
BIOMETRICS Tutorial
Last updated on 19th Sep 2020, Blog, Tutorials
What is Biometrics?
Biometrics is a technology used to identify, analyze, and measure an individual’s physical and behavioral characteristics.
Each human being is unique in terms of characteristics, which make him or her different from all others. The physical attributes such as fingerprints, color of iris, color of hair, hand geometry, and behavioral characteristics such as tone and accent of speech, signature, or the way of typing keys of computer keyboard etc., make a person stand separate from the rest.
This uniqueness of a person is then used by the biometric systems to −
What is a Biometric System?
A biometric system is a technology which takes an individual’s physiological, behavioral, or both traits as input, analyzes it, and identifies the individual as a genuine or malicious user.
Evolution of Biometrics
The idea of biometrics was present a few years from now. In the 14th century, China practiced taking fingerprints of merchants and their children to separate them from all others. Fingerprinting is still used today.
- In the 19th century, an Anthropologist named Alphonse Bertillion developed a method (named Bertillonage) of taking body measurements of persons to identify them. He had realized that even if some features of the human body are changed, such as length of hair, weight, etc., some physical traits of the body remain unchanged, such as length of fingers. This method diminished quickly as it was found that the persons with same body measurements alone can be falsely taken as one. Subsequently, Richard Edward Henry from Scotland Yard developed a method for fingerprinting.
- The idea of retinal identification was conceived by Dr. Carleton Simon and Dr. Isadore Goldstein in 1935. In 1976, a research and development effort was put in at EyeDentify Inc. The first commercial retina scanning system was made available in 1981.
- Iris recognition was invented by John Daugman in 1993 at Cambridge University.
- In 2001, Biometrics Automated Toolset (BAT) was introduced in Kosovo, which provided a concrete identification means.
Today, biometric has come up as an independent field of study with precise technologies of establishing personal identities.
Why is Biometrics Required?
With increasing use of Information Technology in the field of banking, science, medication, etc., there is an immense need to protect the systems and data from unauthorized users.
Biometrics is used for authenticating and authorizing a person. Though these terms are often coupled; they mean different things.
Authentication (Identification)
This process tries to find out the answer to the question, “Are you the same who you are claiming to be?”, or, “Do I know you?” This is one-to-many matching and comparison of a person’s biometrics with the whole database.
Verification
This is the one-to-one process of matching where a live sample entered by the candidate is compared with a previously stored template in the database. If both are matching with more than 70% agreeable similarity, then the verification is successful.
Authorization
It is the process of assigning access rights to the authenticated or verified users. It tries to find out the answer for the question, “Are you eligible to have certain rights to access this resource?”
Shortcomings of Conventional Security Aids
The conventional methods of information system security used ID cards, passwords, Personal Identification Numbers (PINs), etc. They come with the following disadvantages −
- They all mean recognizing some code associated with the person rather than recognizing the person who actually produced it.
- They can be forgotten, lost, or stolen.
- They can be bypassed or easily compromised.
- They are not precise.
In such cases, the security of the system is threatened. When the systems need high levels of reliable protection, biometrics come to help by binding the identity more oriented to the individual.
Basic Components of a Biometric System
In general, a biometric system can be divided into four basic components. Let us see them briefly −
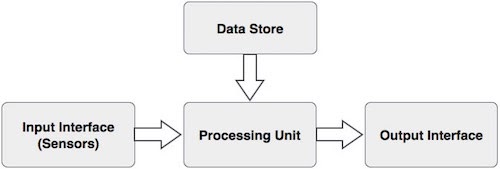
Input Interface (Sensors)
It is the sensing component of a biometrics system that converts human biological data into digital form.
For example,
- A Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) imager or a Charge Coupled Device (CCD) in the case of face recognition, handprint recognition, or iris/retinal recognition systems.
- An optical sensor in case of fingerprint systems.
- A microphone in case of voice recognition systems.
Processing Unit
The processing component is a microprocessor, Digital Signal Processor (DSP), or computer that processes the data captured from the sensors.
The processing of the biometric sample involves −
- Sample image enhancement
- Sample image normalization
- Feature extraction
- Comparison of the biometric sample with all stored samples in the database.
