- ISTQB Interview Questions and Answers [ SOLVED ]
- Jmeter Interview Questions and Answers
- Selenium with Python Interview Questions and Answers
- Software Testing Interview Questions and Answers
- TestComplete Interview Questions and Answers
- Selenium with Java Interview Questions and Answers
- SoapUI Interview Questions and Answers
- IDQ Interview Questions and Answers
- WinRunner Interview Questions and Answers
- API Testing Interview Questions and Answers
- Coded UI Interview Questions and Answers
- Manual Testing Interview Questions and Answers
- Ruby Cucumber Interview Questions and Answers
- QA Interview Questions and Answers
- Selenium Interview Questions and Answers
- Performance Testing Interview Questions and Answers
- QTP Interview Questions and Answers
- Mobile Testing Interview Questions and Answers
- Dot Net Interview Questions and Answers
- Loadrunner Interview Questions and Answers
- ISTQB Interview Questions and Answers [ SOLVED ]
- Jmeter Interview Questions and Answers
- Selenium with Python Interview Questions and Answers
- Software Testing Interview Questions and Answers
- TestComplete Interview Questions and Answers
- Selenium with Java Interview Questions and Answers
- SoapUI Interview Questions and Answers
- IDQ Interview Questions and Answers
- WinRunner Interview Questions and Answers
- API Testing Interview Questions and Answers
- Coded UI Interview Questions and Answers
- Manual Testing Interview Questions and Answers
- Ruby Cucumber Interview Questions and Answers
- QA Interview Questions and Answers
- Selenium Interview Questions and Answers
- Performance Testing Interview Questions and Answers
- QTP Interview Questions and Answers
- Mobile Testing Interview Questions and Answers
- Dot Net Interview Questions and Answers
- Loadrunner Interview Questions and Answers

Dot Net Interview Questions and Answers
Last updated on 25th Sep 2020, Blog, Interview Question, Software Testing
.Net is the most widely used framework for developing applications on windows. It encompasses ASP .Net, languages such as C#, VB .Net, Cobol, Perl, etc.
It is not possible to cover all the vast concepts of .Net in one article. Hence, the following section only consists of questions related to the .Net framework and its core. For more questions on .Net C#, please refer to C# interview questions.
1.What are the advantages of ASP.NET
Ans:
Separation of Code from HTML:
To make a clean sweep, with ASP.NET you have the ability to completely separate layout and business logic. This makes it much easier for teams of programmers and designers to collaborate efficiently.
Support for compiled languages:
Developers can use VB.NET and access features such as strong typing and object-oriented programming. Using compiled languages also means that ASP.NET pages do not suffer the performance penalties associated with interpreted code. ASP.NET pages are precompiled to byte-code and Just In Time (JIT) compiled when first requested. Subsequent requests are directed to the fully compiled code, which is cached until the source changes.
Use services provided by the .NET Framework:
The .NET Framework provides class libraries that can be used by your application. Some of the key classes help you with input/output, access to operating system services, data access, or even debugging. We will go into more detail on some of them in this module.
Graphical Development Environment:
Visual Studio .NET provides a very rich development environment for web developers. You can drag and drop controls and set properties the way you do in Visual Basic 6. And you have full IntelliSense support, not only for your code but also for HTML and XML.
State management:
To refer to the problems mentioned before, ASP.NET provides solutions for session and application state management. State information can, for example, be kept in memory or stored in a database. It can be shared across web farms, and state information can be recovered, even if the server fails or the connection breaks down.
Update files while the server is running:
Components of your application can be updated while the server is online and clients are connected. The framework will use the new files as soon as they are copied to the application. Removed or old files that are still in use are kept in memory until the clients have finished.
XML-Based Configuration Files:
Configuration settings in ASP.NET are stored in XML files that you can easily read and edit. You can also easily copy these to another server, along with the other files that comprise your application.
2.What are the different validators in ASP.NET?
Ans:
ASP.NET validation controls define an important role in validating the user input data. Whenever the user gives the input, it must always be validated before sending it across to various layers of an application. If we get the user input with validation, then chances are that we are sending the wrong data. So, validation is a good idea to do whenever we are taking input from the user.
There are the following two types of validation in ASP.NET,
- Client-Side Validation
- Server-Side Validation
Client-Side Validation:
When validation is done on the client browser, then it is known as Client-Side Validation. We use JavaScript to do the Client-Side Validation.
Server-Side Validation:
When validation occurs on the server, then it is known as Server-Side Validation. Server-Side Validation is a secure form of validation. The main advantage of Server-Side Validation is if the user somehow bypasses the Client-Side Validation, we can still catch the problem on server-side.
The following are the Validation Controls in ASP.NET,
- RequiredFieldValidator Control
- CompareValidator Control
- RangeValidator Control
- RegularExpressionValidator Control
- CustomFieldValidator Control
- ValidationSummary
3.What is View State?
Ans:
View State is the method to preserve the Value of the Page and Controls between round trips. It is a Page-Level State Management technique. View State is turned on by default and normally serializes the data in every control on the page regardless of whether it is actually used during a post-back.
A web application is stateless. That means that a new instance of a page is created every time when we make a request to the server to get the page and after the round trip our page has been lost immediately
Features of View State:
These are the main features of view state.
- Retains the value of the Control after post-back without using a session.
- Stores the value of Pages and Control Properties defined in the page.
- Creates a custom View State Provider that lets you store View State Information in a SQL Server Database or in another data store.
Advantages of View State:
- Easy to Implement.
- No server resources are required: The View State is contained in a structure within the page load.
- Enhanced security features: It can be encoded and compressed or Unicode implementation.
4.What are the different Session state management options available in ASP.NET?
Ans:
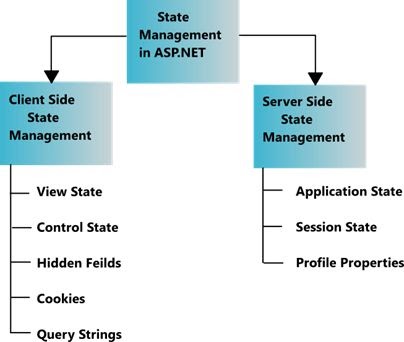
State Management in ASP.NET
- A new instance of the Web page class is created each time the page is posted to the server.
- In traditional Web programming, all information that is associated with the page, along with the controls on the page, would be lost with each roundtrip.
- The Microsoft ASP.NET framework includes several options to help you preserve data on both a per-page basis and an application-wide basis.
These options can be broadly divided into the following two categories -
- Client-Side State Management Options
- Server-Side State Management Options
Client-Side State Management
- Client-based options involve storing information either in the page or on the client computer.
- Some client-based state management options are,
-
- Hidden fields
- View state
- Cookies
- Query strings
Server-Side State Management
- There are situations where you need to store the state information on the server side.
- Server-side state management enables you to manage application-related and session-related information on the server.
- ASP.NET provides the following options to manage state at the server side:
-
- Application state
- Session state
5.What is caching in ASP.NET?
Ans:
Caching is one of the most interesting concepts and operations in ASP.NET. If you can handle it, you can run any web application by applying the caching concept depending on the requirements.
Caching is for providing solutions or the results to the users depending on their request, admin needs to recreate the pages often depending on user requests…STOP!!! “A cache simply stores the output generated by a page in the memory and this saved output (cache) will serve us (users) in the future.”.
Types:

6. How can we apply themes in an ASP.NET application?
Ans:
A theme is a collection of settings that define the look of controls and web pages. These themes are applied across all the pages in a web application to maintain a consistent appearance.Themes include images and skin files; the skin files set the visual properties of ASP.NET controls. Themes are of two types:
Page Theme
A Page theme contains the control skins, style sheets, graphic files, and other resources inside the subfolder of the App_Theme folder in the Solution Explorer window. A page theme is applied to a single page of the web site.
Global Theme
A Global theme is a theme that is applied to all the websites on a web server and includes property settings, and graphics. This theme allows us to maintain all the websites on the same web server and define the same style for all the web pages of the web sites.
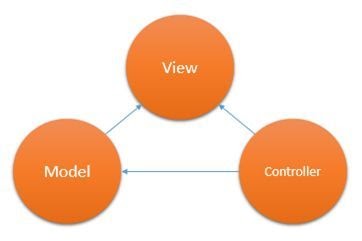
7.What is MVC?
Ans:
Model-View-Controller (MVC) is a pattern to separate an application into the following three main components:
- Model
- 2.View
- 3.Controller
The ASP.NET MVC framework provides an alternative to the ASP.NET Web Forms pattern for creating web applications. The ASP.NET MVC Framework is a lightweight, highly testable presentation framework that (as with Web Forms-based applications) is integrated with existing ASP.NET features, such as master pages and membership-based authentications. The MVC framework is defined in the System.Web.MVC assembly. It provides full control over HTML, JavaScript, and CSS. It’s better as well as a recommended approach for large-scale applications where various teams are working together.
The ASP.NET MVC framework offers the following advantages,
- It makes it very easy to manage complexity by dividing an application into the Model, View and Controller.
- It does not use view state or server-based forms.
- Full control over HTML, JavaScript, and CSS.
- It provides better support for Test-Driven Development (TDD).
- It works well for Web applications that are supported by large teams of developers and for web designers who need a high degree of control over the application behavior.
- By default support of Facebook and Google Authentication.
- It is easy to manage a large application to divide into multiple areas.
8.What are Cookies in ASP.NET?
