- Different Methodologies in Project Management
- Difference between Soap and Rest | Know more about it
- What is Python array? Learn with examples
- Best Career options after Engineering | Everything You Need to Know [OverView]
- What is list in Python ? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Data Modelling? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What are Microservices? : A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Python Programming | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- All You Need To Know About Python List | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What Is a Software Developer | Software Developer job description and duties | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Artificial Intelligence Chatbot?
- Kotlin vs Java | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Abstraction in Java | Implementations of Abstraction in Java | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What are the Important Data Structures and Algorithms in Python?
- Go vs Python | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Best Python IDEs and Code Editors | Expert’s Top Picks | Everything You Need to Know
- Go Programming Language | Expert’s Top Picks | A Definitive Guide [ OverView ]
- Python Scopes and Their Built-in Functions | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Python String Formatting | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Python Serialization | A Complete Guide For Beginners | Learning Guide
- What is .Net FrameWork? Uses and its Benefits | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Quality Assurance ? : A Definitive Guide | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- What is Spike Testing ? : A Definitive Guide | Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Average Full Stack Developer Salary in India [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is WSDL in Web Services ? Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Virtual Instrumentation using Labview | Comprehensive Guide [ Explained ]
- Gradle vs Maven | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Python Sleep Method | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Kotlin vs Python | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Spring Boot vs Spring MVC | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- IT Engineer Salary in India – How much does one earn?
- What is pip ? and Getting Started with Python pip | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Node.js Installation on Windows and Ubuntu | Free Guide Tutorial
- Skills Needed for Full Stack Developers | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Axios in React? and Its Uses [ OverView ]
- What is MEAN Stack? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- How to Install Node.JS on Ubuntu | Everything You Need to Know
- Average Annual Salary of a Python Certified Professional – Career Path
- What is Scala Programming? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What Is User Input in Python? Expert’s Top Picks
- Interface vs Abstract Class | Difference You Should Know
- Final Year Computer Science Project Ideas | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Technical Architect | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Logical Programs in Java | Step-By-Step Process
- C++ vs Java | Difference You Should Know
- What is C Programming? Comprehensive Guide
- What Is a Quality Engineer? ( Everything You Need to Know )
- Python Project Ideas for Beginners | All you need to know
- How to Run Python Scripts? Comprehensive Guide
- Python Operators
- How To Install NumPy in Python?
- Top Software Courses to Get High Paying Jobs
- Loops In Python
- Tips to Avoid Application Rejection
- Top Young App Developers Who Became Millionaires
- Top Technical Courses After Graduation
- Node JS Architecture
- What is PyCharm?
- Resources To Help You Learn Java Programming
- How to Become a Software Engineer?
- Best Programming Languages to Learn in 2020
- Scala vs Python
- How to Become a Full Stack Developer?
- The Most Popular Java Applications Used World-wide
- What is Java String?
- Full Stack Developer vs Front End Developer vs Back End Developer
- Python Collections
- Identifiers in Python
- Dynamic Method Dispatch in Java
- Hadoop Ecosystem
- Method Overloading in Python
- Convert Decimal To Binary In Python
- How To Make A Chatbot In Python?
- How to Input a List in Python?
- Hash Tables and Hashmaps in Python
- Top Python Framework’s
- Python Split Method with Example
- Python Enumerate
- Inheritance in Java
- Init in Python
- Goto Statement in Python
- Literals in Java
- Polymorphism in Oops
- Socket Programming in Python
- Object Class in Java
- Break, Continue, and Pass Statements in Python
- Exception Handling in Java
- Java BASIC Programs
- Different Methodologies in Project Management
- Difference between Soap and Rest | Know more about it
- What is Python array? Learn with examples
- Best Career options after Engineering | Everything You Need to Know [OverView]
- What is list in Python ? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Data Modelling? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What are Microservices? : A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Python Programming | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- All You Need To Know About Python List | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What Is a Software Developer | Software Developer job description and duties | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Artificial Intelligence Chatbot?
- Kotlin vs Java | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Abstraction in Java | Implementations of Abstraction in Java | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What are the Important Data Structures and Algorithms in Python?
