
Oracle SOA
Last updated on 12th Oct 2020, Blog, Oracle, Tutorials
Welcome to the Tutorials of Oracle SOA 11g. The intent of these tutorials is to provide you in depth understanding of Oracle SOA 11g suite. In these tutorials, we will cover topics such as installation of Oracle SOA 11g, configuring adapters, creating business rules and SOA projects. We will also discuss in detail about security in Oralce SOA 11g, and different protocols that we use to connect to partner systems
In addition to Oracle SOA 11g Tutorials, we will look at common interview questions, how to tutorials, issues and their resolutions.
The pace of new business projects continues to grow—from increasing customer self-service to seamlessly connecting all your back office and in-the-field applications. At the same time, there is an urgency to mobile-enable existing applications, integrate with the cloud, and begin development on the latest trend of connecting Internet of Things (IoT) devices to your existing infrastructure. When companies address each of these new integration challenges independently, using a patchwork of niche specialty integration toolsets, the original goals of faster business integration, increased application infrastructure flexibility, and reduced costs are no longer achievable.
This is why Oracle SOA Suite 12c was developed: to simplify IT by unifying the disparate requirements of mobile, cloud, and IoT integration into one unified and standards-based platform.
- Oracle SOA Suite 12c enables you to
- Reduce time to market for new project integration
- Reduce integration cost and complexity
- Efficiently manage business and technology change
- Provide end-to-end solution monitoring with root cause analysis
- Gain increased visibility to quickly react to business events
- Ensure high availability and scalability for your business infrastructure
What is Oracle?
Oracle database is a relational database management system. It is known as Oracle database, OracleDB or simply Oracle. It is produced and marketed by Oracle Corporation.
Oracle database is the first database designed for enterprise grid computing. The enterprise grid computing provides the most flexible and cost effective way to manage information and applications.
Different editions of Oracle database
Following are the four editions of the Oracle database.
- Enterprise Edition:
It is the most robust and secure edition. It offers all features, including superior performance and security.
- Standard Edition:
It provides the base functionality for users that do not require Enterprise Edition’s robust package.
- Express Edition (XE):
It is the lightweight, free and limited Windows and Linux edition.
- Oracle Lite:
It is designed for mobile devices.
The Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation is the largest software company in the field of database business. Its relational database was the first to support SQL which has since become the industry standard.
Oracle database is one of the most trusted and widely used relational database engines. The biggest rival of Oracle database is Microsoft’s SQL Server.
Why to use SOA?
- SOA is widely used in market which responds quickly and makes effective changes according to market situations.
- The SOA keep secret the implementation details of the subsystems.
- It allows interaction of new channels with customers, partners and suppliers.
- It authorizes the companies to select software or hardware of their choice as it acts as platform independence.
Features
- SOA uses interfaces which solves the difficult integration problems in large systems.
- SOA communicates customers, providers and suppliers with messages by using the XML schema.
- It uses the message monitoring to improve the performance measurement and detects the security attacks.
- As it reuses the service, there will be lower software development and management costs.
Challenges in SOA testing
- Lack of interfaces for Services
- Testing process spans across multiple systems thus creating complex data needs
- The application is a collection of various components which tends to change. The need for Regression Testing is more frequent.
- Due to Multilayer architecture, it is difficult to isolate defects.
- Since the service will be used in different interfaces, it is difficult predicting load, hence making performance test planning cumbersome.
- SOA is a collection of heterogeneous technologies. Testing of an SOA application requires people with different skill sets which in turn increase the planning and execution costs.
- Since the application is an integration of multiple services, security testing has its own share of woes. Validation of authentication and authorization is pretty much difficult.
What is SOA middleware?
A service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural pattern in computer software design in which application components provide services to other components via a communications protocol, typically over a network. The principles of service-orientation are independent of any vendor, product or technology.
What is a service oriented architecture?
A Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) in computer software design is an architectural style where in services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network.
What is Application Integration Architecture?
In computing, Application Integration Architecture (AIA) is an integration framework produced by Oracle Corporation. Standards-based, AIA has pre-built common object definitions and services. Oracle AIA is built on Oracle Fusion Middleware’s SOA and Business Process-Management (BPM) products.
