- How to learn Ethical Hacking?
- How to become a Ethical Hacker ? Know about the requirements to become one
- Introduction to Cyber Security | A Complete Guide
- Top Reasons to Learn Cyber Security | Everything You Need to Know to Become an Expert
- CyberSecurity Framework | How to Implement | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices [ OverView ]
- The Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Cybersecurity | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Certification and Why is it Important? [ OverView ]
- Benefits Of ECSA Certification | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Top Most OSINT Tools – Open Source Intelligence | Expert’s Top Picks
- Cyber Security Salary in India : Everything You Need to Know
- What is Computer Security? Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Ethical Hacker Salary and Job Description | Everything You Need to Know
- Hacking Tools and Software | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is DES? Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker?
- Which are the Best Network Security Certifications?
- Cybersecurity Consultant Career Path
- The Most Effective Data Encryption Techniques
- Great CISSP Books and Study Guides for the CISSP Certification
- What Is Kerberos?
- Top CISSP Domains
- Cyber Security Career Path
- CISSP Certification Exam Guide 2020
- Top Cyber Security Trends for 2020
- CISSP Exam Online 2020
- Compare and Contrast Physical and Environmental Security Controls
- What is information security architect?
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Certification
- Top Cyber Security Jobs
- What is CISA Certification?
- What is Threat Modeling?
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) Certification
- Information Security Management Principles
- Network Perimeter Security Design
- Things You Must Know About Cyber Security in the Cloud
- What is ECSA?
- Why is Cybersecurity Important?
- Tips to Clear Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Exam
- Average Annual Salary of a CISSP Certified Professional
- “How to Become a Cyber Security Engineer? “
- Who is an Ethical Hacker?
- What are the requirements to become Cissp certified?
- The Phases of Ethical Hacking
- What is Ethical Hacking?
- Top Ethical Hacking Certifications
- Hash in Python
- How to learn Ethical Hacking?
- How to become a Ethical Hacker ? Know about the requirements to become one
- Introduction to Cyber Security | A Complete Guide
- Top Reasons to Learn Cyber Security | Everything You Need to Know to Become an Expert
- CyberSecurity Framework | How to Implement | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices [ OverView ]
- The Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Cybersecurity | Everything You Need to Know
- What is Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Certification and Why is it Important? [ OverView ]
- Benefits Of ECSA Certification | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Top Most OSINT Tools – Open Source Intelligence | Expert’s Top Picks
- Cyber Security Salary in India : Everything You Need to Know
- What is Computer Security? Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Ethical Hacker Salary and Job Description | Everything You Need to Know
- Hacking Tools and Software | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is DES? Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker?
- Which are the Best Network Security Certifications?
- Cybersecurity Consultant Career Path
- The Most Effective Data Encryption Techniques
- Great CISSP Books and Study Guides for the CISSP Certification
- What Is Kerberos?
- Top CISSP Domains
- Cyber Security Career Path
- CISSP Certification Exam Guide 2020
- Top Cyber Security Trends for 2020
- CISSP Exam Online 2020
- Compare and Contrast Physical and Environmental Security Controls
- What is information security architect?
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Certification
- Top Cyber Security Jobs
- What is CISA Certification?
- What is Threat Modeling?
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) Certification
- Information Security Management Principles
- Network Perimeter Security Design
- Things You Must Know About Cyber Security in the Cloud
- What is ECSA?
- Why is Cybersecurity Important?
- Tips to Clear Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) Exam
- Average Annual Salary of a CISSP Certified Professional
- “How to Become a Cyber Security Engineer? “
- Who is an Ethical Hacker?
- What are the requirements to become Cissp certified?
- The Phases of Ethical Hacking
- What is Ethical Hacking?
- Top Ethical Hacking Certifications
- Hash in Python

The Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Cybersecurity | Everything You Need to Know
Last updated on 04th Nov 2022, Artciles, Blog, Cyber Security
- In this article you will learn:
- 1.Introduction to an AI and Machine Learning on a Cybersecurity.
- 2.AI and Cyber Security.
- 3.Main Challenges Cybersecurity Faces Today.
- 4.How AI Improves a Cybersecurity.
- 5.Drawbacks and Limitations of Using AI for a Cybersecurity.
- 6.Conclusion.
Introduction to an AI and Machine Learning on a Cybersecurity:
Experts are agree that a Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have both the negative and positive effects on a cyber security. AI algorithms use a training data to learn how to respond to various situations. As they progress, they learn by a copying and adding additional information. This article reviews a positive and negative effects of AI on cyber security.
AI and Cyber Security:
- Cyber security is one of many uses of an artificial intelligence. A report by a Norton showed that the global cost of a typical data breach recovery is $3.86 million.
- The report also states that a companies need an average of 196 days to recover from the any data breach. For this reason, organizations should invest a more in AI to avoid wastage of a time and financial losses.
- AI machine learning and a threat intelligence can recognize a patterns in data to enable security systems to learn from a past experience. In addition AI and machine learning enable the companies to reduce an incident response times and adhere to a security best practises.
Main Challenges Cybersecurity Faces Today:
Despite advances ina cyber security, attacks are becoming more and more dangerous. The main challenges of a cyber security include:
Geographically distant IT systems— a Geographical distance makes a manual tracking of incidents more complex . a Cyber security experts need to bridge a gap in infrastructure to successfully monitor the incidents across sectors.
