- ITIL Tutorial – Incident & amp Problem Management | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- ITIL4 Service Value Chain Model Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- The ITIL 4 Service Value System | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- What are the ITIL 4 Management Practices? | Tutorial for Learning Path
- Guiding Principles of ITIL 4 | Learn Now Tutorial
- Four Dimensions of Service Management in ITIL 4 | A Definitive Guide
- What is the Continual Improvement Model? ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL4 Tutorial | A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI)Tutorial | Learn the Methods and Techniques
- Service Transition Overview – ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL® 4 Foundation Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Design an Effective IT Service with ITIL® v3 Tutorial
- Nagios Tutorial
- ITIL – Service management lifecycle Tutorial
- Service Validation and Testing Tutorial
- Service Operation Processes Tutorial
- ITIL Turtorial
- Services Strategy Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate SOA – Demand Management Tutorial
- Availability Management Tutorial
- ITIL Key Concepts of the Service Lifecycle Tutorial
- ITIL Change Evaluation Tutorial
- The principles of COBIT® 5 Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate CSI – Continual Service Improvement Processes Tutorial
- ITIL-Service Level Management Tutorial
- ServiceNow Tutorial
- SCCM Tutorial
- ITIL Tutorial – Incident & amp Problem Management | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- ITIL4 Service Value Chain Model Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- The ITIL 4 Service Value System | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- What are the ITIL 4 Management Practices? | Tutorial for Learning Path
- Guiding Principles of ITIL 4 | Learn Now Tutorial
- Four Dimensions of Service Management in ITIL 4 | A Definitive Guide
- What is the Continual Improvement Model? ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL4 Tutorial | A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI)Tutorial | Learn the Methods and Techniques
- Service Transition Overview – ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL® 4 Foundation Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Design an Effective IT Service with ITIL® v3 Tutorial
- Nagios Tutorial
- ITIL – Service management lifecycle Tutorial
- Service Validation and Testing Tutorial
- Service Operation Processes Tutorial
- ITIL Turtorial
- Services Strategy Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate SOA – Demand Management Tutorial
- Availability Management Tutorial
- ITIL Key Concepts of the Service Lifecycle Tutorial
- ITIL Change Evaluation Tutorial
- The principles of COBIT® 5 Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate CSI – Continual Service Improvement Processes Tutorial
- ITIL-Service Level Management Tutorial
- ServiceNow Tutorial
- SCCM Tutorial

Services Strategy Tutorial
Last updated on 29th Sep 2020, Blog, IT service and Architecture, Tutorials
Service Strategy is the center and origin point of the ITIL Service Lifecycle. It provides guidance on clarification and prioritization of service-provider investments in services. More generally, Service Strategy focuses on helping IT organizations improve and develop over the long term. In both cases, Service Strategy relies largely upon a market-driven approach.
This is a view of ITIL where IT and business align their visions. Its key topics covered include service value definition, business-case development, service assets, market analysis, and service provider types. List of covered processes:
- Strategy Management
- Service Portfolio Management
- IT Financial Management
- Demand Management
- Business Relationship Management
Importance of this view is because this phase is responsible to define service value. When defining a service is important to have in mind four Ps for strategy: Perspective, Position, Plan, Pattern.
