- Functions and Closures in Swift | A Basic Tutorial
- Swift Tutorial – Enumerations & Structures | Everything You Need to Know
- Ionic Native Components | The Ultimate Guide
- Ionic Tutorial – Build Cross Platform Apps | A Complete Guide
- Introduction to Swift Control Flow | Learn in 1 Day FREE Tutorial
- Introduction to Swift | The Definitive Tutorial for Beginners
- Kotlin Tutorial for Beginners | Learn Kotlin at Ease
- Android Studio Tutorial
- React Native Tutorial
- iOS Architecture
- 5G Tutorial
- Functions and Closures in Swift | A Basic Tutorial
- Swift Tutorial – Enumerations & Structures | Everything You Need to Know
- Ionic Native Components | The Ultimate Guide
- Ionic Tutorial – Build Cross Platform Apps | A Complete Guide
- Introduction to Swift Control Flow | Learn in 1 Day FREE Tutorial
- Introduction to Swift | The Definitive Tutorial for Beginners
- Kotlin Tutorial for Beginners | Learn Kotlin at Ease
- Android Studio Tutorial
- React Native Tutorial
- iOS Architecture
- 5G Tutorial

React Native Tutorial
Last updated on 13th Oct 2020, Blog, Mobile app development, Tutorials
What Is React Native?
React Native is a JavaScript framework for writing real, natively rendering mobile applications for iOS and Android. It’s based on React, Facebook’s JavaScript library for building user interfaces, but instead of targeting the browser, it targets mobile platforms. In other words: web developers can now write mobile applications that look and feel truly “native,” all from the comfort of a JavaScript library that we already know and love. Plus, because most of the code you write can be shared between platforms, React Native makes it easy to simultaneously develop for both Android and iOS.
Similar to React for the Web, React Native applications are written using a mixture of JavaScript and XML-esque markup, known as JSX. Then, under the hood, the React Native “bridge” invokes the native rendering APIs in Objective-C (for iOS) or Java (for Android). Thus, your application will render using real mobile UI components, not webviews, and will look and feel like any other mobile application. React Native also exposes JavaScript interfaces for platform APIs, so your React Native apps can access platform features like the phone camera, or the user’s location.
React Native currently supports both iOS and Android, and has the potential to expand to future platforms as well. In this book, we’ll cover both iOS and Android. The vast majority of the code we write will be cross-platform. And yes: you can really use React Native to build production-ready mobile applications! Some anecdota: Facebook, Palantir, and TaskRabbit are already using it in production for user-facing applications.
React Native Features
- JavaScript: React Native lets you build fully native mobile applications using JavScript.
- Cross-Platform: React Native lets you write cross-platform native applications using JavaScript in a single codebase for both Android and iOs, later then Javascript is compiled to native code.
- Community: React Native is backed with a large community of React and React Native developers. So it is easy to find help if you are stuck at some point while developing an application.
- Development Time: It saves development time required to build mobile applications for multiple platforms.
- Cost Effective: It reduces the cost to build mobile apps for multiple platforms.
- Cost effective: It reduces the cost to build mobile apps for multiple platforms.
- Hot Reloading: One of the biggest frustrations as a mobile application developer you have probably faced is constant recompiling of projects. Whenever you make a small change you need to recompile the project completely to check your changes in effect. React Native fixed this problem by taking the advantage of Hot Reload feature that allows developers to view changes live as they make them.
- Single Codebase: This is one of the most appealing features of React Native which lets you write a cross-platform mobile application using JavaScript in a single codebase for both Android and iOs. React Native provides a virtual DOM that renders platform specific components behind the scenes.
- Simple User Interface: React Native offers much more simplified responsive User Interface and reduces the loading time as well.
- Stable Apps: In React Native, the process of data binding is simplified and child components do not have any dependencies on the parent data which makes application more stable and increased level of reliability. In React Native, only permitted components are allowed to be updated when any modification or update is made in application.
- Modular Architecture: React Native follows modular programming, which allows us to split the application into independent reusable components/modules. Module is simply an independent, fully functional and reusable piece of code which usually contains JavaScript code.
- Third-Party Plugin Support: React Native offers the support for Third-party plugins including native modules and javascript modules that is not part of core React Native Framework.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Environment Setup
There are a couple of things you need to install to set up the environment for React Native. We will use OSX as our building platform.
- NodeJs
- NPM
Installation
Step 1: Install create-react-native-app
After installing NodeJS and NPM successfully in your system you can proceed with installation of create-react-native-app (globally as shown below).
- C:\Users\ABC> npm install -g create-react-native-app
Step 2: Create project
Browse through the required folder and create a new react native project as shown below.
