- What is Lean?| Everything You Need to Know
- What is SAP Workflow? : A Complete Guide
- Difference between Tableau and Power BI | Benefits and Special Features
- Data Warehouse in Tableau | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Tableau Server?| Everything You Need to Know | A Definitive Guide
- What is Dax in Power BI? | A Comprehensive Guide
- Upgrade in Tableau Desktop and Web Authoring | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is SAP HANA | SAP HANA Database Connection | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- SAP BPC – What is Business Planning and Consolidation? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Root Cause Analysis: Definition, Examples & Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Seven Basic Quality Improvement Ishikawa Tools | Important asset to control quality in your project [OverView]
- What is Power BI | Its Use Cases and Applications | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- How and why to measure and analyze employee productivity | Everything You Need to Know
- Top 10 Employee Retention Strategies | Everything You Need to Know
- What are LookML Projects and the Developer Mode | How to Create LookML Projects?
- What are Slowly Changing Dimension | SCD Types and Implementations | Step-By-Step Process
- What is Pareto Chart and How to Create Pareto Chart | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- What does an Agile Business Analyst do | Required Skills, Roles and Responsibilities [ Job & Future ]
- What is Lean Management? | Role and Concepts of Lean Management | Expert’s Top Picks
- A Definitive Guide of Working Capital Management with Best Practices & REAL-TIME Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Fundamentals | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- Business Analyst : Job Description | All you need to know [ Job & Future ]
- How to create a Splunk Dashboard | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Splunk Logging ? | The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Alteryx vs Tableau | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Predictive Analytics? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- An Overview of SAS Stored Processes | The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- How to Create Conditional Formatting in Cognos Report Studio | A Complete Guide
- Difference between OLTP vs OLAP | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- ECBA vs CCBA vs CBAP | A Complete Guide For Beginners | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Import Custom Geocode Data in Tableau | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- Data Warehouse Tools : Features , Concepts and Architecture
- PGDM vs MBA | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Most Popular Data Visualization Tools | A Complete Beginners Guide | REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau vs Looker : Comparision and Differences | Which Should You Learn?
- Benefits of Employee Satisfaction for the Organization [ Explained ]
- DAX In Power BI – Learn Power BI DAX Basics [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- Power Bi vs Tableau : Comparision and Differences | Which Should You Learn?
- What is Alteryx Tools | Alteryx ETL Tools | Comprehensive Guide
- What is Tableau Prep? : Comprehensive Guide | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- What are Business Intelligence Tools ? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Tableau Aggregate Functions | A Complete Guide with REAL-TIME Examples
- Intervalmatch Function in Qlikview | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- QlikView Circular Reference | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Data Blending in Tableau | A Complete Guide with Best Practices | Free Guide Tutorial [ OverView ]
- Splunk vs ELK | Differences and Which Should You Learn? [ OverView ]
- QlikSense vs QlikView | Differences and What to learn and Why?
- What Is Measurement System Analysis | Required Skills | Everything You Need to Know
- Splunk Timechart | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- What Is Image Processing ? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is a Business Analysis ? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Top Business Analytics Tools | Comprehensive Guide
- Business Analyst Career Path [ Job & Future ]
- Time Series Analysis Tactics | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is Splunk ? Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Which Certification is Right for You: Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma?
- SAS Vs R
- Top Technology Trends for 2020
- Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist
- What are the Essential Skills That You Need to Master in Data Analyst?
- What is Six Sigma?
- Common Cause Variation Vs Special Cause Variation
- Reasons to Get a Six Sigma Certification
- What Is Strategic Enterprise Management and its Components?
- What Are The Benefits Measurement Constrained Optimization Methods?
- What Is the Benefit of Modern Data Warehousing?
- What Is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
- What Is The Purpose and Importance Of Financial Analysis?
- What is Insights-as-a-Service (IaaS)?
- Business Analytics With R Programming Languages
- Where Are The 8 Hidden Wastes?
