- ITIL Tutorial – Incident & amp Problem Management | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- ITIL4 Service Value Chain Model Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- The ITIL 4 Service Value System | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- What are the ITIL 4 Management Practices? | Tutorial for Learning Path
- Guiding Principles of ITIL 4 | Learn Now Tutorial
- Four Dimensions of Service Management in ITIL 4 | A Definitive Guide
- What is the Continual Improvement Model? ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL4 Tutorial | A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI)Tutorial | Learn the Methods and Techniques
- Service Transition Overview – ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL® 4 Foundation Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Design an Effective IT Service with ITIL® v3 Tutorial
- Nagios Tutorial
- ITIL – Service management lifecycle Tutorial
- Service Validation and Testing Tutorial
- Service Operation Processes Tutorial
- ITIL Turtorial
- Services Strategy Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate SOA – Demand Management Tutorial
- Availability Management Tutorial
- ITIL Key Concepts of the Service Lifecycle Tutorial
- ITIL Change Evaluation Tutorial
- The principles of COBIT® 5 Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate CSI – Continual Service Improvement Processes Tutorial
- ITIL-Service Level Management Tutorial
- ServiceNow Tutorial
- SCCM Tutorial
- ITIL Tutorial – Incident & amp Problem Management | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- ITIL4 Service Value Chain Model Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- The ITIL 4 Service Value System | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- What are the ITIL 4 Management Practices? | Tutorial for Learning Path
- Guiding Principles of ITIL 4 | Learn Now Tutorial
- Four Dimensions of Service Management in ITIL 4 | A Definitive Guide
- What is the Continual Improvement Model? ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL4 Tutorial | A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI)Tutorial | Learn the Methods and Techniques
- Service Transition Overview – ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL® 4 Foundation Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Design an Effective IT Service with ITIL® v3 Tutorial
- Nagios Tutorial
- ITIL – Service management lifecycle Tutorial
- Service Validation and Testing Tutorial
- Service Operation Processes Tutorial
- ITIL Turtorial
- Services Strategy Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate SOA – Demand Management Tutorial
- Availability Management Tutorial
- ITIL Key Concepts of the Service Lifecycle Tutorial
- ITIL Change Evaluation Tutorial
- The principles of COBIT® 5 Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate CSI – Continual Service Improvement Processes Tutorial
- ITIL-Service Level Management Tutorial
- ServiceNow Tutorial
- SCCM Tutorial

ITIL Key Concepts of the Service Lifecycle Tutorial
Last updated on 29th Sep 2020, Blog, IT service and Architecture, Tutorials
Most organizations think about their people, capabilities, processes, and technologies to be strategic assets. These assets help deliver and support the company’s imaginative and prescient and mission. Environment-friendly and efficient alignment of capabilities and sources of companies and merchandise may also help create a strategic benefit within the markets that organizations serve. That is the place ITIL®, the Data Know-how Infrastructure Library, comes into play. ITIL is probably the most broadly accepted strategy to IT service administration on the planet. It helps people and organizations use IT to appreciate enterprise change, transformation, and development.
The ultimate purpose of ITIL is to enhance how IT delivers and helps valued enterprise providers. ITIL is not only an expertise administration or course of administration. It additionally focuses on enhancing the capabilities of individuals, processes, and expertise. ITIL supplies worth for a corporation, its assets, and capabilities, together with workers and prospects.Adoption of the ITIL framework could be the inspiration for the fulfillment of different initiatives comparable to DevOps, cyber security, cyber-resilience, Web of Issues, and different rising developments and applied sciences.
