- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Project Management Process ? : A Complete Guide
- What is Lean Management? : A Complete Guide
- What is ITIL ? Know about the Framework
- What is Six Sigma?| Know the tools used
- What is Kanban Training?|Know more about it
- Project Management Tools and Techniques : A Complete Guide
- What is Project Management? Everything You need to Know | Salary for the role
- Srum Org Certification? All you need to know about it
- MS Project Certification | All you need to know
- What is Project Manager? Know about the salary
- Six Sigma Certification Cost | Know all details about it
- Difference Between PMO and Project Manager? | Expert’s Top Picks
- What are Project Management Tools | Its Techniques | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Agile |Its Methodology and Types | How to Implement [ OverView ]
- What is a Product Roadmap? | How to Create one | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Scrum vs Kanban | Agile at Scale | New Agile BenchMark
- How to Effectively Manage Stakeholders | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Experts Top Picks
- What is Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) | The Leading Framework For Business Agility | Everything You Need to Know
- How to Become a Project Manager | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- Time Management Tools to Help You Succeed as a Professional | Expert’s Top Picks
- Top 10 Tips for Agile Sprint Planning To Implement Efficient Marketing | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is ICP-ACC (ICAgile Certified Agile Coaching)? | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices [ OverView ]
- How To Run An Effective Agile Retrospective-Agile management | Everything You Need to Know
- What Skills Does One Acquire After The PMP Certification?
- A Definitive Guide: Most Effective and Proven Time Management Techniques [ OverView ]
- What Gaps I Filled After CSM Certification For my Scrum Project? [ OverView ]
- How to Create A Plan And Manage Your Projects Better?: Step-By-Step Process [ OverView ]
- What is User Story Mapping? : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is Design Thinking ? : Benefits and Special Features | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What is the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is Sprint Planning ? | A Definitive Guide | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and How Does It Help in Equipment Effectiveness [ OverView ]
- What are Agile Metrics ? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Agile Marketing and Why Do You Need It | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Why is Retrospection Needed? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Developing Project Schedule : Role of Float, Leads, and Lags [ OverView ]
- Project Life Cycle vs Product Life Cycle | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Projects in Business Environments | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Business Agility ? and Why is it Important ? Expert’s Top Picks
- The Most Important Benefits of Blended Learning | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- Can Business Analyst be a Project Manager? : Expert’s Top Picks
- Why A PMO Is Second In Line To A Project Manager ? | Expert’s Top Picks
- Devops vs Waterfall | A Definitive Guide and Which Should You Learn?
- Jira vs Trello | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Key Values and Principles Behind the Agile Manifesto | A Definitive Guide
- What are Scrum Ceremonies : The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Business Analyst vs Financial Analyst | Know Their Differences and Which Role is Better ?
- Learn Burndown Charts With Jira : Comprehensive Guide [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What Is Scrum XP? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Phases of Project Management | Step-By-Step Process | Expert’s Top Picks
- Project Manager Salary in India – How much does a PM earn? [ Job & Future ]
- Why Do Scrum Masters Get Paid so Much? [For Freshers and Experience]
- What Best Describes a Scrum Team? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- JIRA vs TFS | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Anti-patterns of a Scrum Master : Step-By-Step Process
- SCM Tools and Frameworks | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Stages of Team Development | Everything You Need to Know
- Project Management Consultant : Job Description, Skills Required | Everything You Need to Know
- CSM vs PSM : Difference You Should Know
- Top Characteristics of a Project Manager : Expert’s Top Picks
- Roles And Responsibilities Of A Product Owner : Everything You Need to Know
- Common Project Risks and How to Tackle Them | Expert’s Top Picks
- Benefits of Having Shorter Sprints in Agile – Everything You Need to Know
- Group Discussion Tips | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- PMP Certification Cost : All you need to know
- DMAIC Process and Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Agile Scrum Vs Kanban | Know the difference
- Deming vs Juran vs Crosby
- What is Project Scope Management and Why It’s Important?
