- HTML Comments Tutorial | Convert Comments into HTML Codes
- Data Structure and Algorithms Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Gradle Tutorial | For Beginners [ STEP-IN ]
- Encapsulation In Java | Complete Tutorial With Examples
- What is Release Management? | A Comprehensive Tutorial for Beginners
- OOPs Concepts in Java | Learn from Basics with Examples
- The Top Basic Tools of Quality Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Set Environment for C# – Learn How to Setup through this Tutorial
- C# Vs Java Tutorial | Overview and Key Difference
- List of IDEs to run C# Programs | Tutorial for Learning Path
- C Sharp Variables and Constants | The Ultimate Guide
- Unsafe Code in C-Sharp Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- Type Conversion Method in C# | A Complete Tutorial
- What Is Synchronization in c# Tutorial | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- Understanding Structures in C# | Learn in 1 Day FREE Tutorial
- Strings – C# Tutorial | A Definitive Programming Guide
- Static Keyword in C# Tutorial | Learn with Examples
- Stack Collection in C# Tutorial | A Definitive Guide for Beginners
- C# Sorted List Tutorial with Examples | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- C# Serialization Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Regular Expression in C# Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Reflection in C#? | Learn Now Tutorial
- Queue Collection in C# Tutorial | A Definitive Guide
- Properties in C# | The complete Tutorial
- C# Preprocessor Directives Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Polymorphism C# Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- C# Operators Tutorial | Learn Arithmetic, Comparison, Logical Concepts
- Namespaces – The complete C# Tutorial
- Multithreading in C# Tutorial | Learn With Examples and Advantages
- Methods – C# Tutorial | A Complete Programming Guide
- Linked List Implementation in C# Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Introduction to C# Tutorial | Guide for Beginners
- What is Interface in C# | A Defined Free Tutorial
- C# Inheritance Tutorial | A Complete Free Tutorial
- Indexers in C# Tutorial | A Complete Programming Guide
- HashSet Collection in C# Tutorial | Complete Guide Tutorial For Free
- Generics in C# Tutorial | Learn Generic Classes and Methods
- Creating Your First C# Program Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Basics of File Handling in C# Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- C# Exception Handling Tutorial | Learn with Best Practices
- Events – C# Tutorial | A Complete Programming Guide
- C# Enumerations Type Tutorial | Learn Everything about Enum
- Dictionary Collection in C# | Ultimate Guide to Learn [NEW & UPDATED]
- Delegates – C# Programming Guide | The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- Understanding Decision Making Statements in C# | Learn Now Tutorial
- Classes and Objects – C# Fundamentals Tutorial
- C# BitArray Collection Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Attributes in C# Tutorial | Learn to work with attributes in C#
- C# Array Tutorial | Create, Declare, Initialize
- ArrayList Collection on in C# | A Complete tutorial For Beginners
- Anonymous Methods and Lambdas – C# Tutorial | A Complete Guide
- Abstraction in C# Tutorial – Learn the Abstract class and Interface
- Game Development using Unity 3D Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- C++ Reference Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- PHP vs Python | Which Is Better For Web Development
- C++ Constructors Tutorial: Types and Copy Constructors
- JavaScript Arrays Tutorial | Complete Beginner’s Guide
- What Is Maven | Maven Tutorial For Beginners
- Spring Tutorial | Perfect Guide for Beginners
- React Hooks Tutorial for Beginners | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Python for Data Science Tutorial | Quickstart : A Complete Guide
- What is Golang? : A tutorial for beginners | Get started
- Hibernate Validator Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Postman Tutorial for Beginners: API Testing using Postman | A Complete Guide
- Akka Tutorial
- J2EE | Web Development Tutorial for Beginners
- Scala Exception Handling Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day [ STEP-IN ]
- Web development Tutorial
- Visual Studio Tutorial
- PyGame Tutorial
- Python Anaconda Tutorial
- Python Scikit-Learn Cheat Sheet Tutorial
- Mean Stack Tutorial
- Python Requests Tutorial
- Advanced Java Tutorial
- Spring Boot Microservices Tutorial
- Java Servlets Tutorial
- How to Install Pycharm
- Pycharm Tutorial
- Python Version Tutorial
- Python strings
- How to Download Python
- C Data Types Tutorial
- arrays in python
- Python While Loop Tutorial
- JAVA Tutorial
- Loops In C Tutorial
- Java File I/O Tutorial
- Variables in Python Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
- Python Pandas Cheat Sheet Tutorial
- Data Structures Cheat Sheet with Python Tutorial
- Python Tuples Tutorial
- Python If Else Statements Tutorial
- Python Functions Tutorial
- HTML Comments Tutorial | Convert Comments into HTML Codes
- Data Structure and Algorithms Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Gradle Tutorial | For Beginners [ STEP-IN ]
