- Understanding Agile Methodologies and Principles | A Complete Tutorial
- What is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)? | Learn Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Traditional Project Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Complete Guide [STEP-IN]
- Total Productive Maintenance Tutorial | Get an Overview
- Virtual Team Tutorial – Learn Origin, Definition and its Scope
- The Rule of Seven in Project Management – Tutorial
- Make or Buy Decision – A Derivative Tutorial for Beginners
- What is Halo Effect? | Learn More through Tutorial
- Balanced Score Card Tutorial | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Supply Chain Management? | Tutorial with Examples
- Succession Planning Tutorial | A Complete Guide with Definitions
- What is Structured Brainstorming? | Quickstart & Learn the Tutorial
- Stress Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- What is a Statement of Work? | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Stakeholder Management? – The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- How to Create a Staffing Management Plan? | Learn from Tutorial
- What is Resource Leveling? | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Requirements Collection Tutorial: Gather Project Needs
- What Is a RACI Chart? | Learn with Example & Definitions
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control: Tutorial with Definitions & Differences
- Project Workforce Management Tutorial | A Definitive Guide
- Project Time Management Tutorial: Strategies, Tips & Tools
- Project Management Success Criteria Tutorial | Understand and Know More
- Identify Risk Categories in Project Management | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Project Records Management Tutorial | Quickstart -MUST READ
- Project Quality Plan (PQP) Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Project Portfolio Management | A Defined Tutorial for Beginners
- Goals of a Project Manager Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Project Management Triangle Tutorial: What It Is and How to Use
- Project Management Tools Tutorial | Learn Tools & Techniques
- What is PMO (project management office)? | A Complete Tutorial from Scratch
- Project Management Lessons | Learn in 1 Day [ STEP-IN ]
- What is a Project Kickoff Meeting? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Project Cost Management Tutorial | Steps, Basics, and Benefits
- Types of Contracts in Project Management | Learn with Examples
- Project Activity Diagram | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- What is Project Procurement Management? | Tutorial Explained
- Procurement Documents Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Process-Based Project Management Tutorial: A Beginner’s Guide
- What Is PRINCE2 Project Management? | A Definitive Tutorial for Beginners
- Effective Presentation Skills – Learn More through Tutorial
- Powerful Leadership Skills Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- PERT Estimation Technique Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Pareto Chart Tool Tutorial | Learn Analysis, Diagram
- Organizational Structure Tutorial: Definition and Types
- Negotiation Skills for Project Management | Learn from the Basics
- Monte Carlo Analysis in Project Management Tutorial | A Perfect Guide to Refer
- Effective Management Styles Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Management by Objectives (MBO) Tutorial | Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Leads, Lags & Float – Understand the Difference through Tutorial
- What is Knowledge Management? – Tutorial Explained
- What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT)? | Know More through Tutorial
- Gantt Chart Tool Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Extreme Project Management Tutorial – Methodology & Examples
- Introduction for Event Chain Methodology Tutorial | Guide For Beginners
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | A Complete Tutorial for Beginners
- What Is Design of Experiments (DOE)? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Decision Making Tutorial – Know about Meaning, Nature, Characteristics
- Critical Path Method Tutorial | How to use CPM for project management
- What is Critical Chain Project Management? | A Complete Tutorial
- What is Conflict Management? | Learn the Definition, styles, strategies through Tutorial
- Effective Communication Skills Tutorial – Definitions and Examples
- Communication Models Tutorial – Project Management
- Methods of Communication Tutorial | A Complete Learning Path
- Communication Management Tutorial | Know more about Plans & Process
- What are Communication Channels? | Learn Now Tutorial
- Communication Blocker Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Cause and Effect Diagrams Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- What is Benchmarking? | Technical & Competitive Tutorial
- Seven Processes of Prince2 Tutorial | Everything you Need to Know
- Design Thinking Tutorial – Quick Guide For Beginners
- What is Performance Testing | A Complete Testing Guide With Real-Time Examples Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Agile Scrum Tutorial
- PMI-RMP Plan Risk Management Tutorial
- Designing the Blueprint Delivery Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Program Benefits Management Tutorial
- Continuous Improvement – Agile Value Stream Mapping
- Program Organization Tutorial
- Risk and Issue Management Tutorial
- Project Integration Management Tutorial
- Planning and Control Tutorial
- Program Management Principles Tutorial
- program strategy Alignment Tutorial
- PMP Tutorial
- Program Governance Tutorial
- Program Life Cycle Management Tutorial
- PMP Exam Preparation Tutorial
- PMI-PgMP Tutorial
- Agile Methodologies and Frameworks- Kanban and Lean Management Tutorial
- JIRA Tutorial
- Primavera P6 Tutorial
- Understanding Agile Methodologies and Principles | A Complete Tutorial
