- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Project Management Process ? : A Complete Guide
- What is Lean Management? : A Complete Guide
- What is ITIL ? Know about the Framework
- What is Six Sigma?| Know the tools used
- What is Kanban Training?|Know more about it
- Project Management Tools and Techniques : A Complete Guide
- What is Project Management? Everything You need to Know | Salary for the role
- Srum Org Certification? All you need to know about it
- MS Project Certification | All you need to know
- What is Project Manager? Know about the salary
- Six Sigma Certification Cost | Know all details about it
- Difference Between PMO and Project Manager? | Expert’s Top Picks
- What are Project Management Tools | Its Techniques | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Agile |Its Methodology and Types | How to Implement [ OverView ]
- What is a Product Roadmap? | How to Create one | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Scrum vs Kanban | Agile at Scale | New Agile BenchMark
- How to Effectively Manage Stakeholders | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Experts Top Picks
- What is Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) | The Leading Framework For Business Agility | Everything You Need to Know
- How to Become a Project Manager | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- Time Management Tools to Help You Succeed as a Professional | Expert’s Top Picks
- Top 10 Tips for Agile Sprint Planning To Implement Efficient Marketing | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is ICP-ACC (ICAgile Certified Agile Coaching)? | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices [ OverView ]
- How To Run An Effective Agile Retrospective-Agile management | Everything You Need to Know
- What Skills Does One Acquire After The PMP Certification?
- A Definitive Guide: Most Effective and Proven Time Management Techniques [ OverView ]
- What Gaps I Filled After CSM Certification For my Scrum Project? [ OverView ]
- How to Create A Plan And Manage Your Projects Better?: Step-By-Step Process [ OverView ]
- What is User Story Mapping? : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is Design Thinking ? : Benefits and Special Features | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What is the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is Sprint Planning ? | A Definitive Guide | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and How Does It Help in Equipment Effectiveness [ OverView ]
- What are Agile Metrics ? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Agile Marketing and Why Do You Need It | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Why is Retrospection Needed? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Developing Project Schedule : Role of Float, Leads, and Lags [ OverView ]
- Project Life Cycle vs Product Life Cycle | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Projects in Business Environments | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Business Agility ? and Why is it Important ? Expert’s Top Picks
- The Most Important Benefits of Blended Learning | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- Can Business Analyst be a Project Manager? : Expert’s Top Picks
- Why A PMO Is Second In Line To A Project Manager ? | Expert’s Top Picks
- Devops vs Waterfall | A Definitive Guide and Which Should You Learn?
- Jira vs Trello | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Key Values and Principles Behind the Agile Manifesto | A Definitive Guide
- What are Scrum Ceremonies : The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Business Analyst vs Financial Analyst | Know Their Differences and Which Role is Better ?
- Learn Burndown Charts With Jira : Comprehensive Guide [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What Is Scrum XP? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Phases of Project Management | Step-By-Step Process | Expert’s Top Picks
- Project Manager Salary in India – How much does a PM earn? [ Job & Future ]
- Why Do Scrum Masters Get Paid so Much? [For Freshers and Experience]
- What Best Describes a Scrum Team? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- JIRA vs TFS | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Anti-patterns of a Scrum Master : Step-By-Step Process
- SCM Tools and Frameworks | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Stages of Team Development | Everything You Need to Know
- Project Management Consultant : Job Description, Skills Required | Everything You Need to Know
- CSM vs PSM : Difference You Should Know
- Top Characteristics of a Project Manager : Expert’s Top Picks
- Roles And Responsibilities Of A Product Owner : Everything You Need to Know
- Common Project Risks and How to Tackle Them | Expert’s Top Picks
- Benefits of Having Shorter Sprints in Agile – Everything You Need to Know
- Group Discussion Tips | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- PMP Certification Cost : All you need to know
- DMAIC Process and Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Agile Scrum Vs Kanban | Know the difference
- Deming vs Juran vs Crosby
- What is Project Scope Management and Why It’s Important?