- The Basic Principles of Project Management
- Top PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2020
- Risk Management Strategies
- Roles and Responsibilities of A Scrum Master
- ROM Estimate Vs Definitive Estimate
- Guidelines for Creating and Maintaining a WBS Dictionary
- How to Become a Certified ScrumMaster?
- Top Professional Skills for 2020
- Fast Tracking Vs Crashing
- PMP Vs PRINCE2 Vs CAPM
- PMP Earned Value Management (EVM) And Formulas
- What is Certified Scrum Professional (CSM)?
- Top Leadership Theories Every Manager Should Know
- What is Deliverables in Project Management?
- How To Prepare For TOEFL
- History and evolution of the PMP Certification
- What Is Float In Microsoft Project?
- Rules to set you up for success in project
- What is Scrum Project Management?
- What Is Estimating Activity Duration in Project Management?
- What Are The PMP Terminologies Relating To Cost Knowledge Area?
- What is Project Scope Management processes?
- What Are The Types of Organization In PMP?
- Books to Beat the Scrum Master Certification
- Agile Coach Vs Agile Consultant
- What is the cost of quality in project management?
- Signs Your Career May Be Stagnation and Tips to Overcome Downturn
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) Certification
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification
- What is schedule Activity in project management?
- Why Do We Need a Project Charter?
- PMP Certification Exam Preparation Mind Map
- Why Quality Professionals Should Use Infographics In Project Management?
- Role of Earned Value Technique in Project Management
- What is Project Quality Management?
- Tools and Techniques to Estimate Project Cost
- What is a Project Charter And Project Scope in Project Management?
- Why Should You Conduct Project Status Meetings with Your Team?
- The 7 R’s of Change Management
- What Are The Categories and sources of risk in your project?
- What Is a Network Diagram in Project Management?
- What are The Types of Contracts In PMP?
- Residual Risk Vs Secondary Risk
- Impact of the stakeholders on the projects
- Effort Vs Duration Vs Elapsed Time
- Agile vs Scrum
- What Is Six Sigma Quality Assurance?
- How to Close a Project?
- What Qualifications Do You Need to be a Project Manager?
- Project Management Vs General Operations Management
- Enterprise Environmental Factors & Organizational Process Assets
- What is a project manager?
- Important Questions for PMP Certification Exam
- How is the PMP Exam changing, in 2015 & 2020?
- How To Renew Your PMP Certification?
- The Importance of Having Project Acceptance Criteria in Your Projects
- Tips for PMP Exam Preparation
- What is requirement traceability matrix RTM in Project Management?
- Poor Performance Appraisal? Here are the tips to turn any negative feedback into positive.
- How to build a successful Career in Agile and Scrum?
- Importance of Tuckman ladder model in HR management
- How To Apply For The PMP® Exam In Easy Steps
- How to Write a Six Sigma Problem Statement
- What is a lessons learned document in PMI?
- Perform Quality Assurance Vs Perform Quality Control
- How to Improve Quality Management Consistently?
- Interactive Vs Push Vs Pull Communication
- what is risk management?
- Key Appraisal Questions to Prepare For
- What are the MSP Certifications?
- What Is A Six Sigma Control Plan?
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel?
- Agile Prioritization Techniques
- Tips to Help Millennials Climb the Corporate Ladder
- What is an Issue Log?
- Advantages of PMP over MBA
- Top Successful Project Estimation Techniques
- PMP Examination Preparation – ITTO’s
- Employee Training Rewards That Actually Improve Learning
- Lean principles
- What Does It Take to Become a Successful Agile Coach
- Projects VS Programs
- The Role of Six Sigma in Manufacturing
- The Top Formulas to Memorize Before Your PMP Exam
- Roadmap to CSM (Certified Scrum Master) Certification
- What are Some Qualities of a Good Manager and Good Leader?