Database Store
The database stores the enrolled sample, which is recalled to perform a match at the time of authentication. For identification, there can be any memory from Random Access Memory (RAM), flash EPROM, or a data server. For verification, a removable storage element like a contact or contactless smart card is used.
Output Interface
The output interface communicates the decision of the biometric system to enable the access to the user. This can be a simple serial communication protocol RS232, or the higher bandwidth USB protocol. It could also be TCP/IP protocol, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Bluetooth, or one of the many cellular protocols.
General Working of a Biometric System
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
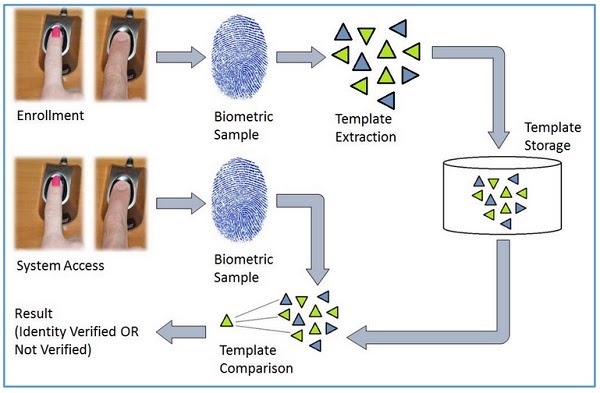
There are four general steps a biometric system takes to perform identification and verification −
The biometric sample is acquired from the candidate user. The prominent features are extracted from the sample and it is then compared with all the samples stored in the database. When the input sample matches with one of the samples in the database, the biometric system allows the person to access the resources; otherwise prohibits.
Biometrics Terminology
Biometric Template − It is a digital reference of the distinct characteristics that are extracted from a biometric sample.
Candidate/Subject − A person who enters his biometric sample.
Closed-Set Identification − The person is known to be existing in the database.
Enrollment − It is when a candidate uses a biometric system for the first time, it records the basic information such as name, address, etc. and then records the candidate’s biometric trait.
False Acceptance Rate (FAR) − It is the measure of possibility that a biometric system will incorrectly identify an unauthorized user as a valid user.
FAR =
Number of False Acceptances
Number of Identification Attempts
A biometric system providing low FAR ensures high security.
False Reject Rate (FRR) − It is the measure of possibility that the biometric system will incorrectly reject an authorized user as an invalid user.
FRR =
Number of False Rejections
Number of Identification Attempts
Open-Set Identification − The person is not guaranteed to be existing in the database.
Task − It is when the biometric system searches the database for matching samples.
Application Areas of Biometrics
There are a number of applications where biometric systems are useful. Few of them are given below −
- Controlling workplace access.
- Identity establishment of people for authentic citizenship and immigration systems.
- Applying access control to sensitive information and systems.
- Identifying criminals by forensics.
- Executing online e-commerce transactions.
- Fraud and theft reduction.
- Law enforcement.
Types of Biometric Modalities
There are various traits present in humans, which can be used as biometrics modalities. The biometric modalities fall under three types −
- 1. Physiological
- 2. Behavioral
- 3. Combination of physiological and behavioral modality
The following table collects the points that differentiate these three modalities −
Advantage of Biometrics
Less Processing time- Biometrics validated systems are usually referred to as a one-to-one process and generally takes less processing time compared to the other identifying systems. This is because, in other recognizing systems, the information is compared to all data already stored in the database.
Accuracy- Biometrics validated systems are also more accurate since they only have to match an individual’s data against his or her stored data in the database and do not need hundreds, thousands or even if there are millions of comparisons like the identifying systems.
Increased Security- Biometric technology has provided an advanced degree of security compared to the traditional authentication methods. It is preferred over conventional techniques for many different reasons which include the fact that the physical presence of the authorized person is required at the point of identification which means that only the authorized person has access to specific resources.
Ease of work- Now you do not need to type the passwords again and again. Or even no need of remembering hard passwords. Just a fingerprint can open or update your electronic devices unlike a phone, office punching machine, etc. Nowadays, the tools are retina and voice sensitive, just by looking at the screen, or only by saying hello the phone opens.