What is a Web service in SOA?
A web service is an example of an SOA with a well-defined set of implementation choices. In general, the technology choices are SOAP and the Web Service Definition Language (WSDL); both XML-based. WSDL describes the interface (the “contract”), while SOAP describes the data that is transferred.
Index
- Oracle SOA ATA (Application Integration architecture)
- Oracle SOA Sample Project Creation
- Oracle SOA customizations
- How to find Oracle SOA Port Numbers
- OSB [oracle service bus] in SOA
- How to find Oracle SOA Port Numbers
- Oracle SOA customizations
- Oracle SOA Sample Project Creation
- Oracle SOA ATA (Application Integration architecture)
- Oracle SOA EDN (Event Delivery Network)
- Oracle SOA PO [Purchase orders] process
- Oracle SOA Rejection handles
- Oracle SOA Business rule engine [BRE]
- Deference’s b/w 10g and 11g In Oracle SOA
- ANT SCRIPT In Oracle SOA
- How to provide a Security in Oracle SOA
- JMS (Java messaging service) in Oracle SOA 11g
- How to work with FTP (File transfer protocol) in Oracle
- What is DVM(Static value mapping) in Oracle SOA
- what is Project fault – policies process in Oracle SOA
- How to implement FLOW ACTIIVTY in Oracle SOA
- How to Create PICK ACTIVITY In Oracle SOA
- XSLT – Operations / Conditions in Oracle SOA
- DB Adapter configuration-11g in Oracle SOA
- Oracle SOA 11g Installation (Partition)
- Oracle SOA URL’S
- Correlation(10g) in Oracle SOA
- Transaction in Oracle SOA
- Explination of Oracle SOA ESB (mediator -11g)
- How to configure DB Adapters in Oracle SOA
- How to Configuration JMS Adapter in Oracle SOA
- Introduction to XML in Oracle SOA
- How to give a JDBC port path in Oracle SOA
- Explaination of Oracle SOA Adapters
- SOA TOPICS
- Oracle SOA 10g – Introduction
- Deploying SOA Applications
- Configuring Log Files in Oracle SOA
SOA Features
Service
Service is the essential concept of SOA. The idea of a service was developed in the world of business.
The use of services provides major benefits:
- In contrast to the use of large applications, which tend to be “information silos” that cannot readily exchange information with each other, the use of finer-grained software services gives freer information flow within and between enterprises. Integrating major applications is often expensive. SOA can save integration costs.
- Organizing internal software as services makes it easier to expose its functionality externally. This leads to increased visibility that can have business value as, for example, when a logistics company makes the tracking of shipments visible to its customers, increasing customer satisfaction and reducing the costly overhead of status enquiries.
- Business processes are often dependent on their supporting software. It can be hard to change large, monolithic programs. This can make it difficult to change the business processes to meet new requirements or to take advantage of new business opportunities. A service-based software architecture is easier to change
- it has greater organizational flexibility, enabling it to avoid penalties and reap commercial advantage. (This is one of the ways in which SOA can make an enterprise more “agile”.)
The service concept also makes possible further features of SOA.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Service Re-Use
Clear service descriptions are a starting point for service re-use, which can provide another major benefit of SOA:
- Using existing software modules rather than writing new ones means lower development and testing costs and – in many cases an even greater saving – lower maintenance costs.
Messaging
You can have an SOA in which software services invoke each other directly; for example, by programming-language function calls. But, in many SOAs, the software services always invoke each other by exchanging messages, even where they are executing on the same processor. This might seem to be an additional overhead but, if the services are loosely-coupled (as they should be), then the number of message exchanges is relatively small, and the overhead is reasonably low.
Consistent use of messaging provides a key benefit:
- Services can very easily be moved between computer systems within the enterprise, and it is reasonably easy to use externally-provided services to replace internal ones, and vice versa. Which services handle which messages can be changed rapidly to meet changing business needs, or to tune performance. In short, messaging provides significant configuration flexibility.
Having a central mechanism by which all messages are exchanged facilitates monitoring, control, transformation, and security of messages.
Message Monitoring
Message monitoring can provide three key benefits:
- Monitoring message streams between business activities, and analyzing them to obtain information about those activities, is known as business activity monitoring. It can be a valuable source of business intelligence.