Strategy activities are:
- Define market
- Develop strategic offer
- Develop strategic assets
- Prepare for execution
Principles
When defining a service, strategist must have in mind list of principles, as stated below:
- Value creation
- Service assets
- Service provider types
- Service structure
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
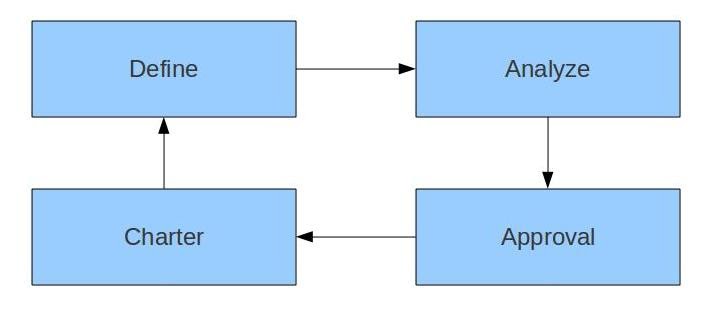
Stages
Stages for definition of strategy are:
- 1.Define
- 2.Analyze
- 3.Approval
- 4.Charter
Service provider types
There are three types of service providers, that may include service provided as well providers for the service:
- 1.Internal service provider: exists within an organization and provides service solely for a unique business unit
- 2.Shared service unit: exists within an organization, but provides service for more than one business unit
- 3.External service provider: operates outside organization
Processes
Service strategy has two processes: Service Portfolio Management and IT Financial Management, as depicted below.
Service Portfolio Management
Owned by service portfolio manager, it is composed of four sub-processes:
- Strategic service assessment: assesses current service in the market.
- Service strategy definition: to define overall goals of the service, as well to define customer and customer segmentation.
- Service portfolio update: adjusts services offered in the portfolio based on strategy definition.
- Strategic planning: defines, initiates and controls the program and projects required to execute Service Strategy.
- Demand Management: Service Strategy.
IT Financial Management
Owned by financial manager, it is composed of four sub-processes:
- Financial management support: defines necessary structure for management of financial planning data and costs.
- Financial planning: determines required financial resources over next planning period.
- Financial analysis and reporting: analysis of financial costs provisioning and service profitability.
- Service invoicing: issues invoices for the provisioned service.
service Assets
Capabilities and Resources combined together build the Service Assets. Organizations use these assets to create value in the form of goods and services. People can be Resources or can be Capabilities based on their skills, experiences, expertise etc.
- 1.What is easier to acquire?
- 2.Capabilities or Resources?
Resources are always easier to acquire as you have to build the Capabilities and that takes time and efforts. Aligning the Service Assets to the customer outcomes is the key to success for any service provider.
Value through Utility & Warranty
The value of a service can be considered to be the level to which that service meets customer’s expectations. It is often measured by how much the customer is willing to pay for the service, rather than the cost to the service provider of providing the service or any other intrinsic attribute of the service itself. With the AND and OR gates, we will understand how the Value gets created.
Service Providers
Types
There are three types of service providers:
- 1.Internal Service Provider
- 2.Shared Services Unit
- 3.External Service Provider
Internal Service Provider
ISPs are service providers that are dedicated and often embedded within, an individual business unit. The business units themselves may be part of a larger enterprise or parent organization. Business functions such as finance, administration, logistics, human resources and IT provide services required by various parts of the business. They are funded by overheads and are required to operate strictly within the mandates of the business.
ISPs have the benefit of tight coupling with their owner- customers, avoiding certain costs and risks associated with conducting business with external parties. Since ISPs are dedicated to specific business units they are required to have an in-depth knowledge of the business and its goals, plans and operations. They are usually highly specialized, often focusing on designing, customizing and supporting specific applications or on supporting a specific type of business process.
ISPs operate within internal market spaces. Their growth is limited by the growth of the business unit they belong to. Each business unit (BU) may have its own ISP
The success of ISPs is not measured in terms of revenues or profits because they tend to operate on a cost-recovery basis with internal funding. All costs are borne by the owning business unit or enterprise.
Shared Services Unit
Functions such as finance, IT, human resources and logistics are not always at the core of an organization’s competitive advantage. Hence, they need not be maintained at the corporate level where they demand the attention of the chief executive’s team.
Instead, the services of such shared functions are consolidated into an autonomous special unit called a shared services unit (SSU). The model allows a more devolved government structure under which SSUs can focus on serving business units as direct customers. SSUs can create, grow and sustain an internal market for their services and model themselves along the lines of service providers in the open market. Like corporate business functions, they can leverage opportunities across the enterprise and spread their costs and risks across a wider base. Unlike corporate business functions, they have fewer protections under the banner of strategic value and core competence.
