- 10 Best Data Analytics Tools for Big Data Analysis | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Azure Databricks | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Elasticsearch Nested Mapping : The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Various Talend Products and their Features | Expert’s Top Picks with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Apache Pig ? : A Definitive Guide | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- Introduction to HBase and Its Architecture | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- What is Azure Data Lake ? : Expert’s Top Picks | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Splunk Rex : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Data Pipelining? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Dedup : Splunk Documentation | Step-By-Step Process | Expert’s Top Picks
- What Is a Hadoop Cluster? : A Complete Guide with REAL-TIME Examples
- Spark vs MapReduce | Differences and Which Should You Learn? [ OverView ]
- Top Big Data Challenges With Solutions : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Hive vs Impala | What to learn and Why? : All you need to know
- What is Apache Zookeeper? | Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- What is HDFS? Hadoop Distributed File System | A Complete Guide [ OverView ]
- Who Is a Data Architect? How to Become and a Data Architect? : Job Description and Required Skills
- Kafka vs RabbitMQ | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Apache Hadoop YARN? Expert’s Top Picks
- How to install Apache Spark on Windows? : Step-By-Step Process
- What is Big Data Analytics ? Step-By-Step Process
- Top Big Data Certifications for 2020
- What is Hive?
- Big Data Engineer Salary
- How Facebook is Using Big Data?
- Top Influencers in Big Data and Analytics in 2020
- How to Become a Big Data Hadoop Architect?
- What Are the Skills Needed to Learn Hadoop?
- How to Become a Big Data Analyst?
- How Big Data Can Help You Do Wonders In Your Business
- Essential Concepts of Big Data and Hadoop
- How Big Data is Transforming Retail Industry?
- How big Is Big Data?
- How to Become a Hadoop Developer?
- Hadoop Vs Apache Spark
- PySpark Programming
- 10 Best Data Analytics Tools for Big Data Analysis | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Azure Databricks | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Elasticsearch Nested Mapping : The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Various Talend Products and their Features | Expert’s Top Picks with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Apache Pig ? : A Definitive Guide | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- Introduction to HBase and Its Architecture | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- What is Azure Data Lake ? : Expert’s Top Picks | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Splunk Rex : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Data Pipelining? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Dedup : Splunk Documentation | Step-By-Step Process | Expert’s Top Picks
- What Is a Hadoop Cluster? : A Complete Guide with REAL-TIME Examples
- Spark vs MapReduce | Differences and Which Should You Learn? [ OverView ]
- Top Big Data Challenges With Solutions : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Hive vs Impala | What to learn and Why? : All you need to know
- What is Apache Zookeeper? | Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- What is HDFS? Hadoop Distributed File System | A Complete Guide [ OverView ]
- Who Is a Data Architect? How to Become and a Data Architect? : Job Description and Required Skills
- Kafka vs RabbitMQ | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Apache Hadoop YARN? Expert’s Top Picks
- How to install Apache Spark on Windows? : Step-By-Step Process
- What is Big Data Analytics ? Step-By-Step Process
- Top Big Data Certifications for 2020
- What is Hive?
- Big Data Engineer Salary
- How Facebook is Using Big Data?
- Top Influencers in Big Data and Analytics in 2020
- How to Become a Big Data Hadoop Architect?
- What Are the Skills Needed to Learn Hadoop?
- How to Become a Big Data Analyst?
- How Big Data Can Help You Do Wonders In Your Business
- Essential Concepts of Big Data and Hadoop
- How Big Data is Transforming Retail Industry?
- How big Is Big Data?
- How to Become a Hadoop Developer?
- Hadoop Vs Apache Spark
- PySpark Programming

How to Become a Big Data Analyst?
Last updated on 05th Oct 2020, Artciles, Big Data, Blog
Who is a Data Analyst?
Nowadays, companies receive a tremendous amount of information every day that can be used to optimize their strategies. To get insights from the massive data collected, they need a highly qualified professional: the Data Analyst.