Ans:
Cookies are a State Management Technique that can store the values of control after a post-back. Cookies can store user-specific information on the client’s machine, such as when the user last visited your site. Cookies are also known by many names, such as HTTP Cookies, Browser Cookies, Web Cookies, Session Cookies and so on. Basically cookies are a small text file sent by the web server and saved by the Web Browser on the client’s machine.
List of properties containing the HttpCookies Class:
- Domain: Using these properties we can set the domain of the cookie.
- Expires: This property sets the Expiration time of the cookies.
- HasKeys: If the cookies have a subkey then it returns True.
- Name: Contains the name of the Key.
- Path: Contains the Virtual Path to be submitted with the Cookies.
- Secured: If the cookies are to be passed in a secure connection then it only returns True.
- Value: Contains the value of the cookies.
Limitation of the Cookies:
- 1.The size of cookies is limited to 4096 bytes.
- 2.A total of 20 cookies can be used in a single website.
9.What is Ajax in ASP.NET?
Ans:
Ajax stands for Asynchronous JavaScript and XML; in other words Ajax is the combination of various technologies such as JavaScript, CSS, XHTML, DOM, etc.
AJAX allows web pages to be updated asynchronously by exchanging small amounts of data with the server behind the scenes. This means that it is possible to update parts of a web page, without reloading the entire page.
We can also define Ajax as a combination of client-side technologies that provides asynchronous communication between the user interface and the web server so that partial page rendering occurs instead of a complete page postback.
Ajax is platform-independent; in other words, AJAX is a cross-platform technology that can be used on any Operating System since it is based on XML & JavaScript. It also supports open source implementation of other technology. It partially renders the page to the server instead of the complete page being post back. We use AJAX for developing faster, better and more interactive web applications. AJAX uses an HTTP request between web server & browser.
- With AJAX, when a user clicks a button, you can use JavaScript and DHTML to immediately update the UI, and spawn an asynchronous request to the server to fetch results.
- When the response is generated, you can then use JavaScript and CSS to update your UI accordingly without refreshing the entire page. While this is happening, the form on the user’s screen doesn’t flash, blink, disappear, or stall.
- The power of AJAX lies in its ability to communicate with the server asynchronously, using a XMLHttpRequest object without requiring a browser refresh.
- Ajax essentially puts JavaScript technology and the XMLHttpRequest object between your Web form and the server.
10.What are Web Services in ASP.NET?
Ans:
A Web Service is a software program that uses XML to exchange information with other software via common internet protocols. In a simple sense, Web Services are a way of interacting with objects over the Internet.
A web service is
- Language Independent.
- Protocol Independent.
- Platform Independent.
- It assumes a stateless service architecture.
- Scalable (e.g. multiplying two numbers together to an entire customer-relationship management system).
- Programmable (encapsulates a task).
- Based on XML (open, text-based standard).
- Self-describing (metadata for access and use).
- Discoverable (search and locate in registries)- ability of applications and developers to search for and locate desired Web services through registries. This is based on UDDI.
Key Web Service Technologies:
- XML- Describes only data. So, any application that understands XML-regardless of the application’s programming language or platform-has the ability to format XML in a variety of ways (well-formed or valid).
- SOAP- Provides a communication mechanism between services and applications.
- WSDL- Offers a uniform method of describing web services to other programs.
- UDDI- Enables the creation of searchable Web services registries.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
11.What are the concepts of Globalization and Localization in .NET?
Ans:
Localization means “the process of translating resources for a specific culture”, and Globalization means “the process of designing applications that can adapt to different cultures”.
Proper Globalization
Your application should be able to Accept, Verify, and Display all kinds of global data. It should well also be able to operate over this data, accordingly.
Localizability and Localization
Localizability stands for clearly separating the components of culture-based operations regarding the user interface, and other operations from the executable code.
.NET framework has greatly simplified the task of creating the applications targeting the clients of multiple cultures. The namespaces involved in creation of globalize, localizing applications are,
- System.Globalization
- System.Resources
- System.Text
12.What is the Web.config file in ASP?
Ans:
Configuration file is used to manage various settings that define a website. The settings are stored in XML files that are separate from your application code. In this way you can configure settings independently from your code. Generally a website contains a single Web.config file stored inside the application root directory. However there can be many configuration files that manage settings at various levels within an application.
Usage of configuration file:
ASP.NET Configuration system is used to describe the properties and behaviors of various aspects of ASP.NET applications. Configuration files help you to manage the settings related to your website. Each file is an XML file (with the extension .config) that contains a set of configuration elements. Configuration information is stored in XML-based text files.
Benefits of XML-based Configuration files:
- ASP.NET Configuration system is extensible and application specific information can be stored and retrieved easily. It is human-readable.
- You need not restart the web server when the settings are changed in configuration files. ASP.NET automatically detects the changes and applies them to the running ASP.NET application.
- You can use any standard text editor or XML parser to create and edit ASP.NET configuration files.
13.What is the App Domain Concept in ASP.NET?
Ans:
ASP.NET introduces the concept of an Application Domain which is known as AppDomain for short. It can be considered as a lightweight process which is both a container and boundary. The .NET runtime uses an AppDomain as a container for code and data, just like the operating system uses a process as a container for code and data. As the operating system uses a process to isolate misbehaving code, the .NET runtime uses an AppDomain to isolate code inside a secure boundary.
The CLR can allow the multiple .NET applications to run in a single AppDomain. Multiple Appdomains can exist in the Win32 process.
How to create AppDomain:
AppDomains are created using the CreateDomain method. AppDomain instances are used to load and execute assemblies (Assembly). When an AppDomain is no longer in use, it can be unloaded.
- public class MyAppDomain: MarshalByRefObject
- {
- public string GetInfo()
- {
- return AppDomain.CurrentDomain.FriendlyName;
- }
- }
- public class MyApp
- {
- public static void Main()
- {
- AppDomain apd = AppDomain.CreateDomain(“Rajendra Domain”);
- MyAppDomain apinfo = (MyAppDomain) apd.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(Assembly.GetCallingAssembly()
- GetName()
- Name, “MyAppDomain”);
- Console.WriteLine(“Application Name = ” + apdinfo.GetInfo());
- }
- }
14. What is Query String in ASP?
Ans:
A QueryString is a collection of characters input to a computer or web browser. A Query String is helpful when we want to transfer a value from one page to another. When we need to pass content between the HTML pages or aspx Web Forms in the context of ASP.NET, a Query String is Easy to use and the Query String follows a separating character, usually a Question Mark (?). It is basically used for identifying data appearing after this separating symbol. A Query String Collection is used to retrieve the variable values in the HTTP query string. If we want to transfer a large amount of data then we can’t use the Request.QueryString. Query Strings are also generated by form submission or can be used by a user typing a query into the address bar of the browsers.
Syntax of Query String:
Request.QueryString(variable)[(index).count]
Advantages:
- Simple to Implement
- Easy to get information from a Query string.
- Used to send or read cross domain (from different domains).
Disadvantages:
- Human Readable
- Client browser limit on URL length
- Cross paging functionality makes it redundant
- Easily modified by end user
15.What is the master page in ASP.NET?
Ans:
The extension of MasterPage is ‘.master’. MasterPage cannot be directly accessed from the client because it just acts as a template for the other Content Pages. In a MasterPage we can have content either inside ContentPlaceHolder or outside it. Only content inside the ContentPlaceHolder can be customized in the Content Page. We can have multiple masters in one web application.A MasterPage can have another MasterPage as Master to it. The MasterPageFile property of a webform can be set dynamically and it should be done either in or before the Page_PreInit event of the WebForm. Page.MasterPageFile = “MasterPage.master”. The dynamically set Master Page must have the ContentPlaceHolder whose content has been customized in the WebForm.
A master page is defined using the following code,
- <%@ master language=”C#” %>
Adding a MasterPage to the Project
1.Add a new MasterPage file (MainMaster.master) to the Web Application.
2.Change the Id of ContentPlaceHolder in <Head> to “cphHead” and the Id “ContentPlaceHolder1” to “cphFirst”.
3.Add one more ContentPlaceHolder (cphSecond) to the Master page.4.To the master page add some header, footer and some default content for both the content placeholders.
.
- <form id=”form1″ runat=”server”> Header…
- <br />
- <asp:ContentPlaceHolder id=”cphFirst” runat=”server”>
- This is First Content Place Holder (Default) </asp:ContentPlaceHolder>
- <br />
- <asp:ContentPlaceHolder ID=”cphSecond” runat=”server”>
16.What is tracing in .NET?
Ans:
Tracing helps to see the information of issues at the runtime of the application. By default Tracing is disabled.
Tracing has the following important features:
- We can see the execution path of the page and application using the debug statement.
- We can access and manipulate trace messages programmatically.
- We can see the most recent tracing of the data.
Tracing can be done with the following 2 types.
- Page Level
When the trace output is displayed on the page and for the page-level tracing we need to set the property of tracing at the page level.
<%@ Page Trace=”true” Language=”C#” - Application Level
In Application-Level tracing the information is stored for each request of the application. The default number of requests to store is 10. But if you want to increase the number of requests and discard the older request and display a recent request then you need to set the property in the web.config file.
<trace enabled=”true”/>
17.What are the data controls available in ASP.NET?
Ans:
The Controls having DataSource Property are called Data Controls in ASP.NET. ASP.NET allows a powerful feature of data binding, you can bind any server control to simple properties, collections, expressions and/or methods. When you use data binding, you have more flexibility when you use data from a database or other means.