- What is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)? | Learn Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Traditional Project Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Complete Guide [STEP-IN]
- Total Productive Maintenance Tutorial | Get an Overview
- Virtual Team Tutorial – Learn Origin, Definition and its Scope
- The Rule of Seven in Project Management – Tutorial
- Make or Buy Decision – A Derivative Tutorial for Beginners
- What is Halo Effect? | Learn More through Tutorial
- Balanced Score Card Tutorial | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Supply Chain Management? | Tutorial with Examples
- Succession Planning Tutorial | A Complete Guide with Definitions
- What is Structured Brainstorming? | Quickstart & Learn the Tutorial
- Stress Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- What is a Statement of Work? | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Stakeholder Management? – The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- How to Create a Staffing Management Plan? | Learn from Tutorial
- What is Resource Leveling? | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Requirements Collection Tutorial: Gather Project Needs
- What Is a RACI Chart? | Learn with Example & Definitions
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control: Tutorial with Definitions & Differences
- Project Workforce Management Tutorial | A Definitive Guide
- Project Time Management Tutorial: Strategies, Tips & Tools
- Project Management Success Criteria Tutorial | Understand and Know More
- Identify Risk Categories in Project Management | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Project Records Management Tutorial | Quickstart -MUST READ
- Project Quality Plan (PQP) Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Project Portfolio Management | A Defined Tutorial for Beginners
- Goals of a Project Manager Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Project Management Triangle Tutorial: What It Is and How to Use
- Project Management Tools Tutorial | Learn Tools & Techniques
- What is PMO (project management office)? | A Complete Tutorial from Scratch
- Project Management Lessons | Learn in 1 Day [ STEP-IN ]
- What is a Project Kickoff Meeting? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Project Cost Management Tutorial | Steps, Basics, and Benefits
- Types of Contracts in Project Management | Learn with Examples
- Project Activity Diagram | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- What is Project Procurement Management? | Tutorial Explained
- Procurement Documents Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Process-Based Project Management Tutorial: A Beginner’s Guide
- What Is PRINCE2 Project Management? | A Definitive Tutorial for Beginners
- Effective Presentation Skills – Learn More through Tutorial
- Powerful Leadership Skills Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- PERT Estimation Technique Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Pareto Chart Tool Tutorial | Learn Analysis, Diagram
- Organizational Structure Tutorial: Definition and Types
- Negotiation Skills for Project Management | Learn from the Basics
- Monte Carlo Analysis in Project Management Tutorial | A Perfect Guide to Refer
- Effective Management Styles Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Management by Objectives (MBO) Tutorial | Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Leads, Lags & Float – Understand the Difference through Tutorial
- What is Knowledge Management? – Tutorial Explained
- What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT)? | Know More through Tutorial
- Gantt Chart Tool Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Extreme Project Management Tutorial – Methodology & Examples
- Introduction for Event Chain Methodology Tutorial | Guide For Beginners
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | A Complete Tutorial for Beginners
- What Is Design of Experiments (DOE)? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Decision Making Tutorial – Know about Meaning, Nature, Characteristics
- Critical Path Method Tutorial | How to use CPM for project management
- What is Critical Chain Project Management? | A Complete Tutorial
- What is Conflict Management? | Learn the Definition, styles, strategies through Tutorial
- Effective Communication Skills Tutorial – Definitions and Examples
- Communication Models Tutorial – Project Management
- Methods of Communication Tutorial | A Complete Learning Path
- Communication Management Tutorial | Know more about Plans & Process
- What are Communication Channels? | Learn Now Tutorial
- Communication Blocker Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Cause and Effect Diagrams Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- What is Benchmarking? | Technical & Competitive Tutorial
- Seven Processes of Prince2 Tutorial | Everything you Need to Know
- Design Thinking Tutorial – Quick Guide For Beginners
- What is Performance Testing | A Complete Testing Guide With Real-Time Examples Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Agile Scrum Tutorial
- PMI-RMP Plan Risk Management Tutorial
- Designing the Blueprint Delivery Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Program Benefits Management Tutorial
- Continuous Improvement – Agile Value Stream Mapping
- Program Organization Tutorial
- Risk and Issue Management Tutorial
- Project Integration Management Tutorial
- Planning and Control Tutorial
- Program Management Principles Tutorial
- program strategy Alignment Tutorial
- PMP Tutorial
- Program Governance Tutorial
- Program Life Cycle Management Tutorial
- PMP Exam Preparation Tutorial
- PMI-PgMP Tutorial
- Agile Methodologies and Frameworks- Kanban and Lean Management Tutorial
- JIRA Tutorial
- Primavera P6 Tutorial

Project Integration Management Tutorial
Last updated on 29th Sep 2020, Blog, Project Management, Tutorials
Project Integration Management
- Project integration management involves unification, consolidation, articulation, and integrative actions that are crucial for successfully completing the project.
