
Terraform vs Ansible: Key Differences Among Terraform and Ansible
Last updated on 28th Oct 2022, Artciles, Blog
- In this article you will get
- 1.What is Terraform?
- 2.What is Ansible?g
- 3.Terraform vs Ansible: Similarities and Differences
- 4.When should you not use Ansible or Terraform?
- 5.Conclusion: Terraform or Ansible?
What is Terraform?
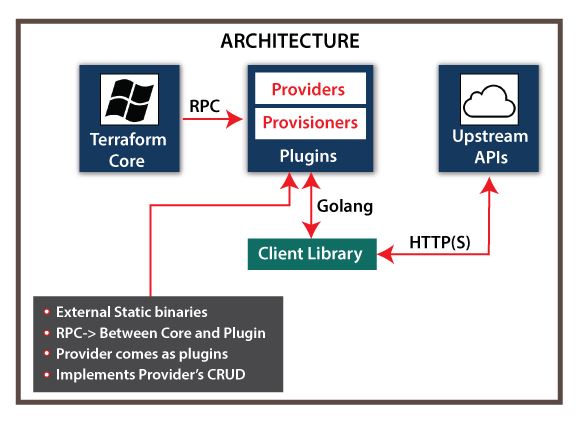
Terraform’s product website explain it as “…an infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that allows to build, change, and version infrastructure safely and efficiently. This includes a low-level components such as compute instances, storage, and networking, as well as a high-level components like DNS entries, SaaS features, etc. Terraform can manage both an existing service providers and custom in-house solutions.”It is open-source platform made for the building, changing, and versioning infrastructure effectively and securely and is more straightforward.
What is Ansible?
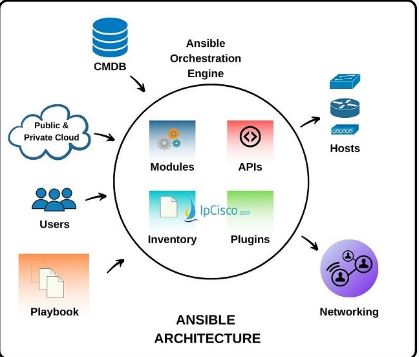
According to Red Hat, Ansible is the open-source IT automation engine that automates a provisioning, configuration management, application deployment, orchestration, and the many other IT processes.”Ansible is the configuration management tool that focuses on a deploying and provisioning applications with IaC.
Terraform vs Ansible: Similarities and Differences
| Terraform | Ansible | |
|---|---|---|
| Category | An Orchestration, provisioning tool | A Configuration management tool |
| Default Approach | Follows a declarative Infrastructure as Code approach | Follows procedural approach. |
| Language | A Declarative | An Imperative |
| Focus | Infrastructure provisioning | Configuration management within an infrastructure |
| Best Known For | Orchestrating setup cloud infrastructure and also cloud services from nothing | Configuring servers with a correct software and updates on an already configured cloud |
| Deployment | Can be used to deploy a load balances, storage, computing, and VPCs | Can deploy the apps on top of the cloud |
| Provisioning | Specializes in an infrastructure provisioning. Doesn’t support bare metal provisioning by a default | Limited support for an infrastructure provisioning. Supports a provisioning of bare metal servers |
| Life Cycle Management | It’s lifecycle aware and maintains state of a deployments. Highly depends on lifecycle or state management | Has no lifecycle awareness. Does not have a lifecycle management at all |
| User intervention | Once given an end instruction, can carry out all the steps to present the final output. | Users must dictate every step to reach the end result |
| Packaging and Templating | Does not provide a better packaging and templating | Provides a full support for packaging and templating |
| Agentless | Yes | Yes |
| Masterless | Yes | Yes |
| Syntax | HCL (Hashicorp Configuration Language) | YAML (YAML Ain’t Markup Language) |
| Infrastructure | Immutable infrastructure. Considered an ideal for keeping the environment in a steady state | Mutable infrastructure. Repairs issues instead of replacing a whole infrastructure |
Similarities: Terraform vs Ansibleg
Both the Terraform and Ansible allow provisioning of infrastructure using a Infrastructure as Code, so can say that they are both used as a IaC platforms.
Additionally, both tools can execute a remote commands on a newly created virtual machine. Or, to put it an another way, both are agentless.
Orchestration and provisioning is when users create a infrastructure, including virtual machines, databases, network components, and other resources.
On a other hand, configuration management automates versioned software component installation, operating system configuration tasks, network and a firewall configuration, and related tasks. Although a Terraform and Ansible can perform configuration management tasks, the latter does a far better job.
They also both work with the cloud APIs and are both open-source. Developers can also use a Terraform and Ansible simultaneously, so the two tools complement each other rather than a replace each other.
Differences: Terraform vs Ansible
Declarative vs. Imperative:
The first thing should tackle is a declarative versus the imperative approach. For example, if wanted to create ten web servers using a Terraform,, want to create a ten web servers.” That is the declarative statement.However, if usinga Ansible, “If these web servers don’t exist be already, create one first, then create other nine.” That is the declarative statement.
Immutable vs. Mutable:
Cannot change the immutable server. Users who want to make a changes in an immutable virtual server destroy the old version and replace it with a version that encompasses the changes. A mutable virtual server allows users to make a changes without blowing up a whole server.Ansible emphasizes mutability, while a Terraform is considered immutable. However, conditions are defaults; both tools can conduct a mutable operations and have immutable elements to one degree or another.
Provisioning:
Terraform is a geared towards infrastructure automation and interprets models described in a HCL. With Terraform, the required environment elements (e.g., networks, servers, etc.) are separately explained , along with their relationships to the one another. Then, Terraform assesses and evaluates a model, develops a plan based on the dependencies, and delivers optimized commands to a IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service).Repeated runs do nothing if there are no changes in an environment or plan. However, any update in the plan or environment synchronizes a cloud infrastructure to the new plan’s intent.
When should not use Ansible or Terraform?
Ansible: If configuration drift is the issue , don’t use a Ansible. Configuration drift occurs when users are change settings so that new versions of virtual infrastructure “drift” away from an original configuration.
Terraform: If using images to provision VMs, and may need dozens of images to accommodate the application servers, messaging servers, web servers, etc. Since Terraform doesn’t allow to change images themselves, need an image with an exact state .If making three changes a day for every day of the working week in a server, that’s fifteen copies of a server.
Conclusion: Terraform or Ansible?
So, which one is a better? It depends on what are b looking for and what features matter . If looking for a user-friendly tool with good scheduling capabilities and smooth Docker integration, then go with a Terraform. On other hand, if more interested in a security, good ACL functionality, and something that plays well with the traditional automated frameworks, then Ansible’s .
Are you looking training with Right Jobs?
Contact Us- Hadoop Tutorial
- Hadoop Interview Questions and Answers
- How to Become a Hadoop Developer?
- Hadoop Architecture Tutorial
- What Are the Skills Needed to Learn Hadoop?
Related Articles
Popular Courses
- Hadoop Developer Training
11025 Learners - Apache Spark With Scala Training
12022 Learners - Apache Storm Training
11141 Learners
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- Difference between Data Lake vs Data Warehouse: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- What does the Yield keyword do and How to use Yield in python ? [ OverView ]
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know
