
Information Security Management Tutorial
Last updated on 29th Sep 2020, Blog, Tutorials
Information Security is not only about securing information from unauthorized access. Information Security is basically the practice of preventing unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, inspection, recording or destruction of information. Information can be physical or electronic one. Information can be anything like Your details or we can say your profile on social media, your data in mobile phone, your biometrics etc. Thus Information Security spans so many research areas like Cryptography, Mobile Computing, Cyber Forensics, Online Social Media etc.
During First World War, Multi-tier Classification System was developed keeping in mind sensitivity of information. With the beginning of Second World War formal alignment of Classification System was done. Alan Turing was the one who successfully decrypted Enigma Machine which was used by Germans to encrypt warfare data.
Information Security programs are build around 3 objectives, commonly known as CIA – Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability.
- 1. Confidentiality – means information is not disclosed to unauthorized individuals, entities and process. For example if we say I have a password for my Gmail account but someone saw while I was doing a login into Gmail account. In that case my password has been compromised and Confidentiality has been breached.
- 2. Integrity – means maintaining accuracy and completeness of data. This means data cannot be edited in an unauthorized way. For example if an employee leaves an organisation then in that case data for that employee in all departments like accounts, should be updated to reflect status to JOB LEFT so that data is complete and accurate and in addition to this only authorized person should be allowed to edit employee data.
- 3. Availability – means information must be available when needed. For example if one needs to access information of a particular employee to check whether employee has outstanded the number of leaves, in that case it requires collaboration from different organizational teams like network operations, development operations, incident response and policy/change management.
Denial of service attack is one of the factor that can hamper the availability of information.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Apart from this there is one more principle that governs information security programs. This is Non repudiation.
- Non repudiation – means one party cannot deny receiving a message or a transaction nor can the other party deny sending a message or a transaction. For example in cryptography it is sufficient to show that message matches the digital signature signed with sender’s private key and that sender could have a sent a message and nobody else could have altered it in transit. Data Integrity and Authenticity are pre-requisites for Non repudiation.
- Authenticity – means verifying that users are who they say they are and that each input arriving at destination is from a trusted source.This principle if followed guarantees the valid and genuine message received from a trusted source through a valid transmission. For example if take above example sender sends the message along with digital signature which was generated using the hash value of message and private key. Now at the receiver side this digital signature is decrypted using the public key generating a hash value and message is again hashed to generate the hash value. If the 2 value matches then it is known as valid transmission with the authentic or we say genuine message received at the recepient side
- Accountability – means that it should be possible to trace actions of an entity uniquely to that entity. For example as we discussed in Integrity section Not every employee should be allowed to do changes in other employees data. For this there is a separate department in an organization that is responsible for making such changes and when they receive request for a change then that letter must be signed by higher authority for example Director of college and person that is allotted that change will be able to do change after verifying his bio metrics, thus timestamp with the user(doing changes) details get recorded. Thus we can say if a change goes like this then it will be possible to trace the actions uniquely to an entity.
ISM Security Policy
It is required for ISM security policies cover all areas of security, be appropriate, meet the needs of business and should include the policies shown in the following diagram −
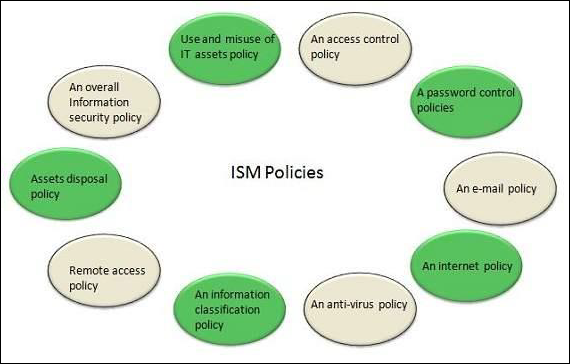
ISM Framework
ISM Process
The following diagram shows the entire process of Information Security Management (ISM) −
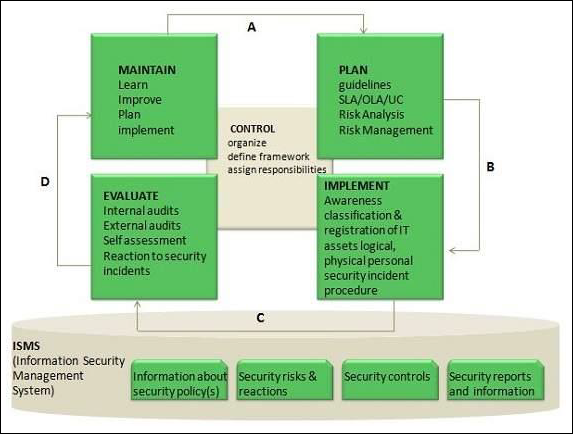
Key elements in ISM Framework
ISM framework involves the following key elements −
Control
The objective of Control element is to −
- Establish an organization structure to prepare, approve and implement the information security policy
- Allocate responsibilities
- Establish and control documentation
Plan
The purpose of this element is to devise and recommend the appropriate security measures, based on an understanding of the requirements of the organization.