The task of a Data Analyst is to process the varied data concerning the customers, the products, or the performances of the company, to release indicators useful for the decision-makers. Thus, the information provided by the data analyst enables companies to define the products to be offered to customers according to their needs, the marketing strategy to adopt, or the improvements to be made to the production process.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Data Analyst Qualifications
How to become a data analyst requires both academic qualifications and skills. Let us see these categories in detail below.
Academic Qualifications
It is recommended that graduate from a data analysis program and have a high GPA, it would be easy for you to land an entry-level data analysis job. Even if you don’t have a specialization in data analysis, but a degree in mathematics, statistics, or economics from a well-reputed University, can easily land a data analysis entry-level job.
Most entry-level data analyst jobs require at least a bachelor level degree. Higher-level data analyst jobs usually guarantee a higher pay and may require you to have a master’s or a doctoral degree. Having a master’s degree in Data Science or Business Analytics is very helpful. If you are interested in data analytics, you should consider earning a master’s degree.
Apart from the degree, you can also enroll in online courses if that what interests you the most, then the path you take to be qualified can be anything. You may want to check out the top 10 data analytics courses here.
Skills
Skills of the candidate can be further classified into three categories, let us discuss them in detail:
- Technical Skills
Programming Languages: As a data analyst, you should be proficient in at least one programming language. However, the more languages you are proficient in, the better it is. Popular programming languages that can be used to manipulate data are R, Python, C++, Java, MATLAB, PHP, and more.
Data Management and Manipulation: As a data analyst, you should be familiar with languages, such as R, HIVE, SQL, and more. Building queries to extract the desired data is an essential aspect of data analysis. Once you have analyzed the data, you would have to create accurate reports. Some standard tools for doing the same are SAS, Oracle Visual Analyzer, Microsoft Power BI, Cognos, Tableau, and more.
- Soft Skills
Domain Knowledge and Excellent Communication Skills: A data analyst’s job is to provide detailed and accurate information to the decision-makers. Hence, data analysts must understand the specific user requirements, along with having a deep understanding of the data. Excellent communication skills are essential for collaboration with the various clients, executives, IT specialists, to ensure that the data aligns well with the business objectives. Ultimately, the analysis done by a data analyst modifies/improves some business processes.
- Practical Skills
High Level of Mathematical Ability: Knowledge of statistics and the right comfort level with formulae required for analyzing data to provide real-world value. As a data analyst, you should have a good grasp of mathematics, and you should be able to solve common business problems, for example, calculating compound interest, depreciation, statistical measures (for example, mean, median, mode). Also, you should know how to use tables, charts, graphs, and more. It is essential to be comfortable with college-level algebra, thereby Making visualization of data more appealing. Knowing linear algebra and multivariate calculus is very helpful for data analysts as they are all extensively used in performing Data Analysis.
Microsoft Excel: Organizing data and calculating numbers are among the main tasks of data analysts. Hence it is beneficial if you are comfortable with using Excel. There are many great online sources where you can learn how to use Excel to its full potential.
Data Analyst Salary
Different factors account for the salary being paid to a data analyst professional, these mainly being education, location, skills, and experience.
Let us see the average salaries for different experience levels in INR and USD.
| Entry Level Data Analyst | ||
|---|---|---|
| Salary Range in INR | ₹172,794 – ₹716,015 | |
| Salary Range in USD | $40,585 – $78,832 | |
| Mid Level Data Analyst | ||
| Salary Range in INR | ₹289,109 – ₹1,186,711 | |
| Salary Range in USD | $45,244 – $91,092 | |
| Experienced Data Analyst | ||
| Salary Range in INR | ₹363,414 – ₹1,970,089 | |
| Salary Range in USD | $45,280 – $99,542 | |
Data Analyst Career Path
Skilled data analysts are in demand in almost every sector. Hence, it doesn’t come as a surprise that the predicted growth rate in demand for data analysts for the next seven years is 19%. Data analysis is considered to be the most crucial skill, so every professional should learn Data Science as soon as possible to excel in a career. Some industries where the demand for data analysts is quite high are as follows:
- Market Research: 72% of marketers consider data analysis to be vital for thriving in the present marketing landscape. The success of the marketing campaigns can be understood using data analysis. Also, data analysis can be used by companies for a market research before launching a new product or service.