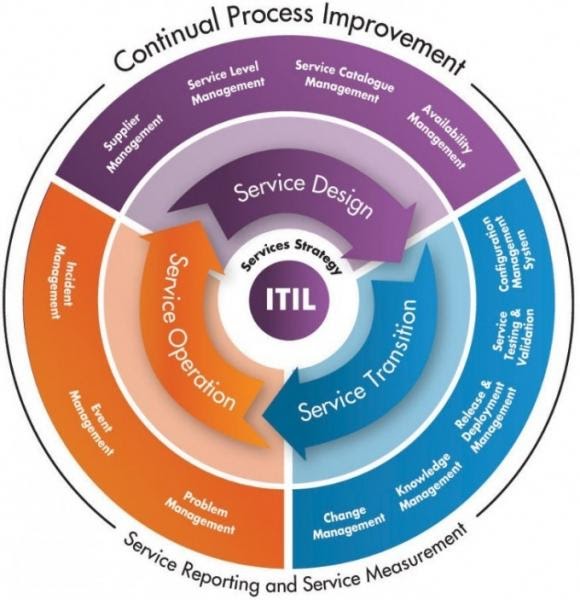
IT Services and ITIL
ITIL is a set of IT Service Administration practices that focuses on aligning IT providers with the wants of the enterprise.
Each group delivers a service or product. For each service or product, the ITIL framework helps handle supply, industrialization, help, and consumerization from inception to retirement. The 5 phases of the ITIL framework embrace:
- Service Strategy
- Service Design
- Service Transition
- Service Operation
- Continuous Service Enhancement
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Every stage of this service lifecycle helps all the opposite phases.
ITIL doesn’t inform any specific group all of the capabilities that it wants. However, for any IT team making roadmap choices, it offers sensible steerage on technique and companies.ITIL additionally enhances different business greatest practices. For instance, if a corporation additionally wants steerage for mission administration, then that group can increase the ITIL framework basis with a venture administration finest follow.
Advantages of ITIL
Organizational benefits of adopting ITIL best practices include:
- 1. Stronger alignment between IT and the enterprise
- 2. Improved service supply and buyer satisfaction
- 3. Decreased prices using improved use of assets
- 4. Greater visibility of IT prices and property
- 5. Better administration of enterprise threat and repair disruption or failure
- 6. More secure service atmosphere to assist fixed business change
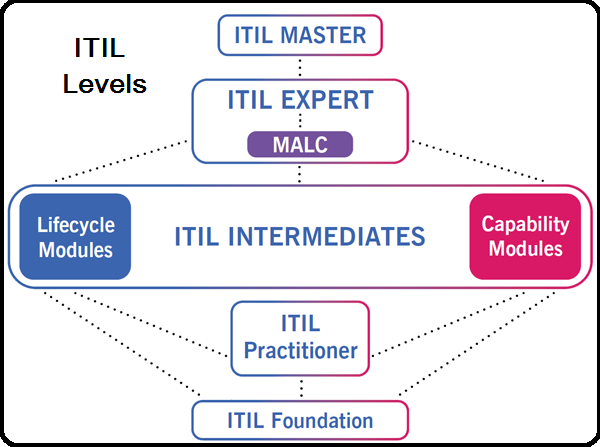
ITIL Certifications
The ITIL certification scheme offers a modular method to the ITIL framework and consists of a collection of qualifications centered on totally different features of ITIL best practice to various degrees of depth and element.
The tiered construction of the qualification gives candidates flexibility regarding the totally different disciplines and areas of ITIL and the ability to focus their research on key areas of interest.
There are five certification ranges throughout the scheme:
Foundation Level : The Foundation level is the entry level certification which provides you a basic consciousness of the important things, ideas, and terminology used within the ITIL service lifecycle, together with the links between lifecycle levels, the processes used and their contribution to service administration practices.
Practitioner Level : The Practitioner level is the next stage within the ITIL scheme. It has been developed to offer a step between Basis and the Intermediate Stage and goals to enhance the flexibility of people to undertake and adapt ITIL of their organizations.
Intermediate Level : The Intermediate level certification has a modular structure with every module providing a unique focus on IT Service Management. You’ll be able to take as few or as many Intermediate qualifications as you want. The Intermediate modules go into more detail than the Foundation level and Practitioner and provide an industry-recognized qualification.
Expert Level : The ITIL Expert level qualification is aimed toward those that are curious about demonstrating data of the ITIL Scheme in its entirety. The certificates are awarded to candidates who’ve achieved a range of ITIL certifications and have attained a well-rounded, superior knowledge and expertise base in ITIL Best Practices.
