
Designing the Blueprint Delivery Tutorial
Last updated on 12th Oct 2020, Blog, Tutorials
Blueprint
- Blueprint is an interesting technical way of showing the design of the conceptual work with details that can be understood by all the technical staff within the team to create the component. This is used in almost all the engineering fields and to explain the details of the workflow and components.
- This concept was introduced by John Herschel in 1842. It is a detailed document to understand the different technicalities of the construction of the project.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
What is Blueprint?
- It is a design or a technical drawing which explains the overall details of the component. We communicate, understand specifications and design the blueprint. It’s a softcopy of imagining the values of the project.
- It can be used to understand and explain the detailed plan of work with the help of design mode. Drawbacks of the design can be identified and improved instantly.
Understanding Blueprint
- 1. The study is very interesting. There is a step by step process to understand it.
- 2. First, you need to know what is the design made of or the purpose of the design. Finalizing the design in all aspects.
- 3. Secondly understand the universal standards of measurement used for design ex:- meters, Feet’s, inches, centimeters, etc.
- 4. Understand the material used and analysis where it’s suitable for a working environment.
- 5. Understanding the assembling and design of components.
- 6. Maintain the standards in a workflow from start to end
- 7. Delivering the product to the client as planned and approved using this.
How does this Make Working so Easy?
- Design costs less, and out of multiple designers one of the blueprint designs gets finalized and as per the finalized design budget of the project gets finalized by considering all constraints such as material, labor, and other effective costs.
- Technical details are already clearly given with design so blueprint workers can quickly have a look at the design and maintain the parameter standards as required in case of any ambiguous situations.
- Work completion rate can be checked using checklists and it can be done at any time using a blueprint at any stage of a project. To know the project status and to estimate completion rate.
Top Blueprint Companies
Every company will have and follow this making for multiple reasons like interior, exterior, complete house, and mechanical technical blueprints for components, electrical wiring related blueprint, civil constructions and many more.
- 1. Blueprint Pvt Ltd
- 2. Ark blueprint Pvt Ltd
- 3. AA Engineering Works
- 4. Space Matrix
- 5. Inovies
- 6. Hometrenz
- 7. DSD Design Associates
- 8. Trimit Rachana
- 9. Co.In
Many more MNCs have their own blueprint design teams for their projects like LNT, Wipro, Cyient, Tech Mahindra spaces, etc.
What Can You do with these prints?
- It is used for understanding the design of the product.
- The material used for the components in the design and cost.
- Work status and its effectiveness of completion rate.
- Errors in the process can be identified as soon as possible.
- Explain the design with conceptual technical understanding which is interesting and encouraged by clients.
- Reduce, educate and maintain standards of process flow with Universal standards.
Working with Blueprint
- 1. It is quick and easy, time takes only to study and understand the design and follow the working procedure as per design standards and approvals.
- 2. It helps in enriching our technical aspects of knowing designs and assemblings. layouts, floor plans, electrical wiring plans, plumbing line pan, and much more construction, HVAC, engineering professionals use a blueprint for their work on a daily basis.
Advantages
It is used to determine the design and technical details of the project. Which is a soft copy of the work containing the details Height, Width and few more measurements of the component will be specified.
Why Should We Use Blueprints?
To maintain industrial stands of workflow with technical aspects. To maintain standards in every stage of process flow and to perform quick checks of the work at any point in time. To explain the needs and technicalities from the client to the layman who is involved in the project.
Scope
There is a huge scope for blueprint designers in various fields of the market such as the study on this improves our technical abilities and helps us in understanding the construction stricture of the design. Engineering component and technical design blueprints for making, maintenance, emergency, stress, strain analyses and many more.
Architecture related design for interior, exterior, floor plans, furniture, and many more jobs are available for blueprint designing experts.
Why Do We Need a Blueprint?
We can perform multiple tests and know the best design or improve the existing by its drawbacks. Stress-strain analysis, visual analysis, and much similar analysis can be done with less cost visually using tools.
It helps the technical staff of the project to be on the same page while working and maintaining the required parameters while doing tasks following a design approved blueprint helps to achieve the imaginary project design to reality.
Who is the Right Audience for Learning?