They are subject to comparisons with external service providers whose business practices, operating models and strategies they must emulate and whose performance they should approximate, if not exceed. Customers of Type II are business units under a corporate parent, common stakeholders and an enterprise-level strategy. What may be suboptimal for a particular business unit may be justified by advantages reaped at the corporate level for which the business unit may be compensated.
Type II can offer lower prices compared to external service providers by leveraging corporate advantage, internal autonomy to function like a business unit, Type II providers can make decisions outside the constraints of business unit level policies. They can standardize their service offerings across business units and use market-based pricing to influence demand patterns.
A successful Type II service provider can find itself in a position where it is able to provide its services externally as well as internally. In these cases they are both Type II and Type III service providers.
In these cases it is important to make a strategic decision to provide services both externally and internally and to set up the appropriate governance and management structures. This is not just a case of delivering existing services externally.
External Service Provider
ESP is a service provider that provides IT services to external customers. The business strategies of customers sometimes require capabilities readily available from a Type lll provider. The additional risks that Type lll providers assume over Type I and Type II are justified by increased flexibility and freedom to pursue opportunities.
ESPs can offer competitive prices and drive down unit costs by consolidating demand. Certain business strategies are not adequately served by internal service providers such as Type I and Type II. Customers may pursue sourcing strategies requiring services from external providers.
The motivation may be access to knowledge, experience, scale, scope, capabilities and resources that are either beyond the reach of the organization or outside the scope of a carefully considered investment portfolio. Business strategies often require reductions in the asset base, fixed costs and operational risks, or the redeployment of financial assets.
The experience of ESPs is often not limited to any one enterprise or market. The breadth and depth of such experience is often the single most distinctive source of value for customers. The breadth comes from serving multiple types of customer or market. The depth comes from serving multiples of the same type.
From a certain perspective, ESPs are operating under an extended large-scale shared services model. They assume a greater level of risk from their customers compared to ISPs and SSUs. But their capabilities and resources are shared by their customers – some of whom may be rivals. This means that rival customers have access to the same bundle of assets, thereby diminishing any competitive advantage those assets bestowed.
Service Strategy Processes
Let’s understand all the five processes under Service Strategy:
- 1.Strategy Management for IT Services: To assess the service provider’s offerings, capabilities, competitors as well as current and potential market spaces in order to develop a strategy to serve customers. Once the strategy has been defined, Strategy Management for IT Services is also responsible for ensuring the implementation of the strategy.
- 2.Service Portfolio Management: Service portfolio management will ensure that every proposed new service or any strategic change to an existing service is analyzed to determine the level of investment required and the proposed return on that investment.
- 3.Financial Management for IT Services: Financial management for IT services indicates that a service costs significantly more or less than anticipated, thus impacting the potential return on investment for that service.
- 4.Demand Management: To understand, anticipate and influence customer demand for services. Demand Management works with Capacity Management to ensure that the service provider has sufficient capacity to meet the required demand.
- 5.Business Relationship Management: To maintain a positive relationship with customers, Business Relationship Management identifies the needs of existing and potential customers and ensures that appropriate services are developed to meet those needs.
Strategy Management for IT Services – Goal and Objectives
The Goal of Strategy Management for IT Services is defining and maintaining an organization’s perspective, position, plans and patterns with regard to its services and the management of those services.
Here are the few Objectives:
- 1.Analyze the internal and external environments, to identify opportunities that will benefit the organization.
- 2.Identify constraints that might prevent the achievement of business outcomes.
- 3.Establish the position of the service provider relative to its customers and other service providers.
- 4.Produce and maintain IT strategy.
- 5.The Service Management Strategy and the Strategy Plans for each service where appropriate.
- 6.You should always remember that IT Strategy must be aligned to Business Strategy.
- 7.Strategy Management for IT Services
Strategy management for IT services is the process of defining and maintaining an organization’s perspective, position, plans and patterns with regard to its services and the management of those services.
