most Popular Data Visualization Tools | A Complete Beginners Guide | REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau vs Looker : Comparision and Differences | Which Should You Learn?
- Benefits of Employee Satisfaction for the Organization [ Explained ]
- DAX In Power BI – Learn Power BI DAX Basics [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- Power Bi vs Tableau : Comparision and Differences | Which Should You Learn?
- What is Alteryx Tools | Alteryx ETL Tools | Comprehensive Guide
- What is Tableau Prep? : Comprehensive Guide | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- What are Business Intelligence Tools ? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Tableau Aggregate Functions | A Complete Guide with REAL-TIME Examples
- Intervalmatch Function in Qlikview | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- QlikView Circular Reference | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Data Blending in Tableau | A Complete Guide with Best Practices | Free Guide Tutorial [ OverView ]
- Splunk vs ELK | Differences and Which Should You Learn? [ OverView ]
- QlikSense vs QlikView | Differences and What to learn and Why?
- What Is Measurement System Analysis | Required Skills | Everything You Need to Know
- Splunk Timechart | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- What Is Image Processing ? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is a Business Analysis ? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Top Business Analytics Tools | Comprehensive Guide
- Business Analyst Career Path [ Job & Future ]
- Time Series Analysis Tactics | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is Splunk ? Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Which Certification is Right for You: Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma?
- SAS Vs R
- Top Technology Trends for 2020
- Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist
- What are the Essential Skills That You Need to Master in Data Analyst?
- What is Six Sigma?
- Common Cause Variation Vs Special Cause Variation
- Reasons to Get a Six Sigma Certification
- What Is Strategic Enterprise Management and its Components?
- What Are The Benefits Measurement Constrained Optimization Methods?
- What Is the Benefit of Modern Data Warehousing?
- What Is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
- What Is The Purpose and Importance Of Financial Analysis?
- What is Insights-as-a-Service (IaaS)?
- Business Analytics With R Programming Languages
- Where Are The 8 Hidden Wastes?
- What Are Market Structures?
- What is Cost of Quality (COQ)?
- What is Build Verification Testing?
- Quality Improvement in Six Sigma
- What is Process Capability Analysis?
- How To Measure The Effectiveness Of Corporate Training
- SAP Financials And SAP Accounting Modules
- Tips to Learn Tableau
- Why Should I Become a CBAP?
- History And Evolution of Six Sigma
- How to use Control Chart Constants?
- Data Analytics Course For Beginners
- How to Build a Successful Data Analyst Career?
- Data Analytics Vs Business Analytics
- What is SAP Certification?
- Books To Read For a Six Sigma Certification
- Six Sigma Green Belt Salary
- What is the ASAP Methodology?
- Complete list of SAP modules

Complete list of SAP modules
Last updated on 21st Sep 2020, Artciles, Blog, Business Analytics
SAP Modules List
ERP SAP software provides various SAP modules, such as FICO, MM, HR, ABAP, SD, PP, PS, CRM, etc for handling day to day business activities of an organization.
SAP Modules are further divided in to two types of modules i.e. SAP Functional modules & SAP Technical modules. Each module of the SAP R/3 system can be integrated with other SAP modules, so the processed data of one module can be used by other modules. The important modules of SAP are
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
List of SAP Functional Modules
| Name of Functional Module | SAP Module |
|---|---|
| Financial Accounting Module | SAP FI |