- How to Handle Project Monitoring and Controlling Processes?
- Top Free Agile Tools For Any Project Manager
- Risk Assessment in Project Management
- The Concept of Zero Defects in Quality Management
- The Importance of Work Packages in Project Scope Management
- How to Get Project Management Experience for PMP Certification
- Different Ways to Calculate the Estimate at Completion (EAC)
- What Is a ScrumMaster?
- What is Risk Register?
- Agile Certifications
- Top-down Approach Vs Bottom-up Approach
- Leadership Vs Management
- What is Feasibility Study and Its Importance in Project Management?
- What Is a Project Management Plan?
- The Professional Advantages of the CAPM Certification
- PRINCE2 Vs PMP
- Rita Mulcahy’s PMP Prep and PMBOK® Guide
- What is Project Cycle Management?
- What is Project and Process Metrics?
- PMBOK® Sixth Edition is Here! What Project Managers Should Know?
- CAPM Certification
- Top Project Selection Methods for Project Managers
- Free Float Vs Total Float
- What is Critical Chain Project Management?
- How to Build a Career in Project Management?
- Scrum Master or Product Owner: What Suits You Better?
- Project Documentation and its Importance
- What is Performance Reporting in the Project Management?
- Top Highest Paying Tech Jobs in India
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Project Management Process ? : A Complete Guide
- What is Lean Management? : A Complete Guide
- What is ITIL ? Know about the Framework
- What is Six Sigma?| Know the tools used
- What is Kanban Training?|Know more about it
- Project Management Tools and Techniques : A Complete Guide
- What is Project Management? Everything You need to Know | Salary for the role
- Srum Org Certification? All you need to know about it
- MS Project Certification | All you need to know
- What is Project Manager? Know about the salary
- Six Sigma Certification Cost | Know all details about it
- Difference Between PMO and Project Manager? | Expert’s Top Picks
- What are Project Management Tools | Its Techniques | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Agile |Its Methodology and Types | How to Implement [ OverView ]
- What is a Product Roadmap? | How to Create one | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Scrum vs Kanban | Agile at Scale | New Agile BenchMark
- How to Effectively Manage Stakeholders | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Experts Top Picks
- What is Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) | The Leading Framework For Business Agility | Everything You Need to Know
- How to Become a Project Manager | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- Time Management Tools to Help You Succeed as a Professional | Expert’s Top Picks
- Top 10 Tips for Agile Sprint Planning To Implement Efficient Marketing | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is ICP-ACC (ICAgile Certified Agile Coaching)? | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices [ OverView ]
- How To Run An Effective Agile Retrospective-Agile management | Everything You Need to Know
- What Skills Does One Acquire After The PMP Certification?
- A Definitive Guide: Most Effective and Proven Time Management Techniques [ OverView ]
- What Gaps I Filled After CSM Certification For my Scrum Project? [ OverView ]
- How to Create A Plan And Manage Your Projects Better?: Step-By-Step Process [ OverView ]
- What is User Story Mapping? : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is Design Thinking ? : Benefits and Special Features | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What is the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is Sprint Planning ? | A Definitive Guide | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and How Does It Help in Equipment Effectiveness [ OverView ]
- What are Agile Metrics ? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Agile Marketing and Why Do You Need It | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Why is Retrospection Needed? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Developing Project Schedule : Role of Float, Leads, and Lags [ OverView ]
- Project Life Cycle vs Product Life Cycle | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Projects in Business Environments | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Business Agility ? and Why is it Important ? Expert’s Top Picks
- The Most Important Benefits of Blended Learning | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- Can Business Analyst be a Project Manager? : Expert’s Top Picks
- Why A PMO Is Second In Line To A Project Manager ? | Expert’s Top Picks
- Devops vs Waterfall | A Definitive Guide and Which Should You Learn?