Strategy Management for IT Services focuses on these four major activities
1. Define the Market:
- Services and strategy
- Understand the customer
- Understand the opportunities
- Classify and visualize
2. Develop the Offerings:
- Understand market space (customer desired outcomes supported by services)
- Outcome-based definition of services
- Service Portfolio (Pipeline, Catalog & Retired services)
3. Develop Strategic Assets:
- Service Management as a closed-loop control System
- Service Management as a strategic asset
4. Prepare for Execution:
- Aligning Service Assets with Customer Outcomes
- Prioritizing investments
Usually, strategy management is the responsibility of the executives of an organization.
It enables them to set the objectives of the organization, to specify how the organization will meet those objectives and to prioritize investments required to meet them.
Service Portfolio Management – Goals & Objectives
Service Portfolio Management is a dynamic method for governing investments in service management across the enterprise & managing them for value.
The Goal of Service Portfolio Management is to manage Service Portfolio by considering services in terms of the business value they provide.
The Objective is to apply comparable practices to manage Service Portfolios maximize value while managing risks and costs.
Service Portfolio
A service portfolio describes a provider’s services in terms of business value. It articulates business needs and the provider’s response to those needs. By definition, business value terms correspond to marketing terms, providing a means for comparing service competitiveness across alternative providers. The Role of Service Portfolio Management is Service Portfolio Manager who manages the entire Service Portfolio.
Service Portfolio includes: Service Pipeline, Live Services and Retired Services.
- Service Pipeline is a database or structured document listing all services that are under consideration or development but are not yet available to customers.
- Service Catalog is a database or structured document with information about all live IT services, including those available for deployment. The service catalog is the only part of the service portfolio published to customers and is used to support the sale and delivery of IT services.
- Some services in the service portfolio are phased out or retired (called Retired Services). There is a decision to be made by each organization, following a service review on when to move a service from catalog to retired.
Another important part in Service Portfolio Management is utilizing and allocating the resources.
The service portfolio represents all the resources presently engaged or being released in various stages of the service life-cycle. Each stage requires resources for completion of projects, initiatives and contracts.
Service Catalog
Service Catalog is the only part which is visible to customers. The service portfolio represents all the resources presently engaged or being released in various stages of the service life-cycle. Service pipeline is related to all services that are under consideration or development, but are not yet available to customers. It includes major investment opportunities that have to be traced to the delivery of services, and the value that will be realized. The service pipeline provides a business view of possible future services and is part of the service portfolio that is not normally published to customers. Service catalog is related to all live IT services, including those available for deployment.
It is the only part of the service portfolio published to customers and is used to support the sale and delivery of IT services. It includes a customer- facing view (or views) of the IT services in use, how they are intended to be used, the business processes they enable, and the levels and quality of service the customer can expect for each service. The service catalog also includes information about supporting services required by the service provider to deliver customer- facing services. Information about servi
Financial Management for IT Services
Financial Management for IT Services – Goals & Objectives
The goal of Financial Management for IT Services is to secure the appropriate level of funding to design, develop and deliver services that meet the strategy of the organization.
Here are the objectives of Financial Management for IT Services:
Defining and maintaining a framework to identify, manage and communicate the cost of providing services.
Evaluating the financial impact of new or changed strategies on the service provider.
Securing funding to manage the provision of services.
Understanding the relationship between expenses and income and ensuring that the two are balanced according to the organization’s financial policies.
The main purpose of Financial Management for IT Services is to provide operational visibility, insight and superior decision making capabilities to the organization (service provider).
Key Terms
Here are the ‘ABC’ of Financial Management for IT Services.
- 1.Accounting
- 2.Budgeting
- 3.Charging
Accounting:
This is the process that enables the IT organization to account fully for the way its money is spent (particularly the ability to identify costs by customer, by service and by activity). It usually involves accounting systems, including ledgers, charts of accounts, journals etc and should be overseen by someone trained in accountancy.