- Monitoring message volumes and response times is a valuable source of performance measurement. Service contracts often include performance clauses. Performance measurement enables service designers to put realistic clauses into the contracts, and enables systems managers to verify that those clauses are being met.
- Monitoring messages and message volumes can provide security attack detection, including detection of denial-of-service attacks as well as of attacks in particular messages.
Message Control
Message control can provide:
- Application of management policy; for example, by restricting a service consumer to a contracted service volume, or giving priority to certain kinds of message
- Application of security policy; for example, by controlling access to certain services, or rejecting messages that could damage the enterprise systems or the enterprise itself (e.g., messages containing viruses that could destroy data)
Message Transformation
Message transformation can provide:
- Data translation – the conversion of data from one format to another through automated field mapping.
- Data conversion by specially-written software is expensive. The use of generic data translators can bring significant cost saving.
Message Security
Message security can include:
- Data confidentiality through encryption of messages
- Data integrity through addition of cryptographic integrity-check fields
Security is a complex area that is of crucial importance to enterprises. The ability to encrypt and apply integrity checking to messages in transit can be a valuable component of an overall security strategy.
Complex Event Processing
In SOA, CEP is often used, not only for external events, but also to detect patterns in the flow of messages between services. When used in this way, it becomes an extension of message monitoring.
CEP provides the following benefits:
- Simplification of software structure – by removing functionality that is not business-related from the business software services
- Ability to adapt quickly to different external environments – by concentrating in one place the logic that relates environmental events to business events
- Improved manageability and security – when used with performance measurement and security event detection
Service Composition
Service composition is the putting together of a number of simple services to make a more complex one. For example, a “product sale” web service could be composed of simpler “product selection”, “shopping cart review”, “payment method selection”, “credit card payment”, and “invoice payment” services. Service composition provides a key benefit:
- Ability to develop new function combinations rapidly
For example, if it is decided that the product sale service should cater for a new method of payment – “Internet cash” – this can be done by developing a new “Internet cash payment” service, and including it in the composition.
Service Discovery
When a program uses a software service, the identity of that service can be explicitly given in the program code. For example, where services are implemented as Java objects, their methods can be invoked by name by user programs. Where messaging is used, the destinations of the messages can be explicitly named at programming time. This is called hard-wiring of service connections.
Hard-wiring is a simple approach, but it has limitations. A different and much more flexible approach is service discovery. In this approach, the identity of the target service is not known at programming time, but is discovered at run time. The user program finds target services that meet its requirements, and chooses one of them.
The benefits of service discovery are:
- Ability to optimize performance, functionality, and cost – by selecting component services by these criteria
- Easier introduction of system upgrades – an upgraded service can be made available for selection in parallel with the one that it replaces, which can then be withdrawn
Asset Wrapping
An important feature of SOA is the recognition that the assets perform services, and the development of software façades that provide access to these assets and have interfaces that are in the same form as the interfaces to other software services of the enterprise. This is called asset wrapping.
When an enterprise adopts an SOA, asset wrapping is typically applied to existing application software packages. This provides a significant benefit:
– Ability to integrate existing assets – which means that the value of an enterprise’s existing assets is preserved, the cost of developing or acquiring replacements is avoided, and there is a smooth migration path from the old architecture to the new one
Virtualization
A façade can present to the consumer a virtual asset that does not correspond to the real underlying assets. This technique is called virtualization. Virtualization can be used to enable programs that were written to use one asset to be executed with a different asset. For example, there are so-called “hypervisors” that can provide different operating system environments to programs running on a single CPU. But in the context of SOA it is more commonly used to create virtual assets that are functionally similar to the underlying assets. This can deliver two benefits:
- Improved reliability – through redundant operation of the underlying assets, so that one can take over when another fails or is withdrawn for maintenance
- Ability to scale operations to meet different demand levels – through dynamically increasing or reducing the number of underlying assets that support a real asset, as demand rises and falls
Model-Driven Implementation
Model-driven implementation refers to the automatic realization of a system or application from an abstract model. Where the model starts at a high level of architectural abstraction, it is usually referred to as Model-Driven Architecture (MDA).
