
What Is Data Processing ? A Step-By-Step Guide
Last updated on 27th Oct 2022, Artciles, Blog
- In this article you will learn:
- 1.Introduction.
- 2.Methods of data Processing.
- 3.Tools for data processing.
- 4.Features of data processing.
- 5.Steam Processing Tools.
- 6.Batch Processing Tools.
- 7.Tools for interactive Analysis.
- 8.How does it work?
- 9.Why data processing?
- 10.Trend in data processing.
- 11.Data Processing in Research Area.
- 12.Advantages of data processing.
- 13.Disadvantages of data processing.
- 14.Application of data processing.
- 15.The Prospects for Data Processing.
- 16Conclusion.
Introduction:
Data in its unprocessed form is useless to any business. Data processing is the act of taking raw data and turning it into information that can be used. Typically, it is performed in a step-by-step manner by a team of data scientists and data engineers within an organization. The raw data is collected, filtered, sorted, processed, analyzed, and then presented in a readable format. Businesses need to process data in order to come up with better business strategies and gain a competitive edge.
Methods of data Processing:
There are three fundamental record processing methods:
Manual Processing of Data:
In this approach to record processing, records are manually processed. The whole process of collecting data, filtering, sorting, calculating, and doing other logical tasks is done by hand, without any digital tools or automation software. It is a low-cost method that requires little to no equipment, but results in high error rates, high labor costs, and a great deal of time.
Mechanical Processing of Data:
The processing of data is automated through the use of devices and machines. These could be relatively straightforward machines like calculators, typewriters, printing presses, and the like With this method, simple information processing operations are possible. It makes a lot fewer mistakes than processing information by hand, but as information has grown, this method has become more complicated and hard to use.
Computerized Data Processing:
Using record-processing software and programs, data is processed utilizing cutting-edge technology. A set of commands tells the software how to process the data and make output. This method is the most expensive, but it provides the fastest processing speeds with the highest output reliability and precision.
Tools for data processing:
The analytics of large datasets cannot be prepared using conventional equipment; consequently, a few of the available tools are described below. The equipment for large records falls into three major categories:
Stream Processing: This type of processing deals with massive amounts of real-time data. Applications such as industry sensors, online streaming, and log report processing require real-time processing of massive amounts of data. Stay processing of large records requires significantly less latency than processing large records. This is handled well by the MapReduce version, which has a high latency because the data from the map segment must be stored on the disc before the reduce segment can start. This causes a greater delay and makes real-time processing of data impossible.
Batch processing: Apache Hadoop is considered the most dominant tool for batch processing in large data sets. It is extensively used in specialized domains such as data mining and machine learning. It balances the load by distributing it through specialized machines. It was made to work well with large amounts of information and was made specifically for batch processing.
Interactive Processing: The interactive evaluation equipment enables the user to interact with and independently evaluate data. In this type of processing, the user can interact with the computer because they are immediately connected to it.
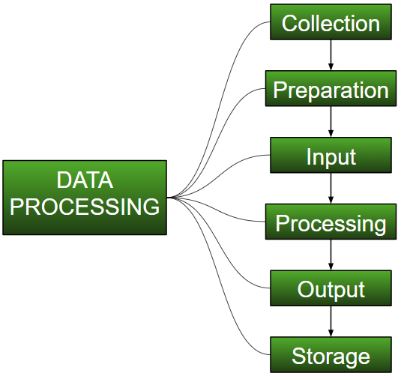
Features of data processing:
The key capabilities of China’s strong-movement statistics processing processes are as follows:
- Consideration is given to the effect of the report period on the extent of digitizing noise history, and a unique method is suggested for digitizing and connecting the successive sections of these lengthy length statistics, requiring repositioning at the digitizer table.
- Accelerograms recorded with accelerographs and a pendulum-galvanometer system are used to develop a device correction technique for both high and low frequency bands.
- In contrast to the band-by-skip clearout parameters suggested by Trifunac et al., quite exceptional cut-off frequencies for low-byskip and high-byskip filters are used, as well as regulations on the LC, the cut-off frequency for high-byskip clearout, which consist of digitizing noise history.