- The Basic Principles of Project Management
- Top PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2020
- Risk Management Strategies
- Roles and Responsibilities of A Scrum Master
- ROM Estimate Vs Definitive Estimate
- Guidelines for Creating and Maintaining a WBS Dictionary
- How to Become a Certified ScrumMaster?
- Top Professional Skills for 2020
- Fast Tracking Vs Crashing
- PMP Vs PRINCE2 Vs CAPM
- PMP Earned Value Management (EVM) And Formulas
- What is Certified Scrum Professional (CSM)?
- Top Leadership Theories Every Manager Should Know
- What is Deliverables in Project Management?
- How To Prepare For TOEFL
- History and evolution of the PMP Certification
- What Is Float In Microsoft Project?
- Rules to set you up for success in project
- What is Scrum Project Management?
- What Is Estimating Activity Duration in Project Management?
- What Are The PMP Terminologies Relating To Cost Knowledge Area?
- What is Project Scope Management processes?
- What Are The Types of Organization In PMP?
- Books to Beat the Scrum Master Certification
- Agile Coach Vs Agile Consultant
- What is the cost of quality in project management?
- Signs Your Career May Be Stagnation and Tips to Overcome Downturn
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) Certification
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification
- What is schedule Activity in project management?
- Why Do We Need a Project Charter?
- PMP Certification Exam Preparation Mind Map
- Why Quality Professionals Should Use Infographics In Project Management?
- Role of Earned Value Technique in Project Management
- What is Project Quality Management?
- Tools and Techniques to Estimate Project Cost
- What is a Project Charter And Project Scope in Project Management?
- Why Should You Conduct Project Status Meetings with Your Team?
- The 7 R’s of Change Management
- What Are The Categories and sources of risk in your project?
- What Is a Network Diagram in Project Management?
- What are The Types of Contracts In PMP?
- Residual Risk Vs Secondary Risk
- Impact of the stakeholders on the projects
- Effort Vs Duration Vs Elapsed Time
- Agile vs Scrum
- What Is Six Sigma Quality Assurance?
- How to Close a Project?
- What Qualifications Do You Need to be a Project Manager?
- Project Management Vs General Operations Management
- Enterprise Environmental Factors & Organizational Process Assets
- What is a project manager?
- Important Questions for PMP Certification Exam
- How is the PMP Exam changing, in 2015 & 2020?
- How To Renew Your PMP Certification?
- The Importance of Having Project Acceptance Criteria in Your Projects
- Tips for PMP Exam Preparation
- What is requirement traceability matrix RTM in Project Management?
- Poor Performance Appraisal? Here are the tips to turn any negative feedback into positive.
- How to build a successful Career in Agile and Scrum?
- Importance of Tuckman ladder model in HR management
- How To Apply For The PMP® Exam In Easy Steps
- How to Write a Six Sigma Problem Statement
- What is a lessons learned document in PMI?
- Perform Quality Assurance Vs Perform Quality Control
- How to Improve Quality Management Consistently?
- Interactive Vs Push Vs Pull Communication
- what is risk management?
- Key Appraisal Questions to Prepare For
- What are the MSP Certifications?
- What Is A Six Sigma Control Plan?
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel?
- Agile Prioritization Techniques
- Tips to Help Millennials Climb the Corporate Ladder
- What is an Issue Log?
- Advantages of PMP over MBA
- Top Successful Project Estimation Techniques
- PMP Examination Preparation – ITTO’s
- Employee Training Rewards That Actually Improve Learning
- Lean principles
- What Does It Take to Become a Successful Agile Coach
- Projects VS Programs
- The Role of Six Sigma in Manufacturing
- The Top Formulas to Memorize Before Your PMP Exam
- Roadmap to CSM (Certified Scrum Master) Certification
- What are Some Qualities of a Good Manager and Good Leader?
- How to Handle Project Monitoring and Controlling Processes?
- Top Free Agile Tools For Any Project Manager
- Risk Assessment in Project Management
- The Concept of Zero Defects in Quality Management
- The Importance of Work Packages in Project Scope Management
- How to Get Project Management Experience for PMP Certification
- Different Ways to Calculate the Estimate at Completion (EAC)
- What Is a ScrumMaster?