Budgeting:
This is the process of predicting and controlling the income and expenditure of money within the organization. Budgeting consists of a periodic negotiation cycle to set budgets (usually annual) and the monthly monitoring of the current budgets.
Charging:
This is the process required to bill customers for the services supplied to them. This requires sound IT accounting practices and systems.
Major Activities of Financial Management for IT Services
Here are the major activities performed under Financial Management for IT Services:
- Service Valuation – To understand if the service is worth investing / continuing.
- Demand Modeling – To shift or influence demands.
- Service Portfolio Management – Right services and their cost / price are captured in the portfolio and catalog.
- Service Provisioning Optimization – Improving time to market and provisioning of service by ensuring right funding is available.
- Planning Confidence – With the effective Service Valuation, help in planning and increase the confidence.
- Service Investment Analysis – Cost / Benefit Analysis and recommendations to make decisions.
- Budgeting, Accounting & Charging
- Compliance – Ensure compliance in financial issues.
- Variable Cost Dynamics – Analyze and Recommend Fixed Cost or Variable Cost Models.
These activities are performed by the key Role in Financial Management for IT Services which is Finance Manager. Finance Manager also provides oversight in some more activities like:
- Assist to identify, document & agree on the value of services to the business.
- Participate in Demand Modeling activities (incentive or penalty).
- Provision of cost information for Service Portfolio Management.
- Maintain regulatory compliance regarding financial issues.
Business Relationship Management
Business Relationship Management is a very important process in Service Strategy which helps building and maintaining the right professional relationships with the customers.
The Purpose & Objective of Business Relationship Management are:
- To establish and maintain business relationships.
- To identify customers’ business needs.
- To identify changes to the customer environment which potentially will impact the value of IT services.
- Establish formal complaint and escalation procedures for customers.
- Mediate in case of conflicting requirements from different businesses.
- Identify technology trends which potentially will impact utilization of services.
The key role in Business Relationship Management is Business Relationship Manager (BRM), sometimes termed as Account Manager or Customer Relationship Manager (CRM).
For internal service providers business relationship management is typically executed between a senior representative from IT (larger organizations may have dedicated BRMs) and senior managers (customers) from the business units.
In external service providers business relationship management is often executed by a separate and dedicated function of BRMs or account managers each one dedicated to a customer or to a group of smaller customers.
The emphasis here is on maximizing contract value through customer satisfaction. Business relationship management focuses on understanding how services meet customer requirements. To achieve this, the process must focus on:
- Understanding and communicating business outcomes that the customer wants to achieve.
- Services that are currently offered to the customer and the way in which they are used by the customer.
- The way in which services are currently offered including who is responsible for the services, what levels of service have been agreed, the quality of services delivered and any changes that are anticipated.
- Technology trends that could impact current services and the customer as well as the nature of the potential impact.
- Levels of customer satisfaction and what action plans have been put in place to deal with the causes of dissatisfaction.
- How to optimize services for the future.
- How the service provider is represented to the customer.
This at times, means raising concerns around commitments that the business made to IT but is not meeting. From the above points, it is clear that business relationship management depends on a number of other service management processes and functions. For example, the mapping of business outcomes and services is done in service portfolio management.
Service level management provides information about the levels of services agreed and achieved.
Configuration management provides a mapping of infrastructure, applications, services, service owners and customers. Capacity management provides information about utilization levels and the potential impacts of new technologies.
Differences between BRM and SLM
Here are some differences between Business Relationship Management(BRM) and Service Level Management(SLM) processes to understand them better.
- 1.Purpose of Business Relationship Management is: To establish and maintain a business relationship between the service provider and the customer based on understanding the customer and their business needs.
- 2.Whereas the purpose of Service Level Management is: To negotiate SLAs (warranty terms) with customers and ensure that all service management processes, OLAs and underpinning contracts are appropriate for the agreed service level targets.
- 3.BRM focuses on Strategic and tactical: The focus is on the overall relationship between the service provider and their customer and which services the service provider will deliver to meet customer needs.