Data Bind controls are container controls:
Controls -> Child Control
Data Binding is binding controls to data from databases. With data binding we can bind a control to a particular column in a table from the database or we can bind the whole table to the data grid.
Data binding provides a simple, convenient, and powerful way to create a read/write link between the controls on a form and the data in their application.
Data binding allows you to take the results of properties, collection, method calls, and database queries and integrate them with your ASP.NET code. You can combine data binding with Web control rendering to relieve much of the programming burden surrounding Web control creation. You can also use data binding with ADO.NET and Web controls to populate control contents from SQL select statements or stored procedures.
Data binding uses a special syntax:
<%# %>
The <%#, which instructs ASP.NET to evaluate the expression. The difference between a data binding tag and a regular code insertion tags <% and %> becomes apparent when the expression is evaluated. Expressions within the data binding tags are evaluated only when the DataBind method in the Page objects or Web control is called.
Data Bind Control can display data in connected and disconnected models.
Following are data bind controls in ASP.NET:
- Repeater Control
- DataGrid Control
- DataList Control
- GridView Control
- DetailsView
- FormView
- DropDownList
- ListBox
- RadioButtonList
- CheckBoxList
- BulletList etc.
18.What are the major events in global.asax?
Ans:
The Global.asax file, which is derived from the HttpApplication class, maintains a pool of HttpApplication objects, and assigns them to applications as needed. The Global.asax file contains the following events,
- Application_Init
- Application_Disposed
- Application_Error
- Application_Start
- Application_End
- Application_BeginReques
19. What is the use of CheckBox in .NET?
Ans:
The CheckBox control is a very common control of HTML, unlike radio buttons it can select multiple items on a webpage. The CheckBox control in ASP.NET has many properties and some of them are listed below.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| AutoPostBack | Specifies whether the form should be posted immediately after the Checked property has changed or not. The default is false. |
| CausesValidation | Specifies if a page is validated when a Button control is clicked. |
| Checked | Specifies whether the check box is checked or not. |
| InputAttributes | Attribute names and values used for the Input element for the CheckBox control. |
| LabelAttributes | Attribute names and values used for the Label element for the CheckBox control. |
| runat | Specifies that the control is a server control. Must be set to “server”. |
| Text | The text next to the check box. |
| TextAlign | On which side of the checkbox the text should appear (right or left). |
| ValidationGroup | Group of controls for which the Checkbox control causes validation when it posts back to the server. |
| OnCheckedChanged | The name of the function to be executed when the Checked property has changed. |
20.What is authentication and authorization in ASP.NET?
Ans:
- Authentication: Prove genuineness
- Authorization: process of granting approval or permission on resources.
In ASP.NET authentication means to identify the user or in other words it’s nothing but validating that he exists in your database and he is the proper user.
Authorization means the user has access to a particular resource on the IIS website. A resource can be an ASP.NET web page, media files (MP4, GIF, JPEG etc), compressed file (ZIP, RAR) etc.
Types of authentication and authorization in ASP.NET
There are three ways of doing authentication and authorization in ASP.NET:
Windows authentication:
In this methodology ASP.NET web pages will use local windows users and groups to authenticate and authorize resources.
Forms Authentication:
This is a cookie based authentication where username and password are stored on client machines as cookie files or they are sent through URL for every request. Form-based authentication presents the user with an HTML-based Web page that prompts the user for credentials.
Passport authentication:
Passport authentication is based on the passport website provided by Microsoft .So when user logins with credentials it will be reached to the passport website ( i.e. hotmail,devhook,windows live etc) where authentication will happen. If Authentication is successful it will return a token to your website.
Anonymous access:
If you do not want any kind of authentication then you will go for Anonymous access.
In ‘web.config’ file set the authentication mode to ‘Windows’ as shown in the below code snippets.
- <authentication mode=”Windows”/>
We also need to ensure that all users are denied except authorized users. The below code snippet inside the authorization tag that all users are denied. ‘?’ indicates any unknown user.
- <authorization>
- <deny users=”?”/>
- </authorization>
21. What are the HTML server controls in ASP.NET?
Ans:
The Microsoft.NET Framework provides a rich set of server-side controls for developing Web applications. You can add these controls to WebForms pages just as you add Windows controls to a form. Server-side controls are often called server controls or Web Forms controls. There are four types of Server controls: HTML server controls. Web server controls, validation control, and user controls.
HTML Server controls
HTML developers must be familiar with old HTML controls, which they use to write GUI applications in HTML. These controls are the same HTML controls; you can run these controls on the server by defining the runat =”server” attribute. These control names start with Html.
| Controls | Description |
|---|---|
| HtmlForm | Create an HTML form control, used as a placeholder of other controls. |
| HtmlInputText | Creates an input text box control used to get input from the user. |
| HtmltextArea | Creates multiline text box control. |
| HtmlAnchor | Creates a Web navigation. |
| HtmlButton | Creates a button control. |
| HtmlImage | Creates an image control, which is used to display an image. |
| HtmlInputCheckBox | Creates a checkbox control. |
| HtmlInputRadioButton | Creates a radio button control. |
| HtmlTable | Creates a table control. |
| HtmlTableRow | Creates a row within a table. |
| HtmlTableCell | Creates a cell within a row. |
- Web Server Controls
- Validation Controls
- User Controls
22.What are the authentication modes in ASP.NET for security?
Ans:
When you begin a program for a customer using ASP.NET, you should consider security. Security is one of the most important components of any application. Security is even more important when you are making a web application which is exposed to million of users. ASP.NET provides classes and methods that ensure that the application is secure from outside attacks. In this article we will investigate the different types of authentication provided by ASP.NET. In the web.config file you can set authentication mode value ‘windows’ or ‘forms’. What’s about difference and how do you use them? (Authentication has some other values too, this article does not consider them.).
How to use mode “Windows”?
Windows Authentication mode provides the developer the ability to authenticate a user based on Windows user accounts. This is the default authentication mode provider by ASP.NET. This will return the computer name along with the user name.
- <authentication mode=”Windows”>
- <forms name=” AuthenticationDemo” loginUrl=”logon.aspx” protection=”All” path=”/”timeout=”30″ />
- </authentication>
How to use mode “Forms”?
Insert the <Forms> tag, and fill the appropriate attributes.
- <authentication mode=”Forms”>
- <forms name=” AuthenticationDemo” loginUrl=”logon.aspx” protection=”All” path=”/”timeout=”30″ />
- </authentication>
For further info click on the link,
- Authentication Modes in ASP.Net for Security
23. What is the web API in ASP.NET?
Ans:
It is a framework provided by Microsoft for writing HTTP services. There are many frameworks available to build HTTP based services. They follow a common guideline of international standardization but with different flavors.
For example, all framework must adhere to these status codes-
- 1xx – Informational Message
- 2xx – Successful
- 3xx – Redirection
- 4xx – Client Error
- 5xx – Server Error
Features
- It is lightweight and thus good for small devices also like tablets, smart phones.
- No tedious & extensive configuration like WCF REST is required.
- MediaTypeFormatter makes it easy to configure your APIs response type in a single line (JSON, XML and so on).
- IIS Hosting dependency is no more and it can be hosted in application too.
- Easy and simple control with HTTP features such as Caching, Versioning, request/response headers and its various content formats.
- It supports content-negotiation (deciding the best response data format that client can accept).
24. Describe application state management in ASP.NET?
Ans:
Application Level State Management is used to maintain the state of all the users accessing the web forms present within the website.
The value assigned for an application is considered as an object.
Application objects will not have any default expiration period.
Whenever the webserver has been restarted or stopped then the information maintained by the application object will be lost.
If any data is stored on the application object then that information will be shared upon all the users accessing the web server.
Since the information is shared among all the users, it is advisable to lock and unlock the application object as per requirement.
Global Application Class(Global.asax)
It is a Class which consists of event handlers which executes the code implicitly whenever a relevant task has been performed on the web server.Design:
- <%@ Application Language=”C#” %>
- <script runat=”server”>
- void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- // Code that runs on application startup
- }
- void Application_End(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- // Code that runs on application shutdown
- }
- void Application_Error(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- // Code that runs when an unhandled error occurs
- }
- void Session_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- // Code that runs when a new session is started
- }
- void Session_End(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- // Code that runs when a session ends.
- }
- </script>
25. What is the code behind and Inline Code?
Ans:
Code Behind:
Code Behind refers to the code for an ASP.NET Web page that is written in a separate class file that can have the extension of .aspx.cs or .aspx.vb depending on the language used. Here the code is compiled into a separate class from which the .aspx file derives. You can write the code in a separate .cs or .vb code file for each .aspx page. One major point of Code Behind is that the code for all the Web pages is compiled into a DLL file that allows the web pages to be hosted free from any Inline Server Code.
Inline Code:
Inline Code refers to the code that is written inside an ASP.NET Web Page that has an extension of .aspx. It allows the code to be written along with the HTML source code using a <Script> tag. It’s major point is that since it’s physically in the .aspx file it’s deployed with the Web Form page whenever the Web Page is deployed.
26. What is the ASP.NET page life Cycle?
Ans:
When a page is requested by the user from the browser, the request goes through a series of steps and many things happen in the background to produce the output or send the response back to the client. The period between the request and response of a page is called the “Page Life Cycle”.
- Request: Start of the life cycle (sent by the user).
- Response: End of the life cycle (sent by the server).
There are four stages that occur during the Page Life Cycle before the HTML Response is returned to the client. Later in this article we”ll study all these stages and their sub events.