- What is Risk Register?
- Agile Certifications
- Top-down Approach Vs Bottom-up Approach
- Leadership Vs Management
- What is Feasibility Study and Its Importance in Project Management?
- What Is a Project Management Plan?
- The Professional Advantages of the CAPM Certification
- PRINCE2 Vs PMP
- Rita Mulcahy’s PMP Prep and PMBOK® Guide
- What is Project Cycle Management?
- What is Project and Process Metrics?
- PMBOK® Sixth Edition is Here! What Project Managers Should Know?
- CAPM Certification
- Top Project Selection Methods for Project Managers
- Free Float Vs Total Float
- What is Critical Chain Project Management?
- How to Build a Career in Project Management?
- Scrum Master or Product Owner: What Suits You Better?
- Project Documentation and its Importance
- What is Performance Reporting in the Project Management?
- Top Highest Paying Tech Jobs in India
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Project Management Process ? : A Complete Guide
- What is Lean Management? : A Complete Guide
- What is ITIL ? Know about the Framework
- What is Six Sigma?| Know the tools used
- What is Kanban Training?|Know more about it
- Project Management Tools and Techniques : A Complete Guide
- What is Project Management? Everything You need to Know | Salary for the role
- Srum Org Certification? All you need to know about it
- MS Project Certification | All you need to know
- What is Project Manager? Know about the salary
- Six Sigma Certification Cost | Know all details about it
- Difference Between PMO and Project Manager? | Expert’s Top Picks
- What are Project Management Tools | Its Techniques | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Agile |Its Methodology and Types | How to Implement [ OverView ]
- What is a Product Roadmap? | How to Create one | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Scrum vs Kanban | Agile at Scale | New Agile BenchMark
- How to Effectively Manage Stakeholders | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Experts Top Picks
- What is Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) | The Leading Framework For Business Agility | Everything You Need to Know
- How to Become a Project Manager | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- Time Management Tools to Help You Succeed as a Professional | Expert’s Top Picks
- Top 10 Tips for Agile Sprint Planning To Implement Efficient Marketing | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is ICP-ACC (ICAgile Certified Agile Coaching)? | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices [ OverView ]
- How To Run An Effective Agile Retrospective-Agile management | Everything You Need to Know
- What Skills Does One Acquire After The PMP Certification?
- A Definitive Guide: Most Effective and Proven Time Management Techniques [ OverView ]
- What Gaps I Filled After CSM Certification For my Scrum Project? [ OverView ]
- How to Create A Plan And Manage Your Projects Better?: Step-By-Step Process [ OverView ]
- What is User Story Mapping? : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What is Design Thinking ? : Benefits and Special Features | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What is the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is Sprint Planning ? | A Definitive Guide | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and How Does It Help in Equipment Effectiveness [ OverView ]
- What are Agile Metrics ? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Agile Marketing and Why Do You Need It | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Why is Retrospection Needed? : A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Developing Project Schedule : Role of Float, Leads, and Lags [ OverView ]
- Project Life Cycle vs Product Life Cycle | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Projects in Business Environments | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Business Agility ? and Why is it Important ? Expert’s Top Picks
- The Most Important Benefits of Blended Learning | A Complete Guide For Beginners
- Can Business Analyst be a Project Manager? : Expert’s Top Picks
- Why A PMO Is Second In Line To A Project Manager ? | Expert’s Top Picks
- Devops vs Waterfall | A Definitive Guide and Which Should You Learn?
- Jira vs Trello | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Key Values and Principles Behind the Agile Manifesto | A Definitive Guide
- What are Scrum Ceremonies : The Ultimate Guide with Expert’s Top Picks
- Business Analyst vs Financial Analyst | Know Their Differences and Which Role is Better ?