- C:\Users\ABC>cd Desktop
- C:\Users\ABC\Desktop>create-react-native-app MyReactNative
After executing the above command, a folder with specifies name is created with the following contents.
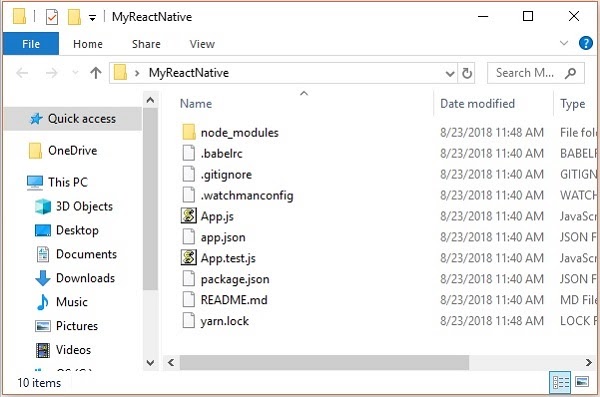
Step 3: NodeJS Python Jdk8
Make sure you have Python NodeJS and jdk8 installed in your system if not, install them. In addition to these it is recommended to install latest version of yarn to avoid certain issues.
Step 4: Install React Native CLI
You can install react native command line interface on npm, using the install -g react-native-cli command as shown below.
npm install -g react-native-cli
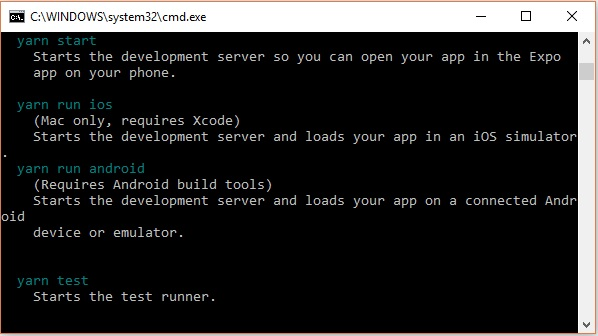
Step 5: Start react native
To verify the installation browse through the project folder and try starting the project using the start command.
- C:\Users\ABC\Desktop>cd MyReactNative
- C:\Users\ABC\Desktop\MyReactNative>npm start
If everything went well you will get a QR code as shown below.
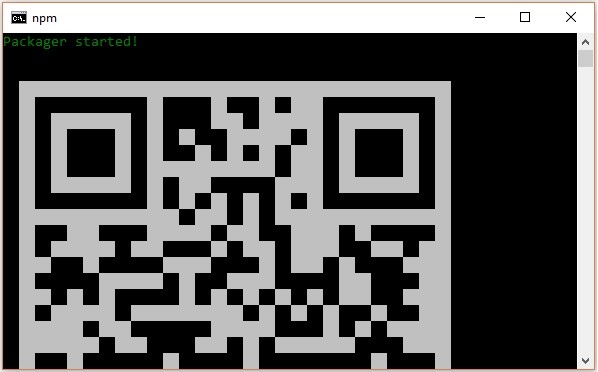
As instructed, one way to run react native apps on your android devise is to using expo. Install expo client in your android devise and scan the above obtained QR code.
Step 6: Eject the project
If you want to run android emulator using android studio, come out of the current command line by pressing ctrl+c.
Then, execute run eject command as
npm run eject
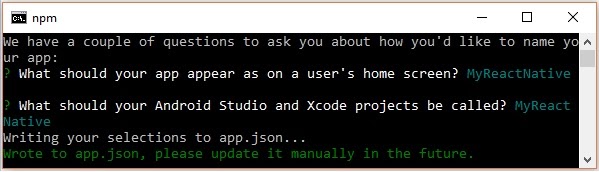
This prompts you options to eject, select the first one using arrows and press enter.
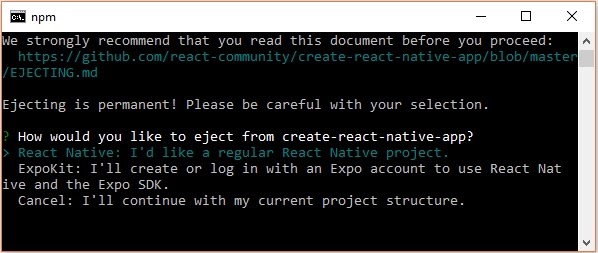
Then, you should suggest the name of the app on home screen and project name of the Android studio and Xcode projects.
