- ITIL Tutorial – Incident & amp Problem Management | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- ITIL4 Service Value Chain Model Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- The ITIL 4 Service Value System | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- What are the ITIL 4 Management Practices? | Tutorial for Learning Path
- Guiding Principles of ITIL 4 | Learn Now Tutorial
- Four Dimensions of Service Management in ITIL 4 | A Definitive Guide
- What is the Continual Improvement Model? ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL4 Tutorial | A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI)Tutorial | Learn the Methods and Techniques
- Service Transition Overview – ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL® 4 Foundation Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Design an Effective IT Service with ITIL® v3 Tutorial
- Nagios Tutorial
- ITIL – Service management lifecycle Tutorial
- Service Validation and Testing Tutorial
- Service Operation Processes Tutorial
- ITIL Turtorial
- Services Strategy Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate SOA – Demand Management Tutorial
- Availability Management Tutorial
- ITIL Key Concepts of the Service Lifecycle Tutorial
- ITIL Change Evaluation Tutorial
- The principles of COBIT® 5 Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate CSI – Continual Service Improvement Processes Tutorial
- ITIL-Service Level Management Tutorial
- ServiceNow Tutorial
- SCCM Tutorial
- ITIL Tutorial – Incident & amp Problem Management | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- ITIL4 Service Value Chain Model Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- The ITIL 4 Service Value System | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- What are the ITIL 4 Management Practices? | Tutorial for Learning Path
- Guiding Principles of ITIL 4 | Learn Now Tutorial
- Four Dimensions of Service Management in ITIL 4 | A Definitive Guide
- What is the Continual Improvement Model? ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL4 Tutorial | A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI)Tutorial | Learn the Methods and Techniques
- Service Transition Overview – ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL® 4 Foundation Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Design an Effective IT Service with ITIL® v3 Tutorial
- Nagios Tutorial
- ITIL – Service management lifecycle Tutorial
- Service Validation and Testing Tutorial
- Service Operation Processes Tutorial
- ITIL Turtorial
- Services Strategy Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate SOA – Demand Management Tutorial
- Availability Management Tutorial
- ITIL Key Concepts of the Service Lifecycle Tutorial
- ITIL Change Evaluation Tutorial
- The principles of COBIT® 5 Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate CSI – Continual Service Improvement Processes Tutorial
- ITIL-Service Level Management Tutorial
- ServiceNow Tutorial
- SCCM Tutorial

Availability Management Tutorial
Last updated on 29th Sep 2020, Blog, IT service and Architecture, Tutorials
What is Availability Management?
The aim of the Availability Management is to ensure that the agreed availability goals are met by the IT services. Also to ensure that the availability goals are met by the new or the changed service without affecting the existing services. The availability is expressed as follows:
(Agreed service time – Down time)/Agreed Service Time
The process owner of this process is the Availability Manager.
What are the objectives of Availability Management?
The objectives of the Availability Management are as follows:
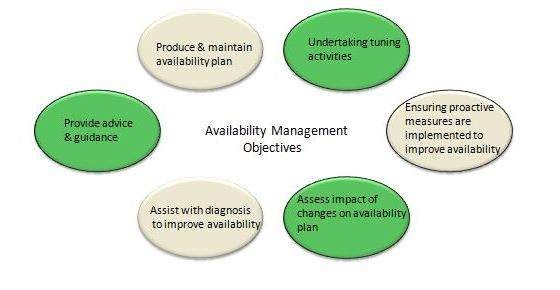
Explain the process of Availability Management?
The key elements of the Availability Management process are as follows:
- Reactive activities
- Proactive activities
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Reactive activities
The activities such as monitoring, measuring, analysis and management of the events, incidents and problems which are involved in the operational roles are known as reactive activities.
Proactive activities
The activities which are involved in the design and planning such as proactive planning, design and improvements of the availability are known as proactive activities.
Availability Management process is completed at following two interconnected levels:
- Service availability
- Component availability
Service availability
The availability and unavailability of the service and the impact of component availability and unavailability on the service availability id dealt at this level.
Component availability
It deals with component availability and unavailability.

What are the sub-processed of Availability Management?