Master Level : To realize the ITIL Master certification, you must have the ability to clarify and justify how you may have personally chosen and utilized a variety of information, ideas, strategies, and plans from ITIL and supporting administration policies, to attain desired enterprise outcomes in a number of sensible assignments.
ITIL – Key Concepts
The five large components of the ITIL Service Lifecycle cover various subcategories/features, together with Demand Administration, Capacity Administration, Release Administration, Incident Administration, Event Administration, and so forth. These are elements that are supposed to cover all areas of ITSM (IT Service Administration).
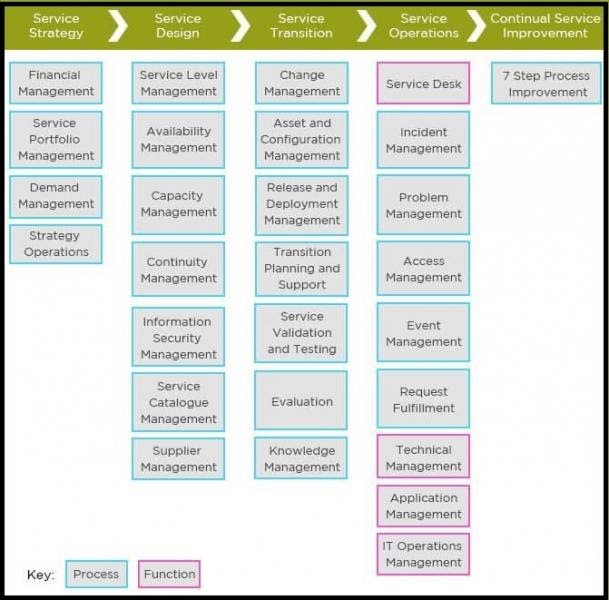
Every of the sub-categories/features of the five components of the ITIL framework could also be labeled both as a ‘Course of’ or as an ‘Operate.’
The ITIL Service Lifecycle
The entire framework of ITIL is divided into 5 large components/categories:
- ITIL Service Strategy
- ITIL Service Design
- ITIL Service Transition
- ITIL Service Operation
- ITIL Continuous Service Improvement
Some Fundamentals IT Service Administration Terminology & Key Ideas
- Companies: It’s a technique of delivering worth to clients without requiring the client to personal particular prices and dangers.
- Service Administration: It’s a set of specialized capabilities for delivering worth to clients within the type of providers.
- Service Belongings: Service Belongings or belongings seek advice from the ‘assets’ and ‘capabilities’ which a Service Supplier should allocate so as to supply a service.
- Worth, Utility and Guarantee: The worth of a service consists of two elements: utility and guarantee. Providers should supply each utility and guarantee so as to have worth. Utility, additionally referred to as ‘health for goal,’ refers to the skill of the service to take away constraints or improve the efficiency of the shopper. Guarantee, additionally referred to as ‘health to be used’ is the flexibility of the service to function reliably.
- Processes: Processes are structured units of actions designed to realize a particular goal.
The 4 primary traits of processes are:
- 1. They remodel inputs into outputs
- 2. They ship outcomes to a particular buyer or stakeholder
- 3. They’re measurable
- 4. They’re triggered by particular occasions
- Features: Features are self-contained subsets of a corporation meant to perform particular duties. They often take the type of a workforce or group of individuals and the instruments they use.
- Roles: Roles are outlined collections of personal obligations and privileges. Roles could also be held by people or groups.
- Assets: Sources are the uncooked supplies which contribute to a service, corresponding to cash, gear, time, workers and so on.
- Capabilities: Capabilities are the functional abilities or skills a corporation applies to assets with a view to creating worth.
