- What is React JS ? Know the features of React JS
- Skills required to become a Full Stack Developer | All you need to know
- What is Angular Version?| Know more about it.
- Exploring the Various Decorators in Angular | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Career Advantages of AngularJS Certification | Everything You Need to Know to Become an Expert
- How to Become a Web Developer? : Everything you Need to Know about the Profile[OverView]
- PHP Cookies and Session Outline | Everything You Need to Know
- Magnific Popup: Responsive jquery | How to Implement Magnific Popup [ OverView ]
- How to Work With Forms In JavaScript?: Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Python vs Node.js | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Top 10 JavaScript Frameworks | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- Learn Ruby on Rails :Understanding Concepts and Career Prospects [ OverView ]
- AEM vs Open Source Content Management | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Average Web Developer Salary in India [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is Context in React ? : Comprehensive Guide [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- Django vs Node.js : Differences and Which Should You Learn? [ OverView ]
- JQuery vs JavaScript : Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Front End Developer Salary in India | Everything You Need to Know [OverView]
- Control Statements in Java – Expert’s Top Picks
- Top 10 Python Libraries for Machine Learning : Step-By-Step Process
- Exploring the Various Decorators in Angular | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Practical Applications of Python | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- AngularJS CDN Integration : Comprehensive Guide
- What are Python KeyError Exceptions ? Expert’s Top Picks
- Best Web Development Languages To Learn | [ Job & Future ]
- How to Become a Front End Developer | Free Guide Tutorial
- What is PHP Developer ? Everything You Need to Know
- How to Become an Angular Developer?
- Basics of Service Design
- Why You Should Learn PHP?
- Top 10 Reasons to Learn JavaScript
- What is React?
- How to Become a PHP Developer?
- AngularJS Vs. Angular 2 Vs. Angular 4
- AngularJS Vs JQuery
- TypeScript Vs JavaScript
- What is UIPath?
- What is Angular?
- What is React JS ? Know the features of React JS
- Skills required to become a Full Stack Developer | All you need to know
- What is Angular Version?| Know more about it.
- Exploring the Various Decorators in Angular | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Career Advantages of AngularJS Certification | Everything You Need to Know to Become an Expert
- How to Become a Web Developer? : Everything you Need to Know about the Profile[OverView]
- PHP Cookies and Session Outline | Everything You Need to Know
- Magnific Popup: Responsive jquery | How to Implement Magnific Popup [ OverView ]
- How to Work With Forms In JavaScript?: Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Python vs Node.js | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Top 10 JavaScript Frameworks | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- Learn Ruby on Rails :Understanding Concepts and Career Prospects [ OverView ]
- AEM vs Open Source Content Management | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Average Web Developer Salary in India [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is Context in React ? : Comprehensive Guide [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- Django vs Node.js : Differences and Which Should You Learn? [ OverView ]
- JQuery vs JavaScript : Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Front End Developer Salary in India | Everything You Need to Know [OverView]
- Control Statements in Java – Expert’s Top Picks
- Top 10 Python Libraries for Machine Learning : Step-By-Step Process
- Exploring the Various Decorators in Angular | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Practical Applications of Python | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- AngularJS CDN Integration : Comprehensive Guide
- What are Python KeyError Exceptions ? Expert’s Top Picks
- Best Web Development Languages To Learn | [ Job & Future ]
- How to Become a Front End Developer | Free Guide Tutorial
- What is PHP Developer ? Everything You Need to Know
- How to Become an Angular Developer?
- Basics of Service Design
- Why You Should Learn PHP?
- Top 10 Reasons to Learn JavaScript
- What is React?
- How to Become a PHP Developer?
- AngularJS Vs. Angular 2 Vs. Angular 4
- AngularJS Vs JQuery
- TypeScript Vs JavaScript
- What is UIPath?
- What is Angular?

What are Python KeyError Exceptions ? Expert’s Top Picks
Last updated on 27th Oct 2022, Artciles, Blog, Website Development
- In this article you will get
- Introduction
- Exceptions versus Syntax Errors
- Raising an Exception
- The Assertion Error Exception
- The try and except Block: The Handling Exceptions
- Cleaning Up After Using finally
- Conclusion
Introduction
A Python program are terminates as soon as it encounters an error. In a Python, an error can be a syntax error or exception. In this article, will see what an exception is and how it varies from a syntax error. After that, will learn about raising an exceptions and making assertions. Then, wi,ll finish with a demonstration of a try and except block.