- The project integration management is high-level work that project managers do and it involves managing interdependencies among the other knowledge areas.
- The other nine knowledge areas involve detailed work in a specific direction. For example, Project Cost Management deals only with how to manage the cost of a project.
- The project management processes do not happen independently. For example, a new resource added to the project may require changes in cost or schedule or both.
- In dealing with such situations, the project manager integrates the processes of project management. The need for integration drives much of the communication and the work of the project manager.
Role of Project Manager, Team, and Sponsor
Project manager, team members, and project sponsors have different roles to play in a project.
Project Manager
- 1. The project manager is supposed to play multiple roles in the project; the key role is to perform the integration. The project manager puts all the pieces of the project together into a cohesive whole.
- 2. In doing so, the project manager tries to ensure that the project is done faster, cheaper, and utilizes resources optimally, while meeting the project objectives.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Project Team
As the project progresses, the team members work on completing the project activities.
Project Sponsor
- The role of the project sponsor is to protect the project from any unnecessary changes and to ensure that it has the required resources for completion.
- The project sponsor is the champion for the project within the performing organization, i.e., the organization in which the work is being performed.
Need For Integration Management
- 1. Integration management ensures that the due dates of various deliverables of the project, its life cycle, and the benefits management plan are well aligned.
- 2. To achieve the project goals, it provides a well-organized management plan that synchronizes various processes perfectly.
- 3. It helps in managing and controlling the performance and changes required in activities/tasks of the project management.
- 4. It coordinates the decisions regarding key changes impacting the project.
- 5. Integration management measures and monitors the project’s progress by taking the necessary steps to meet the objectives.
- 6. It plays a vital role in collecting data on the results achieved, analyzing it for further insights, and then conveying it to the relevant stakeholders.
- 7. With proper integration management, you will be able to finish off all the tasks related to the project smoothly and officially close each phase, contract, the project as a whole and release the resources.
- 8. Helps in coordinating and synchronizing the phase transitions when required.
Project Selection Methods
- An organization can undertake a project under contract with an external organization or take up a project driven by internal business needs.
- There should be a formal process of selecting the project in all organizations, to ensure that it is making the best possible use of limited corporate resources.
For example, if the organization has an option to take up any one out of the two projects, both of which use the same corporate resources, the organization would naturally select the one, which is more profitable.
There are two broad ways to select a project. There are different methods under both these categories and you should be familiar with the names of these methods.
Benefit measurement methods
- 1. One way is the benefit measurement method where one project is compared with other competing projects.
- 2. Broadly, the benefit measurement methods focus on ascertaining the costs and benefits of undertaking the project.
The methods under benefit measurement method include:
- 1. murder board where a panel of experts shoots down a new project idea
- 2. peer review
- 3. scoring models
- 4. economic models
- 5. benefit compared to cost
Constrained optimization methods
- 1. Another approach is based on mathematical models wherein you examine the most optimal selection of projects by trying to optimize a goal – for example, maximize operating profits. Such methods may be called constrained optimization methods.
- 2. The constrained optimization methods rely on mathematical modeling techniques to determine the best selection of projects to achieve certain business objectives.
- 3. The methods of constrained optimization include linear programming.
