- Different Methodologies in Project Management
- Difference between Soap and Rest | Know more about it
- What is Python array? Learn with examples
- Best Career options after Engineering | Everything You Need to Know [OverView]
- What is list in Python ? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Data Modelling? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What are Microservices? : A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Python Programming | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- All You Need To Know About Python List | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What Is a Software Developer | Software Developer job description and duties | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Artificial Intelligence Chatbot?
- Kotlin vs Java | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Abstraction in Java | Implementations of Abstraction in Java | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What are the Important Data Structures and Algorithms in Python?
- Go vs Python | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Best Python IDEs and Code Editors | Expert’s Top Picks | Everything You Need to Know
- Go Programming Language | Expert’s Top Picks | A Definitive Guide [ OverView ]
- Python Scopes and Their Built-in Functions | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Python String Formatting | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Python Serialization | A Complete Guide For Beginners | Learning Guide
- What is .Net FrameWork? Uses and its Benefits | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Quality Assurance ? : A Definitive Guide | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- What is Spike Testing ? : A Definitive Guide | Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Average Full Stack Developer Salary in India [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is WSDL in Web Services ? Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Virtual Instrumentation using Labview | Comprehensive Guide [ Explained ]
- Gradle vs Maven | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Python Sleep Method | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Kotlin vs Python | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Spring Boot vs Spring MVC | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- IT Engineer Salary in India – How much does one earn?
- What is pip ? and Getting Started with Python pip | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Node.js Installation on Windows and Ubuntu | Free Guide Tutorial
- Skills Needed for Full Stack Developers | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Axios in React? and Its Uses [ OverView ]
- What is MEAN Stack? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- How to Install Node.JS on Ubuntu | Everything You Need to Know
- Average Annual Salary of a Python Certified Professional – Career Path
- What is Scala Programming? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What Is User Input in Python? Expert’s Top Picks
- Interface vs Abstract Class | Difference You Should Know
- Final Year Computer Science Project Ideas | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Technical Architect | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Logical Programs in Java | Step-By-Step Process
- C++ vs Java | Difference You Should Know
- What is C Programming? Comprehensive Guide
- What Is a Quality Engineer? ( Everything You Need to Know )
- Python Project Ideas for Beginners | All you need to know
- How to Run Python Scripts? Comprehensive Guide
- Python Operators
- How To Install NumPy in Python?
- Top Software Courses to Get High Paying Jobs
- Loops In Python
- Tips to Avoid Application Rejection
- Top Young App Developers Who Became Millionaires
- Top Technical Courses After Graduation
- Node JS Architecture
- What is PyCharm?
- Resources To Help You Learn Java Programming
- How to Become a Software Engineer?
- Best Programming Languages to Learn in 2020
- Scala vs Python
- How to Become a Full Stack Developer?
- The Most Popular Java Applications Used World-wide
- What is Java String?
- Full Stack Developer vs Front End Developer vs Back End Developer
- Python Collections
- Identifiers in Python
- Dynamic Method Dispatch in Java
- Hadoop Ecosystem
- Method Overloading in Python
- Convert Decimal To Binary In Python
- How To Make A Chatbot In Python?
- How to Input a List in Python?
- Hash Tables and Hashmaps in Python
- Top Python Framework’s
- Python Split Method with Example
- Python Enumerate
- Inheritance in Java
- Init in Python
- Goto Statement in Python
- Literals in Java
- Polymorphism in Oops
- Socket Programming in Python
- Object Class in Java
- Break, Continue, and Pass Statements in Python
- Exception Handling in Java
- Java BASIC Programs
- Different Methodologies in Project Management
- Difference between Soap and Rest | Know more about it
- What is Python array? Learn with examples
- Best Career options after Engineering | Everything You Need to Know [OverView]
- What is list in Python ? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Data Modelling? : All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What are Microservices? : A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Python Programming | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- All You Need To Know About Python List | A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What Is a Software Developer | Software Developer job description and duties | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Artificial Intelligence Chatbot?
- Kotlin vs Java | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- What is Abstraction in Java | Implementations of Abstraction in Java | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What are the Important Data Structures and Algorithms in Python?
- Go vs Python | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Best Python IDEs and Code Editors | Expert’s Top Picks | Everything You Need to Know
- Go Programming Language | Expert’s Top Picks | A Definitive Guide [ OverView ]
- Python Scopes and Their Built-in Functions | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Python String Formatting | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- Python Serialization | A Complete Guide For Beginners | Learning Guide
- What is .Net FrameWork? Uses and its Benefits | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Quality Assurance ? : A Definitive Guide | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- What is Spike Testing ? : A Definitive Guide | Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Average Full Stack Developer Salary in India [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What is WSDL in Web Services ? Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Virtual Instrumentation using Labview | Comprehensive Guide [ Explained ]
- Gradle vs Maven | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Python Sleep Method | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Kotlin vs Python | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Spring Boot vs Spring MVC | Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- IT Engineer Salary in India – How much does one earn?