- Jira vs Trello | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Key Values and Principles Behind the Agile Manifesto | A Definitive Guide
- What are Scrum Ceremonies : The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Business Analyst vs Financial Analyst | Know Their Differences and Which Role is Better ?
- Learn Burndown Charts With Jira : Comprehensive Guide [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What Is Scrum XP? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Phases of Project Management | Step-By-Step Process | Expert’s Top Picks
- Project Manager Salary in India – How much does a PM earn? [ Job & Future ]
- Why Do Scrum Masters Get Paid so Much? [For Freshers and Experience]
- What Best Describes a Scrum Team? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- JIRA vs TFS | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Anti-patterns of a Scrum Master : Step-By-Step Process
- SCM Tools and Frameworks | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Stages of Team Development | Everything You Need to Know
- Project Management Consultant : Job Description, Skills Required | Everything You Need to Know
- CSM vs PSM : Difference You Should Know
- Top Characteristics of a Project Manager : Expert’s Top Picks
- Roles And Responsibilities Of A Product Owner : Everything You Need to Know
- Common Project Risks and How to Tackle Them | Expert’s Top Picks
- Benefits of Having Shorter Sprints in Agile – Everything You Need to Know
- Group Discussion Tips | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- PMP Certification Cost : All you need to know
- DMAIC Process and Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Agile Scrum Vs Kanban | Know the difference
- Deming vs Juran vs Crosby
- What is Project Scope Management and Why It’s Important?
- The Basic Principles of Project Management
- Top PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2020
- Risk Management Strategies
- Roles and Responsibilities of A Scrum Master
- ROM Estimate Vs Definitive Estimate
- Guidelines for Creating and Maintaining a WBS Dictionary
- How to Become a Certified ScrumMaster?
- Top Professional Skills for 2020
- Fast Tracking Vs Crashing
- PMP Vs PRINCE2 Vs CAPM
- PMP Earned Value Management (EVM) And Formulas
- What is Certified Scrum Professional (CSM)?
- Top Leadership Theories Every Manager Should Know
- What is Deliverables in Project Management?
- How To Prepare For TOEFL
- History and evolution of the PMP Certification
- What Is Float In Microsoft Project?
- Rules to set you up for success in project
- What is Scrum Project Management?
- What Is Estimating Activity Duration in Project Management?
- What Are The PMP Terminologies Relating To Cost Knowledge Area?
- What is Project Scope Management processes?
- What Are The Types of Organization In PMP?
- Books to Beat the Scrum Master Certification
- Agile Coach Vs Agile Consultant
- What is the cost of quality in project management?
- Signs Your Career May Be Stagnation and Tips to Overcome Downturn
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) Certification
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification
- What is schedule Activity in project management?
- Why Do We Need a Project Charter?
- PMP Certification Exam Preparation Mind Map
- Why Quality Professionals Should Use Infographics In Project Management?
- Role of Earned Value Technique in Project Management
- What is Project Quality Management?
- Tools and Techniques to Estimate Project Cost
- What is a Project Charter And Project Scope in Project Management?
- Why Should You Conduct Project Status Meetings with Your Team?
- The 7 R’s of Change Management
- What Are The Categories and sources of risk in your project?
- What Is a Network Diagram in Project Management?
- What are The Types of Contracts In PMP?
- Residual Risk Vs Secondary Risk
- Impact of the stakeholders on the projects
- Effort Vs Duration Vs Elapsed Time
- Agile vs Scrum
- What Is Six Sigma Quality Assurance?
- How to Close a Project?
- What Qualifications Do You Need to be a Project Manager?
- Project Management Vs General Operations Management
- Enterprise Environmental Factors & Organizational Process Assets
- What is a project manager?
- Important Questions for PMP Certification Exam
- How is the PMP Exam changing, in 2015 & 2020?
- How To Renew Your PMP Certification?
- The Importance of Having Project Acceptance Criteria in Your Projects
- Tips for PMP Exam Preparation
- What is requirement traceability matrix RTM in Project Management?