All graduated and higher education students can do this course. This course helps them in understanding the work done at ground level and the quantity of infrastructure and logistics technical details and its estimated cost of each design. We can even make multiple designs for the same project and select the best one as per the client’s preference and then start physical work.
Civil, Architecture, plumbing, fire and safety, floor plans and others must learn this making and study to know more technical details and parameters. It is useful for every day to day life for all details such as purchased product details, plot layouts, floor plans, etc.
Blueprint Technologies
It is one of the widely growing job roles in the market because more cultural designers help in technical working, arrangements, components of the project. It helps all the technical staff of the team to understand and work accordingly.
Users must be creative enough to understand concepts and adopt new technologies and apply them in their design to impress clients and get the project.
How will this Technology Help You in Career Growth?
- 1. It helps in making more effective and technical design for many challenging projects which brings name and fame.
- 2. Every physical work procedure must have a soft copy of designing work procedures satisfying the standards and approved form clients.
- 3. Designing softcopy of blueprint costs less than a sample model in real time. Which also improves the technical study on the concept of designing for every designing individual to maintain the workflow.
Designing a Blueprint
A service blueprint allows a company to explore all the issues inherent in creating or managing a service. The process of designing a blueprint involves the consideration of several issues:
Identifying processes: The first step in creating such a blueprint is mapping the processes that constitute the service. Exhibit I maps a shoeshine parlor. As the service is simple and clear-cut, the map is straightforward. For more complex services, identifying and defining the processes involved may be difficult and result in a large, complicated diagram. Tax-return preparation or health care, for example, involves many decision points, alternative courses of action, and variable methodologies. Portfolio management, car repair, and even tailoring require contemplation and observation before diagramming.
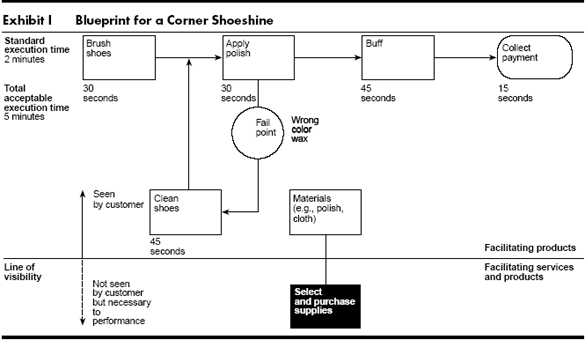
Even within the simplest process, further definition is beneficial; in shoeshining it might be useful to specify how the proprietor will perform the step called “buff.” Definition doesn’t mean you must mechanize all procedures. But identifying the components of a step or action reveals the inputs needed and steps covered, and permits analysis, control, and improvement. For example, a doctor or a lawyer would do well to break down the “problem diagnosis” step.
It is important to watch out for parts of the service that the consumer does not see, like purchasing of supplies. Though invisible, these processes are important because changing them may alter the way consumers perceive the service. If, for example, a bank redesigns a computer program so that it produces a different account statement for customers, the bank may affect its image or other consumer perceptions of value. These subprocesses are integral to the success of the service.
Isolating fail points. Having diagrammed the processes involved, the designer can now see where the system might go awry. The shoe shiner may pick up and apply the wrong color wax. So the designer must build in a subprocess to correct this possible error. The identification of fail points and the design of fail-safe processes are critical. The consequences of service failures can be greatly reduced by analyzing fail points at the design stage. When designers and managers think through potential problems together in advance, the quality of service execution is invariably higher.
Establishing a time frame. After diagramming a service profile, identifying processes and vulnerabilities, and building in fail-safe measures, the designer must consider the execution.
Since all services depend on time, which is usually the major cost determinant, the designer should establish a standard execution time. As a blueprint is a model, the design should also allow for deviation from standard execution time under working conditions. The amount of latitude necessary in the time frame will depend on the complexity of the delivery.
In the shoeshine example, the standard execution time is two minutes. Research showed that the customer would tolerate up to five minutes of performance before lowering his or her assessment of quality. Acceptable execution time for a shoeshine is then five minutes.
Analyzing profitability. The customer can spend the three minutes between standard and acceptable execution time at the corner parlor waiting in line or during service, if an error occurs or if the shoe shiner does certain things too slowly. Whatever its source, a delay can affect profits dramatically. Exhibit II quantifies the cost of delay; after four minutes the proprietor loses money.