SOA lends itself particularly well to model-driven implementation, because it is based on a high-level software module concept (the service) for which there are good definition and interface standards.
Model-driven implementation provides:
- The ability to develop new functions rapidly – an important form of agility
In SOA, model-driven implementation can be applied to service compositions as well as to software services.
Benefits of SOA
- Improves developer productivity through easy-to-use, drag-and-drop features for rapidly assembling metadata-driven business applications
- Enables highly flexible and responsive applications through event-driven SOA
- Delivers visibility, flexibility, and speed through best-of-breed tools that provide industry-leading functionality
- Enables organizations to adopt suite components incrementally to suit the needs of specific projects.
SOA service categories
The service is a kind of operation which is well defined, self contained that performs a specific task.
The following figure shows SOA service categories:
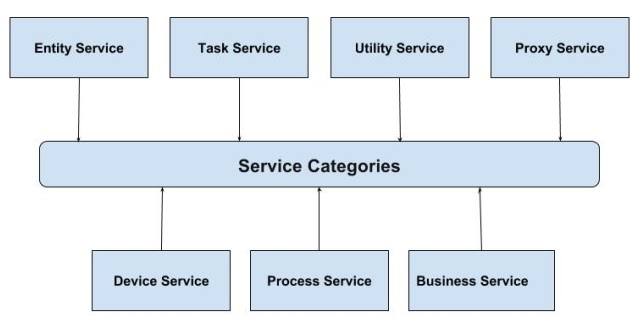
The service can be categorized into following ways:
Entity Service
The entity services include entities of customer such as purchase order, insurance policy, invoice of order, ordered date etc in which you can perform CRUD operations such as Create, Read, Delete and Update on the entities. These services provide information of the business process stored in the databases and handle the business entities.
Task Service
The task service adds the business logic to other services and due to its focus on business entity, it contains low amount of reusability. Task services provide operations on more than one entity such as customer purchase order, creating purchase order number, validating customer details etc. A service is called as task service when it needs to access the multiple entities.
Utility Service
The utility services are technology oriented services which are used to build larger and higher level services and provides other capabilities which are unrelated to the message transfer. The utility services provide reusable functions such as event logging, creating unique number and notification etc to the other functional domains. These services contain small, closely packed services which are used as building blocks in service oriented system.
Proxy Service
The proxy services contain the services which act as connection between members of the service oriented system and conflict subsystem. The device and process services lie under this type of services. Sometimes services which are defined under proxy services are called as gateway services.
Device Service
The device service is a kind of proxy service which is referred as hardware device and used to communicate between other services. The device service does not include the API which is not well suited with the service oriented system.
Process Service
The device service is also a kind of proxy service which acts as interpreter between application and service oriented system members. This service creates and arranges the application services to implement the business processes.
Business Service
Business services are also known as controller service which provides business functions for the completion of the business process and are flexible services that changes the business needs. These services develop the business applications that automate the business process such as managing the customer service, shipping the customer product etc.
SOA Testing Methods
1) Business scenario driven data based testing,
- Various business aspects related to the system should be analyzed.
- Scenarios should be developed based on the integration of
-
- Various Web services of the application
- Web services and application.
- Data set up should be done based on the above scenarios.
- Data set up should be done so as to cover end to end scenarios as well.
2) Stubs
- Dummy interfaces will be created to test services.
- Various inputs can be provided through these interfaces, and the outputs can be validated.
- When an application uses an interface to an external service, which is not under test (third party service), a stub can be created during Integration Testing.
3) Regression testing
- Regression Testing on the application should be done when there are multiple releases so as to ensure the stability and availability of the systems.
- A comprehensive regression test suite will be created covering the services which form an important part of the application.
- This test suite can be reused in multiple releases of the project.
4) Service Level Testing
Service Level Testing includes testing the component for functionality, security, performance and interoperability.
Each and Every Service needs to be first tested independently.
5) Functional Testing
Functional Testing should be done on each service to
- Ensure that service delivers the right response to each request.
- Right errors are received for requests with Invalid data, bad data, etc.
- Check for each request and response for each and every operation the service has to perform in run time.
- Validate the fault messages when an error occurs at the server, client or network level.
- Validate that the responses received are in the right format.