Though your project ejected successfully, you may get an error as −
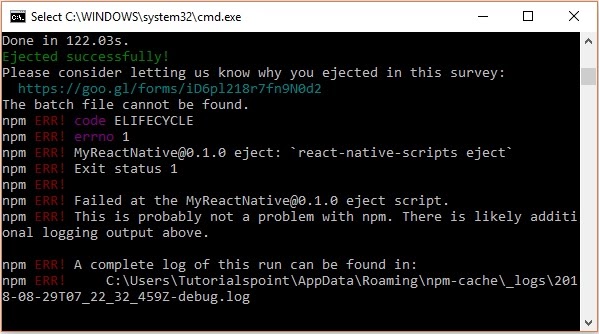
Ignore this error and run react native for android using the following command −
react-native run-android
But, before that you need to install android studio.
Step 7: Installing Android Studio
Visit the web page https://developer.android.com/studio/ and download android studio.
After downloading the installation file of it, double click on it and proceed with the installation.
Step 8: Configuring AVD Manager
To configure the AVD Manager click on the respective icon in the menu bar.
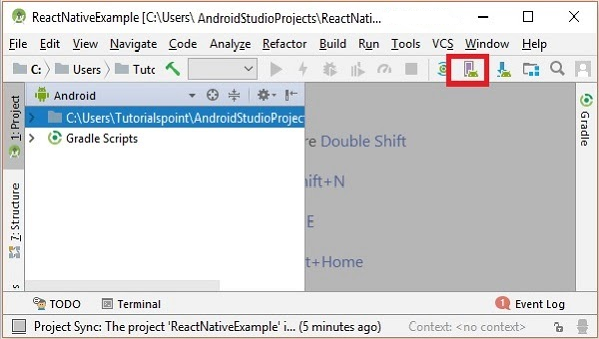
Step 9: Configuring AVD Manager
Choose a device definition, Nexus 5X is suggestable.
Click on the Next button you will see a System Image window. Select the x86 Images tab.
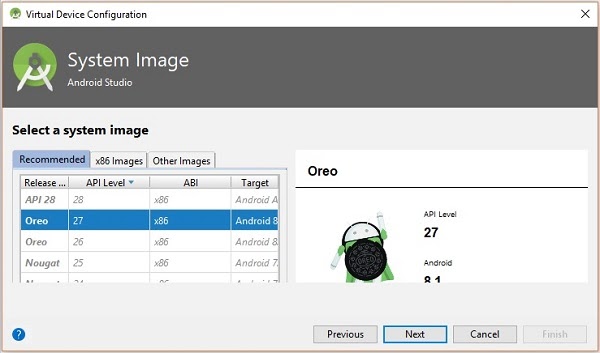
Then, select Marshmallow and click on next.
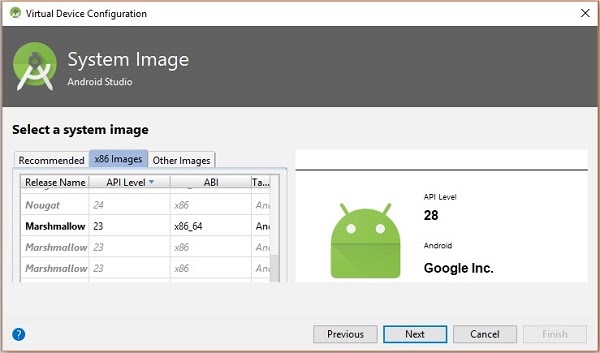
Finally, click on the Finish button to finish the AVD configuration.
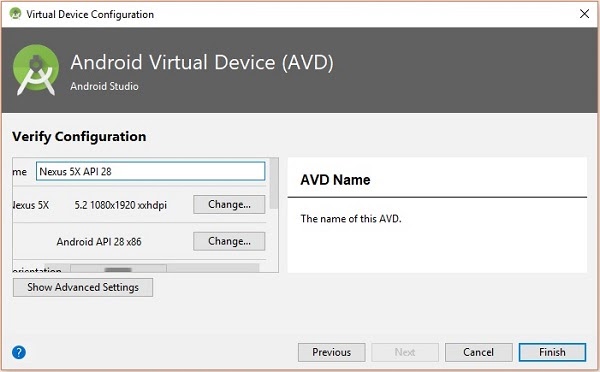
After configuring your virtual device click on the play button under the Actions column to start your android emulator.