- Finance and Investments: Financial institutions generally require entry-level data analysts as well as expert ones. At many financial institutions, such as investment banks, the most common career path taken by data analysts is that of management. If you prove to be the best among your peer group, you are considered for promotion by the senior management as they consider you as someone who could manage new hires well.
- Sales: There are many data related to sales of products and services in a company that is analyzed, which helps in increasing sales and customer satisfaction and also in identifying the potential sales barriers. Hence, a requirement for data analysts arises in this sector, as well.
A data analyst fresher makes a handsome salary, and the range of the salary depends on his/her expertise and skill-set. The skills required as a fresher may vary across the industry.
For example, the typical job of a Data Analyst is to run queries against the available data for finding the important trends and processing the data that might be of use to Data Scientists. In general, the Data Analysts are very good at database query languages, for example, SQL. They may also write scripts and produce visuals on the data available to them for better understanding.
A Data Scientist, on the other hand, builds models using Machine Learning. These models are used to make several predictions and can also explain the future of the organization. Data Scientists work closely with Data Analysts while preparing the data to be used for the machine learning models. However, the salaries of Data Scientists are much higher than those of Data Analysts because of very high demand and low supply.
Many Data Analysts gain relevant skills and become Data Scientists. The transition to becoming a Data Scientist is not very difficult for Data Analysts since they already have some relevant skills. Many Data Analysts go on to become Data Scientists.
The designations of a Data Analyst would depend on the company he/she works. However, generally, the technical work of the Data Analysts keeps on decreasing, and the managerial work keeps on increasing as they climb up the corporate ladder. After a certain point, the promotion starts to depend on the leadership and managerial skills. Hence, Data Analysts need to work on their soft skills as well.
How to Become a Data Analyst?
To become a data analyst, you must first earn a Bachelor’s degree, which is a requirement for most of the entry-level data analyst positions. The relevant disciplines include Finance, Economics, Mathematics, Statistics, Computer Science, and Information Management.
Considering that you don’t have any prior work experience as a data analyst, the most important task is to gain relevant work experience. As with a majority of professions, work experience is invaluable for a data analyst too. Fortunately, because of the massive demand for data analysts, there are many data analysis internship opportunities. You can work as an intern, which would help you gain the relevant work experience and also add a star to your resume.
Data analysis deals with understanding changing trends and technologies, which makes it essential for a data analyst to commit himself/herself to lifelong learning. You can take up MOOCs to ensure that you keep learning new things relevant to data analysis, which helps you stay ahead of the curve.
How to Become a Data Analyst with No Experience?
If you plan to switch being a data analyst but bear no experience in the industry, you can probably start with a degree in an online course in data analysts. The course would make your foundation strong in the subject, also allowing you to build practical projects and learn and develop your skills. Moving on, you can get into an internship or pick up some freelance work to gain experience and add to your profile this way would stand out and have an edge when you start looking for a high profile job as a data analyst.
The three steps to launching a data analyst career
Step 1: Earn a bachelor’s degree in information technology, computer science, or statistics
Minor or study applied statistics or data analysis. Also, take computer science classes that emphasize project management and database management. Find an advisor or career counselor that is familiar with a data analyst career path.
Step 2: Gain data analyst experience
It is difficult to gain employment as a data analyst if you do not have any experience. Interning while in school is a good way to gain valuable experience and will help with insights about additional skill development and training. Even still, most people in technical careers start at entry-level positions in this case including positions such as a statistical assistant or technician. These jobs will provide valuable on-the-job training and experience. Take as many in-house training classes as possible, especially ones about analytical software programs and big data management. Experience, knowledge, and willingness to learn will help you rise to the level you desire.