Implement
This key element ensures that appropriate procedures, tools and controls are in place to underpin the security policy.
Evaluation
The objective of Evaluation element is to −
- Carry out regular audits of the technical security of IT systems
- Supervise and check compliance with security policy and security requirements in SLAs and OLAs
Maintain
The objective of Maintain element is to −
- Improve on security agreements as specified in, for example, SLAs and OLAs
- Improve the implementation of security measures and controls
Preventive
This key element ensures prevention from security incidents to occur. Measures such as control of access rights, authorization, identification, and authentication and access control are required for this preventive security measures to be effective.
Reductive
It deals with minimizing any possible damage that may occur.
Detective
It is important to detect any security incident as soon as possible.
Repressive
This measure is used to counteract any repetition of security incident.
Corrective
This measure ensures damage is repaired as far as possible.
What is the need of information security?
We need information security to reduce the risk of unauthorized information disclosure, modification, and destruction. We need information security to reduce risk to a level that is acceptable to the business (management). We need information security to improve the way we do business.
Advantages of Information Security:
- 1. Information security is extremely easy to utilize. For protection of less sensitive material users can simply password protect files. For the more sensitive material users can install biometric scanners, firewalls, or detection systems.
- 2. As technology increases so will the crimes associated with it. Making the use of information security very worth while.
- 3. It keeps vital private information out of the wrong hands.
- 4. For the government it keeps top secret information and cabalities out of terrorist and enemy nation’s hands.
- 5. Information security protects users valuable information both while in use and while it is being stored.
Disadvantages of Information Security:
- 1. Technology is always changing so users must always purchase upgraded information security.
- 2. Since technology is always changing nothing will ever be completely secure.
- 3. If a user misses one single area that should be protected the whole system could be compromised.
- 4. It can be extremely complicated and users might not totally understand what they are dealing with.
- 5. It can slow down productivity if a user is constantly having to enter passwords.
At the core of Information Security is Information Assurance, which means the act of maintaining CIA of information, ensuring that information is not compromised in any way when critical issues arise. These issues are not limited to natural disasters, computer/server malfunctions etc.
Thus, the field of information security has grown and evolved significantly in recent years. It offers many areas for specialization, including securing networks and allied infrastructure, securing applications and databases, security testing, information systems auditing, business continuity planning etc.
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important CS Theory concepts for SDE interviews at a student-friendly price and become industry ready.
Continuous improvement in information security :
While ISMS is designed to establish holistic information security management capabilities, requires organizations to adopt ongoing improvements and evolution of their security policies and controls. The structure and boundaries defined by an ISMS may apply only for a limited time frame and the workforce may struggle to adopt them in the initial stages. The challenge for organizations is to evolve these security control mechanisms as their risks, culture, and resources change.
According to ISO 27001, ISMS implementation follows a Plan-Do-Check-Act (PCDA) model for continuous improvement in ISM processes:
- Plan. Identify the problems and collect useful information to evaluate security risk . Define the policies and processes that can be used to address problem root causes. Develop methods to establish continuous improvement in information security management capabilities.
- Do. Implement the devised security policies and procedures. The implementation follows the ISO standards, but actual implementation is based on the resources available to your company.
- Check. Monitor the effectiveness of ISMS policies and controls. Evaluate tangible outcomes as well as behavioral aspects associated with the ISM processes.
- Act. Focus on continuous improvement. Document the results, share knowledge, and use a feedback loop to address future iterations of the PCDA model implementation of ISMS policies and controls.
