- Different Methodologies in Project Management
- Difference between Soap and Rest | Know more about it
- What is Python array? Learn with examples
- Best Career options after Engineering | Everything You Need to Know [OverView]
- What is list in Python ? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Data Modelling? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What are Microservices? : A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Python Programming | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- All You Need To Know About Python List | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What Is a Software Developer | Software Developer job description and duties | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Artificial Intelligence Chatbot?
- Kotlin vs Java | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Abstraction in Java | Implementations of Abstraction in Java | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What are the Important Data Structures and Algorithms in Python?
- Go vs Python | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Best Python IDEs and Code Editors | Expert’s Top Picks | Everything You Need to Know
- Go Programming Language | Expert’s Top Picks | A Definitive Guide [ OverView ]
- Python Scopes and Their Built-in Functions | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Python String Formatting | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Python Serialization | A Complete Guide For Beginners | Learning Guide
- What is .Net FrameWork? Uses and its Benefits | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Quality Assurance ? : A Definitive Guide | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- What is Spike Testing ? : A Definitive Guide | Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Average Full Stack Developer Salary in India [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is WSDL in Web Services ? Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Virtual Instrumentation using Labview | Comprehensive Guide [ Explained ]
- Gradle vs Maven | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Python Sleep Method | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Kotlin vs Python | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Spring Boot vs Spring MVC | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- IT Engineer Salary in India – How much does one earn?
- What is pip ? and Getting Started with Python pip | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Node.js Installation on Windows and Ubuntu | Free Guide Tutorial
- Skills Needed for Full Stack Developers | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Axios in React? and Its Uses [ OverView ]
- What is MEAN Stack? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- How to Install Node.JS on Ubuntu | Everything You Need to Know
- Average Annual Salary of a Python Certified Professional – Career Path
- What is Scala Programming? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What Is User Input in Python? Expert’s Top Picks
- Interface vs Abstract Class | Difference You Should Know
- Final Year Computer Science Project Ideas | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Technical Architect | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Logical Programs in Java | Step-By-Step Process
- C++ vs Java | Difference You Should Know
- What is C Programming? Comprehensive Guide
- What Is a Quality Engineer? ( Everything You Need to Know )
- Python Project Ideas for Beginners | All you need to know
- How to Run Python Scripts? Comprehensive Guide
- Python Operators
- How To Install NumPy in Python?
- Top Software Courses to Get High Paying Jobs
- Loops In Python
- Tips to Avoid Application Rejection
- Top Young App Developers Who Became Millionaires
- Top Technical Courses After Graduation
- Node JS Architecture
- What is PyCharm?
- Resources To Help You Learn Java Programming
- How to Become a Software Engineer?
- Best Programming Languages to Learn in 2020
- Scala vs Python
- How to Become a Full Stack Developer?
- The Most Popular Java Applications Used World-wide
- What is Java String?
- Full Stack Developer vs Front End Developer vs Back End Developer
- Python Collections
- Identifiers in Python
- Dynamic Method Dispatch in Java
- Hadoop Ecosystem
- Method Overloading in Python
- Convert Decimal To Binary In Python
- How To Make A Chatbot In Python?
- How to Input a List in Python?
- Hash Tables and Hashmaps in Python
- Top Python Framework’s
- Python Split Method with Example
- Python Enumerate
- Inheritance in Java
- Init in Python
- Goto Statement in Python
- Literals in Java
- Polymorphism in Oops
- Socket Programming in Python
- Object Class in Java
- Break, Continue, and Pass Statements in Python
- Exception Handling in Java
- Java BASIC Programs
- Different Methodologies in Project Management
- Difference between Soap and Rest | Know more about it
- What is Python array? Learn with examples
- Best Career options after Engineering | Everything You Need to Know [OverView]
- What is list in Python ? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Data Modelling? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What are Microservices? : A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Python Programming | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- All You Need To Know About Python List | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What Is a Software Developer | Software Developer job description and duties | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Artificial Intelligence Chatbot?
- Kotlin vs Java | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Abstraction in Java | Implementations of Abstraction in Java | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What are the Important Data Structures and Algorithms in Python?
