- Difference between Waterfall approach and Agile approach
- CCIE Certification Cost in India
- What is IOT? | Know about IOT Application
- How to install Jenkins on Ubuntu? : A Complete Guide
- What is AWS Instance Types? : A Complete Guide
- VMware Site Recovery Manager : Know all about it
- What is Big Engineering? | Know about the salary
- What is Data Model in Salesforce ?
- Splunk architecture| Know from the basics [ OverView ]
- What is Azure Arc? | Integration Guide | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Introduction To Docker Networking: Advantages and Working | Everything You Need to Know
- Introduction to Azure ASR-enabled servers | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Create Alarms in Amazon CloudWatch | Integration Guide | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What’s AWS VPC? Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Explained | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What Makes the Difference between Containers Vs Virtual Machines | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is a CDN? | How Do Content Delivery Networks Work | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Top Real World Applications of Cloud Computing | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What to Expect AWS Reinvent Reinforces the Growth of Cloud Computing|All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Cloud Computing Technology with SalesForce Integration | How its Work [ OverView ]
- Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm | What’s the Difference and Which Should You Learn?
- Big Data vs Data Warehouse | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Public Cloud vs Private Cloud | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Red Hat Certification Path: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- An Overview of AWS SDK and Toolkit | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- An Overview of MuleSoft Anypoint | Benefits and Special Features | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What is Amazon Elastic Load Balancer? : Benefits and Special Features with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is AWS Console ? : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Microsoft Azure Application Gateway | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- A Definitive Guide for Azure Automation | Benefits and Special Features
- Azure ExpressRoute | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- What is Hybrid Cloud? | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- A Complete Citrix Certification Path | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Azure Active Directory B2C ? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Azure DNS ? Azure DNS – Azure Domain Name System | REAL-TIME Examples
- Top AWS Statistics | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Docker Swarm Architecture | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- What is Dell Boomi? | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- Cloud Architect Salary in India | All you need to know [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What Is Multitenancy ? : Characteristics , Features , Benefits | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What Is the Recommended List of AWS Whitepapers? | Expert’s Top Picks
- OSCP vs CEH | Difference You Should Know
- Openshift vs Kubernetes | Difference You Should Know
- AWS Cloud Practitioner and Required Skills | Expert’s Top Picks
- CRISC Certification and Benefits | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Kali vs Parrot | Difference You Should Know
- How to Install Docker on Ubuntu | Comprehensive Guide
- AWS Certification Cost and Types of Exams [ Job & Future ]
- What is the Average AWS Solutions Architect Salary?
- Reasons to Take up A Cloud Computing Certification
- What is Cloud Databases
- What is Cloud Computing Architecture?
- AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
- Top AWS Services
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing 2020: An Analysis Of Cisco’s Cloud Index Survey, 2016
- What Are The Fundamental Microsoft Cloud Services That Are In Demand?
- What are the Issues in cloud computing?
- Top Important Cloud Computing Terms
- From Developer to AWS Cloud Specialist – The AWS Certification Learning Paths
- Why and How to Pursue a Career in AWS?
- The Top In-demand cloud skills for 2020
- Edge Computing Vs. Cloud Computing
- Top 10 Reasons to Learn AWS
- Cloud Computing Career Guide
- What does a AWS solution architect do?
- AWS Career Guide
- VMware vSphere best practices
- The AWS Engineer: Job Roles, Salaries And the Career Path
- What Is Microsoft Azure in Cloud Computing?
- How to Become an Azure Developer?
- Citrix Xenserver Vs Vmware vSphere
- Microsoft’s Project Olympus Delivers Cloud Hardware
- The Future of Cloud Computing
- Why Cloud Computing Is Essential to Your Organization?
- Amazon Web Services – WorkMail
- What is AWS?
- AWS Vs OpenStack
- AWS Certification Path
- AWS ElasticSearch
- AWS EC2 Instance Types
- Microsoft Azure Portal
- AWS Vs Azure
- Amazon Web Services WorkSpaces
- What is AWS Management Console?