Step 3: Advancing your career – consider a master’s degree or certificate program
An advanced degree will offer more job opportunities and ways to advance your career. Employers want candidates to have an array of knowledge and be familiar with the latest technologies and tools. Consider a master’s degree in data science, data analytics or big data management. These programs will generally provide exposure to the newest software programs from experts in field. Many universities partner with corporations to create team assignments, internships, and capstone projects: which will gain invaluable real-world experience while earning an advanced degree
Key Skills Needed by Big Data Analysts
A Big Data Analyst needs a broad range of skills to achieve their goals. Effective interpersonal skills are quite useful in communicating Big Data results to employers and team members. Additionally, Big Data Analysts should have the technical abilities needed for the work, which includes working with Cloud services such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure. It is not uncommon for a freelance Big Data Analyst to have a preferred cloud service, but for security purposes, they may have to work with the company’s cloud. Management skills can also be helpful in overseeing staff and working with assistants.
The following qualifications are generally expected from Big Data Analysts:
- Industry Experience: Analyzing Big Data requires an understanding of the industry, whether it be astronomy or finance. This understanding provides a screening process, or a paradigm, which is used to define and frame the questions being asked. The more experience one has in a particular field and life in general, the more understanding one will have when doing research. A broad background of experience provides an understanding of how to interpret data.
- Statistics: Processing Big Data requires a knowledge of statistics. Statistics is a fundamental building block for Data Science, probability distribution, and random variables.
- Languages: Java, R, Python, C++, Hive, Ruby, SQL, MATLAB, SAS, SPSS, Weka, Scala, Julia. At a minimum, a Big Data Analyst should be familiar with R, Python, and Java.
- Computational Frameworks: Having a solid understanding of frameworks such as Apache Spark, Apache Samza, Apache Flink, Apache Storm, and Hadoop is essential. These technologies support the processing of Big Data, which, for the most part, can be processed as it is streamed.
- Data Warehousing: Understanding how data is stored and how to access it is important. Experience with non-relational database systems is also quite useful. Examples of non-relational (NoSQL) databases include Cassandra, Hbase, CouchDB, HDFS, and MongoDB.
- Data Visualization: Big Data can be difficult to comprehend and discuss. This is why pictures (also known as visuals) make discussing Big Data easier. Exploring even just a sample of data visualizing tools like Tableau or Qlikview can show the shape of data, revealing hidden details.
- Communication: While Data Visualization is a useful tool, the ability to speak intelligently and clearly is a necessity for Big Data Analysts. Results and how they were produced must be explained to the people paying the bill. After researching the data, Big Data Analysts may also have to make presentations to different departments within the organization.
- Written Reports: A written report provides a permanent record of observations and conclusions for clients or employers.
Normal Tasks and Responsibilities
Big Data Analysts are responsible for realizing three key real-time solutions – affordability, speed, and quality – and providing Business Intelligence to clients or employers. They may work with Data Quality teams ensuring data integrity and thoroughness, or perhaps with management to plan and perform data analyses. Big Data Analysts may also participate in planning organizational changes to maximize profits and minimize losses. Abhishek Mehta, the founder and CEO of Tresata, a Predictive Analytics company, stated, “The ability to deliver products and services at the right time, in the right place, and to the right customer, instantly, is the future.”
A Big Data Analyst will, on a regular basis:
- Determine organizational goals
- Work with management, IT teams, or Data Scientists
- Data mine from a variety of sources
- Screen and clean data to remove irrelevant information
- Research trends and patterns
- Find and identify new opportunities
- Provide clear and concise data reports and visualizations for management
Let us now look at some of the key skills needed for being a big data analyst –
1) Programming
While a traditional data analyst might be able to get away without being a full-fledged programmer, a big data analyst needs to be very comfortable with coding. One of the main reasons for this requirement is that big data is still in an evolution phase. Not many standard processes are set around the large complex datasets a big data analyst has to deal with. A lot of customization is required on a daily basis to deal with unstructured data.
Which languages are required – R, Python, Java, C++, Ruby, SQL, Hive, SAS, SPSS, MATLAB, Weka, Julia, Scala. As you can not knowing a language should not be a barrier for a big data scientist. At the minimum one needs to know R, Python, and Java. While working you may end up using various tools. Programming Language is only a tool and more tools you have in your kitty, merrier it is.