- What Are Market Structures?
- What is Cost of Quality (COQ)?
- What is Build Verification Testing?
- Quality Improvement in Six Sigma
- What is Process Capability Analysis?
- How To Measure The Effectiveness Of Corporate Training
- SAP Financials And SAP Accounting Modules
- Tips to Learn Tableau
- Why Should I Become a CBAP?
- History And Evolution of Six Sigma
- How to use Control Chart Constants?
- Data Analytics Course For Beginners
- How to Build a Successful Data Analyst Career?
- Data Analytics Vs Business Analytics
- What is SAP Certification?
- Books To Read For a Six Sigma Certification
- Six Sigma Green Belt Salary
- What is the ASAP Methodology?
- Complete list of SAP modules
- What is Lean?| Everything You Need to Know
- What is SAP Workflow? : A Complete Guide
- Difference between Tableau and Power BI | Benefits and Special Features
- Data Warehouse in Tableau | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Tableau Server?| Everything You Need to Know | A Definitive Guide
- What is Dax in Power BI? | A Comprehensive Guide
- Upgrade in Tableau Desktop and Web Authoring | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is SAP HANA | SAP HANA Database Connection | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- SAP BPC – What is Business Planning and Consolidation? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Root Cause Analysis: Definition, Examples & Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Seven Basic Quality Improvement Ishikawa Tools | Important asset to control quality in your project [OverView]
- What is Power BI | Its Use Cases and Applications | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- How and why to measure and analyze employee productivity | Everything You Need to Know
- Top 10 Employee Retention Strategies | Everything You Need to Know
- What are LookML Projects and the Developer Mode | How to Create LookML Projects?
- What are Slowly Changing Dimension | SCD Types and Implementations | Step-By-Step Process
- What is Pareto Chart and How to Create Pareto Chart | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- What does an Agile Business Analyst do | Required Skills, Roles and Responsibilities [ Job & Future ]
- What is Lean Management? | Role and Concepts of Lean Management | Expert’s Top Picks
- A Definitive Guide of Working Capital Management with Best Practices & REAL-TIME Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Fundamentals | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- Business Analyst : Job Description | All you need to know [ Job & Future ]
- How to create a Splunk Dashboard | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Splunk Logging ? | The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Alteryx vs Tableau | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Predictive Analytics? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- An Overview of SAS Stored Processes | The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- How to Create Conditional Formatting in Cognos Report Studio | A Complete Guide
- Difference between OLTP vs OLAP | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- ECBA vs CCBA vs CBAP | A Complete Guide For Beginners | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Import Custom Geocode Data in Tableau | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- Data Warehouse Tools : Features , Concepts and Architecture
- PGDM vs MBA | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Most Popular Data Visualization Tools | A Complete Beginners Guide | REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau vs Looker : Comparision and Differences | Which Should You Learn?
- Benefits of Employee Satisfaction for the Organization [ Explained ]
- DAX In Power BI – Learn Power BI DAX Basics [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- Power Bi vs Tableau : Comparision and Differences | Which Should You Learn?
- What is Alteryx Tools | Alteryx ETL Tools | Comprehensive Guide
- What is Tableau Prep? : Comprehensive Guide | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- What are Business Intelligence Tools ? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Tableau Aggregate Functions | A Complete Guide with REAL-TIME Examples
- Intervalmatch Function in Qlikview | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- QlikView Circular Reference | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Data Blending in Tableau | A Complete Guide with Best Practices | Free Guide Tutorial [ OverView ]
- Splunk vs ELK | Differences and Which Should You Learn? [ OverView ]
- QlikSense vs QlikView | Differences and What to learn and Why?
- What Is Measurement System Analysis | Required Skills | Everything You Need to Know
- Splunk Timechart | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- What Is Image Processing ? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is a Business Analysis ? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Top Business Analytics Tools | Comprehensive Guide
- Business Analyst Career Path [ Job & Future ]
- Time Series Analysis Tactics | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is Splunk ? Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Which Certification is Right for You: Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma?