- Go vs Python | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Best Python IDEs and Code Editors | Expert’s Top Picks | Everything You Need to Know
- Go Programming Language | Expert’s Top Picks | A Definitive Guide [ OverView ]
- Python Scopes and Their Built-in Functions | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Python String Formatting | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Python Serialization | A Complete Guide For Beginners | Learning Guide
- What is .Net FrameWork? Uses and its Benefits | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Quality Assurance ? : A Definitive Guide | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- What is Spike Testing ? : A Definitive Guide | Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Average Full Stack Developer Salary in India [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is WSDL in Web Services ? Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Virtual Instrumentation using Labview | Comprehensive Guide [ Explained ]
- Gradle vs Maven | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Python Sleep Method | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Kotlin vs Python | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Spring Boot vs Spring MVC | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- IT Engineer Salary in India – How much does one earn?
- What is pip ? and Getting Started with Python pip | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Node.js Installation on Windows and Ubuntu | Free Guide Tutorial
- Skills Needed for Full Stack Developers | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Axios in React? and Its Uses [ OverView ]
- What is MEAN Stack? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- How to Install Node.JS on Ubuntu | Everything You Need to Know
- Average Annual Salary of a Python Certified Professional – Career Path
- What is Scala Programming? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What Is User Input in Python? Expert’s Top Picks
- Interface vs Abstract Class | Difference You Should Know
- Final Year Computer Science Project Ideas | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Technical Architect | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Logical Programs in Java | Step-By-Step Process
- C++ vs Java | Difference You Should Know
- What is C Programming? Comprehensive Guide
- What Is a Quality Engineer? ( Everything You Need to Know )
- Python Project Ideas for Beginners | All you need to know
- How to Run Python Scripts? Comprehensive Guide
- Python Operators
- How To Install NumPy in Python?
- Top Software Courses to Get High Paying Jobs
- Loops In Python
- Tips to Avoid Application Rejection
- Top Young App Developers Who Became Millionaires
- Top Technical Courses After Graduation
- Node JS Architecture
- What is PyCharm?
- Resources To Help You Learn Java Programming
- How to Become a Software Engineer?
- Best Programming Languages to Learn in 2020
- Scala vs Python
- How to Become a Full Stack Developer?
- The Most Popular Java Applications Used World-wide
- What is Java String?
- Full Stack Developer vs Front End Developer vs Back End Developer
- Python Collections
- Identifiers in Python
- Dynamic Method Dispatch in Java
- Hadoop Ecosystem
- Method Overloading in Python
- Convert Decimal To Binary In Python
- How To Make A Chatbot In Python?
- How to Input a List in Python?
- Hash Tables and Hashmaps in Python
- Top Python Framework’s
- Python Split Method with Example
- Python Enumerate
- Inheritance in Java
- Init in Python
- Goto Statement in Python
- Literals in Java
- Polymorphism in Oops
- Socket Programming in Python
- Object Class in Java
- Break, Continue, and Pass Statements in Python
- Exception Handling in Java
- Java BASIC Programs

What are the Important Data Structures and Algorithms in Python?
Last updated on 04th Nov 2022, Artciles, Blog, Software Engineering
- In this article you will learn:
- 1.Important Data Structures in Python.
- 2.Algorithm.
- 3.Conclusion.
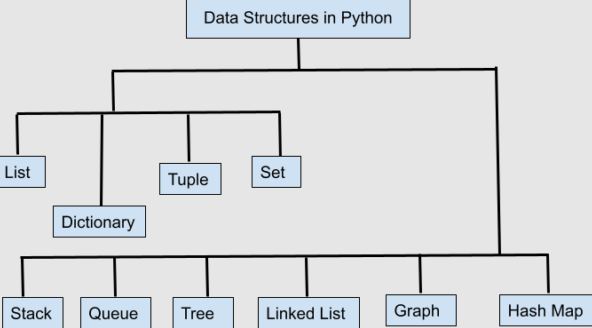
Important Data Structures in Python:
Lists:
Python Lists are the ordered collections of a data just like arrays in the other programming languages. It allows a various types of elements in the list. The implementation of a Python List is similar to Vectors in C++ or ArrayList in JAVA. The costly operation is an inserting or deleting the element from a beginning of the List as all elements are needed to be shifted. An Insertion and deletion at end of the list can also become costly in case where a preallocated memory becomes full.
Example: Creating Python List
Python3
- List = [1, 2, 3, “GFG”, 2.3]
- print(List)
List elements can be accessed by a assigned index. In a python starting index of the list, a sequence is 0 and an ending index is (if N elements are there) N-1.