- Initialization
- Loading
- Rendering
- Unloading
| Initialization | During this stage the IsPostback property is set. The page determines whether the request is a Postback (old request) or if this is the first time the page is being processed (new request). Controls on the page are available and each control’s UniqueID property is set. Now if the current request is a postback then the data has not been loaded and the value of the controls have not yet been restored from the view state. |
| Loading | At this stage if the request is a Postback then it loads the data from the view state. |
| Rendering | Before rendering, the View State is saved for the page and its controls. During this phase, the page calls the render method for each control, providing a text writer that writes its output to the OutputStream of the page’s Response property. |
| Unloading | Unload is called after the page has been fully rendered, sent to the client and is ready to be discarded. At this point also the page properties such as Response and Request are unloaded. |
27.What are the ASP.NET page life cycle events?
Ans:
We have many events in ASP.NET page life cycle let’s see some most important events:
Page request
When ASP.NET gets a page request, it decides whether to parse and compile the page or there would be a cached version of the page; accordingly the response is sent,
Starting of page life cycle
At this stage, the Request and Response objects are set. If the request is an old request or post back, the IsPostBack property of the page is set to true. The UICulture property of the page is also set.
Page initialization
At this stage, the controls on the page are assigned a unique ID by setting the UniqueID property and themes are applied. For a new request postback data is loaded and the control properties are restored to the view-state values.
Page load
At this stage, control properties are set using the view state and control state values.
Validation
Validate method of the validation control is called and if it runs successfully, the IsValid property of the page is set to true.
Postback event handling
If the request is a postback (old request), the related event handler is called.
Page rendering
At this stage, view state for the page and all controls are saved. The page calls the Render method for each control and the output of rendering is written to the OutputStream class of the Page’s Response property.
Unload
The rendered page is sent to the client and page properties, such as Response and Request are unloaded and all cleanup done.
ASP.NET Page Life Cycle Events
Following are the page life cycle events:
PreInit
PreInit is the first event in the page life cycle. It checks the IsPostBack property and determines whether the page is a postback. It sets the themes and master pages, creates dynamic controls and gets and sets profile property values. This event can be handled by overloading the OnPreInit method or creating a Page_PreInit handler.
Init
Init event initializes the control property and the control tree is built. This event can be handled by overloading the OnInit method or creating a Page_Init handler.
InitComplete
InitComplete event allows tracking of view state. All the controls turn on view-state tracking.
LoadViewState
LoadViewState event allows loading view state information into the controls.
LoadPostData
During this phase, the contents of all the input fields defined with the <form> tag are processed.
PreLoad
PreLoad occurs before the post back data is loaded in the controls. This event can be handled by overloading the OnPreLoad method or creating a Page_PreLoad handler.
Load
The Load event is raised for the page first and then recursively for all child controls. The controls in the control tree are created. This event can be handled by overloading the OnLoad method or creating a Page_Load handler.
LoadComplete
The loading process is completed, control event handlers are run and page validation takes place. This event can be handled by overloading the OnLoadComplete method or creating a Page_LoadComplete handler.
PreRender
The PreRender event occurs just before the output is rendered. By handling this event, pages and controls can perform any updates before the output is rendered.
PreRenderComplete
as the PreRender event is recursively fired for all child controls, this event ensures the completion of the pre-rendering phase.
SaveStateComplete
State of control on the page is saved. Personalization, control state and view state information is saved. The HTML markup is generated. This stage can be handled by overriding the Render method or creating a Page_Render handler.
UnLoad
The UnLoad phase is the last phase of the page life cycle. It raises the UnLoad event for all controls recursively and lastly for the page itself. Final cleanup is done and all resources and references, such as database connections, are freed. This event can be handled by modifying the OnUnLoad method or creating a Page_UnLoad handler.
28. Describe login Controls in ASP
Ans:
The Login control provides the user interface to log a user into a web site. The Login control uses the Membership service to authenticate the user in your membership system. The default Membership service from your configuration file will be used automatically, however you can also set the Membership provider that you would like used as a property on the control.
The Login Control consists of
- Username Label and Textbox: Collects the string used to identify the user in the membership system.
- Password Label and Textbox: Collects the password for the specified user. The textbox text is always obscured.
- LoginButton: The button to submit the users request for authentication.
- RememberMe: Configurable to display a checkbox giving the user the option to store a persistent cookie on the user’s machine.
- Title and Instruction: Text to orient and guide the user through the process.
- Links: Configurable links to help, password recovery and user registration information.
- Validators: Required field Validators for the username and password textboxes.
For Example,
- <asp:Login ID=”Login1″ runat=”server” BackColor=”#FFE0C0″ BorderColor=”Red” ></asp:Login>
For further info click on the link,
- How to use Login Control in Visual Studio 2008
29.How to use repeater control in ASP.NET?
Ans:
A Repeater is a Data-bound control. Data-bound controls are container controls. It creates a link between the Data Source and the presentation UI to display the data. The repeater control is used to display a repeated list of items.
The main use of Repeater Control is for displaying a repeated list of items bound to the control. A Repeater Control is faster and lightweight for displaying data compared to a GridView or DataGrid. With the Repeater control we can display data in a custom format. The main drawback of a Repeater Control is that it doesn’t support paging and sorting.
The Repeater Control has the following types of template fields,
- Item Template
- AlternatingItem Template
- Header Template
- Footer Template
- Separator Template
Write connection code and select command in code behind file like:
- protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(“Data Source=MCNDESKTOP34;Initial Catalog=yatendra;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=sa;
- Password = Password$2 “);
- SqlDataAdapter sda = new SqlDataAdapter(“select * from Student_Details1”, con); DataTable dt = new DataTable(); sda.Fill(dt); Repeater1.DataSource = dt; Repeater1.DataBind();
- }
Now use Repeater control object in .aspx file like:
- <asp:Repeater ID=”Repeater1″ runat=”server”>
- <ItemTemplate>
- <div>
- <table>
- <tr>
- <th>Student
- <%#Eval(“S_ID”)%>
- </th>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Student Name</td>
- <td>
- <%#Eval(“Student_Name”)%>
- </td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Registration Number</td>
- <td>
- <%#Eval(“Register_No”)%>
- </td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Date Of Birth</td>
- <td>
- <%#Eval(“D_O_B”)%>
- </td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Date Of Examination</td>
- <td>
- <%#Eval(“D_O_E”)%>
- </td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Department</td>
- <td>
- <%#Eval(“Department”)%>
- </td>
- </tr>
- </table>
- </div>
- </ItemTemplate>
- </asp:Repeater>
When you run this page the output will look like:
30.What are different methods of session maintenance in ASP.NET?
Ans:
Session is a State Management Technique. A Session can store the value on the Server. It can support any type of object to be stored along with our own custom objects. A session is one of the best techniques for State Management because it stores the data as client-based, in other words the data is stored for every user separately and the data is secured also because it is on the server.
We can set the session on one of the following 2 types of configuration files:
- Machine Configuration file: Machine Configuration is applied for all applications.
- Application Configuration file: It’s applied for only application by application basis.
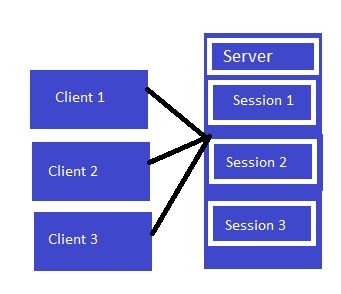
Session Mode
In ASP.NET there are 4 types of Session Mode.
Off
We can disable the session mode for the entire application using the off mode.
According to performance and durability the difference between InProc,State Server and SQL Server is:
| Session mode | Performance Durability |
| InProc | More(1 processor and 1 server) less. |
| State Server | Medium(n processor and 1 server) Medium |
| SQL Server | Less More |
31.What is the Difference between session and caching?
Ans:
The first main difference between session and caching is: a session is per-user based but caching is not per-user based, So what does that mean? Session data is stored at the user level but caching data is stored at the application level and shared by all the users. It means that it is simply session data that will be different for the various users for all the various users, session memory will be allocated differently on the server but for the caching only one memory will be allocated on the server and if one user modifies the data of the cache for all, the user data will be modified.
32.What is the difference between HttpContext.Current.Items and HttpContext.Current.Session in ASP.NET?
Ans:
Session state is one of the popular state management techniques in the ASP.NET environment. Web developer people play with session storage every now and then. It’s pretty simple to manage a session if you understand the basic concept. Here is the syntax to do that.
- Session[“KEY”] =”Value”;
Or
- Session[index] = ”Value”;
- Let’ s a have an example: using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Web;
- using System.Web.UI;
- using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
- namespace WebApp
- {
- public partial class WebForm1: System.Web.UI.Page
- {
- protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- if(!IsPostBack)
- {
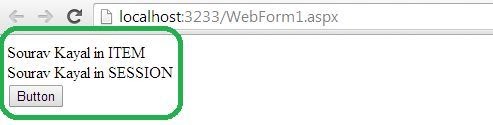
- HttpContext.Current.Items[“Value”] = “Sourav Kayal in ITEM”;
- HttpContext.Current.Session[“Value”] = “Sourav Kayal in SESSION”;
- Response.Write((string)(HttpContext.Current.Items[“Value”]) + “<br>”);
- Response.Write((string)(HttpContext.Current.Session[“Value”]));
- }
- }
- protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- Response.Write((string)(HttpContext.Current.Items[“Value”]) + “<br>”);
- Response.Write((string)(HttpContext.Current.Session[“Value”]));
- }
- }
- }
33. What is the difference between Server.Transfer and Response.redirect?
Ans:
Both Response.Redirect and Server.Transfer methods are used to transfer a user from one web page to another web page. Both methods are used for the same purpose but still there are some differences as follows.