| Controlling Module | SAP CO |
| Material Management Module | SAP MM |
| Sales & Distribution Module | SAP SD |
| Production Planning Module | SAP PP |
| Quality Management Module | SAP QM |
| Project System Module | SAP PS |
| Human Capital Management Module | SAP HCM |
| Investment Management Module | SAP IM |
| Financial Supply Chain Management Module | SAP FSCM |
| Customer Relationship Management Module | SAP CRM |
| Warehouse Management Module | SAP WM |
| Supplier Relationship Management Module | SAP SRM |
| Advanced Planning & Optimization Module | SAP APO |
| Plant Maintenance Module | SAP PM |
| Product Life Cycle Management Module | SAP PLM |
| Treasury Management Module | SAP TR |
| Logistics Execution Module | SAP LE |
| Banking Module | SAP Banking |
| Environment, Health & Safety Module | SAP EHS |
| Governance, Risk and Compliance Module | SAP GRC |
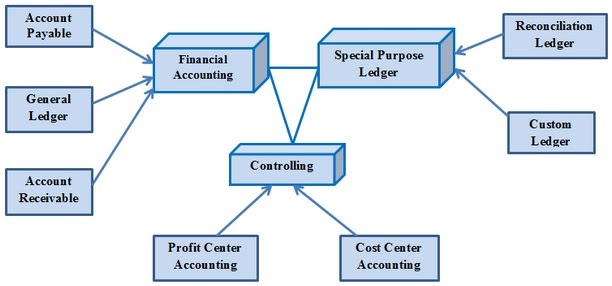
SAP FICO Module
SAP FICO stands for financial accounting and controlling, SAP FICO module handles all the financial transactions of an organization. For e.g. if an organization purchases or sells any assets, it gets recorded in the FICO module. The important sub-modules of SAP FI & SAP CO are
- 1. General ledger accounting
- 2. Accounts payable
- 3. Accounts receivable
- 4. Asset Accounting
- 5. Cost center accounting
- 6. Internal orders
- 7. Profit center accounting
- 8. Product costing
- 9. Profitability analysis
SAP MM Module
SAP material management module is one important module of logistics that deals with procurement and material resources of an organization. The important sub-modules of SAP MM are
- 1. Purchasing
- 2. Inventory management
- 3. Material requirement planning
- 4. Material Master data
SAP HR Module
SAP HR module is also called as Human Capital Management (HCM). It is responsible for performing human resource related activities of an organization. The important sub-modules of SAP HR are
- 1. Personnel administration
- 2. Personnel development
- 3. Time management
- 4. Payroll management
List of SAP Technical Modules
| Name of Technical Module | Module |
|---|---|
| Advanced Business Application Programming | SAP ABAP |
| Security Module | SAP Security |
| Basis Module | SAP Basis |
| Customer Relationship Management | SAP CRM |
| Business Intelligence/ Business Warehouse | SAP BI/BW |
| High Performance Analytics Appliance Module | SAP HANA |
| Business Planning and Consolidation | SAP BPC |
| Application Link Enabling | SAP ALE |
| Business Objects Data Services | SAP BODS |
| Business Objects Module | SAP BO/BOBJ |
| Netweaver | SAP Netweaver |
| FIORI (user interface) module | SAP FIORI |
| Solution Manager | SAP Solution Manager |
| Master Data Management | SAP MDM |
| Business One Module | SAP B1 |
| Governance, Risk and Compliance Module | SAP GRC |
| Enterprise Asset Management | SAP EAM |
| Testing Module | SAP Testing |
| SAP Cloud Platform | SAP Cloud |
| Web Dynpro | SAP Web Dynpro |
| Exchange infrastructure Module | SAP XI |
SAP solutions include a number of functional modules, which support transactions to execute key business processes, such as −
- Financial Accounting (FI)
- Financial Supply Chain Management (FSCM)
- Controlling (CO)
- Materials Management (MM)
- Sales and Distribution (SD)
- Logistics Execution (LE)
- Production Planning (PP)
- Quality Management (QM)
- Plant Maintenance (PM)
- Project System (PS)
- Human Resources (HR)
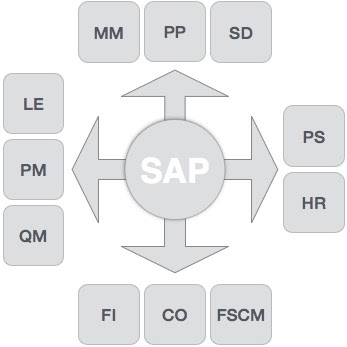
Finance and Controlling (FICO)
SAP FICO is a combination of two ERP modules, i.e., Finance Accounting (FI) and Controlling (CO). Under Finance in SAP and at an enterprise level, the following modules take part −
- FI − Finance
- CO − Controlling
- IM − Investment Management
- TR − Treasury
- EC − Enterprise Controlling
SAP FI (Financial Accounting) is accountable for tracking the flow of financial data across the organization in a controlled manner and integrating all the information for effective strategic decision-making.
