
Ethical Hacking Interview Questions and Answers
Last updated on 25th Sep 2020, Blog, Interview Question
All the network engineers, security analysts, network security engineers, cyber security engineers, network administrators, network specialists etc. will find these questions extremely useful. All freshers, BCA, BE, BTech, MCA and college students wanting to make a career in Networking will be highly benefited by these questions.These Cyber Security questions have been designed for various interviews, competitive exams and entrance tests. We have covered questions on both basic and advanced concepts which will help you improve your skills to face interview questions on Cyber Security.This section covers Cyber Security topics like – Encryption, Firewall, MITM attack, IPS and IDS, HTTPS, SSL, TLS, phishing, Cognitive Cybersecurity etc.
1. What is a Firewall? Explain its need in brief.
Ans:
Firewalls are the defense system to any network that keeps your systems, devices, and other network touchpoints safe from any external threats like viruses, worms, trojans, DDoS attacks, Waterhole attacks and more. Firewalls are additionally used for filtering the communications that are happening between the internal and external touchpoints.
2. What are social engineering attacks?
Ans:
When a cybercriminal manipulates their targets using normal communication mediums like calls, texts, and emails to fetch the confidential information directly from the target without any technical expertise it is called social engineering attacks. For example Tailgating, Spear Phishing, Pretexting, Baiting, Whaling attack, Waterhole attacks and more.
3. What is the difference between penetration testing and vulnerability management?
Ans:
The organization that has set up an outstanding security procedure will hire penetration testers to check how secure and unbreakable is their network, this is called penetration testing. However, vulnerability management is the process of identifying vulnerabilities in the existing network using tools like patch management and endpoint security management and fixing the same using them.
4. Who is a Cryptographer?
Ans:
Any confidential data that is existing in the web has to be encrypted to keep it safe, but due to increased number of data breaches this is better if the same data is being converted into more convoluted using cryptography, a method of encrypting data in a unique way which only the receiver with the code can decrypt. The professional behind this cryptography process is called a cryptographer.
5. How will you secure a server?
Ans:
- Checking servers for SSL protocol to encrypt and decrypt the sensitive data and secure it against anonymous access.
- Create new users using this server and make sure unwanted ports are blocked.
- Removing privileged access to the server data for users.
- Removing remote access to servers.
- Practicing VPN based access to servers.
- Configuring firewalls and proxy settings for secure communications.
6. What is data leakage?
Ans:
Any intentional or unintentional leakage of data from the corporate database to external storage is called data leakage. This leakage can be one of three ways. Accidental breach Intentional breach using an insider threat Hacking attempt to break into the corporate network and steal the data.
7. Can You Name Eight Common cyberattacks?
Ans:
- 1. Ransomware
- 2. DDoS attacks
- 3. Malware
- 4. Phishing
- 5. Zero-day attacks
- 6. Brute force attacks
- 7. XSS
- 8. Man-in-the-middle attacks
8. What is a brute force attack?
Ans:
The process of finding a credential to a website/target by generating the number of combinations and permutations to identify the right password is called the brute force attack. The password breaking mechanism can be defined by password length, complexity, language, and customizing the algorithms for the combinations and permutations.
9. What are the OSI models and name their types?
Ans:
OSI model is an inter-operative framework that developers would need to make their applications work along with the network. The types are:
- 1. Application layer
- 2. Presentation layer
- 3. Network layer
- 4. Transport layer
- 5. Session layer
- 6. Data link layer
- 7. Physical layer
10. Name the difference between Black hat, Whitehat and Grey hat hackers.
Ans:
Black hat hackers – These guys are the bad ones that operate individually or supported by an organization or states to breach into the corporate or public networks to fetch, encrypt or delete data illegally. They have exorbitant skills of hacking and can even create a malware that can breach into networks easily in a short duration.
White hat hackers – These are the good guys, who are otherwise called Ethical hackers. They hack into organizations or cyber-criminal groups legally, they can also be used as the penetration testers for identifying the vulnerabilities and loopholes in an organization.
Grey hat hackers – These are the good guys but sometimes turn into black hat hackers based on their demand and objective. They mostly seek network or system vulnerabilities, identify them without the owner’s permission but report it back to the owner for rewards rather than exploiting the same.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
11. How to set up a firewall?
Ans:
Modify the credentials of a firewall device and disable the remote administration feature, configuring the ports and DHCP server, ensuring the logs are turned ON for analysis, and finally defining the security policies.
12. What is SSL encryption?
Ans:
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is a security layer that is usually deployed between a web server and a browser to keep the communication secured and safe from any external cyber actors. Useful for online transactions and for digital privacy.