The Response.Redirect method redirects a request to a new URL and specifies the new URL while the Server.Transfer method for the current request, terminates execution of the current page and starts execution of a new page using the specified URL path of the page.
Both Response.Redirect and Server.Transfer has same syntax like:
- Response.Redirect(“UserDetail.aspx”);
- Server.Transfer(“UserDetail.aspx”);
Before touching on more points I want to explain some HTTP status codes, these are important for the understanding of the basic differences between these two. The HTTP status codes are the codes that the Web server uses to communicate with the Web browser or user agent.
34.What are page directives in ASP.NET?
Ans:
Basically Page Directives are commands. These commands are used by the compiler when the page is compiled.
How to use the directives in an ASP.NET page
It is not difficult to add a directive to an ASP.NET page. It is simple to add directives to an ASP.NET page. You can write directives in the following format:
- <%@[Directive][Attributes]%>
See the directive format, it starts with “<%@” and ends with “%>”. The best way is to put the directive at the top of your page. But you can put a directive anywhere in a page. One more thing, you can put more than one attribute in a single directive.
Here is the full list of directives,
- @Page
- @Master
- @Control
- @Import
- @Implements
- @Register
- @Assembly
- @MasterType
- @Output Cache
- @PreviousPageType
- @Reference
35.What is HTTP Handler?
Ans:
Every request into an ASP.NET application is handled by a specialized component known as an HTTP handler. The HTTP handler is the most important ingredient while handling ASP.NET requests.
Examples: ASP.NET uses different HTTP handlers to serve different file types. For example, the handler for web Page creates the page and control objects, runs your code, and renders the final HTML.
ASP.NET default handlers
Page Handler (.aspx) – Handles Web pages.
- User Control Handler (.ascx) – Handles Web user control pages.
- Web Service Handler (.asmx) – Handles Web service pages.
- Trace Handler (trace.axd) – Handles trace functionality.
Why we need to create our own HTTP Handler: Sometime we need to avoid ASP.NET full page processing model, which saves lot of overheads, as ASP.NET web form model has to go through many steps such as creating web page objects, persisting view state etc. What we are interested in is to develop some low level interface that provides access to objects like Request and Response but doesn’t use the full control based web form model discussed above.
Examples
- Dynamic image creator – Use the System.Drawing classes to draw and size your own images.
- RSS – Create a handler that responds with RSS-formatted XML. This would allow you to add RSS feed capabilities to your sites.
- Render a custom image,
- Perform an ad hoc database query,
- Return some binary data.
All HTTP handlers are defined in the <httpHandlers> section of a configuration file which is nested in the <system.web> element.
- <httpHandlers>
- <add verb=”*” path=”trace.axd” validate=”true” type=”System.Web.Handlers.TraceHandler” />
- <add verb=”*” path=”*.config” validate=”true” type=”System.Web.HttpForbiddenHandler” />
- <add verb=”*” path=”*.cs” validate=”true” type=”System.Web.HttpForbiddenHandler” />
- <add verb=”*” path=”*.aspx” validate=”true” type=”System.Web.UI.PageHandlerFactory” /> </httpHandlers>
36.What are the differences between ASP.NET HttpHandler and HttpModule?
Ans:
The user requests for a resource on a web server. The web server examines the file name extension of the requested file, and determines which ISAPI extension should handle the request. Then the request is passed to the appropriate ISAPI extension. For example when an .aspx page is requested it is passed to ASP.NET page handler. Then the Application domain is created and after that different ASP.NET objects like Httpcontext, HttpRequest, HttpResponse are created. Then an instance of HttpApplication is created and also an instance of any configured modules. One can register different events of HttpApplication class like BeginRequest, AuthenticateRequest, AuthorizeRequest, ProcessRequest etc.
HTTP Handler:
HTTP Handler is the process which runs in response to a HTTP request. So whenever a user requests a file it is processed by the handler based on the extension. So, custom http handlers are created when you need special handling based on the file name extension. Let’s consider an example to create RSS for a site. So, create a handler that generates RSS-formatted XML. Now bind the .rss extension to the custom handler.
HTTP Modules:
HTTP Modules are plugged into the life cycle of a request. So when a request is processed it is passed through all the modules in the pipeline of the request. So generally http modules are used for,
Security: For authenticating a request before the request is handled.
Statistics and Logging: Since modules are called for every request they can be used for gathering statistics and for logging information.
Custom header: Since response can be modified, one can add custom header information to the response.
37. Explain the AdRotator Control?
Ans:
AdRotator controls are used to create dynamic ads. The AdRotator Control presents ad images each time a user enters or refreshes a web page. When the ads are clicked, it will navigate to a new Web location. The AdRotator control is used to display a sequence of ad images.The AdRotator control to work we need an Advertisement file (XML file) and some sample images.
Adding the AdRotator web server control to your web application. First, select the AdRotator and drag and drop the control to your web form. Map the XML file which contains the details about each and every ad.
The advertisement file is an XML file. The following are some of the elements of this XML file.
- <imageUrl>: Optional. The path to the image file.
- <NavigateUrl>: Optional. The URL to link to if the user clicks the ad.
- <AlternateText>: Optional. An alternate text for the image.
- <Impressions>: Optional. The display rates in percent of the hits.
XML code that has the details about the ads. The file Ads.xml looks like the code below:
- <Advertisements>
- <Ad>
- <ImageUrl>adimages/2.jpg</ImageUrl>
- <NavigateUrl>http://cat2.com</NavigateUrl>
- <AlternateText>Cat 2</AlternateText>
- <Impressions>30</Impressions>
- </Ad>
- <Ad>
- <ImageUrl>adimages/3.jpg</ImageUrl>
- <NavigateUrl>http://cat3.com</NavigateUrl>
- <AlternateText>Cat 3</AlternateText>
- <Impressions>20</Impressions>
- </Ad>
- <Ad>
- <ImageUrl>adimages/4.jpg</ImageUrl>
- <NavigateUrl>http://cat4.com</NavigateUrl>
- <AlternateText>Cat 4</AlternateText>
- <Impressions>10</Impressions>
- </Ad>
- </Advertisements>
38.What is cross-page posting in ASP.NET?
Ans:
ASP.NET 1.1 provides for web forms posting back only to themselves. In many situations, the solution requires posting to a different web page. The traditional workaround alternatives were to use Response.Redirect and/or Server.Transfer to move to a different page and simulate cross page post-back behavior.
ASP.NET 2.0 provides a feature known as Cross Page PostBack for a web form to post-back to a different web form (other than itself)
How to post to a different page:
To set a web form to post back to a different web form, in the source web form, set the PostBackURL property of a control that implements IButtonControl (eg. Button, ImageButton, LinkButton) to the target web form. When the user clicks on this button control, the web form is cross-posted to the target web form. No other settings or code is required in the source web form.
Access source page info within the posted page: FindControl Method
The target web form resulting from the cross-page postback provides a non-null PreviousPage property. This property represents the source page and provides reference to the source web form and its controls.
The controls on the source page can be accessed via the FindControl method on the object returned by the PreviousPage property of the target page.
- protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- …
- TextBox txtStartDate = (TextBox) PreviousPage.FindControl(“txtStartDate “);
- …
- }
At this point the target page does not have any knowledge of the source page. The PreviousPage property is of the type Page. For accessing controls using FindControl, the developer has to presume a certain structure in the source web form. This approach using FindControl has a few limitations. FindControl is dependent on the developer to provide the ids of the controls to access. The code will stop working if the control id is changed in the source web form. The FindControl method can retrieve controls only within the current container. If you need to access a control within another control, you need to first get a reference to the parent control.
Access source page info within the posted page: @PreviousPageType Directive
There is another more direct option to get access to the source page controls if the source page is predetermined. The @PreviousPageType directive can be used in the target page to strongly type the source page. The directive specifies the source page using either the VirtualPath attribute or the TypeName attribute. The PreviousPage property then returns a strongly typed reference to the source page. It allows access to the public properties of the source page.
SourcePage.aspx
- <form runat=”server”> …
- <asp:textbox runat=”server” id=”txtFirstName” />
- <asp:textbox runat=”server” id=”txtLastName” />
- <asp:button runat=”server” id=”btnViewReport” Text=”View Report” PostbackURL=”~/targetpage.aspx” /> … public string FirstName { get { return txtFirstName.Text; } } …
TargetPage.aspx
- <%@ PreviousPageType VirtualPath=”sourcepage.aspx” %>
- string strFirstName;
- strFirstName = PreviousPage.FirstName //Strongly Typed PreviousPage allows direct access to the public properties of the source page
39.Explain GridView control in ASP.NET?
Ans:
The GridView control displays the values of a data source in a table. Each column represents a field, while each row represents a record. The GridView control supports the following features,
- Binding to data source controls, such as SqlDataSource.
- Built-in sort capabilities.
- Built-in update and delete capabilities.
- Built-in paging capabilities.
- Built-in row selection capabilities.
- Programmatic access to the GridView object model to dynamically set properties, handle events, and so on.
- Multiple key fields.
- Multiple data fields for the hyperlink columns.