- Learn Burndown Charts With Jira : Comprehensive Guide [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What Is Scrum XP? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- Phases of Project Management | Step-By-Step Process | Expert’s Top Picks
- Project Manager Salary in India – How much does a PM earn? [ Job & Future ]
- Why Do Scrum Masters Get Paid so Much? [For Freshers and Experience]
- What Best Describes a Scrum Team? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- JIRA vs TFS | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Anti-patterns of a Scrum Master : Step-By-Step Process
- SCM Tools and Frameworks | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Stages of Team Development | Everything You Need to Know
- Project Management Consultant : Job Description, Skills Required | Everything You Need to Know
- CSM vs PSM : Difference You Should Know
- Top Characteristics of a Project Manager : Expert’s Top Picks
- Roles And Responsibilities Of A Product Owner : Everything You Need to Know
- Common Project Risks and How to Tackle Them | Expert’s Top Picks
- Benefits of Having Shorter Sprints in Agile – Everything You Need to Know
- Group Discussion Tips | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- PMP Certification Cost : All you need to know
- DMAIC Process and Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Agile Scrum Vs Kanban | Know the difference
- Deming vs Juran vs Crosby
- What is Project Scope Management and Why It’s Important?
- The Basic Principles of Project Management
- Top PMP Exam Questions and Answers for 2020
- Risk Management Strategies
- Roles and Responsibilities of A Scrum Master
- ROM Estimate Vs Definitive Estimate
- Guidelines for Creating and Maintaining a WBS Dictionary
- How to Become a Certified ScrumMaster?
- Top Professional Skills for 2020
- Fast Tracking Vs Crashing
- PMP Vs PRINCE2 Vs CAPM
- PMP Earned Value Management (EVM) And Formulas
- What is Certified Scrum Professional (CSM)?
- Top Leadership Theories Every Manager Should Know
- What is Deliverables in Project Management?
- How To Prepare For TOEFL
- History and evolution of the PMP Certification
- What Is Float In Microsoft Project?
- Rules to set you up for success in project
- What is Scrum Project Management?
- What Is Estimating Activity Duration in Project Management?
- What Are The PMP Terminologies Relating To Cost Knowledge Area?
- What is Project Scope Management processes?
- What Are The Types of Organization In PMP?
- Books to Beat the Scrum Master Certification
- Agile Coach Vs Agile Consultant
- What is the cost of quality in project management?
- Signs Your Career May Be Stagnation and Tips to Overcome Downturn
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) Certification
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification
- What is schedule Activity in project management?
- Why Do We Need a Project Charter?
- PMP Certification Exam Preparation Mind Map
- Why Quality Professionals Should Use Infographics In Project Management?
- Role of Earned Value Technique in Project Management
- What is Project Quality Management?
- Tools and Techniques to Estimate Project Cost
- What is a Project Charter And Project Scope in Project Management?
- Why Should You Conduct Project Status Meetings with Your Team?
- The 7 R’s of Change Management
- What Are The Categories and sources of risk in your project?
- What Is a Network Diagram in Project Management?
- What are The Types of Contracts In PMP?
- Residual Risk Vs Secondary Risk
- Impact of the stakeholders on the projects
- Effort Vs Duration Vs Elapsed Time
- Agile vs Scrum
- What Is Six Sigma Quality Assurance?
- How to Close a Project?
- What Qualifications Do You Need to be a Project Manager?
- Project Management Vs General Operations Management
- Enterprise Environmental Factors & Organizational Process Assets
- What is a project manager?
- Important Questions for PMP Certification Exam
- How is the PMP Exam changing, in 2015 & 2020?
- How To Renew Your PMP Certification?
- The Importance of Having Project Acceptance Criteria in Your Projects
- Tips for PMP Exam Preparation
- What is requirement traceability matrix RTM in Project Management?
- Poor Performance Appraisal? Here are the tips to turn any negative feedback into positive.
- How to build a successful Career in Agile and Scrum?
- Importance of Tuckman ladder model in HR management
- How To Apply For The PMP® Exam In Easy Steps
- How to Write a Six Sigma Problem Statement
- What is a lessons learned document in PMI?