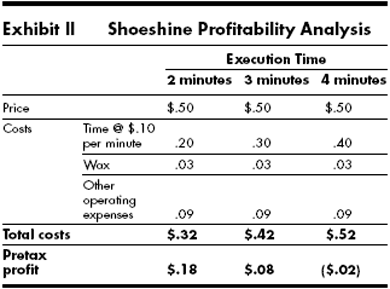
A service designer must establish a time-of-service-execution standard that precludes unprofitable business and maintains productivity. Such a standard not only helps measure performance and control uniformity and quality, it also serves as a model for distribution of the service to far-flung locations.
Delivering the Service
Recruiting, training, and general management are important considerations in services rendered by people, and for complex professional occupations such as legal, consulting, or medical services these factors are of paramount importance. But some services can be rendered mechanically, as banks have demonstrated with automatic tellers, and some can be performed by customers themselves, as at salad bars.
Implementation constantly evolves. Schools, for example, once depended entirely on teachers to render the service of education; today computers and television have an important function in the classroom. A service designer must weigh alternate means of execution, for example, by considering the merits of using a buffing machine in the process of shoeshining. The productivity and profit margin increases must be weighed against a customer’s perception of lower quality. A blueprint facilitates the analysis of cost-benefit trade-offs and can be used to test the appeal of different designs to prospective customers.
A blueprint can help the service developer with other problems. For the pricing department, it provides a basis for a thorough cost analysis; for distribution, a map to be duplicated; for promotion, tangible evidence it can manage and control.
Highlighting Tangible Evidence
To maintain credibility, the service must select and manage products with care. In some cases, products are optional—a consultant may not have to present a written report for instance. Consumers, however, often deduce the nature of the service from this type of circumstantial evidence. The design of a service should therefore incorporate the orchestration of tangible evidence—everything the consumer uses to verify the service’s effectiveness. The setting, including color schemes, advertising, printed or graphic materials, and stationery, all proclaim a service’s style. The design should not be carelessly delegated to outsiders or left to chance.
Airlines have learned this lesson. The interior and exterior decor of the plane, flight attendants’ uniforms, the appearance of the reservation desk, ticket folders, baggage tags, and advertising graphics all tell the customer what kind of service to expect. They either reinforce or contradict personal experience with the airline.
Modifying a Service
- Market research during a service’s operating life enables managers to measure quality and identify needs for redesign.
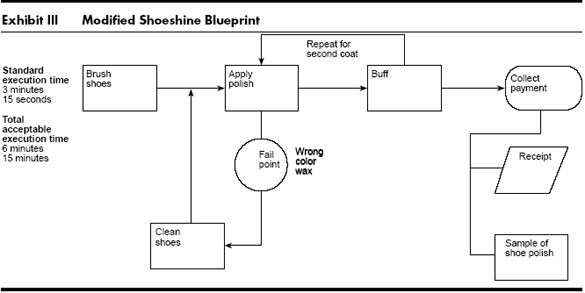
- Exhibit III shows how the designer may add a repeat of steps 2 and 3 in the shoeshine service to create a two-coat shine, and justify a 20—cent price increase, thus increasing the profit margin by nearly 30%. Moreover, the shoeshiner might decide to add a receipt or a sample of shoepolish as tangible evidence of good care. Such service reminders (the shoeshiner could print his or her name and address on the shoe-polish sample) could lead to a premium price for a premium service.
Conclusion
It’s a framework for the design procedure of workflow soft copy before creating and using the component in the real world. This help In creating the technical detailed design for every project and flexible to change as required while still finishing the project. Once the print is finalized all the technical staff will be going through the design and construction work procedure starts and per details in the design.
Maintaining the standards and project completion statue tracking can be done using a blueprint checklist on the floor.
Are you looking training with Right Jobs?
Contact Us- PMP Exam Preparation Tutorial
- CAPM Certification
- PMP Examination Preparation – ITTO’s
Related Articles
Popular Courses
- Web Designing Training
11025 Learners - Sales Fprce Training
12022 Learners - Adobe Training
11141 Learners
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- Difference between Data Lake vs Data Warehouse: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- What does the Yield keyword do and How to use Yield in python ? [ OverView ]
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know