- Customizable appearance through themes and styles.
Creating a GridView
- <asp:GridView ID=”gridService” runat=”server”>
- </asp:GridView>
40.What is the difference between ASP.NET Web API and WCF?
Ans:
The ASP. NET Web API is a framework that uses the HTTP services and makes it easy to provide the response to the client request. The response depends on the request of the clients. The Web API builds the HTTP services, and handles the request using the HTTP protocols. The request may be GET, POST, DELETE, PUT. We can also say that the ASP. NET Web API:
- Is an HTTP service.
- Is designed for reaching the broad range of clients.
- Uses the HTTP application.
We use the ASP. NET Web API for creating the REST ful (Representational State Transfer) services.
The following are some important points of the ASP. NET Web API,
- The ASP. NET Web API supports the MVC application features that are controller, media formatters, routing etcetera.
- It is a platform for creating the REST services.
- It is a framework for creating the HTTP services.
- Responses can be formatted by the APIs MediaTypeFormatter into the Javascript Object Notation (JSON) and Extensible Markup Language (XML) formats.
41.What is the PostBack property in ASP.NET?
Ans:
If we create a web Page, which consists of one or more Web Controls that are configured to use AutoPostBack (every Web controls will have their own AutoPostBack property), the ASP.NET adds a special JavaScript function to the rendered HTML Page. This function is named _doPostBack() . When Called, it triggers a PostBack, sending data back to the web Server.
ASP.NET also adds two additional hidden input fields that are used to pass information back to the server. This information consists of the ID of the Control that raised the event and any additional information if needed. These fields will empty initially as shown below,
- <input type=”hidden” name=”__EVENTTARGET” id=”__EVENTTARGET” value=”” />
- <input type=”hidden” name=”__EVENTARGUMENT” id=”__EVENTARGUMENT” value=”” />
The following actions will be taken place when a user changes a control that has the AutoPostBack property set to true:
- On the client side, the JavaScript _doPostBack function is invoked, and the page is resubmitted to the server.
- ASP.NET re-creates the Page object using the .aspx file.
- ASP.NET retrieves state information from the hidden view state field and updates the controls accordingly.
- The Page.Load event is fired.
- The appropriate change event is fired for the control. (If more than one control has been changed, the order of change events is undetermined.)
- The Page.PreRender event fires, and the page is rendered (transformed from a set of objects to an HTML page).
- Finally, the Page.Unload event is fired.
- The new page is sent to the client.
42.Explain Cookie-less Session in ASP.NET.
Ans:
By default a session uses a cookie in the background. To enable a cookie-less session, we need to change some configuration in the Web.Config file. Follow these steps,
- Open Web.Config file.
- Add a <sessionState> tag under <system.web> tag.
- Add an attribute “cookieless” in the <sessionState> tag and set its value to “AutoDetect” like below:
- <sessionState cookieless=”AutoDetect” regenerateExpiredSessionId=”true”/>
The possible values for “cookieless” attribute are,
- AutoDetect: Session uses background cookies if cookies are enabled. If cookies are disabled, then the URL is used to store session information.
- UseCookie: Session always uses background cookies. This is default.
- UseDeviceProfile: Session uses background cookie if browser supports cookies else URL is used.
- UseUri: Session always uses URL.
“regenerateExpiredSessionId” is used to ensure that if a cookieless url is expired a new url is created with a new session. And if the same cookieless url is being used by multiple users at the same time, they all get a new regenerated session url.
43.What is Themes in ASP.NET?
Ans:
A theme decides the look and feel of the website. It is a collection of files that define the looks of a page. It can include skin files, CSS files & images.
We define themes in a special App_Themes folder. Inside this folder are one or more subfolders named Theme1, Theme2 etc. that define the actual themes. The theme property is applied late in the page’s life cycle, effectively overriding any customization you may have for individual controls on your page.
How to apply themes:
There are 3 different options to apply themes to our website,
- Setting the theme at the page level: the Theme attribute is added to the page directive of the page.
- <%@ Page Language=”C#” AutoEventWireup=”true” CodeFile=”Default.aspx.cs”Inherits=”Default” Theme=”Theme1″%>
- Setting the theme at the site level: to set the theme for the entire website you can set the theme in the web.config of the website. Open the web.config file and locate the <pages> element and add the theme attribute to it:
- <pages theme=”Theme1″>
- ….
- ….
- </pages>
- Setting the theme programmatically at runtime: here the theme is set at runtime through coding. It should be applied earlier in the page’s life cycle ie. Page_PreInit event should be handled for setting the theme. The better option is to apply this to the Base page class of the site as every page in the site inherits from this class.
- Page.Theme = Theme1;
Uses of Themes:
- Since themes can contain CSS files, images and skins, you can change colors, fonts, positioning and images simply by applying the desired themes.
- You can have as many themes as you want and you can switch between them by setting a single attribute in the web.config file or an individual aspx page. Also you can switch between themes programmatically.
- Setting the themes programmatically, you are offering your users a quick and easy way to change the page to their likings.
- Themes allow you to improve the usability of your site by giving users with vision problems the option to select a high contrast theme with a large font size.
44.What are the Navigations techniques in ASP.NET?
Ans:
Navigation can cause data loss if it is not properly handled. We do have many techniques to transfer data from one page to another but every technique has its own importance and benefits.
We will discuss the following techniques in this article.
- Response.Redirect
- Server.Transfer
- Server.Execute
- Cross page posting
45.What is WebParts in ASP.NET?
Ans:
ASP.NET 2.0 incorporates the concept of WEB PARTS in itself and we can code and explore that as easily as we have done with the other controls in the previous sessions.
We can compose web parts pages from “web parts”, which can be web controls, user controls.
Component of Web Parts:
The web parts consist of different components like,
- Web Part Manager
- Web Part Zone
- CatLog Part
- CatLog Zone
- Connections Zone
- Editor Part
- Editor Zone
Web Part Zone:
- Web Part Zone can contain one or more Web Part controls.
- This provides the layout for the Controls it contains. A single ASPX page can contain one or more Web Part Zones.
- A Web Part Control can be any of the controls in the toolbox or even the customized user controls.
46.What are master pages?
Ans:
Some points about Master Pages,
- The extension of MasterPage is ‘.master’.
- MasterPage cannot be directly accessed from the client because it just acts as a template for the other Content Pages.
- In a MasterPage we can have content either inside ContentPlaceHolder or outside it. Only content inside the ContentPlaceHolder can be customized in the Content Page.
- We can have multiple masters in one web application.
- A MasterPage can have another MasterPage as Master to it.
- The content page content can be placed only inside the content tag.
- Controls of MasterPage can be programmed in the MasterPage and content page but a content page control will never be programmed in MasterPage.
- A master page of one web application cannot be used in another web application.
- The MasterPageFile property of a webform can be set dynamically and it should be done either in or before the Page_PreInit event of the WebForm. Page.MasterPageFile = “MasterPage.master”. The dynamically set Master Page must have the ContentPlaceHolder whose content has been customized in the WebForm.
- The order in which events are raised: Load (Page) a Load (Master) a LoadComplete (Page) i.e. if we want to overwrite something already done in Load event handler of Master then it should be coded in the LoadComplete event of the page.
- Page_Load is the name of the method for event handler for Load event of Master. (it’s not Master_Load).
47.What is Data Cache in ASP.NET and how to use it?
Ans:
Data Cache is used to store frequently used data in the Cache memory. It’s much more efficient to retrieve data from the data cache instead of database or other sources. We need to use System.Web.Caching namespace. The scope of the data caching is within the application domain unlike “session”. Every user is able to access this object.
When a client requests the server, the server executes the stored procedure or function or selects statements on the Sql Server database then it returns the response to the browser. If we run again same process will happen on the web server with sql server.
How to create data cache:
- Cache [“Employee”] = “DataSet Name”
We can create data caching use Cache Keyword. It’s located in the System.Web.Caching namespace. It’s just like assigning value to the variable.
How to remove a Data Cache:
We can remove Data Cache manually.
//We need to specify the cache name;- Cache.Remove(String key);
48. What is the Enterprise Library in ASP.NET?
Ans:
Enterprise Library: It is a collection of application blocks and core infrastructure. Enterprise library is the reusable software component designed for assisting the software developers.
We use the Enterprise Library when we want to build application blocks intended for the use of developers who create complex enterprise level applications.
Enterprise Library Application Blocks
Security Application Block:
Security Application Block provides developers the ability to incorporate security functionality in the application. This application can use various blocks such as authenticating and authorizing users against the database.
Exception Handling Application Block:
This block allows the developers to create consistency for processing the errors that occur throughout the layers of Enterprise Application.
Cryptography Application Block:
Cryptography application blocks allows developers to add encryption and hashing functionality in the applications.
Caching Application Block:
Caching Application Block allows developers to incorporate local cache in the applications.
49. How can we improve the Performance of an ASP.NET Web Page?
Ans:
This is the most common question from the ASP.NET forum in any interview. In this post I’m going to point out some of the important points that may help to improve the performance.
Here I used the word “improve performance” in the sense to decrease the loading time of the page. There are various reasons behind this. Some of them we look into from the “backend side” (Database side) and rest of them we need to take care in “front-end” ((UI) side.
For illustrative purposes, you have an ASP.NET Website, one of the aspx pages takes much time to load. Throughout this article, we are going to see how to decrease the loading time.
Back End (DB)
- Try to check the Query performance – that is how much time the query will take to execute and pull the records from DB. Then use SQL Server Profiler and Execution plan for that query so that you can come to a conclusion in which part it took much time.