- 4. In reality, you might not have seen these methods to be followed in project selection. Often, a personal relationship with the sponsor may be more important than anything else.
- 5. This is quite normal and any organization worldwide works this way. However, as a certified project manager, it is important for you to be familiar with more scientific methods of project selection.
Key Terms related to Project Management Processes
Let us look at a few key terms to understand project management processes.
Work Authorization System
- The first is the work authorization system.
- There should be a formal process of authorizing work within the project.
- So be it internal team members or a project contractor, there should be a formal process of giving the go-ahead to start work on the project.
Corrective And Preventive Action
- The next two related terms are corrective and preventive action.
- You will come across these terms throughout this CAPM tutorial.
- Corrective action is any action taken to bring expected future project performance in line with the project management plan.
For example, if a project milestone is delayed, as a corrective action, you include additional resources to ensure that the final project deadline is not delayed. While corrective action involves implementing actions to deal with actual deviations from the performance baselines, preventive action deals with anticipated or possible deviation from performance baselines.
Change Control System
- 1. A very important system that needs to be established early on a project is the change control system.
- 2. Since projects are executed in a dynamic environment, it is quite natural to expect changes in the project requirements. The change control system is the formal documented procedures, paperwork, tracking systems for authorizing changes.
- 3. Therefore, the change control system analyzes each of the incoming change requests and decides whether to accept the change request or reject it. A configurable item is any product, service, or result within the project, whose characteristics need to be identified, documented, and placed under change control mechanism.
Examples of configurable items are project documents, source code, physical parts such as tools, recommended settings for machinery, etc.
Configuration Management System
When a formal configuration management system is put in place, it is essentially establishing a control system that can preserve the characteristics of these items.
Project Integration Management Processes
The entire knowledge area of project integration management is further divided into smaller processes which act as access points for the Project Manager.
Each of these processes is an integral part of project integration management and contributes toward project success. These processes are:
- 1. Develop Project Charter
- 2. Develop Project Management Plan
- 3. Direct and Manage Project Work
- 4. Manage Project Knowledge
- 5. Monitor and Control Project Work
- 6. Perform Integrated Change Control
- 7. Close the Project
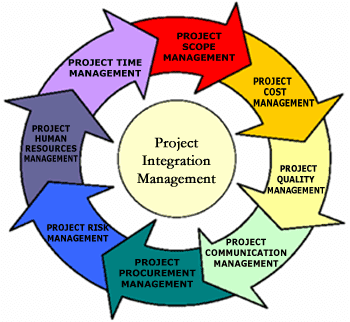
Let me now dive deeper into each of these processes and explain various inputs, outputs, and tools used in the respective processes.
1. Develop Project Charter
- In this process, a formal document is developed that will authorize the existence of a project. It is very important to create a project charter before you start with your project implementation as this charter will provide a step by step delivery plan.
- With the development of the charter, the project manager gains authority over various resources that are applied to the project activities. By developing the project charter, you will be able to establish a direct link between the organization objectives and the undertaken project. It will also serve as formal documentation of the project that an organization can use to legit its commitment towards the project and convince the stakeholders to support the project.
The process of developing a project charter typically include the following points:
- 1. Project vision: The project vision basically defines the overall objective of the project which includes clear visions and mission of the project, the effect of the project on the organization and the final deliverable.
- 2. Project organization: Next is to specify the roles and responsibilities of the entire team participating in the project development that will include everyone starting from the relevant stakeholders, their relation with the project, internal and external human resources and the customers.
- 3. Implementation: After the project organization, the next step is to create an implementation plan. This plan will keep the customers and stakeholders updated regarding the key milestones, changes or updates in project progress and distinct dependencies toward project completion.
- 4. Risk management: Performing risk management is very important as it will identify any potential risks or areas of concern that may hamper the smooth delivery of the project.
Various inputs, tools, techniques, and outputs involved in this process are listed in the below table:
| Inputs | Tools & Techniques | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Business Documents Business Case Benefits Management Plan Agreements Enterprise Environmental Factors Organizational Process Assets | Expert Judgement Data Gathering Brainstorming Focus Groups Interviews Interpersonal and Team Skills Conflict Management Facilitation Meeting Management Meetings | Project Charter Assumption Log |
2. Develop Project Management Plan
- The process of developing a project management plan includes defining, preparing, and coordinating other plan components to finally integrate them into the project management framework. The key advantage of developing a project management plan is that it acts as a road map for all the team members. It gives them a direction to move forward, towards a unified goal for successful project delivery.