- Perform Quality Assurance Vs Perform Quality Control
- How to Improve Quality Management Consistently?
- Interactive Vs Push Vs Pull Communication
- what is risk management?
- Key Appraisal Questions to Prepare For
- What are the MSP Certifications?
- What Is A Six Sigma Control Plan?
- How to Create a Project Plan in Excel?
- Agile Prioritization Techniques
- Tips to Help Millennials Climb the Corporate Ladder
- What is an Issue Log?
- Advantages of PMP over MBA
- Top Successful Project Estimation Techniques
- PMP Examination Preparation – ITTO’s
- Employee Training Rewards That Actually Improve Learning
- Lean principles
- What Does It Take to Become a Successful Agile Coach
- Projects VS Programs
- The Role of Six Sigma in Manufacturing
- The Top Formulas to Memorize Before Your PMP Exam
- Roadmap to CSM (Certified Scrum Master) Certification
- What are Some Qualities of a Good Manager and Good Leader?
- How to Handle Project Monitoring and Controlling Processes?
- Top Free Agile Tools For Any Project Manager
- Risk Assessment in Project Management
- The Concept of Zero Defects in Quality Management
- The Importance of Work Packages in Project Scope Management
- How to Get Project Management Experience for PMP Certification
- Different Ways to Calculate the Estimate at Completion (EAC)
- What Is a ScrumMaster?
- What is Risk Register?
- Agile Certifications
- Top-down Approach Vs Bottom-up Approach
- Leadership Vs Management
- What is Feasibility Study and Its Importance in Project Management?
- What Is a Project Management Plan?
- The Professional Advantages of the CAPM Certification
- PRINCE2 Vs PMP
- Rita Mulcahy’s PMP Prep and PMBOK® Guide
- What is Project Cycle Management?
- What is Project and Process Metrics?
- PMBOK® Sixth Edition is Here! What Project Managers Should Know?
- CAPM Certification
- Top Project Selection Methods for Project Managers
- Free Float Vs Total Float
- What is Critical Chain Project Management?
- How to Build a Career in Project Management?
- Scrum Master or Product Owner: What Suits You Better?
- Project Documentation and its Importance
- What is Performance Reporting in the Project Management?
- Top Highest Paying Tech Jobs in India

DMAIC Process and Methods | All you need to know [ OverView ]
Last updated on 27th Oct 2022, Artciles, Blog, Project Management
- In this article you will learn:
- 1.Introduction
- 2.What is DMAIC?
- 3.Why the DMAIC Method?
- 4.How do you assess these circumstances?
- 5.DMAIC Benefits
- 5.The Five DMAIC Phases
- 6.Conclusion
Introduction
Companies have always tried to boost their sales and profits, which, in a way, show how good their products and services are. With new technologies being added to the business world all the time, the race to the bottom line is tougher than ever. In general, organizations are rushing to enhance their operations and become more efficient. This is one reason why more companies are starting to use DMAIC, which is one of the core methods for Six Sigma projects or any process improvement project.
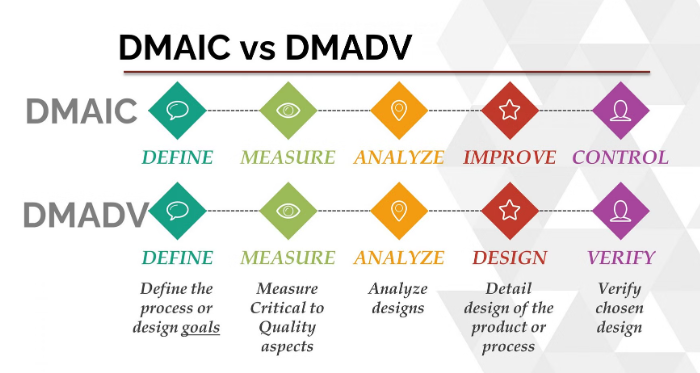
What is DMAIC?
DMAIC is a data-driven cycle of process improvement that strives to enhance, optimize, and stabilize business processes and designs. DMAIC is the improvement cycle that guides a Six Sigma project.