- Check in every table (who are all part of the query) Index is created properly.
- If your query involves a complex stored procedure, which in turn uses a lot of joins, then you should focus on every table. In some cases, subquery performs better than joins.
- If your web page involves paging concepts, try to move the paging concepts to SQL Server. I meant that based on the page count the SP will return the records, instead of bringing the records as a whole.
50.Explain the difference between a class and an object.
Ans:
In short, a class is the definition of an object, and an object is an instance of a class.
We can look at the class as a template of the object: it describes all the properties, methods, states and behaviors that the implementing object will have. As mentioned, an object is an instance of a class, and a class does not become an object until it is instantiated. There can be more instances of objects based on the one class, each with different properties.
51. State the difference between a managed and an unmanaged code.
Ans:
Managed code is a code created by the .NET compiler. It does not depend on the architecture of the target machine because it is executed by the CLR (Common Language Runtime), and not by the operating system itself. CLR and managed code offers developers few benefits, like garbage collection, type checking and exceptions handling.
On the other hand, unmanaged code is directly compiled to native machine code and depends on the architecture of the target machine. It is executed directly by the operating system. In the unmanaged code, the developer has to make sure he is dealing with memory usage and allocation (especially because of memory leaks), type safety and exceptions manually.
In .NET, Visual Basic and C#, the compiler creates managed code. To get unmanaged code, the application has to be written in C or C++.
52.Explain the difference between the while and for loop. Provide a .NET syntax for both loops.
Ans:
Both loops are used when a unit of code needs to execute repeatedly. The difference is that the for loop is used when you know how many times you need to iterate through the code. On the other hand, the while loop is used when you need to repeat something until a given statement is true.
The syntax of the while loop in C# is:
- while (condition [is true])
- {
- // statements
- }
The syntax of the while loop in VB.NET is:
- While condition [is True]
- ‘ statements
- End While
The syntax of the for loop in C# is:
- for (initializer; condition; iterator)
- {
- // statements
- }
The syntax of the for loop in VB.NET is:
- For counter [ As datatype ] = start To end [ Step step ]
- ‘ statements
- Next [ counter ]
53.Explain the difference between boxing and unboxing. Provide an example.
Ans:
Boxing is the process of converting a value type to the type object, and unboxing is extracting the value type from the object. While the boxing is implicit, unboxing is explicit.
Example (written in C#):
- int i = 13;
- object myObject = i; // boxing
- i = (int)myObject; // unboxing
54.Discuss the difference between constants and read-only variables.
Ans:
While constants and read-only variable share many similarities, there are some important differences:
- Constants are evaluated at compile time, while the read-only variables are evaluated at run time.
- Constants support only value-type variables (the only exception being strings), while read-only variables can hold reference-type variables.
- Constants should be used when the value is not changing during run time, and read-only variables are used mostly when their actual value is unknown before run time.
- Read-only variables can only be initialised at the time of declaration or in a constructor.
55.Explain LINQ.
Ans:
LINQ is an acronym for Language Integrated Query, and was introduced with Visual Studio 2008. LINQ is a set of features that extends query capabilities to the .NET language syntax by adding sets of new standard query operators that allow data manipulation, regardless of the data source. Supported data sources are: .NET Framework collections, SQL Server databases, ADO.NET Datasets, XML documents, and any collection of objects that support IEnumerable or the generic IEnumerable<T> interface, in both C# and Visual Basic. In short, LINQ bridges the gap between the world of objects and the world of data.
56.Discuss what garbage collection is and how it works. Provide a code example of how you can enforce garbage collection in .NET.
Ans:
Garbage collection is a low-priority process that serves as an automatic memory manager which manages the allocation and release of memory for the applications. Each time a new object is created, the common language runtime allocates memory for that object from the managed Heap. As long as free memory space is available in the managed Heap, the runtime continues to allocate space for new objects. However, memory is not infinite, and once an application fills the Heap memory space, garbage collection comes into play to free some memory. When the garbage collector performs a collection, it checks for objects in the managed Heap that are no longer being used by the application and performs the necessary operations to reclaim the memory. Garbage collection will stop all running threads, it will find all objects in the Heap that are not being accessed by the main program and delete them. It will then reorganize all the objects left in the Heap to make space and adjust all the Pointers to these objects in both the Stack and the Heap.
To enforce garbage collection in your code manually, you can run the following command (written in C#):
- System.GC.Collect();
57.What do the following acronyms in .NET stand for: IL, CIL, MSIL, CLI and JIT?
Ans:
IL, or Intermediate Language, is a CPU independent partially compiled code. IL code will be compiled to native machine code using current environmental properties by Just-In-Time compiler (JIT). JIT compiler translates the IL code to an assembly code and uses the CPU architecture of the target machine to execute a .NET application. In .NET, IL is called Common Intermediate Language (CIL), and in the early .NET days it was called Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL).
CLI, or Common Language Infrastructure, is an open specification developed by Microsoft. It is a compiled code library used for deployment, versioning, and security. In .NET there are two CLI types: process assemblies (EXE) and library assemblies (DLL). CLI assemblies contain code in CIL, and as mentioned, during compilation of CLI programming languages, the source code is translated into CIL code rather than into platform or processor specific object code.
To summarize:
- When compiled, source code is first translated to IL (in .NET, that is CIL, and previously called MSIL).
- CIL is then assembled into a bytecode and a CLI assembly is created.
- Before code execution, CLI code is passed through the runtime’s JIT compiler to generate native machine code.
- The computer’s processor executes the native machine code.
58.Explain the difference between the Stack and the Heap.
Ans:
The short answer would be: in the Stack are stored value types (types inherited from System.ValueType), and in the Heap are stored reference types (types inherited from System.Object).
We can say the Stack is responsible for keeping track of what is actually executing and where each executing thread is (each thread has its own Stack). The Heap, on the other hand, is responsible for keeping track of the data, or more precise objects.
59.Explain what inheritance is, and why it’s important.
Ans:
Inheritance is one of the most important concepts in object-oriented programming, together with encapsulation and polymorphism. Inheritance allows developers to create new classes that reuse, extend, and modify the behavior defined in other classes. This enables code reuse and speeds up development. With inheritance, developers can write and debug one class only once, and then reuse that same code as the basis for the new classes. The class whose members are inherited is called the base class, and the class that inherits those members is called the derived class. By default, all classes in .NET are inheritable.
60.Explain the differences between an Interface and an Abstract Class in .NET.
Ans:
An interface merely declares a contract or a behavior that implementing classes should have. It may declare only properties, methods, and events with no access modifiers. All the declared members must be implemented.
An abstract class provides a partial implementation for a functionality and some abstract/virtual members that must be implemented by the inheriting entities. It can declare fields too.
Neither interfaces nor abstract classes can be instantiated.
61.Explain deferred execution vs. immediate execution in LINQ. Provide examples.
Ans:
In LINQ, deferred execution simply means that the query is not executed at the time it is specified. Specifically, this is accomplished by assigning the query to a variable. When this is done, the query definition is stored in the variable but the query is not executed until the query variable is iterated over. For example:
- DataContext productContext = new DataContext();
- var productQuery = from product in productContext.Products
- where product.Type == “SOAPS”
- select product; // Query is NOT executed here
- foreach (var product in productQuery) // Query executes HERE
- {
- Console.WriteLine(product.Name);
- }
You can also force immediate execution of a query. This can be useful, for example, if the database is being updated frequently, and it is important in the logic of your program to ensure that the results you’re accessing are those returned at the point in your code where the query was specified. Immediate execution is often forced using a method such as Average, Sum, Count, List, ToList, or ToArray. For example:
- DataContext productContext = new DataContext();
- var productCountQuery = (from product in productContext.Products
- where product.Type == “SOAPS”
- select product).Count(); // Query executes HERE
62.What is a delegate in .NET?
Ans:
A delegate in .NET is similar to a function pointer in C or C++. Using a delegate allows the programmer to encapsulate a reference to a method inside a delegate object. The delegate object can then be passed to code which can call the referenced method, without having to know at compile time which method will be invoked. In addition, we could use delegates to create custom events within a class. For example,
- public delegate void FooDelegate();
- class FooClass
- {
- // custom event
- public event FooDelegate FooEvent;
- }
- FooClass FooObj = new FooClass()
- FooObj.FooEvent += new FooDelegate();
63.How do you implement a generic action in WebAPI?
Ans:
It’s not possible, as the WebAPI runtime needs to know the method signatures in advance.
64.Why can’t you specify access modifiers for items in an interface?
Ans:
It is always public
65.When break is used inside two nested for loops, control comes out of which loop, the inner or the outer for loop? (I.e. does it break from all the present loops?)
Ans:
It breaks from the inner loop only.
66.You would know that System.Object is the parent class of all .NET classes; In other words all types in .NET (whether implicit, explicit, or user-created) derive from the System.Object class.What are the various methods provided to System.Object’s deriving classes/types?
Ans:
System.Object provides the following important methods, among others:
- ToString—Returns a string that represents the current object
- both overrides of Equals(object), Equals(object, object)
- GetHashCode
- Finalize
- GetType
- ReferenceEquals
- MemberwiseClone
Most of these methods provide the basic implementation required of any type that a developer will work with in the .NET stack.
67.What languages does the .NET Framework support?