The sub-processes of the Availability management process are depicted below:
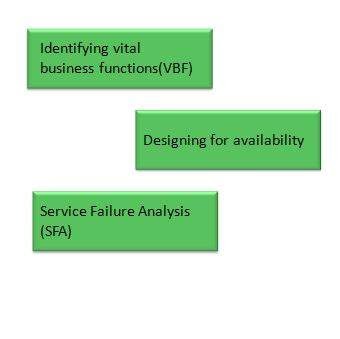
Identifying vital business function (VBF)
The elements supported by the IT service and are critical to the business are referred as Vital Business Function. In order to obtain a better business alignment and focus, all VBFs need to be documented.
Designing for availability
Even though high availability needs are associated with additional costs, sometimes it is essential in providing high availability services in order to support VBFs.
Service Failure Analysis (SFA)
Service Failure Analysis is designed to:
- In order to identify the causes of the service interruption to the user, a structured approach is provided.
- The shortfalls occurring in the availability are assessed.
- By providing a set of improvements for implementation of the Activity plan, the overall availability of the IT services is improved.
What is the ITIL Availability Management Process?
Availability Management is one of the well-defined main processes under Service Design process group of the ITIL best practice framework.
According to the definition, ITIL Availability Management is used to ensure the availability of services whenever needed. This usually means making sure every service is up for use under the conditions of service level agreements (SLAs).
To achieve this, the Availability Management team periodically reviews business process availability requirements. And then, they make sure that the most cost-effective contingency plans are in place.
These plans are tested on a regular basis to make sure that it meets the business needs.
ITIL Availability Management Scope
As stated in ITIL V3, Availability Management process plays a leading role in component failure impact analysis (CFIA) and service outage analysis (SOA) initiatives.
Typically, the Availability Management team determines the cause of the problem, analyzes any related trends, and then takes the steps to ensure service availability according to SLAs.
Availability Management (ITIL V3) is tightly bound with other ITIL processes.
The ITIL Availability Management process works jointly with Capacity Management, Service Level Management, and IT Service Continuity Management to plan for the infrastructure requirement needed to meet the targeted service level and quality.
It also works closely with Incident Management and Event Management processes to help them meet the operation level service targets and quality standards.
ITIL Availability Management Objective
The primary objective of ITIL Availability Management process is to define, analyze, plan, measure and improve all aspects of the availability of IT services.
It is responsible for ensuring that all IT infrastructure, processes, tools, roles etc are appropriate for the agreed availability targets.
ITIL V3 Availability Management Components
Availability Management (in ITIL V3) basically has six components which determine the accuracy service availability. Those are as follows:
- Availability: Determines the ability of the service or component to provide the agreed-upon functionality when required.
- Reliability: Determines ability of a service or component to perform at an agreed level at described conditions.
- Maintainability: Describes the ability of a service or component to remain operational, or be restored to an operational state.
- Serviceability: Describes the ability for an external supplier to maintain the availability of service or component under a third-party contract.
- Resilience: It’s a method of keeping services reliable in an event of major failure and it also measures the chances of such failure. This broadly describes the need to service redundancy.
- Security: Security refers to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all service related data.
Availability Management also has the responsibility of continual monitoring, measuring, analyzing and reporting of the above mentioned components.
Proactive activities can be further divided into two categories: Service Availability & Component Availability. Activities performed under this proactive category are:
- 1. Participate in IT infrastructure design.
- 2. Monitor actual IT availability achieved.
- 3. Create, maintain & review Availability Plan.
- 4. Schedule Availability Testing.
- 5. Attend CAB meetings.
- 6. Assessment & Testing after a major business change.
- 7. Assess & Manage Risk in an economically viable way.
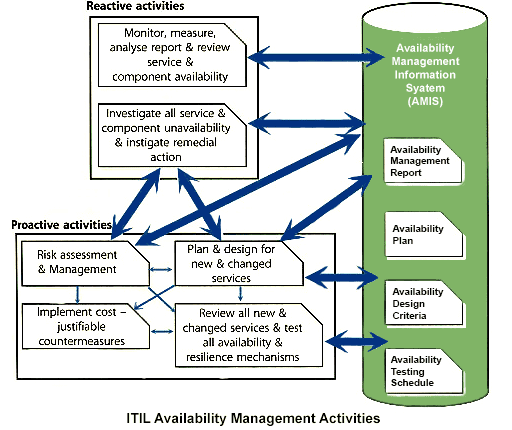
ITIL Availability Management Sub-Process
According to ITIL v3, Availability Management Process has three sub-process operating under it.