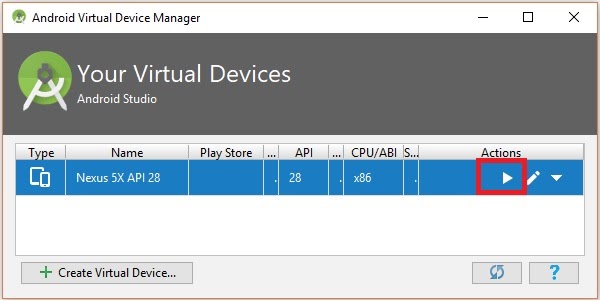
Step 10: Running android
Open command prompt, browse through your project folder and, execute the react-native run-android command.
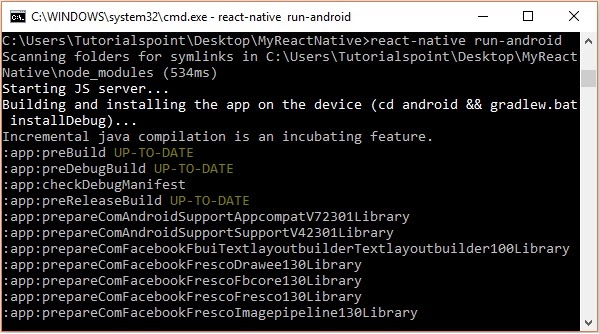
Then, your app execution begins in another prompt you can see its status.
In your android emulator you can see the execution of the default app as −
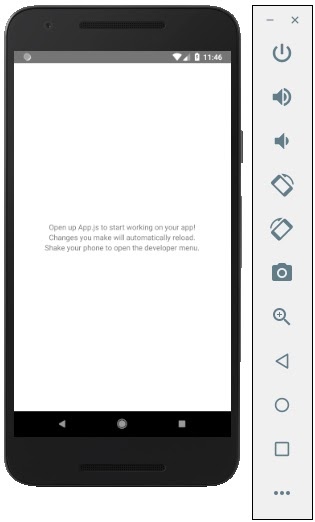
Step 11: local.properties
Open the android folder in your project folder SampleReactNative/android (in this case). Create a file with named local.properties and add the following path in it.
- sdk.dir = /C:\\Users\\ABC\\AppData\\Local\\Android\\Sdk
here, replace ABC with your username.
Step 12: Hot Reloading
And to build applications modify the App.js and the changes will be automatically updated on the android emulator.
If not, click on the android emulator press ctrl+m then, select Enable Hot Reloading option.
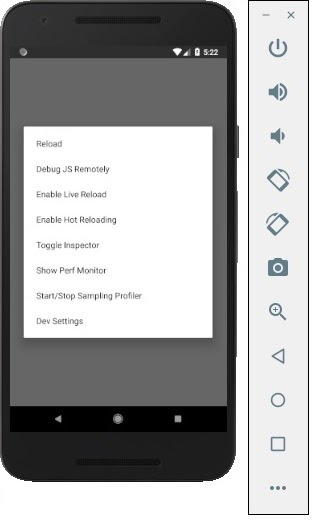
React and React Native: what is the difference?
All technical differences between them are caused by platform aims.
- While ReactJS uses Virtual DOM to render browser code, React Native uses native APIs as a bridge to render components on mobile. For example, for Android components, it uses Java APIs and it invokes Objective-C API to render to iOS.
- React Native doesn’t use HTML. So, if you worked with ReactJS before, you’ll have to get familiar with React Native syntax. For example, it uses <Text> instead of <p> and <View> instead of <div>.
- Because React Native doesn’t use CSS, standard CSS-features like animation run with React Native special APIs.
How React Native is different?
There are already hybrid and cross-platform mobile application development frameworks available such as Ionic, Phone Gap, Titanium and Xamarin etc. All of these frameworks let you create applications using web technologies and the application runs over a Web View component.
In React Native, you build real mobile applications that are not different in any way from the applications you created usingnative programming languages such as Objective C and Java. React Native lets you write native applications using JavaScript in a single codebase for both Android and iOS, later then javascript is compiled to native code. It uses the same platform specific fundamental UI components such as sliders, switches, labels, and tab bars that gives users seamless experience.
Pros of React Native
Right now, the React Native framework is one of the fastest and most efficient environments for mobile app development. It’s analogous to ReactJS, and here’s what you should know in terms of mobile:
React Native uses JavaScript – fast and popular programming language
JavaScript remains one of the fastest and widely-used programming languages, 67.7 percent of developers use JavaScript according to the annual Stack Overflow survey. The maturity of the JS community allows specialists to quickly learn the language and constantly progress working with it. So, you should typically be able to quickly find a React Native developer for your project. Besides, React Native leverages and combines the main advantages of JavaScript and ReactJS.
Due to the prevalence of JS code, engineers can work faster and more efficiently because they don’t have to restart a developed app after each update to see changes; they can simply refresh the viewing page.