Ans:
Answering this question shows you have the basic knowledge and skills required to fulfill the needs of the position. The right candidate should be a knowledgeable programmer who is comfortable coding within the .NET Framework. In addition to telling what languages the framework supports, you can also provide your experience programming within those languages.
Example: “The .NET Framework supports more than 60 languages. This includes both Microsoft and non-Microsoft languages. The most common languages are VB.NET, Cobol, Perl, C#, C++ and F# languages.
68. What are the most important aspects of .NET?
Ans:
.NET is an infrastructure that consists of multiple features like application domain, a common type system and profiling. Isolating one or two important pieces may be a challenge, but the interviewer may be looking for the answers “class library” and “Common Language Runtime.” It’s critical to make a case for why those are the most essential features. This is an opportunity to show your skills go beyond just technical because you can also apply critical thinking.
Example: “Common Language Runtime and Class library are the most important aspects of the .NET Framework. CLR provides building tools and resources that help developers set the foundation for application building. The class library holds essential classes used for providing commonly known functionality that is shareable across applications.”
69. Explain in basic terms how to execute managed code.
Ans:
Executing code is an essential function of any developer, but knowledge of executing managed code is specific to the .NET Framework. Your answer should explain how to execute code that runs inside the common language runtime environment the framework provides.
Additionally, whenever an interviewer asks you to explain something in “basic terms,” it’s important to pay attention to the language you use to make it as clear as possible. These types of questions are often asked when the position requires the candidate to be both very technical and also a good communicator who can explain their work to a broad audience. In some organizations, a lead developer may be responsible for reporting progress on an application to stakeholders. During these exchanges, they should be able to break down their work without using technical jargon or overly complicated language.
Example: “First, I would write the code. Then I would compile the code with a resource called a compiler. Using the compiler, I would convert the managed code into an intermediate language. The intermediate language will be targeted by the Common Language Runtime within .NET Framework and converted to native code that can then be executed inside the framework.
In my previous role as a developer, I was tasked with speeding up application delivery times. Using .NET and this process for executing managed code, I was able to reduce delivery timelines by 5% overall.”
70.What is the difference between Web Site and Web Application?
Ans:
Web Site:
- On a website, you cannot add multiple projects.
- There is no project file (.csproj or .vbproj). All the files in a folder structure are automatically included in the site.
- By default, compilation produces multiple assemblies.
- The website is easy to create and deploy.
- You can use different .NET languages on a single web site such as VB.NET pages and C# pages can be used on a single website.
- You can edit a single page/file after deployment recompilation is not required.
- Choose a website when one developer will be responsible for creating and managing an entire website. Since decoupling is not possible on the website.
- You cannot establish dependencies on the website.
Web Application:
- In a web application, you can add multiple projects.
- It has a Visual Studio project file (.csproj or .vbproj) stores information about the project like as the list of files that are included in the project, and any project-to-project references.
- By default, compilation of code files (excluding .aspx and .ascx files) produces a single assembly.
- It is easy to develop compared to the website.
- You cannot use different .NET languages in a Web Application such as
- C# and VB.NET both cannot be used in a web application.
- You cannot edit a single file. Recompilation is required.
- The right choice for enterprise environments where multiple developers work for creating, testing and deployment. Different groups work on various components independently like one group work on the domain layer, other work on the UI layer hence, decoupling is possible here
- You can establish dependencies in a Web Application
71.What is a round trip?
Ans:
The trip of a Web page from the client to the server and then back to the client is known as a round trip. In ASP.NET Response.Redirect() causes a round trip.
72 .What is the difference between Web.config and Machine.config file?
Ans:
Both files are used to define configurations for your ASP.NET application. There are the following differences between these two configuration files.
Web.config
The Web.config is used to define application-level settings.
If any setting is not specified in Web.config it inherits from Machine.config by default.
Web.config is an XML-based configuration file for an ASP.NET application which includes the setting for Data Connection, Customizing Security, State Management, Memory Management, Error Handling and much more.
It is sometimes called application and session level configuration file.
You can have more than one Web.config file in your ASP.NET application.
Machine.configThis file is at the highest level in the configuration hierarchy.
You can find it at <WinDir>\Microsoft.NET\Framework\<version>\config\machine.config
Machine.config is used for defining server level setting.
It defines the supported configuration file section and ASP.NET work process.
It registers providers that can be used for advanced features such as profiles membership and role-based security.
It is automatically installed while installing Visual Studio.NET.
It is sometimes called machine level configuration file.
Only one Machine.config file can be at the machine level.
73.How to define a connection string in a Web.config file?
Ans:
Following is the way to define a connection string in Web.config for SQL Server database.
<connectionStrings>
- <add name=”strcon” connectionString=”Data Source=DonetApp; Initial Catalog=dotnetDB; Persist Security Info=True; User ID=asif@123; Password=123@asif” providerName=”System.Data.SqlClient”/>
</connectionStrings>
74.What are server controls in ASP.NET ?
Ans:
The ASP.NET server controls are objects on the ASP.NET pages that run when the Web page is requested. Many server controls, such as button and text box, are similar to the HTML controls. In addition to the HTML controls, there are many controls, which include complex behaviour, such as the controls used to connect to data sources and display data.
75.What is the difference between Hyperlink and LinkButton?
Ans:
Hyperlink control does not have the Click and Command events; whereas the LinkButton control has these events, which can be handled in the code-behind file of the Web page.
76.What are navigation controls?
Ans:
Navigation controls help us to navigate in a Web application easily. These controls store all the links in a hierarchical or drop-down structure; thereby facilitating easy navigation in a Web application.
77.How many navigation controls are in ASP.NET?
Ans:
There are three navigation controls in ASP.NET.
- SiteMapPath
- Menu
- TreeView
78.What is the difference between client-side and server-side validations?
Ans:
Client-side validations work at the client end with the help of scripting languages such as JavaScript or jQuery and VBScript. On the other hand, server-side validations work at the server end with the help of programming languages like C#, VB, F# etc. Server validations work when you submit or send data to the server.
79.What are Globalization and Localization?
Ans:
Globalization is the process of designing and developing an application that functions for multiple cultures or locales. In other words, Globalization is the process of designing and developing an application in such a way that it can be used by users of multiple cultures. Globalization makes your application ready for international markets. This process involves:
- Identifying the culture and locale that must be supported by the application.
- Designing features to support those cultures and locales.
- Writing code that functions equally well with all the supported cultures and locales.
Localization is the process of customizing your application for a given culture or locale. In other words, Localization is the process of customizing your application in such a way that it behaves as per current culture or locale. Typically, Localization translates your application UI into current culture or locale.
80.What is a Resource File?
Ans:
ASP.NET provides resource files to implement globalization and localization. The resource file is an XML file having extension resx. Each resource in the resx file is in the form of a key-value pair. For each culture which your application needs to support create a separate resource file. For example, WebResources.en.resx is a resource file for English language and WebResources.hi.resx is a resource file for the Hindi language.
81.What are Local Resources and Global Resources?
Ans:
There are two types of resource files as given below :
- Local Resources: Local resources are specific to a single web page and used for providing versions of a web page in different languages. These are stored in the App_LocalResources folder.
- Global Resources: Global resources are common for the whole web application and can be accessed by all the web pages. These are stored in the App_GlobalResources folder.
82.What is Neutral Culture, Culture, and Language?
Ans:
A neutral culture is a culture that is associated with a language but not with a country or region. For example, “en” for English and in for Hindi. Culture consists of language and the country or region. It is denoted by culture code which contains two lowercase letters denoting the language and two uppercase letters denoting the country or region like en-US for English in the US, en-GB for UK etc. A language is any spoken language like English (en), Hindi (hi), and German (de) etc.
83.What are the differences between GridView and DataGrid?
Ans:
The differences between GridView and DataGrid are given below :
GridView:
- It was introduced with ASP.NET 2.0
- Built-in supports for Paging and Sorting.
- Built-in supports for Update and Delete operations.
- Supports auto format or style features.
- Performance is slow as compared to DataGrid
Datagrid:
- It was introduced with ASP.NET 1.0
- For sorting, you need to handle SortCommand event and rebind grid required and for paging, you need to handle the PageIndexChanged event and rebind grid required
- Need to write code for implementing Update and Delete operations.
- This feature is not supported.
- Performance is fast as compared to GridView.
84.What are the differences between ListView and Repeater?
Ans:
The differences between ListView and Repeater are given below :
ListView:
- 1.It was introduced with ASP.NET 3.5
- 2.Built-in supports for paging and sorting.
- 3.Built-in supports for Data grouping.
- 4.Built-in supports for insert update and delete operation.
- 5.Performance is slow as compared to Repeater
Repeater:
- 1.It was introduced with ASP.NET 1.0
- 2.Need to write custom code.
- 3.Need to write custom code.
- 4.Need to write custom code.
- 5.Performance is fast as compared to ListView
85.What are the different modes for the Session state in ASP.NET?
Ans:
There are following the different modes of session state which can be defined in a Web.config file.
Off: Specify that Session state is not enabled.
InProc: This is the default mode of the session. In this mode session state is stored on the web server i.e. IIS where an application is running.
OutProc: The OutProc mode can be handled by using the following ways –
- State Server: In this mode, the session is stored in a separate process called ASP.NET state service. This ensures that the session state will be available if the web application is restarted. This way also makes the session state availability to multiple web servers in a web farm.
- SQL Server: In this mode, the session is stored in a SQL Server database. This also ensures that the session state will be available if the web application is restarted. This way also makes the session state availability to multiple web servers in a web farm.