- Poor Performance Appraisal? Here are the tips to turn any negative feedback into positive.
- How to build a successful Career in Agile and Scrum?
- Importance of Tuckman ladder model in HR management
- How To Apply For The PMP® Exam In Easy Steps
- How to Write a Six Sigma Problem Statement
- What is a lessons learned document in PMI?
- Perform Quality Assurance Vs Perform Quality Control
- How to Improve Quality Management Consistently?
- Interactive Vs Push Vs Pull Communication
- what is risk management?
- Key Appraisal Questions to Prepare For
- What are the MSP Certifications?
- What Is A Six Sigma Control Plan?
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel?
- Agile Prioritization Techniques
- Tips to Help Millennials Climb the Corporate Ladder
- What is an Issue Log?
- Advantages of PMP over MBA
- Top Successful Project Estimation Techniques
- PMP Examination Preparation – ITTO’s
- Employee Training Rewards That Actually Improve Learning
- Lean principles
- What Does It Take to Become a Successful Agile Coach
- Projects VS Programs
- The Role of Six Sigma in Manufacturing
- The Top Formulas to Memorize Before Your PMP Exam
- Roadmap to CSM (Certified Scrum Master) Certification
- What are Some Qualities of a Good Manager and Good Leader?
- How to Handle Project Monitoring and Controlling Processes?
- Top Free Agile Tools For Any Project Manager
- Risk Assessment in Project Management
- The Concept of Zero Defects in Quality Management
- The Importance of Work Packages in Project Scope Management
- How to Get Project Management Experience for PMP Certification
- Different Ways to Calculate the Estimate at Completion (EAC)
- What Is a ScrumMaster?
- What is Risk Register?
- Agile Certifications
- Top-down Approach Vs Bottom-up Approach
- Leadership Vs Management
- What is Feasibility Study and Its Importance in Project Management?
- What Is a Project Management Plan?
- The Professional Advantages of the CAPM Certification
- PRINCE2 Vs PMP
- Rita Mulcahy’s PMP Prep and PMBOK® Guide
- What is Project Cycle Management?
- What is Project and Process Metrics?
- PMBOK® Sixth Edition is Here! What Project Managers Should Know?
- CAPM Certification
- Top Project Selection Methods for Project Managers
- Free Float Vs Total Float
- What is Critical Chain Project Management?
- How to Build a Career in Project Management?
- Scrum Master or Product Owner: What Suits You Better?
- Project Documentation and its Importance
- What is Performance Reporting in the Project Management?
- Top Highest Paying Tech Jobs in India

What is ITIL ? Know about the Framework
Last updated on 30th Jan 2023, Artciles, Blog, Project Management
- In this article you will get
- What is ITIL?
- What are the ITIL concepts?
- ITIL Framework
- Conclusion
What is ITIL?
ITIL stands for an Information Technology Infrastructure Library. It is the set of best practices for delivering an IT services—it standardizes the selection, planning, delivery, and support of a IT services to maximize efficiency and keep predictable levels of service. It has a roots going back to the 1980s in United Kingdom as a government initiative, and a framework is now covered in a five books that are updated periodically.
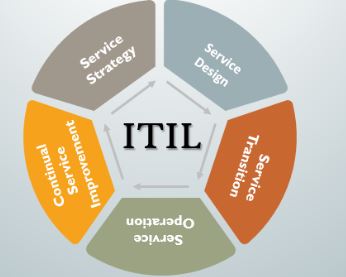
What are ITIL concepts?
ITIL has a several key principles that are realized through the five core components. Some key ITIL concepts and a principles are below :
- Delivering a maximum value to the customers.
- An Optimizing resources and capabilities.
- Offering a services that are useful and reliable.
- Planning processes with a specific goals in mind.
- Explaining a roles clearly for every task.