- What is pip ? and Getting Started with Python pip | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Node.js Installation on Windows and Ubuntu | Free Guide Tutorial
- Skills Needed for Full Stack Developers | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Axios in React? and Its Uses [ OverView ]
- What is MEAN Stack? All you need to know [ OverView ]
- How to Install Node.JS on Ubuntu | Everything You Need to Know
- Average Annual Salary of a Python Certified Professional – Career Path
- What is Scala Programming? A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What Is User Input in Python? Expert’s Top Picks
- Interface vs Abstract Class | Difference You Should Know
- Final Year Computer Science Project Ideas | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Technical Architect | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Logical Programs in Java | Step-By-Step Process
- C++ vs Java | Difference You Should Know
- What is C Programming? Comprehensive Guide
- What Is a Quality Engineer? ( Everything You Need to Know )
- Python Project Ideas for Beginners | All you need to know
- How to Run Python Scripts? Comprehensive Guide
- Python Operators
- How To Install NumPy in Python?
- Top Software Courses to Get High Paying Jobs
- Loops In Python
- Tips to Avoid Application Rejection
- Top Young App Developers Who Became Millionaires
- Top Technical Courses After Graduation
- Node JS Architecture
- What is PyCharm?
- Resources To Help You Learn Java Programming
- How to Become a Software Engineer?
- Best Programming Languages to Learn in 2020
- Scala vs Python
- How to Become a Full Stack Developer?
- The Most Popular Java Applications Used World-wide
- What is Java String?
- Full Stack Developer vs Front End Developer vs Back End Developer
- Python Collections
- Identifiers in Python
- Dynamic Method Dispatch in Java
- Hadoop Ecosystem
- Method Overloading in Python
- Convert Decimal To Binary In Python
- How To Make A Chatbot In Python?
- How to Input a List in Python?
- Hash Tables and Hashmaps in Python
- Top Python Framework’s
- Python Split Method with Example
- Python Enumerate
- Inheritance in Java
- Init in Python
- Goto Statement in Python
- Literals in Java
- Polymorphism in Oops
- Socket Programming in Python
- Object Class in Java
- Break, Continue, and Pass Statements in Python
- Exception Handling in Java
- Java BASIC Programs

Loops In Python
Last updated on 13th Oct 2020, Artciles, Blog, Software Engineering
Loops in Python
In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first, followed by the second, and so on. There may be a situation when you need to execute a block of code several number of times.
Programming languages provide various control structures that allow for more complicated execution paths.
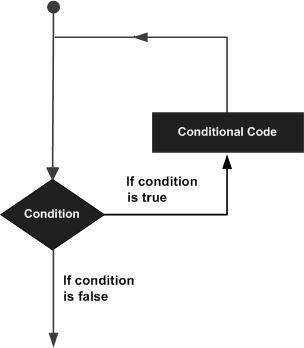
A loop statement allows us to execute a statement or group of statements multiple times. The following diagram illustrates a loop statement −
Python programming language provides the following types of loops to handle looping requirements.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
| S.No. | Loop Type & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | while loopRepeats a statement or group of statements while a given condition is TRUE. It tests the condition before executing the loop body. |
| 2 | for loopExecutes a sequence of statements multiple times and abbreviates the code that manages the loop variable. |
| 3 | nested loopsYou can use one or more loops inside any another while, for or do..while loop. |
While Loop
A while loop statement in Python programming language repeatedly executes a target statement as long as a given condition is true.
Syntax
The syntax of a while loop in Python programming language is −
- while expression:
- statement(s)
- Here, statement(s) may be a single statement or a block of statements. The condition may be any expression, and true is any non-zero value. The loop iterates while the condition is true.
- When the condition becomes false, program control passes to the line immediately following the loop.
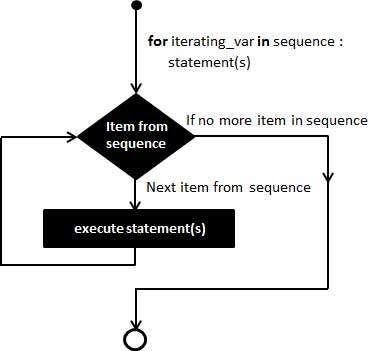
For Loop
It has the ability to iterate over the items of any sequence, such as a list or a string.
Syntax
- for iterating_var in sequence:
- statements(s)
- If a sequence contains an expression list, it is evaluated first.
- Then, the first item in the sequence is assigned to the iterating variable iterating_var.
- Next, the statements block is executed.
- Each item in the list is assigned to iterating_var, and the statement(s) block is executed until the entire sequence is exhausted.
Flow Diagram
Nested Loop
The Python programming language allows one loop inside another loop. Following section shows a few examples to illustrate the concept.
Syntax
- for iterating_var in sequence:
- for iterating_var in sequence:
- statements(s)
- statements(s)
The syntax for a nested while loop statement in Python programming language is as follows −
- while expression:
- while expression:
- statement(s)
- statement(s)
- A final note on loop nesting is that you can put any type of loop inside of any other type of loop.
- For example a for loop can be inside a while loop or vice versa.
Loop Control Statements
Loop control statements change execution from its normal sequence. When execution leaves a scope, all automatic objects that were created in that scope are destroyed.
Python supports the following control statements. Click the following links to check their detail.
Let us go through the loop control statements briefly
| S.No. | Control Statement & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | break statementTerminates the loop statement and transfers execution to the statement immediately following the loop. |
| 2 | continue statementCauses the loop to skip the remainder of its body and immediately retest its condition prior to reiterating. |
| 3 | pass statementThe pass statement in Python is used when a statement is required syntactically but you do not want any command or code to execute. |