An SSL connection can be established when a browser requests for an SSL with the web browsers and the webserver confirms the same with its SSL certificate showing it is trustworthy, and that’s when the browsers initiate the communication after verifying the SSL certificate and believes the connection would be trustworthy.
13.Explain Port Scanning
Ans:
Port scanning is the process of identifying the opened ports in a host. Hackers exploit these opened ports to breach into a network while security pros try to close the same for safety. There are different types of port scan techniques,
- Ping scan
- UDP
- TCP connect
- Stealth scanning
- TCP half-open
14. What is VPN?
Ans:
Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a safe private network that would allow employees to connect to their original corporate network even when they are away from their corporate office.
The server believes the employee is accessing the network within the office only but actually he/she is not in that location physically.
VPNs are encrypted and are practiced to avoid data breaches via public networks in cafes, train stations, and airports. Users can view movies, series and other games that are from a different location by using a proxy or VPN.
There is the number of VPN services available on the web to escape the geographical limitations and march forward with your browsing objectives.
15. What is a DDoS attack?
Ans:
When a huge amount of traffic is sent to a single device to crash the device’s normal functioning it is called a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. This is the basis behind the cyber fame Mirai Botnet, and the DDoS attacks are of two types, flooding, and crash attacks. The former we discussed, while in the case of the latter the hacker just identifies a bug or more in the system and deploys the crash algorithms to crash the device.
16. What is a Botnet?
Ans:
Botnet is a group of devices that could be laptops, desktops, IoT which is run by one or more bots for a certain purpose like crashing a targeted system, stealing data or spamming the targets through DDoS framework, malware or using scripts. Mirai Botnet is one good example to explore.
17. Explain about authentications in General
Ans:
Authentications are procedures to verify the credential and the individuality of a user by validating the same using different means of identification. There are different types of authentication in the industry,
- 1. Two factor authentication (2FA)
- 2. Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- 3. Biometric authentication (BFA)
Two-factor authentication is something that includes usernames, password and a OTP (an example) for verification.
Multi-factor authentication may require you to type in the username, password, OTP and a secret phrase for verification.
Biometric authentication will include username, password and a biometric verification like retina, fingerprint and face scan.
18. Hackers were able to break into your network using a port and outdated software. What will you do to fix it?
Ans:
Initially, we need to block the ports that are kept open, followed by that we can either remove that software if it is not required or update the software to its secured version by deploying the patches to the devices that have the software.
19. What is an XSS attack?
Ans:
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks are malicious scripts that run on a web page injected by hackers to hijack sessions, perform phishing, track cookies, remote code executions and more. XSS attacks can be prevented by validating user inputs, using XSS HTML filters, or by using anti-XSS tools.
20. What is Cyber Espionage?
Ans:
Cyber espionage is the process of gaining access to sensitive business documents through malicious practices and using the same as an advantage against the company or government agency. Cyber espionage has become prevalent, thanks to the ransomware trends.
21. What is enterprise mobility management?
Ans:
Organizations need to take care of the roaming devices that either belong to them or the users, in other words, the BYOD, CYOD, and COPE. When employees are out of the corporate network so are their devices which include smartphones, tablets, and laptops. Organizations need to manage these roaming devices and users to keep their business-sensitive data secured and safe from any public threats. Additionally, IT departments need to manage these devices from a single console for better efficiency.
22. How to secure the IoT devices from cyberattacks?
Ans:
Users need to ensure they have a solid router that does not compromise on network security. They also need to check for good firewalls and build an IoT customized Wi-Fi network with the right passwords and hosted as WAP2 or WAP3. Above all users need to make sure they have got their IoT devices updated and free from vulnerabilities. Patching the IoT devices can prevent any application-level breaches while the former will help with network-level breaches.
23. Explain about CIS critical security controls?
Ans:
Centre for Internet Security(CIS) is an organization established by a group of security researchers to make the internet a better place for the end-users. CIS group of researchers have defined 20 critical security controls that are at three different levels. They are,
- Basic security controls
- Foundation security controls
- Organizational security controls
24. What is ransomware, give some examples
Ans:
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts users data, leaves a ransom note requesting a certain amount of ransom to decrypt the data. Ransomware has become very common in recent years, their motive could be to either encrypt and request ransom, encrypt and steal the data, or encrypt and erase the data thus causing havoc to the targeted audience. Examples: WannaCry, Ryuk, NotPetya, SamSam, and GandCrab.
25. How will you increase the security over network browsers?
Ans:
Browsers are the touchpoints for any digital communication. With so much information being communicated via browsers it’s important to establish the right cybersecurity policies for your browsers to keep them safe from cyberattacks like MITD, XSS and remote code execution flaws.
Browsers need to be,
- 1. Updated with the right security policies, by channeling the network traffic via the right proxy server.