- SAS Vs R
- Top Technology Trends for 2020
- Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist
- What are the Essential Skills That You Need to Master in Data Analyst?
- What is Six Sigma?
- Common Cause Variation Vs Special Cause Variation
- Reasons to Get a Six Sigma Certification
- What Is Strategic Enterprise Management and its Components?
- What Are The Benefits Measurement Constrained Optimization Methods?
- What Is the Benefit of Modern Data Warehousing?
- What Is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
- What Is The Purpose and Importance Of Financial Analysis?
- What is Insights-as-a-Service (IaaS)?
- Business Analytics With R Programming Languages
- Where Are The 8 Hidden Wastes?
- What Are Market Structures?
- What is Cost of Quality (COQ)?
- What is Build Verification Testing?
- Quality Improvement in Six Sigma
- What is Process Capability Analysis?
- How To Measure The Effectiveness Of Corporate Training
- SAP Financials And SAP Accounting Modules
- Tips to Learn Tableau
- Why Should I Become a CBAP?
- History And Evolution of Six Sigma
- How to use Control Chart Constants?
- Data Analytics Course For Beginners
- How to Build a Successful Data Analyst Career?
- Data Analytics Vs Business Analytics
- What is SAP Certification?
- Books To Read For a Six Sigma Certification
- Six Sigma Green Belt Salary
- What is the ASAP Methodology?
- Complete list of SAP modules

Business Analyst Career Path [ Job & Future ]
Last updated on 27th Oct 2022, Artciles, Blog, Business Analytics
- In this article you will learn:
- 1.Introduction
- 2.What is an Business analyst?
- 3.What is the role of a business analyst?
- 4.Business Analyst Educational Requirements
- 5.Characteristics of Business Analyst
- 6.Six Outstanding Business Analyst Career Paths
- 7.Tendencies in Business Analyst
- 8.Advantages of a Business Analyst
- 9.Conclusion
Introduction
A Business Analyst acts as a link between theoretical company concepts and practical business experience. They help to interpret the destiny of businesses, which they do by recognising, finishing, and scoping an infinite number of modifications and improvements to company revolutions. This gives them a function that is incredibly significant, and it is for this reason that they play such an important part.
What is an Business analyst?
Business analysts examine a company’s processes, operating procedures, and massive data sets in order to discover ways to improve an organization’s operational efficiency and performance. Although business analysts are also known as management analysts, data analysts should not be confused with them.
Corporate analysts collaborate with management to cut costs, eliminate or minimise inefficiencies, and increase the company’s competitiveness in the contemporary business environment. They employ their analytical talents to comprehend and implement the data-driven methods most suited to boost a company’s profitability.
What is the role of a business analyst?
The primary role of a business analyst is to identify those areas of a company that require greater efficiency and those that can be enhanced to increase revenue. This is a research-intensive position in which business analysts from all levels of the organisation collaborate to share their reports and identify greater opportunities for the firm to improve.Here are some of the most critical responsibilities of a career as a business analyst:
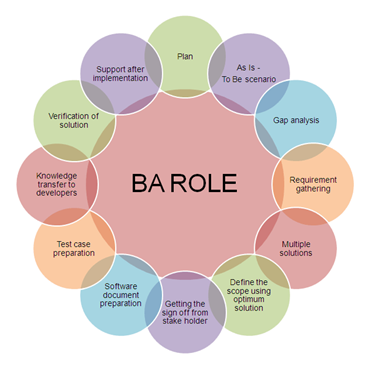
- Conducting research, analysis, and evaluation of the business’s functional and technological requirements
- Finding better strategies to increase productivity and employee effectiveness
- Analyze large datasets with Excel and SQL
- Combining visual elements such as tables and graphs to represent data
- Providing and enhancing operational effectiveness to achieve improved performance
- Developing financial models that are responsive to an organization’s revenues.