Tuple:
- Python tuples are similar to the lists but Tuples are immutable in nature i.e. once created it cannot be a modified. Just like List, a Tuple can also contain elements of different types.
- In a Python, tuples are created by a placing a sequence of values separated by ‘comma’ with or without use of a parentheses for grouping of the data sequence.
- To create tuple of one element there must be trailing comma. For example, (8,) will create tuple containing 8 as a element.
Set:
- Python set is the mutable collection of data that does not allow the any duplication. Sets are basically used to include the membership testing and eliminating a duplicate entries. The data structure used in this Hashing, a famous technique to perform insertion, deletion, and traversal in O(1) on a average.
- If a Multiple values are present at a same index position, then value is appended to that index position, to form Linked List. In, CPython Sets are implemented using dictionary with a dummy variables, where key beings members set with greater optimizations to time complexity.
Frozen Sets:
Frozen sets in a Python are immutable objects that are only support methods and operators that produce result without affecting a frozen set or sets to which they are be applied. While elements of set can be modified at a any time, elements of the frozen set remain a same after creation.
String:
- Python Strings is an immutable array of a bytes representing Unicode characters. Python does not have character data type, a single character is simply a string with the length of 1.
- As strings are be immutable, modifying a string will result in a creating new copy.
Dictionary:
Python dictionary is the unordered collection of data that saves data in a format of key:value pair. It is like hash tables in the any other language with a time complexity of O(1). Indexing of a Python Dictionary is done with help of keys. These are of any hashable type i.e. an object whose can never change like a strings, numbers, tuples, etc. Can create a dictionary by using a curly braces ({}) or dictionary comprehension.
Matrix:
A matrix is the 2D array where each element is of a strictly the same size. To create matrix will be using a NumPy package.
Bytearray:
Python Bytearray gives the mutable sequence of an integers in range 0 <= x < 256.
Linked List:
A linked list is the linear data structure in which an elements are not stored at a contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using a pointers A linked list is be represented by a pointer to first node of the linked list. The first node is called head. If linked list is empty, then value of the head is a NULL. Every node in the list consists of at least two parts:
- Data.
- Pointer (Or Reference) to the next node.
Linked List Traversal:
In a previous program, have created a simple linked list with the three nodes. Let us traverse a created list and print the data of every node. For traversal, let us write general-purpose function of printList() that prints any given list.
Stack:
A stack is the linear data structure that stores items in the Last-In/First-Out (LIFO) or First-In/Last-Out (FILO) manner. In a stack, a new element is added at a one end and an element is removed from that end only. The insert and delete operations are be often called a push and pop.
Queue:
As a stack, a queue is a linear data structure that saves an items in a First In First Out (FIFO) manner. With queue, the least recently added item is a removed first. A good example of a queue is any queue of the consumers for a resource where a consumer that came first is served first.
Binary Tree:
The topmost node of a tree is called the root whereas bottommost nodes or the nodes with the no children are called the leaf nodes. The nodes that are be directly under a node are called its a children and the nodes that are directly above something are called its be a parent.A binary tree is the tree whose elements can have almost a two children. Since every element in a binary tree can have only a 2 children, typically name them a left and right children. A Binary Tree node contains a following parts.
- Data.
- Pointer to left child.
- Pointer to the right child.
Algorithm:
Algorithm Inorder(tree):
- Traverse a left subtree i.e. call Inorder(left-subtree).
- Visit a root.
- Traverse a right subtree i.e. call Inorder(right-subtree).
Algorithm Preorder(tree):
- Visit a root.
- Traversea left subtree i.e. call Preorder(left-subtree).
- Traverse a right subtree i.e. call Preorder(right-subtree).
Algorithm Postorder(tree):
- Traverse a left subtree i.e. call Postorder(left-subtree).
- Traverse a right subtree i.e. call Postorder(right-subtree).
- Visit a root.
Conclusion:
Data structures deal with how a data is organised and held in memory, when a program processes it. It is an important to note that, the data that is saved in a disk as part of persistent storages (like relational tables) are not referred as a data structure here.An Algorithm is step by step set of an instruction to process the data for a particular purpose. So, an algorithm utilises a different data structures in a logical way to solve the specific computing problem.