DMAIC is a five-step technique for optimizing a wide range of organizational processes, such as software development, manufacturing, and others. This method, while linked with Six Sigma, can also be used to lean and other process-improvement strategies. DMAIC is a data-driven problem-solving technique aimed to discover and eliminate inefficiencies in a process, hence enhancing its results and making them more predictable.
- UMass PGP in Lean Six Sigma With Modules
- Here is Your Key to Six Sigma Career Success!
- VIEW COURSEPGP in Lean Six Sigma Including UMass Modules
- DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control and is pronounced “duh-may-ik.”
The DMAIC methodology evolved from the PDSA (“plan, do, study, act”) cycle devised by statistician Walter A. Shewhart in the 1930s at Bell Laboratories. But the technique as it exists now was shaped by some of the world’s top corporations, including Toyota, Motorola, General Electric, and Ford Motor Company. Here you may discover more about the history behind the development of DMAIC and Six Sigma.
Why the DMAIC Method?
Before we delve into the primary process, there is one additional step that some organizations take to determine if DMAIC is the best method for solving their challenges. This process is known as “recognize.”
Even though it’s not a formal part of DMAIC, this step is important because DMAIC can’t be used in every situation. There are various scenarios under which this process improvement technique may be appropriate. To figure out if DMAIC is the right tool for you, it’s important to know the right conditions and choose the right problem to solve.
How do you assess these circumstances?
Here are three primary considerations:
- There are obvious inefficiencies and flaws in the current procedure.
- There is the ability to minimize variables like lead times or other defects while simultaneously increasing others such as productivity or cost savings.
- The situation is evaluable, and the consequences can be adequately quantified and comprehended.
- You can be sure that your process would benefit from DMAIC implementation after looking at all of the above factors.
DMAIC Benefits:
- DMAIC and six sigma applications leverage the DMAIC paradigm to improve the quality of the results provided by a company’s processes.
- Companies have always tried to boost their sales and profits, which, in a way, show how good their products and services are. With new technologies being added to the business world all the time, the race to the bottom line is tougher than ever.
- In general, organizations are rushing to enhance their operations and become more efficient. This is one of the reasons why more firms are adopting DMAIC, one of the foundational approaches for Six Sigma projects or any process improvement project.
- With the right application of DMAIC, organizations have reaped numerous benefits, including a reduction in the cost of poor quality, an increase in revenue, and an overall improvement in corporate performance and efficiency.
- The Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification course explains what Six Sigma is and how the DMAIC method works. Register Now!
The Five DMAIC Phases
The DMAIC method has five steps that are meant to set up the structure for process improvement, set goals, track progress, and evaluate results. The five phases (with a description of each) are as follows:
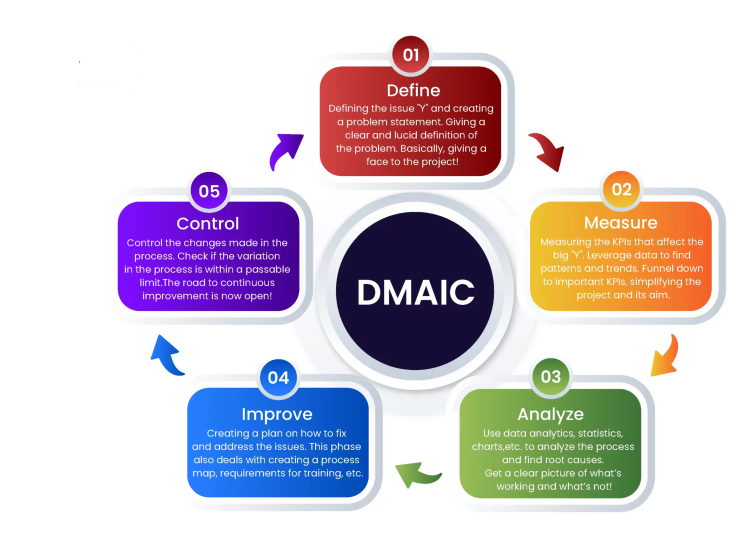
1. Define
During this step, we choose the most important and consequential improvement opportunities. In this step, you will map out the method, focus, scope, and final goal. You will also figure out how the problem affects all stakeholders. The method for initiating a DMAIC cycle is to create an issue statement.Other crucial stages at this stage include:
- Determine the prospects with the greatest potential for development
- Outline the project’s scope and create a value stream map (VSM) to describe each process step.