- Difference between Waterfall approach and Agile approach
- CCIE Certification Cost in India
- What is IOT? | Know about IOT Application
- How to install Jenkins on Ubuntu? : A Complete Guide
- What is AWS Instance Types? : A Complete Guide
- VMware Site Recovery Manager : Know all about it
- What is Big Engineering? | Know about the salary
- What is Data Model in Salesforce ?
- Splunk architecture| Know from the basics [ OverView ]
- What is Azure Arc? | Integration Guide | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Introduction To Docker Networking: Advantages and Working | Everything You Need to Know
- Introduction to Azure ASR-enabled servers | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Create Alarms in Amazon CloudWatch | Integration Guide | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What’s AWS VPC? Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Explained | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What Makes the Difference between Containers Vs Virtual Machines | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is a CDN? | How Do Content Delivery Networks Work | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Top Real World Applications of Cloud Computing | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What to Expect AWS Reinvent Reinforces the Growth of Cloud Computing|All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Cloud Computing Technology with SalesForce Integration | How its Work [ OverView ]
- Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm | What’s the Difference and Which Should You Learn?
- Big Data vs Data Warehouse | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Public Cloud vs Private Cloud | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Red Hat Certification Path: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- An Overview of AWS SDK and Toolkit | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- An Overview of MuleSoft Anypoint | Benefits and Special Features | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What is Amazon Elastic Load Balancer? : Benefits and Special Features with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is AWS Console ? : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Microsoft Azure Application Gateway | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- A Definitive Guide for Azure Automation | Benefits and Special Features
- Azure ExpressRoute | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- What is Hybrid Cloud? | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- A Complete Citrix Certification Path | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Azure Active Directory B2C ? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Azure DNS ? Azure DNS – Azure Domain Name System | REAL-TIME Examples
- Top AWS Statistics | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Docker Swarm Architecture | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- What is Dell Boomi? | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- Cloud Architect Salary in India | All you need to know [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What Is Multitenancy ? : Characteristics , Features , Benefits | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What Is the Recommended List of AWS Whitepapers? | Expert’s Top Picks
- OSCP vs CEH | Difference You Should Know
- Openshift vs Kubernetes | Difference You Should Know
- AWS Cloud Practitioner and Required Skills | Expert’s Top Picks
- CRISC Certification and Benefits | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Kali vs Parrot | Difference You Should Know
- How to Install Docker on Ubuntu | Comprehensive Guide
- AWS Certification Cost and Types of Exams [ Job & Future ]
- What is the Average AWS Solutions Architect Salary?
- Reasons to Take up A Cloud Computing Certification
- What is Cloud Databases
- What is Cloud Computing Architecture?
- AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
- Top AWS Services
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing 2020: An Analysis Of Cisco’s Cloud Index Survey, 2016
- What Are The Fundamental Microsoft Cloud Services That Are In Demand?
- What are the Issues in cloud computing?
- Top Important Cloud Computing Terms
- From Developer to AWS Cloud Specialist – The AWS Certification Learning Paths
- Why and How to Pursue a Career in AWS?
- The Top In-demand cloud skills for 2020
- Edge Computing Vs. Cloud Computing
- Top 10 Reasons to Learn AWS
- Cloud Computing Career Guide
- What does a AWS solution architect do?
- AWS Career Guide
- VMware vSphere best practices
- The AWS Engineer: Job Roles, Salaries And the Career Path
- What Is Microsoft Azure in Cloud Computing?
- How to Become an Azure Developer?
- Citrix Xenserver Vs Vmware vSphere
- Microsoft’s Project Olympus Delivers Cloud Hardware
- The Future of Cloud Computing
- Why Cloud Computing Is Essential to Your Organization?
- Amazon Web Services – WorkMail
- What is AWS?
- AWS Vs OpenStack
- AWS Certification Path
- AWS ElasticSearch
- AWS EC2 Instance Types
- Microsoft Azure Portal
- AWS Vs Azure
- Amazon Web Services WorkSpaces
- What is AWS Management Console?

AWS Vs OpenStack
Last updated on 25th Sep 2020, Artciles, Blog, Cloud Computing
AWS
It is a platform where we can perform mostly any kind of process. It can be storage, processing unit, Big Data platform, ML platform etc. For these platforms, it changes very less amount, anyone can afford according to their needs. But aws is not open source, how it works internally, we aren’t able to know. We can only use it as a user. This makes a difference with OpenStack.