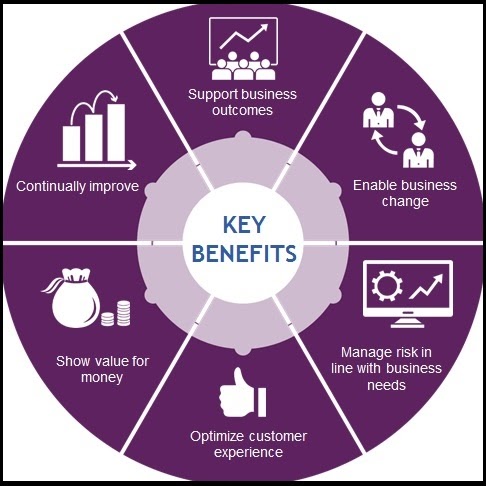
ITIL – Key Benefits
It is amazing to know that the IT Infrastructure Library or ITIL® is 20 years old. On its third model now, ITIL is essentially the most broadly accepted framework for IT Service Management in the IT world. It’s a practical, no-nonsense strategy to the identification, planning, supply and help of IT workers to the enterprise.
Since ITIL is an approach to IT “service” management,” the idea of a service has to be mentioned. A service is one thing that gives worth to clients. Companies that prospects can straight make the most of or consume are often called “enterprise” providers. An instance of an enterprise service that has widespread applicability throughout industries could be Payroll. Payroll is an IT service that’s used to consolidate info, calculate compensation and generate paychecks on a daily periodic foundation. Payroll might depend on different “enterprise” providers akin to “Time Monitoring” or “Reward Management” for data essential to calculate the proper compensation for a worker throughout a given time interval.
The Core Benefits Of ITIL Includes:
- Alliance with business needs: ITIL becomes a benefit to the business when IT can proactively recommend solutions as a response to one or more business needs. The IT Strategy Group recommended in Service Strategy, and the execution of Service Portfolio Management gives IT the opportunity to understand the business’ current and future needs and develop service offerings that can address them.
- Negotiated achievable service levels: Business and IT become true partners when they can agree upon realistic service levels that deliver the necessary value at an acceptable cost.
- Anticipated, consistent processes: Customer outlooks can be set and are easier to meet with through the use of predictable processes that are consistently used. As well, good practice processes are foundational and can assist in laying the groundwork to meet regulatory compliance requirements.
- Effectiveness in service delivery: Well-defined processes with clearly documented accountability for each activity as recommended through the use of a RACI matrix can significantly increase the efficiency of processes. In conjunction with the evaluation of efficiency metrics that indicate the time required to perform each activity, service delivery tasks can be optimized.
- Quantifiable, improvable services and processes: The adage that you can’t manage what you cannot measure rings true here. Consistent, repeatable processes can be measured and therefore can be better tuned for accurate delivery and overall effectiveness. For example, presume that a critical success factor for incident management is to reduce the time to restore service. When predictable, consistent processes are used, key performance indicators such as MeanTime ToRestore Service can be captured to determine whether thisKPI is trending in a positive or negative direction so that the appropriate adjustments can be made. Additionally, underITIL guidelines, services are designed to be measurable. With the proper metrics and monitoring in place, IT organizations can monitor SLAs and make improvements as necessary.
- A communal language – terms are defined.
ITIL – Service Strategy
The service strategy of any service provider must be grounded upon a fundamental acknowledgment that its customers do not buy products, they buy the satisfaction of particular needs. Therefore, to be successful, the services provided must be perceived by the customer to deliver sufficient value in the form of outcomes that the customer wants to achieve.
Achieving a deep understanding of customer needs, regarding what these needs are, and when and why they occur, also requires a clear understanding of exactly who is an existing or potential customer of that service provider. This, in turn, requires the service provider to understand the wider context of the current and potential marketplaces that the service provider operates in, or may wish to operate in.
A service strategy can not be created or exist in isolation of the over-arching strategy and culture of the organization that the service provider belongs to. The service provider may exist within an organization solely to deliver service to one specific business unit, to service multiple business units, or may operate as an external service provider serving multiple external businesses. The strategy adopted must provide sufficient value to the customers and all of the service provider’s stakeholders – it must fulfill the service provider’s strategic purpose.
Irrespective of the context in which the service provider operates, its service strategy must also be based upon a clear recognition of the existence of competition, an awareness that each side has choices, and a view of how that service provider will differentiate itself from the competition. All providers need a service strategy.Hence, the Service Strategy publication sits at the core of the ITIL V3 lifecycle. It sets out guidance to all IT service providers and their customers, to help them operate and thrive in the long term by building a clear service strategy, i.e. a precise understanding.