- Evaluating corporate strategies and future plans
- Internally and outwardly defining the structure of an organisation
- Analysis of budgetary foresight, prognosis, and prediction.
Business Analyst Educational Requirements
Here are the requirements required to pursue a job as a business analyst:
Business administration, company acumen, operational management, human resources, logistics, finance, accounting, and business management will be covered in a graduate business degree, which is a good starting point.
A master’s degree in business, such as an MBA, can also provide you with the necessary skills for this position.
Aside from these requirements, it is advisable to complete a certification course before applying for an entry-level business analyst position. These credentials are:
- Certified Professional Business Analyst (CBAP)
- Certified Management Consultant
Also essential to apply for an entry-level business analyst position is industry experience. This can refer to any internship or industrial training that can be completed while studying a bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Characteristics of Business Analyst:
If you possess the following traits and skills, your journey as a business analyst will be easier:
- Effective listening and communication skills.
- He is open to the possibility of change.
- Capability to successfully perform several tasks.
- Capability to establish priorities depending on the numerous demands of participants.
- As a competent facilitator, you may obtain timely participant buy-in on crucial choices.
- Identify opportunities for developing processes that can increase performance and outcomes.
- Working as a member of a team, including collaboration with individuals and groups outside the team.
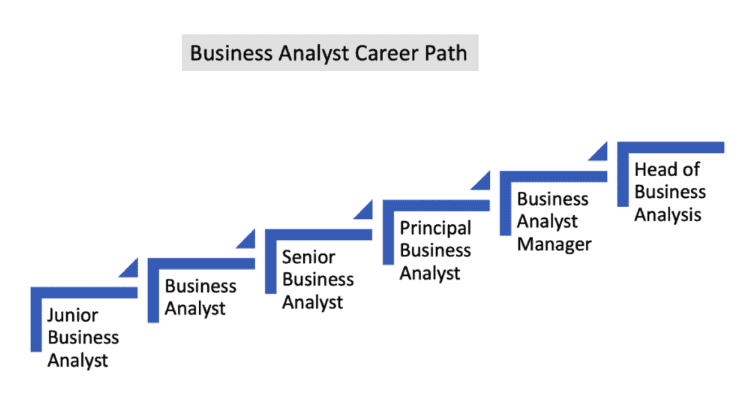
Six Outstanding Business Analyst Career Paths
Before beginning your business analyst profession, you must complete the necessary preparations. Either a solid business background or expertise of information technology is required. Most business analyst entry-level employment require a bachelor’s degree, typically in accounting, finance, management, or IT. These are the six most in-demand career pathways for business analysts:
- Business Analyst Manager Data Business Analyst Expert in Data Analysis
- Analyst of Information Security IT Quantitative Analyst, Business Analyst
Business Analyst Supervisor
These managers select and hire members of the business analyst team, supervise the training of new hires, set best practises, and carry out organisational objectives.
Data Business Analyst
Using enormous data sets, these analysts detect trends, construct charts, and make visual presentations to aid in business decision-making.
Data Analysis Expert
This is a very difficult job path since data analysis scientists must extract meaning from obtained data, evaluate it, and use it to provide actionable insights. This post requires knowledge of machine learning and statistics for success.
Analyst in Information Security
Cybercrime is a trending topic, and cyber security experts are in high demand. By evaluating security data and monitoring IT networks, information security analysts safeguard enterprises from cybercriminals. If you are interested in ethical hacking, you will enjoy this career, as it typically involves locating and eliminating system vulnerabilities.
Business Analyst in IT
This position requires working on numerous projects and operating systems concurrently with the development of more substantial business process responsibilities. This profession is ideal for those who enjoy analysing numbers.