OpenStack
OpenStack-It is also a platform where we can perform the tasks that aws provided. But OpenStack is an open source platform. We can create our own cloud and customize things according to our needs. We can see how it works internally. You can go through the below link for more information.
The dilemma of choosing AWS or OpenStack cloud services by an enterprise or the customers, in general, has been a serious question in recent times that needs to be answered. From a superficial point of view firstly if we talk about OpenStack, OpenStack by its shared services can manage your applications data storage, computation, and network through a dashboard or its command line. On the other hand, AWS enables access to web services with the help of infrastructure which is owned and maintained by the Amazon company itself.
Different services of AWS and OpenStack for different key aspects of computer science.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Computation
To compute means to run any application on a virtual server. You will have to provide a CPU and other necessary hardware along with Operating system applications pre-installed (or not). On both, OpenStack and AWS users can upload their own images.
AWS has EC2, which are scalable virtual networks with Xen and EMR Hadoop based big data analytics.
OpenStack, on the other hand, boasts of an Iaas infrastructure. It scales horizontally and is designed to scale on hardware without specific requirements.
Networking
It is important to connect your servers to other internal as well as external servers. This basically means connecting the user to virtual servers. When such a facility is offered to the admin, he or she must have the right to know who has access to the networks.
AWS has DNS scalable route 53, Amazon ELB (Elastic Load Balancing), and, Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) which extends its ability to connect to corporate servers. The AWS will allocate private IP addresses to instances running on DHCP and ELB just helps in distributing incoming traffic to Amazon EC2 instances.
Openstack LBaas and flat networks VLAN allows automatic as well as manual management of Ip addresses and networks. You have the power to create networking functions and networks
Identity
Keystone for OpenStack and IAM for AWS decides the identity functions.
Identity servers allow you to have power over who is going to access your cloud by implementing multi-factor authentication. This can also be integrated with some external providers such as AD or LAPD. These are the key services that OpenStack and AWS have to provide.
All of the other services run in accordance with these services and applications and are subsets to the main functionalities.
Security
The term basically means access control over Virtual servers and machines. Whenever an instance is launched a separate security group(s) should be available to attach to it.
The OpenStack security lags behind that of AWS in terms of this condition and may not render the desired array of services when needed.
AWS instills a more private approach to gain access to instances locked by the user making it the clear winner between AWS Vs OpenStack.
Storage
You need two types of storage units when you come to cloud computing – Block Storage and Object Storage.
The block storage is used to assign values to virtual servers to increase their capacity when reaching threshold as well as backing up the virtual servers.
Object storages contain media files, images and so on.
AWS has S3 and OpenStack has Swift as their block storage services while Cinder and EBS are their object storage counterparts.
AWS vs OpenStack in terms of Popularity
Based on Google Trends Graph below, AWS is still far ahead in popularity. But Companies has started in contributing to OpenStack these days.
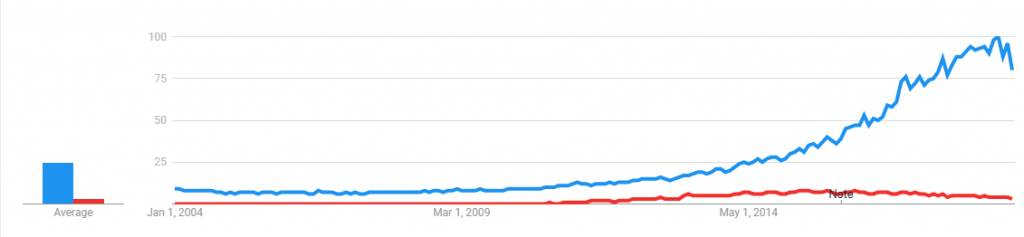
The popularity of AWS application programming interface (API) is growing steadily since its inception in 2006. The first jump was gained by AWS in March 2008 and interest surge again in May 2015. OpenStack has also grown in popularity since its inception in 2010 and got a nice jump in the year 2013. Some of the notable Companies contributed to OpenStack include AT&T, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Ericsson, HP, Google, Hitachi, IBM, Oracle, RedHat, Linux, Yahoo, VMWare etc.