Key Concepts
- 1. What services should be offered to 4 Service Strategy?
- 2. How the internal and external marketplaces for their services should be.
- 3. Developed the existing and potential competition in these marketplaces, and the objectives that will differentiate the value of what you do or how you do it.
- 4. How the customer(s) and stakeholders will perceive and measure value, and how this value will be created how customers will make service sourcing decisions on use of different types of service providers
- 5. How visibility and control over value creation will be achieved through financial management.
- 6. How robust business cases will be created to secure strategic investment in service assets and service management capabilities.
- 7. How the allocation of available resources will be tuned to optimal effect across the portfolio of services.
- 8. How service performance will be measured.
The Service Strategy Defines Some Key ITIL Concepts
The four Ps of Strategy:
- 1. Perspective – the distinctive vision and direction
- 2. Position – the basis on which the provider will compete
- 3. Plan – how the provider will achieve their vision
- 4. Pattern – the fundamental way of doing things – distinctive patterns in decisions and actions over time.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
The Service Strategy defines some specific roles and responsibilities associated with the execution of a successful service strategy, including:
- Business Relationship Manager (BRM) – BRMs establish a strong business relationship with the customer by understanding the customer’s business and their customer outcomes. BRMs work closely with the
- Product Manager (PM) – PMs take responsibility for developing and managing services across the life-cycle, and have responsibilities for productive capacity, service pipeline, and the services, solutions, and packages that are presented in the service catalogs.
- Chief Sourcing Officer (CSO) – the CSO is the champion of the sourcing strategy within the organization, responsible for leading and directing the sourcing office and development of the sourcing strategy in close conjunction with the CIO.
ITIL – Service Design
The design of appropriate and innovative IT services, including their architectures, processes, policies and documentation, to meet current and future agreed business requirements.
Objectives of Service Design:
- 1. New or changed services
- 2. Service management systems and tools, especially the service portfolio, including the service catalog
- 3. Technology architecture and management systems
- 4. The processes required
- 5. Measurement methods and metrics
The service design stage of the lifecycle starts with a set of new or changed business requirements and ends with the development of a service solution designed to meet the documented needs of the business. This advanced solution is then passed to service transition to evaluate, build, test and deploy the new or changed service.
Other Objectives Include:
- Design services to satisfy business objectives, based on the quality, compliance, risk and security requirements, delivering more effective and efficient IT and organization solutions and services aligned to organizational needs
- Design services that can be easily and efficiently developed and enhanced within appropriate timescales and costs and, wherever possible, reduce, minimize or constrain the long-term costs of service provision
- Design efficient and effective processes for the design, transition, operation, and improvement of high quality
- IT services, together with the supporting tools, systems and information, especially the service portfolio, to manage services through their lifecycle
- Design secure and resilient IT infrastructures, environments, applications and data/information resources, and capability, that meet the current and future needs of the organization
- Design measurement methods and metrics for assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of the design processes and their deliverables
- Produce and maintain IT plans, processes, policies, architectures, frameworks and documents for the design of quality IT solutions, to meet current and future agreed organization need
- Assist in the development of policies and standards in all areas of design
- Develop the skills and capability within IT by moving strategy and design activities into operational tasks, making effective and efficient use of all IT service resources
- Contribute to the improvement of the overall quality of IT service within the imposed design constraints, especially by reducing the need for reworking and enhancing services, once they have been implemented in the live environment
Value to the Organization of Service Design
- 1. Agreeing service targets across the whole organization, ensuring critical business processes receive most attention
- 2. Measuring IT quality in these business terms, reporting what is relevant to users (e.g. customer satisfaction, business value)
- 3. Appropriate mapping of the IT infrastructure to the business processes
- 4. Providing end to end business focused performance monitoring and measurement
- 5. Periodic reporting against targets
- 6. Reduced Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- 7. Improved quality of service
- 8. Improved consistency of service
- 9. Easier implementation of new or changed services
- 10. Improved service alignment
- 11. More active service performance
- 12. Improved IT governance
- 13. More efficient service management and IT process Improved information and decision making
The Four Ps of Service Design
ITIL, in particular, service design, is built primarily upon the four Ps.