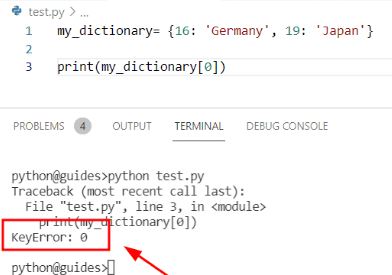
Exceptions versus Syntax Errors
Syntax errors occur when a parser detects an incorrect statement. Observe a following example:
- >>> print( 0 / 0 ))
- File “<"stdin">“, line 1
- print( 0 / 0 ))
- ^
- SyntaxError: invalid syntax
The arrow indicates where a parser ran into syntax error. In this example, there was a one bracket too many. Remove it and run a code again:
This time, ran into an exception error. This type of an error occurs whenever syntactically correct a Python code results in an error. The last line of a message indicated what type of an exception error ran into.
Instead of a showing the message exception error, Python details what type of an exception error was encountered. In this case, it was ZeroDivisionError. Python comes with a various built-in exceptions as well as possibility to create a self-defined exceptions.
Raising an Exception
Can use raise to throw exception if a condition occurs. The statement can be a complemented with custom exception.If need to throw an error when a certain condition occurs using raise, and could go about it like this:
- x = 10
- if x > 5:
- raise Exception(‘x should not be exceed 5. The value of a x was: {}’.format(x))
- When run this code, the output will be a following:
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File “<"input">“, line 4, in <"module">
- Exception: x should not be exceed 5. The value of a x was: 10
The program comes to be a halt and displays our exception to a screen, offering a clues about what went wrong.
The Assertion Error Exception
Instead of waiting for the program to crash midway, and can also start by making the assertion in Python. Assert that a certain condition is met. If this condition turns out to be a True, then that is excellent! The program can be continue. If condition turns out to be False, can have the program throw the AssertionError exception.
Have a look at a following example, where it is an asserted that a code will be executed on Linux system:
- import sys
- assert (‘linux’ in sys.platform), This code runs on a Linux only.
If run this code on a Linux machine, an assertion passes. If were to run this code on Windows machine, the outcome of a assertion would be False .In this example, throwing the AssertionError exception is a last thing that the program will do. The program will come to be halt and will not continue.
The try and except Block: Handling Exceptions
The try and except block in a Python is used to catch and also handle exceptions. Python executes a code following the try statement as a “normal” part of a program. The code that follows an except statement is a program’s response to any exceptions in preceding try clause.
As saw earlier, when syntactically correct a code runs into an error, Python will throw the exception error.This exception are error will crash the program if it is be unhandled. The except clause a determines how a program responds to an exceptions The linux_interaction() can only run on Linux system. The assert in this function will throw the AssertionError exception if call it on an operating system other then a Linux.
The way handled the error here is by handing out the pass. If were to run this code on the Windows machine,got nothing. The good thing here is that a program did not crash. To this end, can change the pass into the something that would generate informative message, like so:
- When an exception occurs in the program running this function, the program will be continue as well as inform about the fact that the function call was not be successful.
- What did not get to see was a type of error that was thrown as a result of a function call. In order to see an exactly what went wrong, and would need to catch error that a function threw.
- The first message is an AssertionError, informing that the function can only be an executed on a Linux machine. The second message are tells which function was not be executed.
- In the previous, called a function that are wrote yourself. When executed a function, caught a AssertionError exception and printed it to screen.
- Can have more than one function call in a try clause and anticipate catching the various exceptions. A thing to note here is that a code in the try clause will stop as soon as exception is encountered.
If a file does not exist, running this code on the Windows machine will output are following:
Function can only run on a Linux systems.
- Linux linux_interaction() function was not be executed
Inside a try clause, you ran into an exception immediately and did not get to a part where you attempt to open file.log. Here are key takeaways:
- A try clause is an executed up until the point where a first exception is encountered.
- Inside a except clause, or the exception handler, find how the program responds to an exception.
- Can anticipate the multiple exceptions and differentiate how a program should respond to them.
- Avoid using a bare except clauses.
Cleaning up after using finally
Imagine that always had to implement a some sort of action to clean up after an executing a code. Python enables to do so using a finally clause.Everything in the finally clause will be an executed. It does not matter if can encounter an exception somewhere in a try or else clauses. Running a previous code on a Windows machine.
Conclusion
Raise allows to throw an exception at a any time.Assert enables to verify if a certain condition is met and throw the exception if it isn’t.In a try clause, all statements are executed until a exception is be encountered.Except is used to catch and handle exception(s) that are encountered in a try clause.Else lets code sections that are should run only when no exceptions are be encountered in a try clause.Finally enables to execute sections of code that are should always run, with or without any previously encountered exceptions.