- 2. Defined with browser configurations thus preventing users from visiting malicious and anonymous websites.
- 3. Updated with the latest extension and plugin patches.
26. Tell me about Meltdown and Spectre bugs?
Ans:
Meltdown and Spectre are processor bugs that exploit a speculative execution flaw in the processors that allows hackers and cybercriminals to access sensitive data that is being stored in the cache. Both these bugs were later mitigated when OS manufacturers and AV vendors gave their compatibility patches. The Internet went berserk when these processor bugs were reported in Jan 2018.
27. Explain about automated patch management in detail.
Ans:
Automated patch management is a process in which the IT admin scans the network for missing patches, identifies the missing patches and downloads them from the vendors websites, test them in a closed environment and later deploy them to the targeted devices based on the criticality of patches by scheduling them according to the convenience of the organization.
28. Explain the difference between penetration tester and vulnerability assessor
Ans:
Penetration tester tries to break into a network or software to identify potential loopholes associated with that particular entity, however, vulnerability assessor will check for the potential vulnerabilities about the given body alone, unlike the penetration tester where the assessment is done combining all the components of the target environment. A vulnerability assessment will be narrow compared to penetration testing.
29. How to avoid Zero-Day Exploits?
Ans:
Keeping your applications and devices up-to-date with the latest patches, both security and non-security irrespective of their reason for an update can keep your application and device safe against external threats. Enterprises need to employ automated patch management procedures to maintain the MS Patch Tuesday updates and third party patches, but updating them with the latest patches may have performance hits in some cases but it is better than to get screwed by cyberthreats.
30. How to secure roaming devices?
Ans:
Security professionals can use mobile device management (MDM) or unified endpoint management solutions (UEM) to take care of roaming devices even if they are connected to public Wi-Fi’s. Organizations can also request their employees to use VPN for safe and secure browsing and business data accessing routines. Sandbox technique that is being implemented in these solutions will help security professionals and IT administrators to secure their corporate data.
31. How will you Secure the USB Devices?
Ans:
USB devices need to be secured based on how trustworthy they are to the enterprise. IT security professionals need to restrict and allow USB devices based on whether those devices are recognized or not. USB security management can help organizations prevent data leaks, cause havoc through USB sticks, and booby-trapped USB sticks.
32. What is common between GDPR, LGPD, CCPA, and POPI?
Ans:
All these are data protection laws. GDPR is for Europe, LGPD is for Brazil, CCPA is for California (USA) and POPI is for South Africa. All these laws are being introduced to secure the personal data of the data subjects and maintain privacy in the country. Any business who is doing business in these organizations needs to get compliant towards these data protection laws.
33. What is DPO?
Ans:
Data Protection Officer (DPO) is a new role created as per the norms of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the year 2018. The demand for this role is high considering the huge risk associated with it. The Data Protection Officer will be the official touchpoint and responsible for all the data that is existing inside any corporate environment. He must be aware of the different types of data collected, their source, why they are being collected, what is the process associated with the data collection, whether users have given their consent for processing the data, and when these data are erased from the organization database.
34. Difference Between Threat, Vulnerability, and Risk?
Ans:
Your organization is exposed to a threat when a malicious actor is trying to leverage a vulnerability existing in a network that was not fixed as there is not a proper identification system to define this as a risk. Another way to explain these three would be, IT security professionals should not risk their network allowing device and applications vulnerabilities to exist as this could cause potential cyber threats.
35. What is Deception Technology?
Ans:
Not all attacks can be prevented proactively and that is why an organization additionally needs to equip the reactive approach to keep themselves safe against any unforeseen breaches. Deception Technology is a reactive approach where IT security professionals use their skills and tools, to lure hackers into a path that they did not intend to take.
For example, let us assume a hacker is trying to take down a system in the targeted location with its IP address.
36. What is PKI?
Ans:
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a framework that is compiled of policies, hardware, software, standards, configurations, to facilitate the trust among the entities that are using the data encryption.
Public key encryption is imperative for communication over emails, any sensitive information communicated over an email can be public-key encrypted, thus leaving the receiver with the information that is very much valid and ensuring it has not reached an incorrect inbox. This is because public key encryption works with a digital certificate, even duplication of the key cannot be successful in this case. Public key encryption is for better security and private key encryption is for storage purposes.
37. Name the difference between process, guidelines, and policies?
Ans:
The process is a step by step procedure where the readers will be shown what to do next, in case of guidelines, its little high-level recommendations and suggestions for networks or applications to formulate a strategy or process to implement the same. Policies are the criteria that have to be defined to maintain security and compliance in a network or application.