To deliver the benefits of service management and ITIL, these 4 Ps need to overlap each other; a popular misconception is that 1 P will fix all the rest, and many organizations believe this is the product. There has to be a balance of all 4 Ps to ensure the right mix of the appropriate design.
Many designs, plans, and projects fail through a lack of preparation and management. The implementation of ITIL service management as a practice is about preparing and planning the effective and efficient use of the four Ps: the People, the Processes, the Products (services, technology, and tools) and the Partners (suppliers, manufacturers, and vendors).
Aspects of Service Design
Service Design focuses on the following aspects:
- IT Services designed to meet business objectives.
- Services designed to be both fit for purpose and fit for use.
- The cost of ownership planned to achieve a return on investment.
- Balanced functionality, cost, and performance.
- IT services are more stable and more predictable.
- Potential risk mitigated, so the IT service is protected from security threats.
- Design technology architectures, management architectures, and system management tools.
- The design of the measurement systems, methods, and metrics for services, processes, structures and underlying components.
- The design of the service solution including all agreed functional requirements, resources, and capabilities.
ITIL – Service Management
What is Service Management?
To understand what Service Management is, we have to understand what companies are, and the way Service Management might help service suppliers to ship and handle these companies.
Service: It’s a technique of delivering worth to prospects by facilitating outcomes that prospects wish to obtain without taking possession of any dangers or prices incurred. They facilitate outcomes by enhancing the efficiency of related duties and decreasing the impact of constraints.
Service Management is what allows service suppliers to:
- 1. Perceive the companies they supply,
- 2. Be certain that the companies facilitate the outcomes their prospects wish to obtain,
- 3. Perceive the worth of the companies to their prospects,
- 4. Perceive and handle all the prices and dangers related to these companies.
Service Management is a set of specialized organizational capabilities that present worth to prospects within the type of enterprises:
- 1. These specialized organizational capabilities embrace the processes, actions, features and roles that service suppliers use to allow them to ship companies to their prospects. Also, they embrace the flexibility to arrange and handle information and perceive the right way to facilitate outcomes that create worth.
IT Service Management: The implementation and Management of high-quality IT companies that meet the wants of the enterprise.
Stakeholders in Service Management:
Stakeholders have a curiosity in a company, mission or companies and so forth. And will have an interest in the actions, targets, sources or deliverables from service Management. A function is a team or group of individuals and the tools or other resources they use to perform some processes or actions.
- 1. Capabilities are models of organizations specialized to carry out certain varieties of work and charge for particular outcomes.
- 2. They’re self-contained, with capabilities and sources obligatory for his or her efficiency and outcomes. Capabilities embrace work methods internal to the capabilities.
What are the Career Prospects after Having ITIL certification?
ITIL is tied to ISO/IEC 20000 norms; as more and more organizations are trying to become ISO/IEC 20000 certified, the demand for ITIL certified professionals is bound to go high. The hundreds of companies and top brands in diverse sectors including finance, retail, IT, technology, entertainment, manufacturing, medical etc have adopted ITIL framework; and many more are going to adopt it. The top brands relying on ITIL include Boeing, Sony, Honda, Microsoft, Procter & Gamble, Citibank, Barclays, Disney, Toyota, Pfizer, Bank of America etc. Combining the ITIL certification with other project management certifications significantly increases the salary range. BusinessWire predicts that the ITSM industry will grow from $4.4 billion in 2016 to $8.78 billion in 2021. CRN Magazine included ITIL certification among the top 15 certifications that boost your career dramatically.
Conclusion
The globally acknowledged ITIL qualification is going to be the most desired prerequisite for IT project manager jobs in 2020 and after. The above detailed ITIL concepts, core components, benefits and career scope make it simple to understand why the ITIL certification is the most preferred choice of experienced IT professionals poised to boost their competency level. ITIL certification ensures that all the team members understand all the aspects of service management holistically and not just the tasks assigned to them. The online and classroom trainings for different level ITIL certification, as conducted by ACTE, are of great help for ITIL certification preparation; so, don’t wait – explore your options.