Other than this, AWS is the fifth largest web hosting provider after GoDaddy, Blue Host, Host Gator, OVH.com then AWS is ranked on number five.
- GoDaddy – 4.26 %
- Blue Host – 2.56 %
- HostGator – 2.15 %
- OVH.com – 1.91 %
- AWS – 1.81 %
Highlights of AWS Services
Let us go a little deep in comparing Aws vs OpenStack in terms of features:
- Amazon Elastic Beanstalk for quick deployment and cloud app management.
- Amazon Identity Access Management (IAM) to authenticate various services.
- Amazon director services for setting up a new and stand-alone AWS directory.
- Amazon Cloud Watch to monitor application or resources.
- Amazon Security modules for data regulatory compliance requirements.
- AWS key management services (KMS) to create or manage encryption keys.
- Amazon beta for billing or accounting management.
- Amazon Elastic Transcoder (ETS) for mobile video transcription from S3.
- Amazon Simple Email Service (SES) to send bulk or transactional email.
- Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Services) to push notifications in a multi-tenant architecture.
- Amazon Cognito tools for synchronization and user data management.
- Amazon machine learning service for building regression models from publicly available datasets.
OpenStack Highlights
OpenStack is not so convincing cloud platform, there are still a number of selling points to consider when planning to opt for OpenStack.
- WalMart uses OpenStack to coordinate more than one lac cores, it provides 100 percent uptime during Black Friday last year.
- In Tokyo, Developers gave more than 300 talks at the OpenStack in October.
- RedHat, SUSE Linux, Debian, Canonical all are active contributors and support OpenStack since the time of its inception.
- OpenStack has enabled Companies like Bloomberg, Disney to manage their private clouds at very manageable costs like AWS.
- OpenStack is the only platform that supports mixed hypervisor and bare metal server environments.
It is clear from the discussion that adoption and development in OpenStack are likely to keep pace in the near future. Moving ahead, here are the main components of modular OpenStack architecture.
A). Compute (Nova)
- It is an IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-service) solution that allows the management and automation of computer resources.
- It allows bare metal, high-performance computing configurations (HPC), and containerization capabilities.
- It offers python-based external libraries for concurrent programming, seamless communication, and quick database access.
- It is designed to scale horizontally on standard with no proprietary software or hardware requirements.
B). Image Service (Glance)
- This service is applicable to discover, register, and deliver services for disk or server images.
- It allows template building with stored images.
- It facilitates unlimited backups and chances of failure are very less.
- There is REST interface for querying disk image information.
- It helps to streamline images with servers.
- It helps to maintain image metadata.
- It creates, deletes, and identifies duplicate images.
C). Object Storage (Swift)
- It is a scalable redundant storage system
- It automatically replicates content from failed disks to active nodes.
- It is suitable for inexpensive servers and commodity hard drives.
D). Dashboard Horizon
- It offers a GUI to access and automate cloud-based resources for administrators and users.
- It allows third-party billing, monitoring, and management tool integration.
- It offers a customized dashboard with EC2 compatibility.
E). Identity Service (Keystone)
- It offers a unified authentication system across the cloud OS.
- It can be quickly integrated with existing backend directory such as LDAP.
- The service has various authentication methods like token-based authentication, username/password authentication, and AWS style logins.
- It offers a single repository of all deployed services with a programmatic determination of access for users and third-party tools.
F). Networking (Neutron)
- It allows manual or automatic management of networks or IP addresses.
- There is a flat network or VLAN to separate traffic or servers.
- It offers management of intrusion detection systems, firewalls, load balancing, or virtual private networks etc.
While OpenStack clearly lacks some of the predefined services when compared to AWS, you need to research carefully and decide yourself which cloud computing platform is just the right choice for you. Both platforms are good in terms to offer corporate profitability and also increased resiliency. However, a list of options is available to you if you choose AWS from Amazon.
This article covers all the necessary information required to help you make a better decision. It explains features provided by both of the service providers,