ITIL Framework
The ITIL framework is used to manage IT services effectively throughout an entire service lifecycle. ITIL offers a guidelines and best practices for implementing five phases of the IT service lifecycle: strategy, design, transition, operations, and continual improvement.
ITIL’s structure is organised into five basic stages or categories:
- Service Strategy
- Service Design
- Service Transition
- Service Operation
- Continual Service Improvement
1.Service Strategy
The purpose of a Service Strategy is to provide a strategy for a service lifecycle. The strategy should be in sync with the business objectives. The utility and warranty of a component are designed to be an ensure that the service is fit for purpose and fit for use, respectively. Ensuring this is important, as these are two components are what add value to a delivery of services to the customers.
a)Service Portfolio Management:The Service Portfolio is an entire set of services under management by service provider. It consists of a three major parts: Service Pipeline, Service Catalog, and Retired Services. A Service Portfolio Management organizes a process by which services are identified, described, evaluated, selected and chartered.
b)Demand Management:The Demand Management process is be concerned with understanding and influencing customer demand. It involves the User Profiles, which characterize various typical groups of users for the given service, and Patterns of a Business Activity, which represent the way users in various user profiles access a service over a course of a given time period.
c)Financial Management:Financial Management process are provides a means of a understanding and managing a costs and also opportunities associated with services. It includes the three basic activities:
Accounting:
Tracking how money is spent by the service provider.
Budgeting:
Planning how money will be spent by the service provider.
Charging:
Securing payment from a customers for a services provided.
d)Strategy Operations:Strategy Operations ensure that a services such as fulfilling user requests, resolving the service failures, fixing problems and carrying out a routine operational tasks are be performed efficiently and effectively.
2.Service Design:
The Service Design lifecycle phase is about a design of services and all supporting an elements for introduction into live environment. The Four Ps of a Service Design represent areas that are should be taken into the consideration when designing service. They are:
People:Human resources and organizational structures are required to be support the service.
Processes:Service Management processes are required to support service.
Products:Technology and the other infrastructure required to be support the service.
Partners:Third parties that offer an additional support required to support service.
There are seven processes are included in a Service Design:
a) Service Catalog Management
The Service Catalog is the subset that contains services available to the customers and users. It is often only portion of a Service portfolio visible to customers.
b) Service Level Management
Service Level Management is charged with the securing and managing agreements between customers and a service provider regarding the level of a performance (utility) and level of reliability (warranty) associated with the specific services.
c) Availability Management
The Availability Management process is concerned with a management and achievement of agreed-upon availability requirements as established in a Service Level Agreements. In ITIL, “availability” is explained as “the ability of system, service or configuration item to perform its function when be required.”
d) Capacity Management
In ITIL, “capacity” is explained as “the maximum throughput a service, system or device can handle.” Capacity Management is divided into the three major activities:
- Business Capacity Management (BCM).
- Service Capacity Management (SCM).
- Component Capacity Management (CCM).
e) Service Continuity Management
The Service Continuity Management process (ITSCM) ensures that a service provider can always provide a minimum agreed-upon levels of service.
f) IT Security Management
Confidentiality:Assurance that are asset is available only to an appropriate parties.
Integrity:Assurance that a asset has not been modified by an unauthorized parties.
Availability:Assurance that asset may be utilized when be required.
Authenticity:Assurance that are transactions and the identities of the parties to transactions are genuine.
Nonrepudiation:Assurance that are transactions, once completed, may not be reversed are without approval.
g)Supplier Management
Supplier Management is charged with an obtaining value for a money from third-party suppliers. It plays the more similar role to that of Service Level Management, but with the respect to external suppliers rather than an internal suppliers and internal/external customers. Supplier Management handles the supplier evaluation, contract negotiations, performance reviews, renewals, and terminations.