38. What is the Zero Trust Network?
Ans:
Zero trust Network is an evolving framework, where organizations will not trust any device or user so easily, according to this model there will be zero trust that will not allow the devices to directly connect with the corporate network unless they verify their identity every time they join the intended network. This Zero Trust is already being implemented in a few fortune 500 companies however, it will take a while before this is being implemented across industries. With the Zero Trust Model, business-sensitive data can stay safe from outside and insider threats.
39. Difference between EU personal data and US personal information?
Ans:
EU personal data will be a superset for US personal information, as the EU personal data is very vast and it can include anything from the data subject’s name, age, email, phone number, social security number, country etc however in case of US personal information it does not consider these vast details. Anything that will allow an entity to narrow down and identify the target data subject is personal data. GDPR deals with personal data handling and companies are moving their infrastructure from personal information to personal data handling.
40. Explain the server-client based model?
Ans:
Server-client based model is composed of two key components: server and clients. When one of the machines is hosted as a server, then its clients are generated through these servers and will be deployed to a targeted set of machines. The server will not be able to define settings, policies, configurations and actions to all the clients, or only hand-picked clients which can again be defined based on a workgroup and domains.
Server-client model is mostly used in IT management applications, to facilitate IT administrators to manage, control, monitor, troubleshoot, and update the clients (machines). These clients could be laptops, desktops, smartphones, tablets, IoT devices, virtual machines, hypervisors and more.
41. Explain about IPS and IDS.
Ans:
Cyberattacks can be prevented proactively and detected when they are happening. Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) detects the cyberattacks and helps in preventing the cyberattacks from further progress into the network. However, the Intrusion Detection System (IDS) will alert IT administrators for any potential threat that is trying to infiltrate the corporate network.
42. Can you name the difference between false positive and false negative?
Ans:
If the IDS shows an alert for a network breach but there is not any in real-time then it is called as false positive and if there is a real-time breach inside the network but the IDS is not showing any alert for the attack then it is called as a false negative.
43. What do you know about the red and blue team in cyberspace?
Ans:
Organizations usually split their teams for better cybersecurity, the red team will act like attackers and the blue team will act as defenders. The Red team needs to study different methods of breaching into a network, system and account’s while the blue team will study different protections, security best practices and more to secure their network, system, and accounts from the red team’s actions.
This will help the organization understand the security loopholes and release its security advisory in-time before an external malicious cyber actor takes advantage of any existing vulnerabilities.
44. How will you improve data leak prevention in the network?
Ans:
Data leakage can happen at any given touchpoint in a network, it could be your routers, servers, laptops, mobile devices, servers, IoT and more. Data from these components can be secured by practicing good firewall policies, USB security, internet upload metrics, corporate content management, BYOD management, browser configurations, and strong password policies. All these can be incorporated using an endpoint security tool if the strategies are built the right way.
45. Explain the difference between AI, Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
Ans:
Deep learning is the process of using artificial neural networks to solve the complicated issue, while Machine learning will help machines decide on a problem without being programmed, a superset of deep learning and AI is the universal or parent set for deep learning and machine learning where the machine thinks for itself just like human beings.
AI can be broadly classified into three types,
- 1. Artificial Narrow Intelligence- Very narrow scope, for example: AlphaZero
- 2. Artificial General Intelligence- The ultimate AI that can think far better than humans. Still in development.
- 3. Artificial Super Intelligence- This is the stage where AI becomes more powerful than humans, as it starts processing the entire historical data and improves the overall results.
46. What is Steganography?
Ans:
Steganography is the process of hiding and delivering a message to a receiver without showing any identification for the existence of the message itself is called Steganography. In the case of cryptography, the message will be encrypted but in steganography, the presence of the message itself is kept hidden.
47. What is Quantum Computing? Why is it evolving?
Ans:
The process of developing a computer which works based on the principle of quantum theory considering the atomic and subatomic particles to define the working mechanism of the computer is called Quantum Computing. In the future, humans are in need of super-fast computers than can process billions of data at a given time, and the existing machines are not capable of doing the same in the short duration but with quantum computing millions of combinations and permutations are possible in a concise duration thus offering better efficiency for the users.
48. What privacy features are essential for a VPN?
Ans:
VPN in recent times comes with a lot of features like kill switch, multi-hopping and more for retaining privacy. However, what’s often ignored while choosing a VPN is a good logging policy. Many VPNs retain logs of personally identifiable information of the end-user and destroy the mere purpose of using a VPN.
Understanding and analyzing the VPN comparison in general illuminates what types of log tracking are being offered in the market along with their storing mechanisms. Users should make the right call by evaluating the VPN’s based on their network demands.