Statistical Analyst
This expert develops, implements, and provides mathematical models that assist financial decisions affecting risk management, investments, and pricing.The trip along your chosen business analyst professional path will be easier if you possess the following traits and abilities:
- Being an excellent communicator and listener
- Willing to consider modification
- Effective multitasking ability
- Understanding how to prioritise based on the needs of multiple stakeholders
- Being a skilled negotiator who can obtain timely buy-in from stakeholders on key matters
- Identifying chances to optimise procedures that could result in increased efficiency and output.
- Collaborating with individuals and groups external to the team as part of a team
Tendencies in Business Analyst
Business Analysis is usually recognised as a position, as opposed to a function, and is renowned for providing IT/product development solutions in both the IT and non-IT industries. Almost everyone (change agents) engages in analytical activities in different realms of life. Another consideration is whether these change agents are aware of the values, the governing body, etc. In Sri Lanka, business analysts have the opportunity to play a larger role as a maker rather than a thinker.
Unless there is a beginning, the possibility for meditation and initiation may be limited. But nonetheless! The adoption of technology is thriving, and more and more Business analysts are able to voice their ideas and opinions. Nonetheless, I believe it is essential for analysts to recognise that IIBA and BABOK provide the basis and building blocks upon which everything else is founded.
Advantages of a Business Analyst:
1.Possibility for interaction and networking
Business Analysts are expected to collaborate with nearly all project stakeholders, including the project Team (Project Manager, project development team, evaluation team), clients (key stakeholders, end users), finance or purchasing teams, not to mention senior management (president, directors, and delivery/program Managers), and dealers. Analysts often get to go to client sites, where they can learn about complicated processes in new and difficult areas and build their networks.
2. rapid work
Business analysts frequently work on multiple tasks simultaneously, and their employment is far from “sitting in a chair all day.” Participate in customer consultation procedures, assess needs, explore alternatives, document operational and technical requirements, manage team members, manage modifications, attend and record meetings, and present to the client/management – sometimes all in the same day.
3. Promising profession with substantial expansion
After gaining a significant amount of experience (three to five years) as a Business Analyst, you will reach a pivotal point in your analysis process and be able to determine the next step. You can become an Active Analyst by specializing in a particular technology or topic, or you can act as a liaison between business and technology without identifying as an IT business analyst. Moreover, if you intend to advance to management, “project management” is the logical next step for experienced Business analysts, as they have the relevant expertise and skills. Thus, Business Analysts are involved in nearly every aspect of the project, and their contribution will never be questioned. Business analysis is an energizing and adaptable profession that can help you realize your ambitions and attain the type of development you seek.
4. Possibility of seeing the vast picture
Almost everyone, regardless of his or her experience or the organization for which he or she works, desires to see his or her contribution and position in the larger scheme of things. However, because of expert limits, this is not true for all job areas, and Business Analysts are among the fortunate few who can capture a comprehensive view of the project. They are involved in the project from the pre-sale phase until the project closes and understand the project bidding, customer communication, team strength, change management, and purchasing processes. They are frequently considered face-to-face (after the project manager). Now it is simple to comprehend why the majority of active project managers are former business analysts!
5. The highest visibility and respect for the Organization
Due to the value, the business analyst brings to the project, their participation in the project’s success has never been questioned, which increases the business analyst’s visibility and interest. As we have seen, business analysts influence the foundation’s project, operational, financial, and administrative aspects (learn more here), and their writing skills and technical understanding make them beneficial to technical architects and the sales/marketing team. In addition, analysts are frequently required to explain their understanding of the project in which they are involved to senior management, the CEO, and the CFO. Very few job titles have this level of collaboration and visibility inside the business in such a short period of time.
Conclusion:
The position of business analyst calls for both soft and hard talents. Business analysts must be able to report, assess, and extract data trends, as well as transfer and utilize the data for business purposes. As long as they have a thorough understanding of how tools, products, and systems function, not all business analysts require a specialization in IT. On the other hand, some business analysts with a strong IT background and less business experience are willing to transition from IT to a mixed business role.