3.Service Transition
The objective of a Service Transition process is to build and can deploy IT services, making sure that are changes to services and Service Management processes are carried out in this coordinated way.
a)Change Management:The goal of this processing activity is to govern the lifetime of all modifications while causing the least amount of disturbance to IT services.
b)Evaluation:The objective of an Evaluation process is to assess main changes, such as the introduction of new service or a substantial change to an existing service before those changes are allowed to be proceed to a next phase in their lifecycle.
c)Transition Planning and Support (Project Management):This process focuses on a planning and coordinating the use of a resources to deploy a major release within a predicted cost, time and quality estimates.
d)Release and Deployment Management:The objective of this process is to be plan, schedule, and control a movement of releases to testing and live environments, ensuring that are integrity of a live environment is protected and that a correct components are released.
4.Service Validation and Testing
This process ensures that are deployed releases and the resulting services are meet customer expectations, and verifies that of IT operations are able to support a new service.
a) Service Asset and Configuration Management:The objective is to keep information about configuration items are required to deliver an IT service, including their relationships.
b) Knowledge Management:objective is to be gather, analyze, store, and share knowledge and information within an organization, improving efficiency by reducing need to rediscover a knowledge.
5.Service Operations
This stage focuses on a meeting end-users’ expectations while balancing costs and discovering any potential problems.
a)Event Management (process):objective is to make sure of configuration items (CIs) and services are constantly monitored and to filter a categorize events in order to decide a appropriate actions.
b)Incident Management (process):The objective is to manage a lifecycle of all incidents, returning an IT service to users as a quickly as possible.
c)Request Fulfilment (process):The objective is to be fulfill service requests, which in a most cases are minor changes or requests for information.
d)Access Management (process):The objective is to be grant authorized users a right to use a service while preventing access to be unauthorized users. The Access Management process essentially an executes a policies explained in Information Security Management.
e)Problem Management (process):The objective is to manage a lifecycle of all problems, preventing incidents from happening, and minimizing the impact of an incidents that cannot be prevented. Proactive Problem Management analyses incident records and uses a data collected by other IT Service Management processes to identify trends or be significant problems.
f)IT Operations Management (function):The objective is to be monitor and control the IT services and underlying infrastructure, executing day-to-day routine tasks related to a operation of infrastructure components and also applications. This includes the job scheduling, backing up and restoring, print and output management, and routine maintenance.
g)Service Desk (function):This is a point of contact between users and a service provider. A service desk be usually handles the communication with the users and also manages incidents and a service requests.
h)Application Management (function):Application Management is a responsible for managing the applications throughout their lifecycle.
i)Technical Management (function):Technical Management provides a technical expertise and support for management of an IT infrastructure.It aims to continually improve an effectiveness and efficiency of a IT processes and services in line with concept of a continual improvement adopted in ISO 2000:
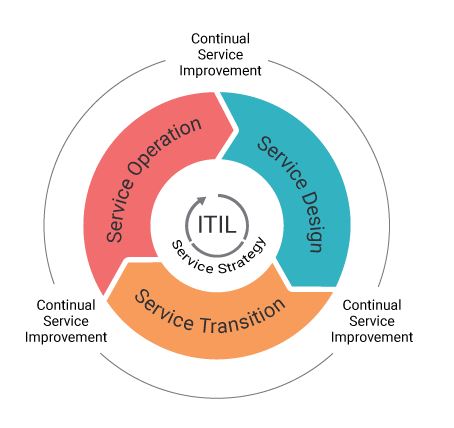
- 1.Identifying a improvement strategies.
- 2.Explaining what will be measured.
- 3.Gathering data.
- 4.Processing data.
- 5.Analyzing data.
- 6.Presenting and using an information drawn from data.
- 7.Using an information to improve.
Conclusion
ITIL is an acronym that stands for an Information Technology Infrastructure Library. It is the collection of best practices for delivering a IT services; it standardizes the planning, selection, delivery, and support of IT services to can optimize efficiency and maintain predictable service levels.