The objectives and descriptions of those sub-processes are given below, followed by a diagram illustrating the ITIL Availability Management Process Flow:
1) Design Services for Availability:
As the name suggests, this sub-process is responsible for designing the procedures and technical features required to fulfill the agreed availability levels.
2) Availability Testing:
This sub-process is responsible for scheduling and arranging for regular testing of all availability, resilience and recovery mechanisms.
3) Availability Monitoring and Reporting:
Used to monitor the current availability achievements of services and components, compare that result with the agreed availability benchmarks, identify the improvement areas, and prepare a detailed report.
It also circulates the report to other Service Management processes and IT Management for decision-making purposes.
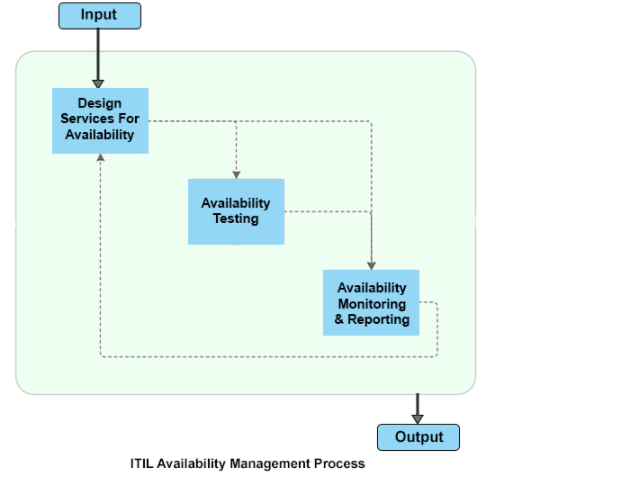
Important Terminologies and Definitions:
Below lists describes the important terminologies and definitions used in ITIL Availability Management:
- 1. Availability Design Guidelines: It draws the guidelines from a technical point of view, that how the required availability levels can be achieved, including specific instructions for application development and for externally sourced infrastructure components.
- 2. Availability Guidelines for the Service Desk: Guidelines for Service Desk on how to manage Incidents causing unavailability. The goal of this guideline is to prevent minor incidents from becoming major Incidents.
- 3. Availability Management Information System: A virtual repository of all Availability Management data, typically stored in multiple physical locations.
- 4. Availability Plan: The Availability Plan contains detailed information about initiatives taken for improving the availability of service or component.
- 5. Availability/ ITSCM/ Security Testing Schedule: A schedule for the periodic testing of all availability, continuity and security mechanisms, jointly regulated by Availability Management, IT Service Continuity Management (ITSCM), and Information Security Management.
- 6. Availability Report: A Report containing information related to service and infrastructure component availability. This Report is then circulated to other Service Management processes and IT Management for decision making purposes.
- 7. Event Filtering and Correlation Rules: Rules and Criteria are used to determine if an Event is significant and to decide upon an appropriate response. Event Filtering and Correlation Rules are typically used by Event Monitoring Systems in the Event Management process. But some of those rules are defined during the Availability Management process of Service Design Stage, to ensure that events are triggered when the required service availability is endangered.
- 8. Maintenance Plan/ SOP: Define the frequency and scope of preventative maintenance.
- 9. Recovery Plan: It is jointly created by Availability Management and IT Service Continuity Management. This recovery plan contains specific instructions for restoring specific services or components to a working state from a major failure.
- 10. Technical/ Administration Manual: A document detailing the required procedures to run and maintain application or infrastructure components.
- 11. Test Report: A Test Report provides a summary of testing and assessment activities performed by any ITSM process.
- 12. Vital Business Function (VBF): VBF refers to business-critical elements that are supported by an IT service.
- 13. Service Failure Analysis (SFA): It is a structured approach to identifying causes of service interruption.
ITIL Availability Management Roles and Responsibilities:
Availability Manager:
- 1. Availability Manager role is the Process Owner of Availability Management Process.
- 2. This role is responsible for defining, analyzing, planning, measuring and improving all aspects of the availability of IT services & components.
- 3. Availability Manager also has to coordinate with Capacity Manager to ensure that all IT infrastructure, processes, tools, roles etc. are appropriate for achieving the agreed service level targets for availability.