This project management plan comprises of few aspects:
- 1. An initial brainstorming meet: Through this meeting, the key stakeholders are brought together to discuss the minutes of the project. This proves to be an effective way of initiating the very first process of the project management life cycle i.e planning; while building trust among the team members of the project.
- 2. Explanation of overall project goals to stakeholders: Despite having a project management plan, change is inevitable and a project manager must acknowledge this fact. Through the course of this project, there are some modifications and changes that are bound to happen to adjust and overcome the unpredictable issues.
- 3. Duties of team members and stakeholders: Along with getting the project kickstarter, it is very important to determine among the stakeholders, who will be responsible for approving the various project plan aspects.
- 4. A scope statement: The scope statement helps in securing the sponsorship and specify the project outcomes in order to prevent any type of miscommunication and unify the team.
- 5. Develop baselines: Before you step into the development phase of the project, it is very important to set the baseline for various aspects like cost, resources, schedules, deliverable etc.
- 6. Create a staffing plan: Staffing plan is a timeline that indicates the time and the duration each of the human resources will be involved with the project.
- 7. Analyze risks: It will help in assessing and mitigating the potential risks thus ensuring that the project quality remains intact.
- 8. Develop a communication plan: Proper communication plan provides a structure to the employees where the team members are allotted proper communication points to report their issues and progress.
Various inputs, tools, techniques and outputs involved in this process are listed in the table below:
| Inputs | Tools & Techniques | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Project Charter Outputs from other processes Enterprise Environmental Factors Organizational Process Assets | Expert JudgementData Gathering Brainstorming Checklist Focus Groups Interviews Interpersonal and Team Skills Conflict Management Facilitation Meeting Management Meetings | Project Management Plan |
3. Direct and Manage Project Work
As per the project management plan, this process helps in directing and managing the project work and making required changes to meet the promised goal. With the correct direction and management of the project, the probability of project success increases while elevating the deliverable quality.
This process is followed throughout the project life cycle and mainly comprised of the following aspects:
- 1. Approved Change Requests: Any authorized changes required/requested in a project’s plan, scope, cost or schedule are documented in a systematic way.
- 2. Enterprise Environmental Factors: Tracking any type of internal or external factors that may affect the final outcome positively or negatively. These factors may include market condition, infrastructure, organizational culture or project management plan.
- 3. Organizational Process Assets: Along with the factors, organizational assets like policies, procedures, formal & informal plans, historical information etc., that might affect the final deliverable must be properly tracked and assessed.
Various inputs, tools techniques and the outputs involved in this process are listed in the below table:
| Inputs | Tools & Techniques | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Project Management Plan Any Component Project Documents Change Log Lessons learned register Milestone List Project Communications Project Schedule Requirements Traceability Matrix Risk Register Risk Report Approved Change Requests Enterprise Environmental Factors Organizational Process Assets | Expert Judgement Project Management Information System Meetings | Deliverables Work Performance Data Issue Log Change Requests Project Management Plan Updates Any Component Project Document Updates Activity List Assumption Log Lessons Learned Register Requirements documentation Risk Register Stakeholder Register Organizational Process Assets Update |
4. Manage Project Knowledge
- Management of the project knowledge is very necessary for achieving the promised project objective and further contributing to future learning and references. It is primarily done by using historical or existing organizational data and curating new knowledge. This majorly helps in leveraging the organizational knowledge and improving the project results.
- This process is followed throughout the project life cycle which involves various inputs, tools, techniques, and the outputs
| Inputs | Tools & Techniques | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Project Management PlanAll Component Project Documents Lessons learned RegisterProject Team AssignmentsResource Breakdown StructureSource Selection CriteriaStakeholders RegisterDeliverablesEnterprise Environmental FactorsOrganizational Process Assets | Expert JudgementKnowledge ManagementInformation ManagementInterpersonal and Team SkillsActive ListeningFacilitationLeadershipNetworkingPolitical Awareness | Lessons Learned RegisterProject Management Plan UpdatesAny ComponentOrganizational Process Assets Update |
5. Monitor and Control Project Work
In order to achieve the performance objectives as defined in the project management plan, this process is implemented. In the monitoring and controlling process, the project is tracked, reviewed, and its overall progress is reported which enables the stakeholders to get the exact idea of the project state. This process is performed throughout the project lifecycle and acts as a guide for the project manager to ensure that the project is on schedule. Few of the aspects of this process are:
- 1. Provide consistent updates: Regular performance reports and project status updates are very necessary for properly driving the project to success.