Manual Threat Hunting – can be a costly and time-consuming, resulting in a more going unnoticed.
Reactive nature of cyber security – Companies can solve a problems only when they have already been happened. Predicting threats before they occur is the major challenge for a security experts.
Hackers often hide and change their IP addresses— Hackers use a different programs such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), proxy servers, a Tor browser and more. These programs are help hackers to remain for anonymous and undetected.
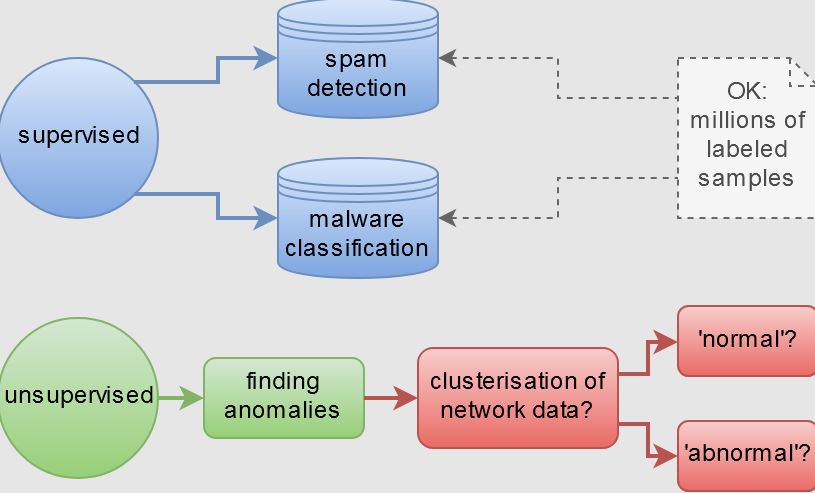
How AI Improves a Cybersecurity:
Threat hunting:
- Traditional security techniques use a signatures or indicators of the compromise to identify threats. This technique may work well for a threats already encountered, but they are not be effective for threats that have not yet discovered.
- The signature based on technology can detect about 90% of a threats. Replacing traditional techniques with an AI can increase the detection rate to 95%, but will get an explosion of false positives.
- The best solution would be to combine the both traditional methods and AI. This can result in 100% detection rate and reduce a false positives.
- Companies can also use the AI to enhance a threat hunting process by integrating behavioral analysis. For example, can leverage AI models to develop profiles of the each application within an organization’s network by a processing high amounts of an endpoint data.
Vulnerability management:
- There were a 20,362 new vulnerabilities reported in a 2019 a 17.8% increase over 2018. An Organisations are struggling to be prioritise and manage the massive amount of a new vulnerabilities they encounter on daily basis.
- Traditional vulnerability management methods are wait for hackers to exploit a high-risk vulnerabilities before deactivating them.
- While traditional vulnerability databases are the critical to managing and containing known vulnerabilities, AI and machine learning techniques such as a User and Event Behavioural Analytics (UEBA) can analyze a baseline behavior of user accounts, endpoints, servers and identify anomalous behavior.
- Can identify what may be indicate a zero-day unknown attack. This can help keep to organisations secure even before vulnerabilities are officially reported and also patched.
Data centers:
AI can optimise and monitor more essential data center processes like backup power, cooling filters, power consumption, internal temperature and bandwidth usage. AI’s computational powers and a continuous monitoring capabilities provide the insight into what values will improve an effectiveness and security of a hardware and infrastructure.
Network security:
There are two time-intensive aspects of a traditional network security, creating security policies and understanding the organization’s network topography:
- Policies—Security policies are identify which network connections are be legitimate and which should monitor for a malicious behavior. Can use these policies to effectively implement zero-trust model. The real challenge lies in formulating and maintaining policies in view of large number of networks.
- Topography—Most organizations do not have a precise naming conventions for the applications and workloads. As a result, security teams spend a lot of time determining what type of a workload a given application is be concerned with.
- Companies can leverage AI to improve the network security by learning a network traffic patterns and recommending functional set of workloads and also security policy.
Drawbacks and Limitations of Using AI for a Cybersecurity:
Resources— Companies need to invest the lot of time and money into resources are computing power, memory, and data to build and maintain AI systems.
Data set- AI model is trained with a learning data set. Security teams need to get their hands on many various data sets of malicious code, malware code, and anomalies. Some companies are do not have a resources and time to obtain all these accurate data sets.
Hackers- also use a AI-attackers’ tests and improve their malware to made it resistant to AI-based security tools. Hackers are learn from existing AI tools to develop a more advanced attacks and attack traditional security systems or an even AI-boosted systems.
Neural Fuzzing – Fuzzing is a process of testing large amounts of a random input data within software to identify its weaknesses. Neural Fuzzing leverages AI to quickly test a large amounts of random input. However, a fuzzing has a creative side as a well. Hackers can learn about weaknesses of a target system by gathering information with the power of a neural networks. A Microsoft developed a method for implementing this approach to improve software, resulting in a more secure code that is harder to use.
Conclusion:
Artificial intelligence and machine learning can improve the security, as well as make it simpler for a cybercriminals to systems without any human intervention. This can cause a lot of loss to the any company. It is highly recommended to get a some sort of protection against cybercriminals if need to minimize losses and stay in a business.