Popular ISMS frameworks :
ISO 27001 is a leader in information security, but other frameworks offer valuable guidance as well. These other frameworks often borrow from ISO 27001 or other industry-specific guidelines.
- 1. ITIL, the widely adopted ITSM framework, has a dedicated component called Information Security Management (ISM). The goal of ISM is to to ensure InfoSec is effectively managed in all activities.
- 2. another IT-focused framework, spends significant time on how asset management and configuration management are foundational to information security as well as nearly every other ITSM function—even those unrelated to InfoSec.
ISMS security controls :
ISMS security controls span multiple domains of information security. The catalog contains practical guidelines with the following objectives:
- Information security policies: An overall direction and support help establish appropriate security policies. The security policy is unique to your company, devised in context of your changing business and security needs.
- Organization of information security: This addresses threats and risks within the corporate network, including cyberattacks from external entities, inside threats, system malfunctions, and data loss. This component covers organizational assets within and beyond the corporate IT network., which may involve the exchange of sensitive business information.
- Human resource security: Policies and controls pertaining to your personnel, activities, and human errors, including measures to reduce risk from insider threats and workforce training to reduce unintentional security lapses.
- Physical and environmental security: These guidelines cover security measures to protect physical IT hardware from damage, loss, or unauthorized access. While many organizations are taking advantage of digital transformation and maintaining sensitive information in secure cloud networks off-premise, security of physical devices used to access that information must be considered.
- Communications and operations management: Systems must be operated with respect and maintenance to security policies and controls. Daily IT operations, such as service provisioning and problem management, should follow IT security policies and ISMS controls.
- Access control: This policy domain deals with limiting access to authorized personnel and monitoring network traffic for anomalous behavior. Access permissions relate to both digital and physical mediums of technology. The roles and responsibilities of individuals should be well defined, with access to business information available only when necessary.
- Information system acquisition, development, and maintenance: Security best practices should be maintained across the entire lifecycle of the IT system, including the phases of acquisition, development, and maintenance.
- Information security: Identify and resolve IT issues in ways that minimize the impact to end users. In complex network infrastructure environments, advanced technology solutions may be required to identify insightful incident metrics and proactively mitigate potential issues.
- Business continuity management: Avoid interruptions to business processes whenever possible. Ideally, any disaster situation is followed immediately by recovery and procedures to minimize damage.
- Compliance: Security requirements must be enforced per regulatory bodies.
- Cryptography: Among the most important and effective controls to protect sensitive information, it is not a silver bullet on its own. Therefore, ISMS govern how cryptographic controls are enforced and managed.
- Supplier relationships: Third-party vendors and business partners may require access to the network and sensitive customer data. It may not be possible to enforce security controls on some suppliers. However, adequate controls should be adopted to mitigate potential risks through IT security policies and contractual obligations.
The following screen explains the objectives covered in this lesson. After completing this lesson, you will be able to:
- 1. Mitigate issues associated with users who have multiple accounts/roles and/or shared accounts.
- 2. Enforce different account policy settings for securing the systems.
- 3. Apply privileges to groups and individual users for access control monitoring, and
- 4. Describe the significance of reviewing and continuous monitoring of what the user actually accesses through the system.
CONCLUSION:
All the information required by ISM should be contained within the SMIS (Security Management Information System). This should include all security controls, risks, breaches, processes and reports necessary to support and maintain the Information Security Policy and the ISMS. This information should cover all IT services and components and needs to be integrated and maintained in alignment with all other IT information management systems, particularly the Service Portfolio and the CMS. The SMIS will also provide the input to security audits and reviews and to the continual improvement activities so important to all ISMSs. The SMIS will also provide invaluable input to the design of new systems and services.
Are you looking training with Right Jobs?
Contact Us- Security Implications Tutorial
- SAP Security Interview Questions and Answers
- Information Security Management Principles
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) Certification
- Information Security Governance Tutorial
Related Articles
Popular Courses
- Cyber Security Online Training
11025 Learners - Online Training Courses/Ethical Hacking Course Training
12022 Learners - Hardware and Networking Courses Training
11141 Learners
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- Difference between Data Lake vs Data Warehouse: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- What does the Yield keyword do and How to use Yield in python ? [ OverView ]
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know