Steam Processing Tools:
Apache Storm:
This is one of the most well-known platforms for movement processing. It is scalable, open source, can handle errors, and can stream an unlimited amount of data. It was made for streaming data, is easy to use, and makes sure that all data is processed. It processes tens of thousands of bytes of data per second, making it a sustainable platform for data streaming.
Splunk:
This is yet another smart, real-time platform that makes it easy to get machine-generated data from huge databases. It permits users to monitor, access, and review records via an internet interface. The outcomes are illustrated through reports, indicators, and graphs. Splunk’s unique characteristics, including the indexing of structured and unstructured data, dashboard creation, online searching, and real-time reporting, distinguish it from other flow processing tools.
Batch Processing Tools:
Mapreduce Model:
Hadoop is primarily a software platform developed for distributed, data-intensive applications. It employs map-reduce as its computational model. Google and other internet companies have developed MapReduce, a programming model useful for analyzing, processing, and producing large data sets. It breaks a complicated problem into smaller problems and keeps doing this until each smaller problem is solved on its own.
Dryad:
It is a version of programming that can handle packages in both a parallel and a distributed way. It can handle clusters of all sizes, from the very small to the very large. It employs the cluster-to-cluster technique and executes in a distributed manner. With the aid of the Dryad framework, developers can work on as many machines as possible, including those with multiple cores and processors.
Talend Open Studio:
Customers are able to visually examine data through this device’s graphical interface. Talend was introduced by Apache Hadoop as open-source software. In contrast to Hadoop, customers can solve problems without having to write Java code. Users can also drag and drop icons to match the tasks they have been given.
Tools for interactive Analysis:
Google’s Dremel:
Google, a well-known company that facilitates interactive processing, proposed it. Dremel’s architecture may be quite different from Apache Hadoop, which has become advanced for batch processing. Using column data and multi-level trees, it can also run a series of queries over a table with trillions of rows in just a few seconds. It can also work with many processors and store petabytes of data for many Google users.
Apache Drill:
Apache Drill is a platform that helps with the interactive evaluation of a lot of data. It is more flexible than Google’s dremel in terms of support for unique query languages, numerous reassessments, and information types. Drill is designed to address hundreds of servers, to process trillions of user records, and to process petabytes of data in very little time.
How does it work?
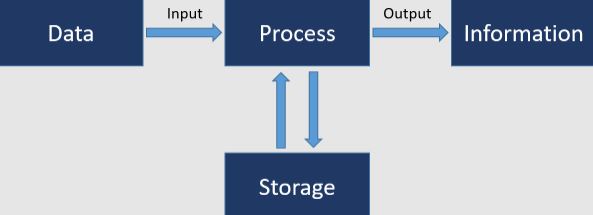
Statistics processing is the computer-aided manipulation of statistics. It includes putting raw data into a format that a computer can understand, moving data through the CPU and memory to output devices, and formatting or changing the output. Any use of computers to perform the enumerated operations on statistics can be protected under “statistics processing.” In the context of the economy, statistics processing means putting together the numbers that businesses and corporations need to run.
Why data processing?
The significance of data processing consists of increased productivity and profits, better decisions that are more precise and dependable. Using higher evaluation and presentation has clear benefits, such as lowering prices, making it easier to store, distribute, and make documents. In all fields of work, people now research and think a lot about the need to process data. Whether the work is performed in a business environment or for educational research purposes, every enterprise utilizes information management systems.
Trend in data processing:
Hybrid and Multiple Cloud Information Strategies:
- In terms of enterprise adoption of cloud-based information sources, the pandemic was like adding gasoline to a fire that was already burning. Suddenly, hundreds of thousands of employees needed to access company information and collaborate remotely, and cloud-based solutions were frequently the clear winners. Hybrid and multi-cloud approaches, in particular, were key drivers of cloud data control strategies.