Activities Involved in SAP FI
- 1. Creation of Organizational Structure (Defining Company, Company Codes, business Areas, Functional Areas, Credit Control, Assignment of Company Codes to Credit Controls)
- 2. Financial Accounting Global Settings (Maintenance of Fiscal Year, Posting Periods, defining Document types, posting keys, Number ranges for documents)
- 3. General Ledger Accounting (Creation of Chart of Accounts, Account groups, defining data transfer rules, creation of General Ledger Account)
- 4. Tax Configuration & Creation and Maintenance of House of Banks
- 5. Account Payables (Creation of Vendor Master data and vendor-related finance attributes like account groups and payment terms)
- 6. Account Receivables (Creation of Customer Master data and customer-related finance attributes like account groups and payment terms
- 7. Asset Accounting
- 8. Integration with SD and MM
SAP CO (Controlling) module facilitates coordinating, monitoring, and optimizing all the processes in an organization. It controls the business flow in an organization. This module helps in analyzing the actual figures with the planned data and in planning business strategies.
Two kinds of elements are managed in CO −
- Cost elements
- Revenue elements
These elements are stored in the FI module.
Activities Involved in SAP CO
- 1. Cost Element Accounting (Overview of the costs and revenues that occur in an organization)
- 2. Cost Center Accounting
- 3. Activity-Based-Accounting (Analyzes cross-departmental business processes)
- 4. Internal Orders
- 5. Product Cost Controlling (Calculates the costs that occur during the manufacture of a product or provision of a service)
- 6. Profitability Analysis (Analyzes the profit or loss of an organization by individual market segments)
- 7. Profit Center Accounting (Evaluates the profit or loss of individual, independent areas within an organization)
Sales & Distribution Management (SD)
SAP SD is one of the most important modules in SAP. It has a high level of integration complexity. SAP SD is used by organizations to support sales and distribution activities of products and services, starting from enquiry to order and then ending with delivery.
SAP SD can monitor a plethora of activities that take place in an organization such as products enquiries, quotation (pre-sales activities), placing order, pricing, scheduling deliveries (sales activity), picking, packing, goods issue, shipment of products to customers, delivery of products and billings.
In all these processes, multiple modules are involved such as FI (Finance Accounting), CO (Controlling), MM (Material Management), PP (Production Planning), LE (Logistics Execution), etc., which shows the complexity of the integration involved.
Activities Involved in SAP SD
- 1. Setting up Organization Structure (creation of new company, company codes, sales organization, distribution channels, divisions, business area, plants, sales area, maintaining sales offices, storage location)
- 2. Assigning Organizational Units (Assignment of individual components created in the above activities with each other according to design like company code to company, sales organization to company code, distribution channel to sales organization, etc.)
- 3. Defining Pricing Components (Defining condition tables, condition types, condition sequences)
- 4. Setting up sales document types, billing types, and tax-related components
- Setting up Customer master data records and configuration
Material Management (MM)
Material Management deals with movement of materials via other modules like logistics, supply chain management, sales and delivery, warehouse management, production and planning.
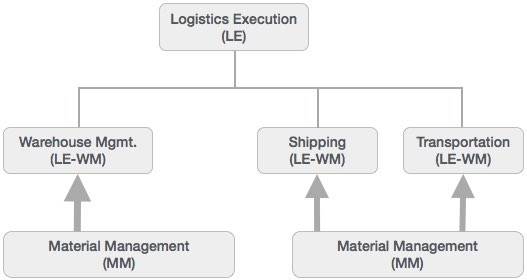
Logistic Execution (LE)
Logistic Execution can be divided into two sub-modules, i.e., shipment of goods (purchase to procurement process) and warehouse management (storage of goods). These two modules are integrated with sale and distribution, material management, and production and planning.
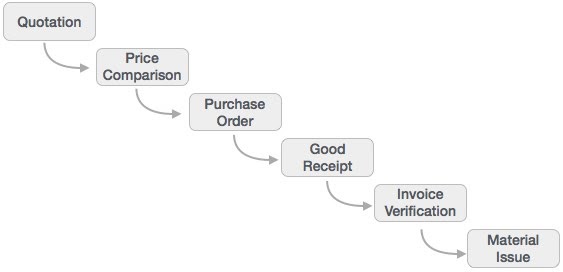
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
As the name SRM suggests, this module deals with the effective and efficient transition of products and services between an organization and its suppliers. The main process covered in this section is procurement of products like direct materials, indirect materials, and services. This module can effectively integrate with planning, accounting, and inventory systems.