In some cases, after-launch updates can be done faster. For instance, Apple allows JavaScript-based changes in application behavior in real-time mode with no review cycle required.
Native controls and native modules in React Native improve performance
React Native renders some code components with native APIs, unlike other cross-platform frameworks such as PhoneGap, which render code via WebView, a mobile engine. While the WebView approach greatly reduces performance, React Native communicates with targeted components for iOS or Android and renders code to native APIs directly and independently. Doing that, React uses a separate thread from UI, which also increases the performance score.
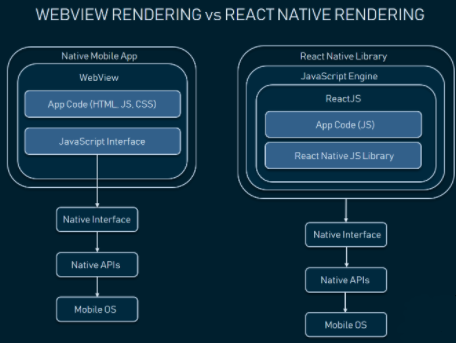
Native modules perform another important role. Currently, React provides a set of native modules written in Objective-C and Java out-of-the-box. These modules can’t be reused across two platforms but they aim at higher performance in computationally heavy operations like image editing or video playback. Basically, your team can apply the existing modules or, if they have Java and Objective-C experience, write custom modules themselves. As the React community grows, some things are already available. The rest of the codebase can be reused. For instance, Facebook Ads Manager shares 87 percent of code across Android and iOS.
On top of that, React Native provides simple debugging and error messaging tools. For instance, similar to web-programming, specialists can use Chrome or Safari developer tools, both of which they’re usually familiar with.
Built-in debugging
React Native has become officially debugged by default. In the latest 0.62 version released in late March 2020, React Native added built-in support for Flipper, a mobile apps debugging tool for developers, popular in both Android and iOS communities.
Starting with the latest release, React Native has default Flipper support from now on for React Native apps.
The Flipper tool has a bunch of options to work with. The toolset allows for such options as viewing crash reports from Android and iOS devices, viewing all network requests by device applications, viewing and editing the device databases and preferences, using the latest version of React DevTools together with other tools, and many more. Due to its extensible nature, Flipper also presents a marketplace that pulls plugins from NPM, which enables developers to publish and install custom plugins according to particular workflows.
React Native contains all ReactJS features, aimed at improving UI
React Native uses ReactJS as the JavaScript library, so it has all its advantages. To create a React Native app across platforms, developers don’t need to know the language of the native platform. They must only be proficient in JavaScript and familiar with the React syntax. But, as mentioned, they can easily add native components to code as well.
Downward data flow is also preserved, so core components can be edited without influence on child components. This makes UI development smooth while positively impacting user experience. The apps look and feel native.
Cons of React Native
Documentation
Unfortunately, React Native inherits the main ReactJS disadvantage. The community is young so the available documentation is poor, especially for integration with additional tools.
Expertise for native modules
We’ve discussed the native modules in the pros section. They definitely bring flexibility to the framework by filling the missing performance links. If you need to handle computationally heavy operations, you can inject native modules and achieve a truly native feel to your app.
However, to some extent, it could negate the point of cross-platform development as you still need some native engineers (Objective-C, Java, or both) in reserve. So maybe you don’t need React Native to build the next mobile Photoshop. But, if you aren’t aiming at brute-force demanding tasks, JS expertise is enough.
Third-party components
That said, React Native has a number of native modules for iOS and Android out-of-the-box, but the number of third-party components is still limited. And we can’t know for sure that community-built modules will be supported by the next releases of the framework. It remains a disadvantage because React Native doesn’t offer a wide spectrum of possible features that developers may want to implement in their apps.
Lagging SDK Updates
React Native often drags its feet when iOS or Android updates their SDKs. React Native’s team should integrate a code library with new software. And despite the fact they work pretty fast, they cannot update every part of the APIs at once. That’s why the full synchronization between React Native and new SDKs often takes too long.
Instability, compatibility issues, and errors
In this section, it’s worth highlighting in bold a broad number of problems that developers report after dealing with React Native here’s just a short list of problems that engineers stumble over when working with React Native:
- Hot reloading failures
- Incompatibilities between community libraries and different versions of React Native
- Emulator issues
- Problems with react-navigation
- The need to frequently reinstall packages
- Various other errors
Also, it still should be noted that creating custom modules with React Native can be tough as developers can often find themselves having three codebases (React Native, Android, and iOS ) for a component instead of a single one.
Keep in mind that the tool is still in development and the path to smooth engineering experience won’t be easy.