2) Data Warehousing
Experience with relational and non -relational database systems is a must. Examples of non- relational database include – Mysql, Oracle, DB2. Examples of non-relational database include – NoSql : Hbase, HDFS, MongoDB, CouchDB, Cassandra, Teradata, etc.
3) Computational frameworks
A good understanding and familiarity with frameworks such as Apache Spark, Apache Storm, Apache Samza, Apache Flink and the classic MapReduce and Hadoop. These technologies help in Big Data processing which can be streamed to a great extent.
4) Quantitative Aptitude and Statistics
While the processing of Big Data requires great use of technology, fundamental to any analysis of data is good knowledge of Statistics and linear algebra. Statistics is a basic building block of data science and understanding of core concepts like summary statistics, probability distribution, random variables, Hypothesis testing framework is important if you are data scientist of any genre.
5) Business Knowledge
To keep the analysis focused, to validate, sort, relate, evaluate the data, the most critical skill of a big data scientist is to have a good knowledge of the domain one is working on. In fact, the reason big data analysts are so much in demand is that it’s very rare to find resources who have a thorough understanding of technical aspects, statistics and business. There are analysts good in business and statistics but not in programming. There are expert programmers without the know-how of how to put the programs in the context of the business goal.
Data Analyst Skills
Other than the fact that you absolutely love data, there are certain other skills that a Data Analyst must possess.
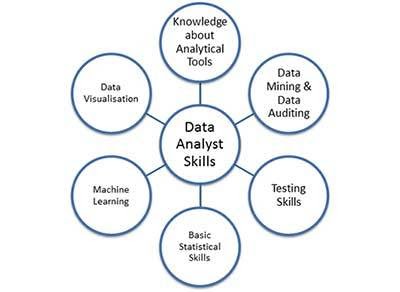
Knowledge about the various Tools/Programming Languages
As a data analyst, you are expected to have knowledge about the best data analytical tools or programming languages like R or Python or SAS Only after using one of the scripting languages it will be possible for the data analyst to find new meaningful insights.
Data Mining and Data Auditing Skills
As mentioned above, data mining and data auditing are must-have skills for any data analyst. Data mining is the practice of examining large pre-existing databases in order to generate new information whereas data auditing involves profiling the data and assessing the impact of poor quality data on the organization’s performance and profits. So make sure to brush on these skills.
Testing Skills
Testing skills are required by a Big Data analyst as he/she will be carrying out A/B testing based on different hypotheses that directly and indirectly impact different Key Performance Indicators
Basic Statistical Skills
Usually it is the Data Scientist that works on the statistical part but even as a data analyst you should have basic statistical knowledge as it will help you to select the right approach while dealing with a particular situation.
Machine Learning
Again like Statistical Skills, machine learning is something that most data scientists work on but if you are working in a large organization then there are chances that you will need to know about the machine learning methods like Decision Tress , K-Means, etc.
Data Visualization and Communication
This is one of the most important skills that a data analyst must possess. Data visualization is the presentation of data in a pictorial or graphical format. This helps the management to understand the data easily and quickly. The success of data visualization depends on how well you can communicate it to the management.
Big Data Analyst Job Description

- Importing/Collecting, cleaning, converting and analyzing the data for the purpose of find insights and making conclusions.
- Presenting data in graphs, charts, tables, etc and designing and developing relational databases for collecting data.
- Conduct research and make recommendations on data mining products, protocols, services, and standards in support of procurement and development efforts.
- Monitor the performance of data mining system and if there are any issues then respond to the same.
- Keep a track of trends, patterns, and correlation in the case of complex data sets.
- Prepare concise data reports and data visualizations for the management that will help in the decision making process.
- Work closely with the IT team and data scientists to determine and achieve the organizational goals.
- Assist the data scientist in development of new analytical tools and methods as and when required.
- Create data definitions for new database file/table development and/or changes to existing ones as needed for analysis.