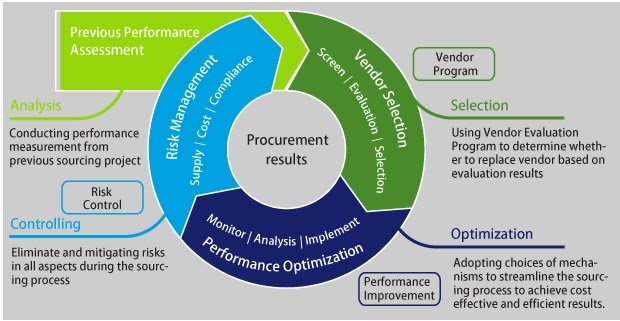
End-to-End Procurement Cycle
Procurement process with SAP Enterprise Buyer comprises of the following major steps −
- 1. Shopping Carts
- 2. Approval of Shopping Cart
- 3. Sourcing of Requirements
- 4. Purchase Orders
- 5. Purchase Order Approval
- 6. Confirm Goods/Services
- 7. Confirmation Approval
- 8. Process Invoice
- 9. Invoice Approval
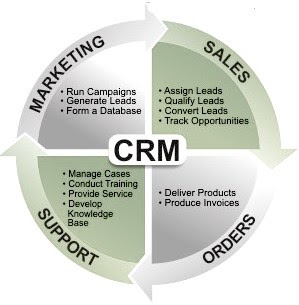
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM deals with end-to-end customer related processes. CRM is designed to centralize the data related to all the customers associated with an organization. It helps an organization −
- Maintain its sales, services, and build marketing strategies according to market demand and customer data analysis.
- Remain focused on its customers and via information analysis, help the business to know more about its customers.
- Improve sales and services and build better relationships with customers.
Human Resource (HR)
The most important objective of master data administration in Human Resources is to enter employee-related data for administrative, time-recording, and payroll purposes.
A new employee can be hired without using Recruitment. Instead you can hire someone by running a personnel action in Personnel Administration, thereby creating the necessary data for the employee to be hired.
Employee data must be kept current. After an employee is hired, circumstances can always arise which necessitate either the entry of new data or the correction of current data. For instance −
- An employee moving to his or her new address must be stored in the system.
- An employee gets a pay hike at the start of the year. The new salary must be stored for the relevant date.
- An employee changes jobs within the organization. His or her organizational assignment, working time, and salary also change.
- Data can be stored for the past, present, or future.
Note − Entering payroll-relevant data in the past triggers retroactive accounting.
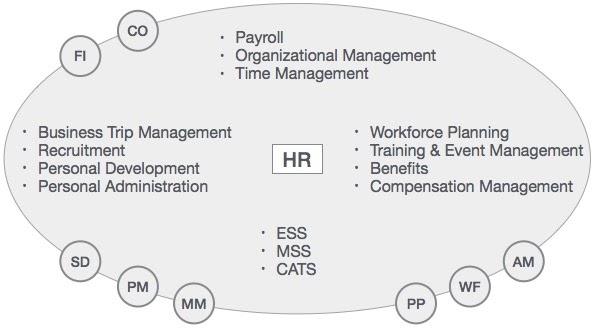
The HR module comprises major areas of functionality known as sub-modules. The HR module is a true demonstration of the strength of the SAP product in Enterprise Resource Planning.
The HR system has very strong integration points (where data is passed back and forth without human intervention) with just about all of the other SAP modules. In addition, there is very tight integration amongst the HR sub-modules.
The above illustration highlights some of the basic SAP HR terms as listed below.
- 1. Business trip management
- 2. Recruitment
- 3. Payroll
- 4. Personal development
- 5. Organizational Management
- 6. Time Management
- 7. Workforce Planning
- 8. ESS
- 9. MSS
- 10. Training and event management
- 11. CATS
- 12. Benefits
- 13. Compensation management
- 14. Personal Administration
Advancing your career in SAP, you can move into different roles such as −
- 1. SAP ABAP Application Developer (design SAP Application)
- 2. SAP Functional Consultant (in different modules)
- 3. SAP Technical Architect
- 4. SAP Solution Architect
- 5. SAP Portal Consultant
- 6. SAP Portal Developer
You can look for the above opportunities in companies such as −
- SAP Labs
- Accenture
- Tata Consultancy Services
- Cognizant
- IBM Global Business Services
- Wipro
- Tech Mahindra
- L & T InfoTech
- Deloitte
- KPMG