- Go vs Python | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Best Python IDEs and Code Editors | Expert’s Top Picks | Everything You Need to Know
- Go Programming Language | Expert’s Top Picks | A Definitive Guide [ OverView ]
- Python Scopes and Their Built-in Functions | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Python String Formatting | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Python Serialization | A Complete Guide For Beginners | Learning Guide
- What is .Net FrameWork? Uses and its Benefits | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Quality Assurance ? : A Definitive Guide | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- What is Spike Testing ? : A Definitive Guide | Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Average Full Stack Developer Salary in India [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is WSDL in Web Services ? Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Virtual Instrumentation using Labview | Comprehensive Guide [ Explained ]
- Gradle vs Maven | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Python Sleep Method | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Kotlin vs Python | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Spring Boot vs Spring MVC | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- IT Engineer Salary in India – How much does one earn?
- What is pip ? and Getting Started with Python pip | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Node.js Installation on Windows and Ubuntu | Free Guide Tutorial
- Skills Needed for Full Stack Developers | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Axios in React? and Its Uses [ OverView ]
- What is MEAN Stack? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- How to Install Node.JS on Ubuntu | Everything You Need to Know
- Average Annual Salary of a Python Certified Professional – Career Path
- What is Scala Programming? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What Is User Input in Python? Expert’s Top Picks
- Interface vs Abstract Class | Difference You Should Know
- Final Year Computer Science Project Ideas | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Technical Architect | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Logical Programs in Java | Step-By-Step Process
- C++ vs Java | Difference You Should Know
- What is C Programming? Comprehensive Guide
- What Is a Quality Engineer? ( Everything You Need to Know )
- Python Project Ideas for Beginners | All you need to know
- How to Run Python Scripts? Comprehensive Guide
- Python Operators
- How To Install NumPy in Python?
- Top Software Courses to Get High Paying Jobs
- Loops In Python
- Tips to Avoid Application Rejection
- Top Young App Developers Who Became Millionaires
- Top Technical Courses After Graduation
- Node JS Architecture
- What is PyCharm?
- Resources To Help You Learn Java Programming
- How to Become a Software Engineer?
- Best Programming Languages to Learn in 2020
- Scala vs Python
- How to Become a Full Stack Developer?
- The Most Popular Java Applications Used World-wide
- What is Java String?
- Full Stack Developer vs Front End Developer vs Back End Developer
- Python Collections
- Identifiers in Python
- Dynamic Method Dispatch in Java
- Hadoop Ecosystem
- Method Overloading in Python
- Convert Decimal To Binary In Python
- How To Make A Chatbot In Python?
- How to Input a List in Python?
- Hash Tables and Hashmaps in Python
- Top Python Framework’s
- Python Split Method with Example
- Python Enumerate
- Inheritance in Java
- Init in Python
- Goto Statement in Python
- Literals in Java
- Polymorphism in Oops
- Socket Programming in Python
- Object Class in Java
- Break, Continue, and Pass Statements in Python
- Exception Handling in Java
- Java BASIC Programs

What Is a Quality Engineer? ( Everything You Need to Know )
Last updated on 27th Oct 2022, Artciles, Blog, Software Engineering
- In this article you will learn:
- 1.What Is a Quality Engineer?
- 2.What Does a Quality Engineer Do?
- 3.How to Become a Quality Engineer.
- 4.What Are Quality Engineer’s Responsibilities?
- 5.Analyze a manufacturing data and reports.
- 6.Conclusion.
What Is a Quality Engineer?
A quality engineer’s mission is to keep a production process running as efficiently and effectively as possible while still ensuring that the finished products are safe dependable and meet customer expectations. They design quality tests create documentation and test procedures maintain quality standards and specify the requirements that a test result must meet. A quality engineer monitors the quality of a process and is critical in resolving problems that arise.
What Does a Quality Engineer Do?
At every stage of a manufacturing process quality engineers collaborate with different stakeholders such as testing by a design team to determine product robustness and weak points. They engage with the suppliers to ensure that raw materials and parts match the company’s quality standards. Teams in charge of manufacturing make sure that tools and procedures adhere to set quality standards. The development of quality practices standard operating procedures (SOPs) and pertinent documentation for a specific product or plant are frequently assigned to quality engineers. They set out relevant tests and acceptable findings to ensure adequate quality testing throughout a production process. They analyze complaints received through consumer feedback keep track of events and change production as necessary. Additionally it is a responsibility of the quality engineer to thoroughly document any errors and collaborate with the other engineers to identify a fix. A quality engineer must work with all departments to ensure that the product is up to date.