- Encapsulation In Java | Complete Tutorial With Examples
- What is Release Management? | A Comprehensive Tutorial for Beginners
- OOPs Concepts in Java | Learn from Basics with Examples
- The Top Basic Tools of Quality Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Set Environment for C# – Learn How to Setup through this Tutorial
- C# Vs Java Tutorial | Overview and Key Difference
- List of IDEs to run C# Programs | Tutorial for Learning Path
- C Sharp Variables and Constants | The Ultimate Guide
- Unsafe Code in C-Sharp Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- Type Conversion Method in C# | A Complete Tutorial
- What Is Synchronization in c# Tutorial | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- Understanding Structures in C# | Learn in 1 Day FREE Tutorial
- Strings – C# Tutorial | A Definitive Programming Guide
- Static Keyword in C# Tutorial | Learn with Examples
- Stack Collection in C# Tutorial | A Definitive Guide for Beginners
- C# Sorted List Tutorial with Examples | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- C# Serialization Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Regular Expression in C# Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Reflection in C#? | Learn Now Tutorial
- Queue Collection in C# Tutorial | A Definitive Guide
- Properties in C# | The complete Tutorial
- C# Preprocessor Directives Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Polymorphism C# Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- C# Operators Tutorial | Learn Arithmetic, Comparison, Logical Concepts
- Namespaces – The complete C# Tutorial
- Multithreading in C# Tutorial | Learn With Examples and Advantages
- Methods – C# Tutorial | A Complete Programming Guide
- Linked List Implementation in C# Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Introduction to C# Tutorial | Guide for Beginners
- What is Interface in C# | A Defined Free Tutorial
- C# Inheritance Tutorial | A Complete Free Tutorial
- Indexers in C# Tutorial | A Complete Programming Guide
- HashSet Collection in C# Tutorial | Complete Guide Tutorial For Free
- Generics in C# Tutorial | Learn Generic Classes and Methods
- Creating Your First C# Program Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Basics of File Handling in C# Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- C# Exception Handling Tutorial | Learn with Best Practices
- Events – C# Tutorial | A Complete Programming Guide
- C# Enumerations Type Tutorial | Learn Everything about Enum
- Dictionary Collection in C# | Ultimate Guide to Learn [NEW & UPDATED]
- Delegates – C# Programming Guide | The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- Understanding Decision Making Statements in C# | Learn Now Tutorial
- Classes and Objects – C# Fundamentals Tutorial
- C# BitArray Collection Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Attributes in C# Tutorial | Learn to work with attributes in C#
- C# Array Tutorial | Create, Declare, Initialize
- ArrayList Collection on in C# | A Complete tutorial For Beginners
- Anonymous Methods and Lambdas – C# Tutorial | A Complete Guide
- Abstraction in C# Tutorial – Learn the Abstract class and Interface
- Game Development using Unity 3D Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- C++ Reference Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- PHP vs Python | Which Is Better For Web Development
- C++ Constructors Tutorial: Types and Copy Constructors
- JavaScript Arrays Tutorial | Complete Beginner’s Guide
- What Is Maven | Maven Tutorial For Beginners
- Spring Tutorial | Perfect Guide for Beginners
- React Hooks Tutorial for Beginners | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Python for Data Science Tutorial | Quickstart : A Complete Guide
- What is Golang? : A tutorial for beginners | Get started
- Hibernate Validator Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Postman Tutorial for Beginners: API Testing using Postman | A Complete Guide
- Akka Tutorial
- J2EE | Web Development Tutorial for Beginners
- Scala Exception Handling Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day [ STEP-IN ]
- Web development Tutorial
- Visual Studio Tutorial
- PyGame Tutorial
- Python Anaconda Tutorial
- Python Scikit-Learn Cheat Sheet Tutorial
- Mean Stack Tutorial
- Python Requests Tutorial
- Advanced Java Tutorial
- Spring Boot Microservices Tutorial
- Java Servlets Tutorial
- How to Install Pycharm
- Pycharm Tutorial
- Python Version Tutorial
- Python strings
- How to Download Python
- C Data Types Tutorial
- arrays in python
- Python While Loop Tutorial
- JAVA Tutorial
- Loops In C Tutorial
- Java File I/O Tutorial
- Variables in Python Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
- Python Pandas Cheat Sheet Tutorial
- Data Structures Cheat Sheet with Python Tutorial
- Python Tuples Tutorial
- Python If Else Statements Tutorial
- Python Functions Tutorial

Java File I/O Tutorial
Last updated on 29th Sep 2020, Blog, Software Engineering, Tutorials
What is File I/O?
Java I/O stream is the flow of data that you can either read from, or you can write to.
It is used to perform read and write operations in file permanently. Java uses streams to perform these tasks. Java I/O stream is also called File Handling, or File I/O. It is available in the java.io package.