- This trend toward information control is the continuation of one that has been on the rise for a number of years, typically driven by massive information concerns. Companies have to deal with more data than ever before, but the tech industry as a whole and information-focused jobs in particular have a hard time finding people to fill open positions.
- AI and machine learning (ML) add very useful automation to strategies that are prone to mistakes when done by humans. With the help of advanced AI/ML technology, information control tasks like figuring out the identity and type of information can be done more quickly and correctly.
Data Augmented Analytics:
- Gartner thinks that by the end of 2021, better management of records will cut the amount of manual work needed to manage records by 45%. Given that the amount of data is growing at an exponential rate and the number of skilled IT workers is decreasing, it is hard to overstate how important this change is.
- When businesses are able to recruit information technology specialists, they must maximize their skills rather than assigning them manual tasks such as document cleaning. Frequently using AI and ML, augmented record management solutions acquire, store, organize, and maintain data. Enhanced record-keeping strategies can facilitate the completion of labor-intensive tasks such as record maintenance and instruction.
Data Processing in Research Area:
The essential steps in this procedure are as follows:
- The initial step involves determining whether or not there are questionnaires. Few of the questionnaires that are no longer relevant contain incomplete or partial data, and insufficient knowledge.
- Unprocessed data is checked to see if there are any mistakes that need to be edited and fixed.
- Coding is the process of giving each answer a symbol so that it can be put into its own category.
- For greater comprehension, information is primarily categorized based on instructions reminiscent of magnitude interval, frequency, or attributes like city and inhabitants.
- After classifying, the entire system is tabulated according to the specific applicable columns and rows.
- Then, organize them in a bar graph or statistical format.
- After that, we look at all of the records again to make sure they are all the same, and if any are missing, we add them.
- In order to improve quality, a supplementary concept of adjusting records is implemented.
Advantages of data processing:
The benefits of statistical processing include:
- Highly effective.
- Time-saving.
- Rapid speed.
- Reduces errors.
Disadvantages of data processing:
The disadvantages of statistics processing include:
- High energy consumption.
- Largely occupies memory.
- The cost of installation is costly.
- Misuse of memory.
Application of data processing:
The benefits of statistical processing include:
- In the banking industry, this processing is used by bank customers to confirm their institution information, transactions, and other data.
- In educational departments such as schools and colleges, this processing is important for locating student information such as biodata, class, roll number, grades, etc.
- Throughout the transaction procedure, the utility updates its records as customers request information.
- This processing makes it possible to get the specified client records in a monitoring area for logistics online.
- In hospitals, patients can search for information without difficulty.
The Prospects for Data Processin:
The future of data processing is encapsulated in a single phrase: cloud computing.
- Even though the six steps of data processing haven’t changed, cloud technology has made huge strides in data processing technology, giving data analysts and scientists access to the fastest, most advanced, cost-effective, and efficient data processing methods available today.
- The cloud enables businesses to combine their platforms into a centrally managed, easily-managed, and adaptable system. Cloud technology enables the seamless incorporation of new upgrades and updates into legacy systems and provides organizations with enormous scalability.
- Cloud platforms are also inexpensive and serve as a great leveler between large and small businesses.
- So, the same IT innovations that led to big data and the problems it brought with it also led to the solution. The cloud can manage the massive workloads typical of big data operations.
Conclusion:
It is the transformation of the data into information that can be used. Information processing can be broken down into six main steps: collecting the data, storing the data, sorting the data, processing the data, and presenting the results and conclusions based on the data.
Are you looking training with Right Jobs?
Contact Us- Hadoop Tutorial
- Hadoop Interview Questions and Answers
- How to Become a Hadoop Developer?
- Hadoop Architecture Tutorial
- What Are the Skills Needed to Learn Hadoop?
Related Articles
Popular Courses
- Hadoop Developer Training
11025 Learners - Apache Spark With Scala Training
12022 Learners - Apache Storm Training
11141 Learners
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- Difference between Data Lake vs Data Warehouse: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- What does the Yield keyword do and How to use Yield in python ? [ OverView ]
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know