- 4.SLM focuses on Tactical and operational. The focus is on reaching agreement on the level of service that will be delivered for new and existing services and whether the service provider was able to meet those agreements.
- 5.Primary KPI for BRM are customer satisfaction, also an improvement in the measure customer’s intention to better use and pay for the service. Whereas for SLM, it is: Achieving agreed levels of service (which leads to customer satisfaction).
The marketing strategy of the service industry focuses on delivering experiences, processes and other intangibles to the customers and not physical goods like the product industry. It also involves a focus on all functions equally.
Roles of the functions of a company like selling, marketing, operations, human resources, and other functions must work efficiently and together in order to create an excellent service strategy. A service strategy is more customer-centric and is centered on the usage of customers and their relationships.
Many of the service sectors such as hospitality healthcare transport our offerings of themselves and also the primary revenue-generating activities of the respective companies. Service industries are categorized into another category which is called customer service which includes providing technical support for the product of the company to the customers and assisting the customer with any technicalities required.
Customer services is a segment of an organization which does not produce revenue but rather is a form of a troubleshooting service which provides answers and solutions to the queries of the customers. Services can also be considered as a value addition for the company.
In case of services, there is a requirement of 7 P’s of marketing instead of 4 Ps of marketing which is product place price promotion people process and physical evidence since 4 P’s are not enough to describe the intricacies of services marketing. Because unlike a product, services are produced and consumed at the same time.
The company should also take care of their employees and personal appearance and all other small factors which influence the perceptions of the customers towards the service. there should also be an effective calculation of the service so as to be on par with the industry standards. There is often a gap between the perception of the company and the expectations of the customer.
The companies strive to devise a service strategy in such a way that the gap is minimum. The wider the gap, the more difficult it will be for the company to sustain in the market. The strategies used by the organizations vary on the nature of the offering and the business
Flowcharting in services – Service flow chart
Both of these companies provide products which are electronics and they also provide after Sales service. In both of them, Apple stands out as the best because of efficient after sales service.
Table of Contents
Importance of service strategy

It is very important in a highly competitive business environment that there is a service strategy present in order to address customer needs and wants. Following are a few of the reasons which elaborate on the importance of service strategy:
- 1.The cost of getting a new customer is much more than entering the retention of the existing customers. The customer strategy for service strategy should be in sync with the marketing strategy of the company.
- 2.It is a well-known fact that to get a new customer the cost would be 5 to 10 times more than that of the cost of retaining a current customer. More often than not customers are lost because of poor services and bad treatment which gives them dissatisfaction. It is also estimated that an unhappy customer will talk about his dissatisfaction to at least 8 to 16 other potential customers. Adding social media and that the satisfied customer’s voice will reach 1600 more people which is why customer retention is of crucial importance to the organization.
- 3.Looking on the other side of service strategy a customer who is satisfied or who is loyal will cost not even a single penny but will add value to the business by being word-of-mouth ambassador. This will save millions of bucks of the company since it is free publicity from the customer to a potential customer. This is the reason why every customer should be satisfied with the service strategy.
- 4.It is also stated that customer loyalty can have any impact on the business. Making the customer is important creates all customers and those all customers will continue to do business in spite of increasing competition. Higher customer loyalty translates into higher customer retention and better sustainable- competitive advantage.
- 5.Companies should ensure that the service strategy is in sync with the vision and mission of the organization. They should complement the strategy of the organization. Companies take time in order to develop and implement an efficient service strategy which will be responsible for the retention of the existing customers.
7 Steps to create an efficient service strategy
In most of the cases, the Service strategy depends on the nature of the business but here are the following steps which can generally be used and implemented by most of the service organizations.
Perishability in services marketing
1) Crafting a service vision

The primary step is to communicate the vision of the service to the employees associated with the business. The employees associated with the organization should understand and comprehend the organizational goals and the vision of the organization and should be able to write their responsibility to help the company achieve that vision.