49. What is an Evil Twin?
Ans:
Evil twin is a fake Wi-Fi access point that appears to be a legible network. When users connect to this fake network they accidentally disclose the usernames and passwords, allowing the hacker to access the same later. This is more like endpoint security, but at the network level, using Wi-Fi replication techniques.
50. What are the advantages and disadvantages of hacking?
Ans:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| It can be used to foil security attacks | It creates massive security issues |
| To plug the bugs and loopholes | Get unauthorized system access |
| It helps to prevent data theft | Stealing private information |
| Hacking prevents malicious attacks | Violating privacy regulations |
51. What is the difference between Asymmetric and Symmetric encryption?
Ans:
| Asymmetric encryption | Symmetric encryption |
|---|---|
| Asymmetric encryption uses different keys for encryption and decryption. | Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. |
| Asymmetric on the other hand is more secure but slow. Hence, a hybrid approach should be preferred. | Symmetric is usually much faster but the key needs to be transferred over an unencrypted channel. |
52. How can you avoid ARP poisoning?
Ans:
ARP poisoning is a type of network attack that can be resolved through these techniques:
Using Packet filtering: Packet filters can filter out & block packets with clashing source address data.
Keeping away from trust relationships: Organizations ought to develop a protocol that depends on trust relationships as little as they can.
Utilize ARP spoofing software: Some programs assess and certify information before it is transmitted and blocks any information that is spoofed.
53. What can an ethical hacker do?
Ans:
An ethical hacker is a computer system and networking master who systematically endeavours to infiltrate a PC framework or network for the benefit of its owners to find security vulnerabilities that a malicious hacker could potentially exploit.
54. Why is Python utilized for hacking?
Ans:
Most broadly utilized scripting language for Hackers is Python. Python has some very critical highlights that make it especially valuable for hacking, most importantly, it has some pre-assembled libraries that give some intense functionality.
55. What is Pharming and Defacement?
Ans:
Pharming : In this strategy the attacker compromises the DNS (Domain Name System) servers or on the user PC with the goal that traffic is directed towards malicious site
Defacement : In this strategy the attacker replaces the firm’s site with an alternate page. It contains the hacker’s name, images and may even incorporate messages and background music.
56. What is Cowpatty?
Ans:
Cowpattyis implemented on an offline dictionary attack against WPA/WPA2 networks utilizing PSK-based verification (e.g. WPA-Personal). Cowpatty can execute an enhanced attack if a recomputed PMK document is accessible for the SSID that is being assessed.
57. What is Network Enumeration?
Ans:
Network Enumeration is the revelation of hosts/gadgets on a network, they tend to utilize obvious disclosure protocols, for example, ICMP and SNMP to gather data, they may likewise check different ports on remote hosts for looking for surely known services trying to further recognize the function of a remote host.
58. Distinguish between phishing and spoofing?
Ans:
Phishing and spoofing are totally different beneath the surface. One downloads malware to your PC or network, and the other part tricks you into surrendering sensitive monetary data to a cyber-crook. Phishing is a technique for recovery, while spoofing is a method for delivery.
59. What is network sniffing?
Ans:
System sniffing includes utilizing sniffer tools that empower real- time monitoring and analysis of data streaming over PC systems. Sniffers can be utilized for various purposes, regardless of whether it’s to steal data or manage systems. Network sniffing is utilized for ethical and unethical purposes. System administrators utilize these as system monitoring and analysis tools to analyse and avoid network related issues, for example, traffic bottlenecks. Cyber criminals utilize these devices for untrustworthy purposes, for example, character usurpation, email, delicate information hijacking etc.
60. What do you mean by DOS (Denial of administration) assault? Explain. What are the regular types of DOS assault?
Ans:
Denial of Service, is a malicious attack on a network that is executed by flooding the system with useless traffic. Despite the fact that DOS does not cause any data breach or security breach, it can cost the site proprietor a lot of cash and time.
- Buffer Overflow Attacks
- SYN Attack
- Teardrop Attack
- Smurf Attack
- Viruses
61. What do you understand by footprinting in ethical hacking? What are the techniques utilized for footprinting?
Ans:
Footprinting is nothing but accumulating and revealing as much as data about the target network before gaining access into any network. Open Source Footprinting : It will search for the contact data of administrators that will be utilized for guessing password in Social Engineering Network Enumeration : The hacker attempts to distinguish the domain names and the network blocks of the target network Scanning : After the network is known, the second step is to spy the active IP addresses on the network. For distinguishing active IP addresses (ICMP) Internet Control Message Protocol is a functioning IP addresses Stack Fingerprinting : the final stage of foot printing step can be performed, once the hosts and port have been mapped by examining the network, this is called Stack fingerprinting.