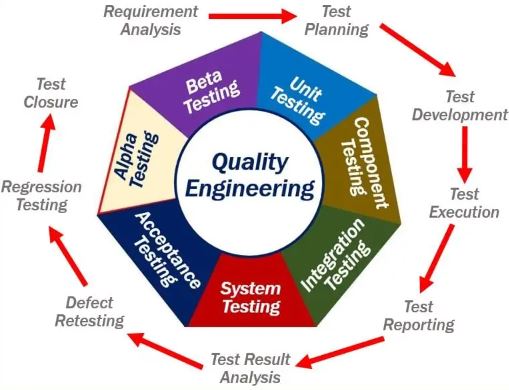
Quality Assurance:
A quality management system is often used to implement quality assurance on a factory floor . A codified quality management system (QMS) records the processes, methods and roles involved in accomplishing quality policies and objectives. A Quality Assurance is process-oriented, focusing on a reducing process variance through a development revision and strict application of a set of precisely specified processes or quality standards that when properly adhered to guarantee a final product’s quality. By its nature quality assurance is a preventative and it aids in directing and also coordinating an organization’s operations to satisfy a client and legal obligations.
Quality Control:
People who work in a quality control (QC) typically (but not always) have a scientific or a laboratory background because sample testing is done in a lab when pharmaceuticals are manufactured. In a product-oriented quality control a manufacturing process sample is examined to find whether it complies with necessary design requirements or quality standards.
Six Sigma:
By locating and eliminating the root causes of errors and reducing unpredictability in production and business processes it seeks to increase the quality of the output of a process. The Six Sigma methodology, created by Motorola and popularized by Jack Welch at General Electric is a set of tools and procedures for process improvement.
Quality By Design:
Quality by design is essential because more testing only sometimes results in a higher-quality product quality by a design is crucial and it frequently has an opposite impact. Most quality crises and problems stem from how the product was initially created.
The Taguchi Method:
Taguchi advises are using materials that function under different situations low-cost off-the-shelf tested components, and a statistical experimentation. What Taguchi refers to as a loss function mathematically in a process defines the loss.
Quality Risk Management:
It is the technique for anticipating disaster and devising preventive measures are involving designing the issue or a proceduralizing the case. This process frequently requires a manufacturing, testing and distributing the pharmaceutical and medical device items. A Worst-case scenario planning is heavily utilized to an identify a potential problems and develop solutions to be reduce risks.
Reliability Engineering:
Reliability Engineering is an employed to avoid failures or to lessen frequency or likelihood. It is used to find and address the root causes of failures that nonetheless happen despite best attempts to prevent them. If reasons for failures are not be fixed, it decides how to handle them when they are do occur. It utilizes a techniques for figuring out how reliable a new designs will be. Additionally it makes use of a statistical analysis and engineering methods to increase dependability or a reliability of a process or product that is exposed to an environmental factors such as vibration, shock loading, voltage, radiation, extremely high or low temperatures fatigue or the other environmental factors for a predetermined amount of time in the predetermined environment.
How to Become Quality Engineer:
1. Get Educated:
Quality engineers are needed to have, at minimum an associate’s degree in a quality engineering. Through an education learn the basics of a quality assurance including regulations (both the state and national), documentation and testing practices. A Some senior positions may also need a master’s degree in a quality assurance.
2. Get Experienced:
Before getting a certified in this field must be build an experience in the field. Get a feet wet with an entry-level positions or internships to exercise the education and gain a real-world experience required to become successful.
3. Get Certified:
With the associate’s degree and work experience under a belt ready to get a quality engineer certification by an American Society for Quality. The CQE Certification Exam covers a topics such as management and leadership the quality system product and process design product and process control continuous improvement quantitative methods and tools and also risk management.
What Are Quality Engineer’s Responsibilities?
A major player within a production of goods a quality engineer is responsible for an overall quality of manufactured products. Though a tasks may vary depending on an organization common responsibilities are include:
- Establish and implement a quality standards.
- Monitor a workflows, processes and products.
- Create a quality documentation.
- Collaborate with an operations managers to identify a opportunities for improvements to workflow and controls to ensure they are comply with health and safety codes and also regulations.
- Review systems and processes to be develop a continued improvements and efficiencies.
- Inspect and test processes and products to ensure a meet or exceed standards.
Analyze a manufacturing data and reports:
A Work toward continuous improvement within a manufacturing process through a variety of a techniques including but not limited to be Six Sigma quality by design quality by control and a quality assurance.
Conclusion:
Quality engineering is a key to many products that shape a day to day lives. From a phone we talk on, computer work on or vehicle commute in a quality engineer plays a vital role in making goods and devices and spend so much of their lives relying on.