- Validate that the data received on the response corresponding to the data requested.
6) Security Testing
Security testing of the web service is an important aspect during service level testing of the SOA application; this ensures the safety of the application.
The following factors need to be covered during testing:
- Industry Standard defined by WS-Security testing should be abided by the Web Service.
- Security measures should work flawlessly.
- Encryption of data and Digital signatures on the documents
- Authentication and Authorization
- SQL Injection, Malware, XSS, CSRF, other vulnerabilities are to be tested on the XML.
- Denial of Service attacks
7) Performance Testing
Performance Testing of the service needs to be done since the services are reusable and multiple applications might be using the same service.
The following factors are considered during testing:
8) Performance and functionality of the service need to be tested under heavy load.
- The performance of the service needs to be compared while working individually and within the application, it is coupled with.
- Load testing of service should be performed
-
- to verify response time
- to check for bottlenecks
- to verify the utilization of CPU and memory
- to predict scalability
9) Integration level testing
- Service level testing ensures proper working of only the services individually, it does not guarantee the working of the coupled components.
- Integration Testing is done focusing mainly on the interfaces.
- This phase covers all the possible business scenarios.
- The Non-Functional testing of the application should be done one more time in this phase. Security, compliance, and Performance Testing ensure the availability and stability of the system in all aspects.
- The communication and network protocols should be tested to validate the consistency of the data communication between the services.
10) End to End testing
This phase ensures that the application confirms to the business requirements both functionally and non-functionally.
The below items are ensured to be tested during the end to end testing
- All services working as expected after integration
- Exception handling
- User Interface of the application
- Proper data flow through all the components
- Business process
Challenges in SOA testing
- Lack of interfaces for Services
- Testing process spans across multiple systems thus creating complex data needs
- The application is a collection of various components which tends to change. The need for Regression Testing is more frequent.
- Due to Multilayer architecture, it is difficult to isolate defects.
- Since the service will be used in different interfaces, it is difficult predicting load, hence making performance test planning cumbersome.
- SOA is a collection of heterogeneous technologies. Testing of an SOA application requires people with different skill sets which in turn increase the planning and execution costs.
- Since the application is an integration of multiple services, security testing has its own share of woes. Validation of authentication and authorization is pretty much difficult.
SOA User Interface
Service-oriented applications mostly focus on the interaction between machines. However, in applications, the interaction between user and machine also plays an important role. A user can act as a service provider so that he can set SOA User Interface(SOAUI) design into an overall system design where the user interaction workflow is a part of system workflow.
The SOA User Interface follows MVC (Model View Controller) architectural pattern. SOA applications provide the model layer, and User Interfaces occupy the view layer.
The environments hosting components in the SOA approach are abstracted as containers that provides infrastructure services. From a User Interface view, below are the containers for hosting client-side UI components:
- Basic Web browser.
- Web browser augmented with Java™Script and dynamic HTML.
- IBM Workplace™ Client Technology™ — the Eclipse-rich client plus native IBM WebSphere® Application Server client support.
By supporting technologies like servlets, JavaServer Pages (JSP), JSP Tags etc, the above containers can be expanded.
The user that interacts with a business process consists of initiating and awaiting the result of a process. It is important for a human to involve in a process cycle where processes rarely run completely and automatically. In such environment, WS-Human Task can fulfil this requirement.
A standardize API can be used to fill a mailbox with tasks that was defined for a workflow service. For example, during a process cycle, if input of addtional data is required, the process establishes correct actor and places the task in their mailbox through the task service. This process resumes its work in the background and the users recieve the entries in their mailbox by processing the pending tasks sequentailly.
SOA Testing Tools
There are many tools available in the market to help testers in testing SOA applications. Few of them are listed below.
1) SOAP UI
“SOAP UI” is an open source Functional testing tool for Services and API Testing.
- Desktop application
- Supports multiple protocols – SOAP, REST, HTTP, JMS, AMF, JDBC
- Web services can be developed, inspected and invoked.
- Can also use for load testing, Automation Testing, and security testing
- Stubs can be created by MockServices
- Web Service requests and tests can be generated automatically through its web service client.
- Have inbuilt reporting tools
- Developed by SmartBear
2) iTKO LISA
“LISA” is a product suite which provides a functional testing solution for distributed systems like SOA.