62. What is the difference between encryption and hashing?
Ans:
| Encryption | Hashing |
|---|---|
| Encryption is reversible | Hashing is irreversible |
| Encryption ensures confidentiality | Hashing ensures Integrity |
63. What is the CIA Triangle?
Ans:
- Confidentiality : Keeping the information secret.
- Integrity : Keeping the information unaltered.
- Availability : Information is available to the authorised parties at all times.
64. What is the difference between VA and PT?
Ans:
| Vulnerability Assessment | Penetration testing |
|---|---|
| Vulnerability Assessment is an approach used to find flaws in an application/network | It is the practice of finding exploitable vulnerabilities like a real attacker will do |
| It is like travelling on the surface | It is digging for gold. |
65. What is data leakage? How will you detect and prevent it?
Ans:
Data leak is nothing but data knowledge getting out of the organization in an unauthorized manner. Data will get leaked through numerous ways in which – emails, prints, laptops obtaining lost, unauthorized transfer of data to public portals, removable drives, pictures etc. There are varied controls which may be placed to make sure that the info doesn’t get leaked, many controls will be limiting upload on web websites, following an internal encryption answer, limiting the emails to the interior network, restriction on printing confidential data etc.
66. What are the hacking stages? Explain each stage.
Ans:
Hacking, or targeting on a machine, should have the following 5 phases :
- 1. Surveillance : This is the principal stage where the hacker endeavours to gather as much data as possible about the target
- 2. Scanning : This stage includes exploiting the data accumulated amid the Surveillance stage and utilizing it to inspect the casualty. The hacker can utilize computerized devices amid the scanning stage which can incorporate port scanners, mappers and vulnerability scanners.
- 3. Getting access : This is where the real hacking happens. The hacker attempts to exploit data found amid the surveillance and Scanning stage to get access.
- 4. Access Maintenance : Once access is gained, hackers need to keep that access for future exploitation and assaults by securing their exclusive access with backdoors, rootkits and Trojans.
- 5. Covering tracks : Once hackers have possessed the capacity to pick up and maintain access, they cover their tracks and to keep away from getting detected. This likewise enables them to proceed with the utilization of the hacked framework and keep themselves away from legitimate activities.
67. What are the tools used for ethical hacking?
Ans:
There are several moral hacking tools out there within the marketing for different purposes, they are:
- NMAP – NMAP stands for Network plotter. It’s an associate degree open source tool that’s used widely for network discovery and security auditing.
- Metasploit – Metasploit is one amongst the most powerful exploit tools to conduct basic penetration tests.
- Burp Suite – Burp Suite could be a widespread platform that’s widely used for playing security testing of internet applications.
- Angry IP Scanner – Angry information processing scanner could be a light-weight, cross-platform information processing address and port scanner.
- Cain & Abel – Cain & Abel is a password recovery tool for Microsoft operational Systems.
- Ettercap – Ettercap stands for local area network Capture. It is used for Man-in-the-Middle attacks using a network security tool.
68. What is MAC Flooding?
Ans:
MAC Flooding is a kind of a technique where the protection of a given network switch is compromised. In MAC flooding the hacker floods the switch with sizable amounts of frames, then what a switch can handle. This makes the switch behave as a hub and transmits all packets to all the ports existing. Taking the advantage of this the attacker can attempt to send his packet within the network to steal the sensitive information.
69. Explain how you can stop your website getting hacked?
Ans:
By adapting following methodology you’ll be able to stop your web site from obtaining hacked
- Using Firewall : Firewall may be accustomed drop traffic from suspicious information processing address if attack may be an easy DOS
- Encrypting the Cookies : Cookie or Session poisoning may be prevented by encrypting the content of the cookies, associating cookies with the consumer information processing address and temporal arrangement out the cookies once it slow
- Validating and confirmative user input : This approach is prepared to stop the type tempering by confirmative and verifying the user input before processing it
- Header Sanitizing and validation : This technique is beneficial against cross website scripting or XSS, this method includes verifying and sanitizing headers, parameters passed via the address, type parameters and hidden values to cut back XSS attacks.
70. What is Burp Suite? What are the tools it contains?
Ans:
Burp Suite is an integrated platform used for attacking net applications. It contains all the tools a hacker would need for attacking any application. a number of these functionalities are
- Proxy
- Spider
- Scanner
- Intruder
- Repeater
- Decoder
- Comparer
- Sequencer
71. What is SQL injection and its types?
Ans:
If the application doesn’t sanitize the user input then the SQL injection happens. Thus a malicious hacker would inject SQL questions to gain unauthorized access and execute administration operations on the database. SQL injections may be classified as follows:
- 1. Error-based SQL injection
- 2. Blind SQL injection
- 3. Time-based SQL injection
72. What’s a denial of service (DOS) attack and what are the common forms?
Ans:
DOS attacks involve flooding servers, systems or networks with traffic to cause overconsumption of victim resources. This makes it troublesome or not possible for legitimate users to access or use targeted sites.