2) Contemplating the customer needs
More often than not the companies fail and waste their valuable resources in creating services or products that the company thought customers would want only to know that the offering was not what the customers wanted at all.
The important part is to know what the customer needs and to put it in sync with the organization’s vision and mission. Taking the feedback of customers is the first step in order to know and determine what their expectations are so that the company can form a strategy around the feedback obtained in order to deliver and meet the expectations of customers.
The market needs for customer needs can be assessed using a method such as satisfaction surveys for focus groups and the customer feedback forms. Development of such feedback forms and questionnaires is very important and should focus on the questions that need to be answered by the customers.
It is also very important to keep in mind that the needs of customers keep on changing with time and are like a moving target. Since it constantly keeps changing it is very important for the companies to form a process which will continuously keep on updating them about the changing needs of the customer so that the companies can prepare and modify themselves and their offerings accordingly.
3) Right hiring

When it comes to facing the customers it is not the company who is going to face them rather it is the employees who are going to face the customers. Employees are the face of the organization and organization has to ensure that the face is represented correctly.
The employees should have the right skill set which meets the goals of the organization and helps to form a strong network and backbone to provide service to the customers. Having a right attitude and personality is something which companies cannot develop in their employees which is why they should take care of these things with hearing.
Most of the things can be incepted and developed in the employees but most of the other things have to be built in. Interacting with customers and providing services is an art more than science and not everyone can achieve it.
4) Goal setting for the service team
Wednesday identification of customer needs and the parameters for customer satisfaction is done then the organizations have to create goals for the service team in order to achieve customer satisfaction. These goals should be measurable and quantifiable so that the organization can grow the employees as well as along with the growth of the business.
The employees should be able to understand the vision and mission and the target of the organization so that they can align themselves to reach the chief and exceed those objectives. An example of customer satisfaction can be given as follows:
The service team of a refrigerator company provides after sales service. Once the customer causes the machine the time taken by the service team to reach the place of the customer and correct the machine is measured.
The lesser the time to attend the customer breakdown calls the higher would be the customer satisfaction. This can be a measurable parameter in order to appraise the employees.
5) Constant training and development

Once the hiring is done in a proper and correct way the employees will have some inborn cause it is which the organization will be able to utilize them in order to serve the customers correctly. The other part of having a good service team is providing them with constant training in order to upgrade their technical skills.
The training should focus not only on technical skills but also on interacting with customers. Right service strategy requires suitable training for the service team so that not only the customer but also your organization benefit from it.
The employees need to know about the goals of the organization so that they can modify themselves to fit accordingly. The need to be trained not only on the technical skills but also on other soft skills like answering the customer phone calls and customer complaints and providing services.
6) Accountability
Organizations should ensure that the employees have a suitable understanding of the importance of good customer service and how their actions affect the organization’s performance overall. The organizations should also ensure that the employees are held accountable in order to achieve the service goals.
This also forms the part of the performance management system and should be embedded in the culture of the company.
For example, rewarding the employee with the highest customer satisfaction and working on the employee with over customer satisfaction.
7) Awards and recognitions

Positive reinforcement always works in every organization which is why it is very important to recognize the performing employees who are responsible for excellent customer service. This will help the other employees to perform well and live up to the set goals or exceed them.
This also reinforces the vision and mission of the organization and the service strategy which is chalked out for everyone. A successful organization is categorized by strong customer service.
Conclusion
Because manufacturing has been the dominant economic force of the last century, most managers have been educated through experience and/or formal education to think about strategic management in product-oriented terms. Unfortunately, a large part of this experience is irrelevant to the management of many service businesses. The general manager of a service business must develop a healthy skepticism about his and others’ approaches to strategy.
One of the best ways to change managers’ thinking patterns and thus to avoid the trap of force-fitting product-oriented management techniques into a service-oriented business is to change the language system in the company. If managers talk about services instead of products, they also think about services and those characteristics that make services unique.