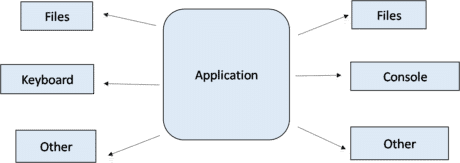
Java.io package provides classes for system input and output through files, network streams, memory buffers, etc.

Some input-output streams will be initialized automatically by the JVM and these streams are available in System class as in, out, and err variables.
- In reference refers to the default input device, i.e. keyboard.
- Out and err refers to the default output device, i.e. console.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Streams:
Streams are the sequence of bits(data).
There are two types of streams:
- Input Streams
- Output Streams
Input Streams: Input streams are used to read the data from various input devices like keyboard, file, network, etc.
Output Streams: Output streams are used to write the data to various output devices like monitor, file, network, etc.
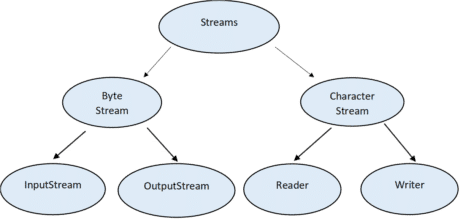
There are two types of streams based on data:
- Byte Stream: used to read or write byte data.
- Character Stream: used to read or write character data.
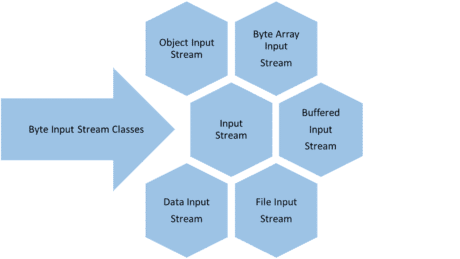
Byte Input Stream:
- These are used to read byte data from various input devices.
- InputStream is an abstract class and it is the super class of all the input byte streams.
List of Byte Input Streams:
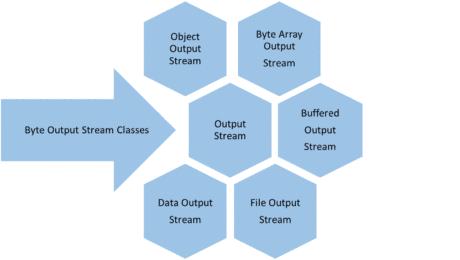
Byte Output Stream:
- These are used to write byte data to various output devices.
- Output Stream is an abstract class and it is the superclass for all the output byte streams.
List of Byte Output Streams:
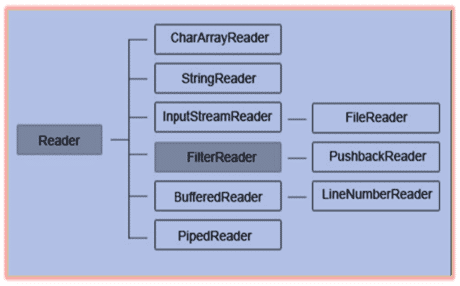
Character Input Stream:
- These are used to read char data from various input devices.
- Reader is an abstract class and is the super class for all the character input streams.
List of Character Input Streams:
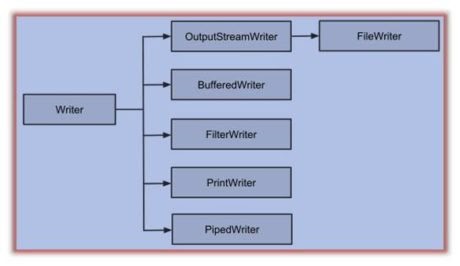
Character Output Stream:
- These are used to write char data to various output devices.
- Writer is an abstract class and is the super class of all the character output streams.
List of Character Output Stream:
Example to read contents of file:
Example 1:
- import java.io.*;
- class ReadHello{
- public static void main(String args[]){
- try{
- FileInputStream fin=new FileInputStream(“hello.txt”);
- int i=0;
- while((i=fin.read())!=-1){
- System.out.println((char)i);
- }
- fin.close();
- } catch(Exception e){
- system.out.println(e);}
- }
- }
- }
- Refer write file example to see contents of hello.txt
Output:
Hello ACTE
Example 2:
- import java.io.*;
- public class ReadFileDemo {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- BufferedReader br = null;
- BufferedReader br2 = null;
- try{
- br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(“B:\\myfile.txt”));
- String contentLine = br.readLine();
- while (contentLine != null) {
- System.out.println(contentLine);
- contentLine = br.readLine();}
- }
- catch (IOException ioe)
- {
- ioe.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
Output:
Now you know how to create & read
Example to write in a file:
Example 1:
- import java.io.*;
- public class ACTE{
- public static void main(String args[]){
- try{
- FileOutputstream fos=new FileOutputStream(“hello.txt”);
- String i=”Hello ACTE “;
- byte b[]=i.getBytes();/ /converting string into byte array
- fo.write(i);
- fo.close();
- }
- catch(Exception e){
- system.out.println(e);}
- }
- }
This will create a file hello.txt
Output:
Hello ACTE
Example 2:
- import java.io.*;
- public class write ACTE First{
- public static void main(String args[]){
- File file=new File(“visiters.txt”);
- try{
- PrintWriter output=new PrintWriter(file);
- output.println(“Hello Visitors! Welcome to ACTE”);
- output.close();
- } catch(IOException ex){ System.out.println(“Error:”+ex);}
- }
- }
Similarly, different subclasses can also be used to read and write.