Common DOS attacks include:
- Buffer overflow attacks
- ICMP flood
- SYN flood
- Teardrop attack
- Smurf attack
73. Which programming language is used for hacking?
Ans:
It’s best, actually, to master all 5 of Python, C/C++, Java, Perl, and LISP. Besides being the foremost vital hacking languages, they represent totally different approaches to programming, and each of it can educate you in valuable ways.
74. What is meant by a spoofing attack?
Ans:
A spoofing attack is when a malicious party impersonates another device or user on a network so as to launch attacks against network hosts, steal data, unfold malware or bypass access controls. Different Spoofing attacks are deployed by malicious parties to achieve this.
75. What are the different types of spoofing?
Ans:
- ARP Spoofing Attack.
- DNS Spoofing Attack.
- IP Spoofing Attack.
76. What is active and passive reconnaissance?
Ans:
Passive reconnaissance is nothing but to gain info regarding targeted computers and networks while not actively participating with the systems. In active reconnaissance, in distinction, the attacker engages with the target system, usually conducting a port scan to find any open ports.
77. Differentiate Between a MAC and an IP Address?
Ans:
All networks across devices are assigned a number which is unique, which is termed as MAC or Machine Access Control address. This address may be a personal mail box on the net. The network router identifies it. the amount may be modified anytime.All devices get their distinctive information processing address so they can be located easily on a given laptop and network. Whoever is aware of your distinctive information processing address will contact you through it.
78. What is SSL and why is it not enough when it comes to encryption?
Ans:
SSL is identity verification, not hard encryption. it’s designed to be able to prove that the person you’re engaging on the other side is who they say they are. SSL and TLS are each used by almost everyone online, however because of this it is a huge target and is mainly attacked through its implementation (The Heartbleed bug for example) and it’s far-famed methodology.
79. What is Hacking?
Ans:
We are yet to wrap 2019 and Cybercriminals have already earned close to $600 billion. Undoubtedly, hackers are the key players here. The term was coined in 1951 and refers to accessing a system or network without authorized access. The person who conducts the process is called a hacker.
A general modus operandi of a hacker is to steal some personal information of the system or network and demand ransom or use it to steal money.
80. What is Ethical Hacking?
Ans:
How can hacking be ethical? Well, this term came into play when some hobbyist hackers started helping organizations to identify the network vulnerabilities. And the need is so strong that it has now turned into a full-time role in the security departments. An ethical hacker attacks the network or system with the permission of the network owners. He tries to find the soft spots and then fixes them.
81. Why is the demand for ethical hackers increasing?
Ans:
According to a study by IBM, the average cost of a data breach has grown up to $3.92 million. Thus more and more ethical hacking professionals are being sought. If you are the one, this Ethical hacking interview questions and answers guide will prove to be a big help.
82. Who is a Black Hat Hacker?
Ans:
Black Hat: This is the category of hackers who makes it to the FBI’s most-wanted list generally. Thus it is clear that they gain un-permission access to the systems and networks with any ill-intent.
83. How is a grey hat hacker different from a black hat hacker?
Ans:
Grey hat hackers are the ones who penetrate a network or system without the permission of the owner. And once they are into the system, they share the details with the owners. For this either they receive an incentive or do it for the public good.
84. What is a White Hat hacker?
Ans:
White Hat: Also called the ethical hackers, their aim is to strengthen the security system. While they approach the system or network from a malicious hacker’s perspective, they never intend to do any harm. When you apply for the post of an ethical hacker, most of the ethical hacking interview questions are related to White hat hackers.
85. What is SQL Injection?
Ans:
Data-driven applications are attacked using SQL statements. These are inserted into an entry field for execution.
86. Are there any other kinds of hackers too?
Ans:
Some of the other hacker terms you might have heard are the Script Kiddie, Hacktivist, Blue hat and red hat hackers. These are hackers who work unethically at a very granular level.
87. What are the different types of hacking?
Ans:
Before you set out your foot into the ethical hacking territory, you must know what the most common target objects are. And these ethical hacking interview questions and answers will help you get detailed knowledge:
Computer hacking or system hacking was the one where it all evolved. And it continues to happen till today. As we moved a more digital world, hacks like website hacking, network hacking, email hacking, and password hacking started to evolve. The Website hackers try to gain access over the web server while network hackers try to penetrate the network and grab some sensitive data.