- Can also use for regression, integration, load and Performance Testing.
- Developed by iTKO (CA Technologies)
- Can be used to design and execute tests.
3) HP Service Test
“Service Test” is a functional testing tool, which supports both UI and shared services testing
- Both functional and performance test of services can be done by a single script.
- Integrated with HP QC.
- The massive amount of service and data can be managed.
- Supports interoperability testing by simulating JEE, AXIS, and DotNet client environments.
- Developed by HP.
4) Parasoft SOA Test
SOA Test is a testing and analysis tool suite developed for API and API applications testing.
- Supports Web Services, REST, JSON, MQ, JMS, TIBCO, HTTP, XML technologies.
- Functional, Unit, Integration, Regression, Security, Interoperability, Compliance and Performance Testing are possible.
- Stubs can be created using Parasoft Virtualize, which are intelligent than SOAP UI.
- Developed by ParaSoft
securing SOA
Most importantly, securing Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) is necessary to make sure that the services and applications run safely. For many reasons, including service exposures and loose coupling of components, securing SOA is essential because sometimes, exposed services becomes unprotected to attacks.
SOA Attacks
There are different types of attacks to which SOA environment may become unprotected, espcially if it was implemented using web service technology. Most of the people all around the world uses both SOA and web services which are rapidly developing areas, as a result they become more complex and open to attacks. On SAO and web services, most of the attacks takes place on the application service layer since web services communicate using XML and soap messages.
Following is a list of attacks in SOA:
- Injection Attacks:
This attack occurs when no validation on the user input is performed and no separation is done between user input and application. For example, SQL injection, XML injection etc.
- Schema Poisoning Attack:
This attack when occurs, modifies, replaces or even damages XML schemeas that provides the structure of XML documents.
- Denial Of Service Attacks (DoS):
This attack when occurs, do not change the service or its behaviour but can block the use of the service.
Research Contributions
The main contributions are as follows:
- Providing an integrity for SOA that provides enough conditions for securing data integrity.
- Implementing testbed for SOA and setting environment of specification based IDS.
- Proposing intrusion detection system for SOA networks that are capable of detecting intrusions affecting behaviour of services.
- Recommending SOA testbed where SOAP messages can be monitored.
Advantages
- SOA allows reuse the service of an existing system alternately building the new system.
- It allows plugging in new services or upgrading existing services to place the new business requirements.
- It can enhance the performance, functionality of a service and easily makes the system upgrade.
- SOA has capability to adjust or modify the different external environments and large applications can be managed easily.
- The companies can develop applications without replacing the existing applications.
- It provides reliable applications in which you can test and debug the independent services easily as compared to large number of code.
Disadvantages
- SOA requires high investment cost (means large investment on technology, development and human resource).
- There is greater overhead when a service interacts with another service which increases the response time and machine load while validating the input parameters.
- SOA is not suitable for GUI (graphical user interface) applications which will become more complex when the SOA requires the heavy data exchange.
Conclusion
The Oracle Scheduler is a new job management utility introduced in Oracle Database 10g. It is far superior to its predecessor, DBMS_JOB. Using the Scheduler you can schedule both PL/SQL code units (stored procedures and anonymous blocks) and operating system executables for execution. It allows you to use an almost English-like notation to specify a calendar showing the desired times of execution. All Scheduler-related activities are available as APIs in the DBMS_SCHEDULER built-in package. In addition, Enterprise Manager in Oracle Database 10g provides a graphical user interface that may be used to manage job scheduling, making scheduling extremely easy even for those using the utility for the first time. The Scheduler allows you to define a named schedule that can be called independently to execute an action, which may be a complete executable name or a named program that references the executable. Jobs may also be subject to Oracle’s resource management framework, which may be used to control the amount of resources (e.g., CPU, parallel query servers) available to individual jobs. In summary, the Scheduler is the only job management system you will need for any jobs except those that definitely need to be de-linked from the database—for example, for starting the database itself.You created an SOA composite application using the following components:
- Oracle Mediator
- Oracle BPEL Process Manager
- Human Oracle Human Workflow (using a human task)
- Oracle Business Rules
- Oracle Messaging Service