Java I/O Classes
Below is the list of classes that are used to perform the I/O operations:
1. FileInputStream:
In Java, FileInputStream class is used to read the data such as audio, video, images, etc in byte format. i.e. this class simply read the bytes from the source file.
2. FileOutputStream:
In Java, FileOutputStream class works opposite of FileInputStream class, it writes the data such as audio, video, image, etc in a byte and character format. i.e. this class writes the data to file.
3. DataInputStream:
This class allows the application to read the primitive data from the input stream in a machine independent way.
4. DataOutputStream:
This class allows an application to write the primitive data to the output stream in a machine independent way.
5. BufferedReader:
This class allows to read the text from a character based input stream in line by line format by inheriting the reader class.
6. BufferedWriter:
In java, this method provides buffering to write the instances by inheriting the writer’s class.
7. BufferedInputStream:
This class is used to read the data from the input stream. The internal buffer array is initialized automatically once the BufferedInputStream is created. When bytes from the stream are read, the internal buffer is automatically refilled from the source input stream.
8. BufferedOutputStream:
This class is used to buffer the output stream. To store the data, this class uses an internal buffer. i.e. this class adds buffer in OutputStream.
9. FilePermission:
This class is used to give the appropriate permission to file or directory, these permissions are related to the file path. File path can be of two types
10. D:\\IO\\:
This path indicates that the permission is associated with all sub files and directories respectively.
11. D:\\IO\\*:
This path indicates that the permission is associated with all files and directories within this specified directory except subdirectories.
12. Console:
This class is internally attached to the system console, used to get the input from the console by providing various methods. Console class can read both text and password where the text will be displayed to the user and the password will not be displayed (can be shown in star format).
13. Scanner:
This class in inbuilt, found in java.util package. This class is used to read the data from the keyboard, allow to get the input from the user in primitive data types (int, float, long, double, string, etc) To get the scanner class to read the input from a user, we need to pass the input stream i.e. System.in.
14. FilterInputStream:
This class implements the InputStream and uses various subclasses such as BufferedInputStream and DataInputStream to provide additional functionality. It simply overrides all InputStream methods.
15. FilterOutputStream:
This class works opposite of FilterInputStream. It implements OutputStream and uses various subclasses such as BufferedOutputStream and DataOutputStream to provide additional functionality. It simply overrides all OutputStream methods.
16. SequenceInputStream:
As the name suggests, this class read the data in sequential format i.e. one by one. This class starts reading the data from the first one until the end of the file reached, then it starts reading the second one, then third, and so on.
17. RandomAccessFile:
This class is used to access the random file, this random access file is a large array of bytes. It is commonly used for reading and writing to a random file, read and write operations are performed using a cursor
18. InputStreamReader:
This class acts as a bridge that joins the byte stream to the character stream. It first reads byte and then decodes it into character using a specified charset.
19. OutputStreamWriter:
This class works opposite of InputStreamReader. It converts the character stream to the byte stream. It first read the character and then decodes it into byte using a specified charset.
20. StringReader:
This class is a character stream that takes an input string and converts it into a character stream using reader class.
21. StringWriter:
This class is a character stream that takes output string which can be used to construct a string. It inherits the writer class.
22. FileReader:
FileReader is a character oriented class used to read the data from the specified file and return the data in byte format.
23. FileWriter:
FileWriter is a character oriented class used to write the data to a specified file.
24. ObjectStreamClass:
This class acts as a serialization description of classes. It stores the name and serialVersionID of the class.
25. ObjectStreamField:
In Java, this class is used to initialize the serializable filed of class.
26. ByteArrayInputStream:
This class uses an internal buffer to read the byte array from the input stream.
This class is used to write the data into a byte array.
CONCLUSION
Input and Output processes using standard java methods are somewhat more complex as compared to java I/O. By using, understanding and experimenting with each of the concepts mentioned here, you will be able to perform some of the most common Input-Output operations on the java applications.