Screening- As part of the enhanced procedures, most visitors traveling on visas will have two fingerprints scanned by an inkless device and a digital photograph taken. All of the data and information is then used to assist the border inspector in determining whether or not to admit the traveler. These enhanced procedures will add only seconds to the visitor’s overall processing time. The electronic fingerprint scanner will allow inspectors to check identities of visitors against those on terrorist watch lists.
Disadvantage of Biometrics
Like all other security methods, biometrics also has limitations and threats which can impact its effectiveness and efficiency which are as follows:
- Intra-class variability and inter-class similarity
- Segmentation
- Noisy input & population coverage
- System performance (error rate, speed, cost)
- The individuality of biometric characteristics
- Fusion of multiple biometric attributes
- Scalability
- Attacks on the biometric system
- Privacy Issues
Issues and Concerns
Several Issues and concerns of biometrics are listed below:
The Effect of Biometric on System Performance: The signature biometrics system is extensively used in every verification area but it is not attainable for users with highly inconsistent signatures. Besides, there often exist people whose signatures are very simple and can be forged easily. It degrades the performance of the biometric system. Similarly, the facial recognition system may be confusing in distinguishing duplicate twins.
Biometrics is not private- Biometrics seems to be secure on the surface, but that doesn’t necessarily make it more secure than passwords. A password is integrally a secret because only you have the authority to know it. Although the hackers can acquire it by brute force attacks or phishing, but in general, people can’t access it. On the other hand, biometrics is innately public. You reveal your eyes, ears whenever you look at things. With fingerprint recognition, you leave your fingerprints everywhere you go. With the invention of so many gadgets, someone can anytime record your voice without your acknowledgment. Fundamentally, there’s easy access to all these identifiers. Even a hacker can easily rupture any of those databases to leak and steal your biometric identification.
Robustness of a Biometric System Environment- The high system performances claimed by biometric manufacturers were often difficult to be realized in actual operating environments. Most of the functional tests are conducted in controlled laboratory environments where everything was supervised in ideal environmental setups, and because of that the recognition system also interacts correctly. But the same is not possible in a real-world scenario because the voice recognition system which has worked well with a quiet background might affect the accuracy of the voice verification system due to undesirable noises. Even the same is for a facial recognition system that is based on conventional cameras is also severely affected by the problem of illumination.
The Need for ‘Liveness’ Detection in Capturing Devices- As with the growing cases of signature forgery, several researchers developed signature databases for testing and reporting of skilled forgery detection. There are also research efforts to automatically synthesize forged handwritten specimens to overcome the limitation of naive forgers in producing positive forgery samples.
Biometrics can be hacked – If a hacker has managed to click or arrange the picture of an individual’s finger, ear or eye, they could easily gain the access of their accounts. While Apple’s Touch ID was broadly recognized as a biometric advancement, but the famous hacker Jan Krissler was able to hack the technology just a day after the iPhone was released. Likewise, researchers from the Chaos Computer Club generated fake fingers to unlock iPhones.
Biometrics hacks may have greater consequences- Biometric reveals the part of an individual’s identity, if it gets stolen, then it can be used to falsify legal documents, passports, or criminal records, which can do more damage than a stolen credit card pin or number. Unlike passwords, credit cards, or other documents, you can’t replace physical identifiers. If someone has managed to get the photos of your iris, you can’t get another eye.
Biometric is a technology that identifies and authenticates individuals based on their physical characteristics. Biometrics may be the extensively used technology in the future, as it provides another level of security and biometric traits are highly unique and consistent across the user population. So, it is supposed to be fool-proof security, but it’s not a foolproof security solution.
Are you looking training with Right Jobs?
Contact Us- Cybersecurity Tutorial
- Windows Networking Interview Questions and Answers
- Information Security Management Tutorial
- What are IT security policies?
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) Certification
Related Articles
Popular Courses
- Cyber Security Online Training
11025 Learners - Online Training Courses/Ethical Hacking Course
12022 Learners - Hardware And Networking Courses
11141 Learners
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- Difference between Data Lake vs Data Warehouse: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- What does the Yield keyword do and How to use Yield in python ? [ OverView ]
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know