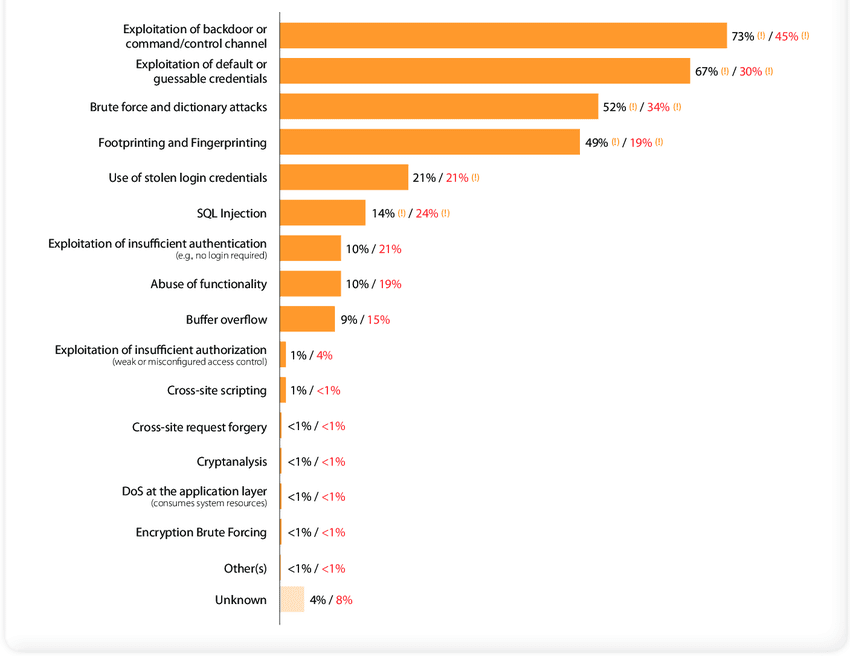
Types of Hacking Source – ResearchGate
88. What is Cross-site Scripting?
Ans:
It is a kind of security vulnerability present on the web. This allows attackers to inject client-side script into web pages that are being viewed by other users.
89. What is a Phishing attack?
Ans:
It is a fraud that is executed using an e-mail. The legitimate-looking email defrauds the readers.
90. What does social engineering mean?
Ans:
Social engineering is utilizing hacking techniques to acquire sensitive and personal details from a victim.
Email, password and computer hacking is done with an intent to get hold of private data that leads to extortions. As an ethical hacker, one needs to ensure the entire security set-up is immune to these attacks.
91. What is the task flow of ethical hacking and why is this the most asked ethical hacking technical interview questions?
Ans:
Hacking is conducted in 5 primary stages. These stages are:
- Reconnaissance
- Scanning
- Gaining Access
- Maintaining Access
- Clearing Tracks
Every ethical hacker is required to have complete knowledge of all these stages.
92. What does reconnaissance mean in ethical hacking?
Ans:
This is the phase where all the information is gathered to know the system better. The information varies from determining network range to discover open ports and access points.
93. Are there different types of reconnaissance?
Ans:
Two types of reconnaissance are active and passive. In active reconnaissance, an ethical hacker is given permission to interact with the system or the network. On the contrary, passive reconnaissance is carried out without any connection to the network.
94. What is defined as Scanning and how is it used in ethical hacking?
Ans:
Using the data collected in the first stage, a profile of the network to be attacked is created. Three different types of scanning are carried out primarily. These are network scanning, port scanning, and vulnerability scanning.
95. What is Gaining access and how does an ethical hacker do this?
Ans:
After the reconnaissance and scanning phase, the ethical hacker pins down the tools and techniques to penetrate the system. And this phase is called gaining access, where he is able to gain unauthorized access. As you read ahead you will find many ethical hacking technical interview questions about this stage.
96. How does an ethical hacker maintain access to a network?
Ans:
A hacker might not be able to get all the information from the network or system at once. He might choose to just stay there and keep extracting data. This is what is achieved during this phase. The malware or Trojan is used to keep the hacker connected and maintain access.
97. What does the clearing of tracks mean and why is it important?
Ans:
It is important for any hacker not to leave a trail behind. And this is achieved by clearing out the sent emails, server logs, uninstalling apps, deleting folders and any temp files and more.
Are you looking training with Right Jobs?
Contact Us- Ethical Hacking Tutorial
- CCNA Interview Questions and Answers
- Top Ethical Hacking Certifications
- Who is an Ethical Hacker?
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker?
Related Articles
Popular Courses
- CCNA Training
11025 Learners - CCNP Training
12022 Learners - Hardware and Networking Courses Training
11141 Learners
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- Difference between Data Lake vs Data Warehouse: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- What is Dimension Reduction? | Know the techniques
- What does the Yield keyword do and How to use Yield in python ? [ OverView ]
- Agile Sprint Planning | Everything You Need to Know