- Create a “voice of the customer table” (VOCT) to identify customer requirements.
- Identify all stakeholders
- Estimate the project’s effect and duration
- Recognize and record business opportunity
- Consider additional associated procedures
- A successful The define phase enables you to proceed with well-defined, crystal-clear objectives and a schedule for project completion.
2. Procedure
In the measure phase, baselines are established to evaluate the performance of a specific process. Without reliable reference points, it is difficult to track improvements. Consequently, at this point, we:
- Create the data collection techniques that will be used to assess success.
- Recognize signs of input, process, and output
- Compile and investigate current state data
- Describe the investigation of failure types and their effects
- Application of process capability analysis
- At this point, you can get better results by using visual management tools like control charts, bar charts, and run charts, among others.
3. Analyze
During this phase, the goal is to find and test the root causes of problems to make sure that they are fixed at their source. Important measures at this stage include:
- Performing a thorough root cause analysis (RCA), which encompasses a wide variety of approaches and methodologies, such as change analysis, events and causal factor analysis, and the Kepner-Tregoe problem solving and decision making model.
- Conducting a failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) in order to discover all potential problem areas, inefficiencies, faults, defects, and deficiencies.
- Using a multivari chart to obtain a visual depiction of the variations within a given process.
- Developing process management
- Creating a plan for enhancement
- After this phase, you will be able to successfully identify and record all chances for change, and your action plan will begin to take shape.
4. Improve
Now that the analysis has been completed and the data is available, it is time to begin making improvements.This phase consists of the following actions:
- Conceptualize and provide solutions
- Design an experiment (DOE) to determine the anticipated advantages of a proposed solution.
- Refine process maps and plans based on the information gathered in the previous phase.
- Describe a test solution and strategy.
- Utilize Kaizen events to enhance the process.
- Inform all parties involved of the solution.
- Utilizing improvement management software at this point is beneficial. This facilitates the smooth progression of the process, promotes cross-functional collaboration, and makes it easier for management and executives to track the development of a particular DMAIC project.
5. Control
After modifications have been implemented and are successfully resolving problems to improve your operations, it is necessary to bring the process under control to assure its durability. Here’s where you’ll find:
- Determine and record the new work standard
- Make a plan for quality control that makes sure everyone on the team follows the same steps and uses the same measurements.
- Confirm decrease of failures attributable to the identified cause
- Utilize statistical process control (SPC) to monitor process execution and identify problems.
- Determine, if necessary, additional enhancements to fulfill process objectives.
- Streamline process enhancements by implementing the “Five S’s” of Lean
- Integrate, record, and convey learnt lessons
- After the control phase, the total impact of process modifications may be quantified in terms of cost reduction, efficiency, quality improvement, productivity growth, and customer satisfaction.
- This phase lasts as long as there are new ways to improve, after which the DMAIC cycle starts over from the beginning. To start a DMAIC process, it takes time, work, and discipline, but once your team gets the hang of it, they will get used to the method.
Conclusion
The DMAIC process, a core component of the six sigma technique, is intended to increase efficiency and production. By obtaining the Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification, professionals will not only grasp DMAIC, but also how to implement these principles in real-world scenarios. The online Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification course from ACTE will help you pass the certification exam and prepare you for a job in the newest six sigma techniques, all without leaving your house. Here are a few things that should come to mind whenever Six Sigma is mentioned:
- Business Process Enhancement Technique
- Defects based on million possible outcomes
- Customer-centric Uses data and statistics
- Determine the monetary benefits.
- Structured development technique