- 2. Revisit the scope statement: Time to time, revisiting the project scope helps a project manager in ensuring that the modifications made are well preserved.
- 3. Control baselines: The baselines promised at the beginning of the project must be strictly followed and if any changes are introduced, must be documented in detail. This will later help in keeping the team in focus and on track.
- 4. Focus on quality control: Quality control is a major pillar of project success and must not be performed leniently. Thus, for a project manager, it is very crucial to perform a constant evaluation of various project components to ensure their efficiency.
- 5. Monitor and control risks: Separate processes for risk monitoring and control are very necessary, as risks are something that can result in project failure or deviation from the original outcome. Thus, assessing new risks through each and every project stage helps in early detection of potential risk/threat and mitigate it in advance.
Various inputs, tools, techniques and outputs involved in this process are listed in the below table:
| Inputs | Tools & Techniques | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Project Management PlanAny ComponentProject DocumentsAssumption LogBasis of estimatesCost ForecastsIssue LogLessons learned registerMilestone ListProjectQuality ReportsRisk RegisterRisk ReportSchedule ForecastsWork Performance InformationAgreementsEnterprise Environmental FactorsOrganizational Process Assets | Expert JudgementData AnalysisAlternatives AnalysisCost-Benefit AnalysisEarned Value AnalysisRoot Cause AnalysisTrend AnalysisVariance AnalysisDecision MakingMeetings | Work Performance ReportsChange RequestsProject Management Plan UpdatesAny ComponentProject Document UpdatesCost ForecastsIssue LogsLessons Learned RegisterRisk RegisterSchedule Forecasts |
6. Perform Integrated Change Control
- This process is performed to control the various change requests received throughout the project life cycle. Here, all the change requests, approved changes, modifications of the final deliverable, project documents, project management plan etc., are reviewed. Performing this process helps in keeping an integrated document containing the list of changes while assessing the overall risks which might arise due to the new changes.
- Various inputs, tools, techniques and outputs involved in this process are listed in the below table:
| Inputs | Tools & Techniques | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Project Management PlanChange Management Plan Configuration Management PlanScope BaselineSchedule BaselineCost BaselineProject DocumentsBasis of estimatesRequirements Traceability matrixRisk ReportWork Performance ReportsChange RequestsEnterprise Environmental FactorsOrganizational Process Assets | Expert JudgementChange Control ToolsData AnalysisAlternatives AnalysisCost-Benefit AnalysisDecision MakingVotingAutocratic Decision MakingMulticriteria Decision AnalysisMeetings | Approved Change RequestsProject Management Plan UpdatesAny ComponentProject Document UpdatesChange Log |
7. Close the Project
This is the final process of project integration management, where the various project activities, phases, and contracts are finalized. It provides a controlled environment where the project can be successfully wrapped up. The closing process includes the activities like preservation of the project information, completion of planned work, the release of involved resources etc.
Various inputs, tools techniques and outputs involved in this process are listed in the below table:
| Inputs | Tools & Techniques | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Project CharterProject Management Plan Any Component Project Documents Assumption LogBasis of estimates Change Log Issue LogLessons learned register Milestone List Project Communication Quality Control Measurements Quality Reports Requirements Documentation Risk Register Risk Report Accepted Deliverables Business Documents Business Case Benefits Management PlanAgreements Procurement Documentation Organizational Process Assets | Expert Judgement Data Analysis Document Analysis Regression AnalysisTrend Analysis Variance Analysis Meetings | Project Documents Updates Lessons Learned Register Final Product, Service, or Result Transition Final Report Organizational Process Assets Updates |
This brings us to the end of this Project Integration Management article. Hope it helped in adding value to your knowledge. If you wish to learn more about project management or project management certifications you can check my other articles as well.

