- Financial Performance – A Complete Tutorial
- How Six Sigma Principles Can Progress Your Productivity – Tutorial
- Google Analytics Pro Tutorial | Fast Track your Career
- Activity-Based Costing Tutorial | Know about Definition, Process, & Example
- Create a workbook in Excel Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Excel ROUNDUP Formula Tutorial | Learn with Functions & Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Tutorial | Learn In 1 Day
- SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- IBM SPSS Statistics Tutorial: Getting Started with SPSS
- SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [Updated]
- SAP FIORI Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Introduction to Business Analytics with R Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Tableau Desktop Tutorial | Step by Step resource guide to learn Tableau
- Implementing SAP BW on SAP HANA | A Complete Guide
- SAP HANA Administration | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau API Tutorial | Get Started with Tools, REST Basics
- SAP FICO ( Financial Accounting and Controlling ) Tutorial | Complete Guide
- Alteryx Tutorial | Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- Getting started with Amazon Athena Tutorial – Serverless Interactive | The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction to Looker Tutorial – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Sitecore Tutorials | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE |Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Adobe Analytics Tutorial – The Ultimate Student Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- Pentaho Tutorial – Best Resources To Learn in 1 Day | CHECK OUT
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Spotfire Tutorial for Beginners | Quickstart – MUST- READ
- JasperReports Tutorial: Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Charts and Tables – Qlikview Tutorial – Complete Guide
- TIBCO Business Works | Tutorial for Beginners – Learn From Home
- Cognos TM1 Tutorial : Learn Cognos from Experts
- Kibana
- Power BI Desktop Tutorial
- Tableau Tutorial
- SSAS Tutorial
- Creating Tableau Dashboards
- MDX Tutorial
- Tableau Cheat Sheet
- Analytics Tutorial
- Lean Maturity Matrix Tutorial
- MS Excel Tutorial
- Business Analysis Certification Levels & Their Requirements Tutorial
- Solution Assessment and Validation Tutorial
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Enterprise Analysis Tutorial
- Create Charts and Objects in Excel 2013 Tutorial
- Msbi Tutorial
- MicroStrategy Tutorial
- Advanced SAS Tutorial
- OBIEE Tutorial
- Tableau Server Tutorial
- OBIA Tutorial
- Business Analyst Tutorial
- Cognos Tutorial
- Qlik Sense Tutorial
- SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
- SAS Tutorial
- PowerApps Tutorial
- Financial Performance – A Complete Tutorial
- How Six Sigma Principles Can Progress Your Productivity – Tutorial
- Google Analytics Pro Tutorial | Fast Track your Career
- Activity-Based Costing Tutorial | Know about Definition, Process, & Example
- Create a workbook in Excel Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Excel ROUNDUP Formula Tutorial | Learn with Functions & Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Tutorial | Learn In 1 Day
- SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- IBM SPSS Statistics Tutorial: Getting Started with SPSS
- SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [Updated]
- SAP FIORI Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Introduction to Business Analytics with R Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Tableau Desktop Tutorial | Step by Step resource guide to learn Tableau
- Implementing SAP BW on SAP HANA | A Complete Guide
- SAP HANA Administration | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau API Tutorial | Get Started with Tools, REST Basics
- SAP FICO ( Financial Accounting and Controlling ) Tutorial | Complete Guide
- Alteryx Tutorial | Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- Getting started with Amazon Athena Tutorial – Serverless Interactive | The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction to Looker Tutorial – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Sitecore Tutorials | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE |Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Adobe Analytics Tutorial – The Ultimate Student Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- Pentaho Tutorial – Best Resources To Learn in 1 Day | CHECK OUT
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Spotfire Tutorial for Beginners | Quickstart – MUST- READ
- JasperReports Tutorial: Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Charts and Tables – Qlikview Tutorial – Complete Guide
- TIBCO Business Works | Tutorial for Beginners – Learn From Home
- Cognos TM1 Tutorial : Learn Cognos from Experts
- Kibana
- Power BI Desktop Tutorial
- Tableau Tutorial
- SSAS Tutorial
- Creating Tableau Dashboards
- MDX Tutorial
- Tableau Cheat Sheet
- Analytics Tutorial
- Lean Maturity Matrix Tutorial
- MS Excel Tutorial
- Business Analysis Certification Levels & Their Requirements Tutorial
- Solution Assessment and Validation Tutorial
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Enterprise Analysis Tutorial
- Create Charts and Objects in Excel 2013 Tutorial
- Msbi Tutorial
- MicroStrategy Tutorial
- Advanced SAS Tutorial
- OBIEE Tutorial
- Tableau Server Tutorial
- OBIA Tutorial
- Business Analyst Tutorial
- Cognos Tutorial
- Qlik Sense Tutorial
- SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
- SAS Tutorial
- PowerApps Tutorial

SAS Tutorial
Last updated on 26th Sep 2020, Blog, Business Analytics, Tutorials
SAS (Statistical Analysis Software) is a widely used software for Data Analytics. It is a software suite that can alter, mine, manage and retrieve data from different sources and performs statistical analysis on it. It is also used for data management, statistical analysis, report writing, business modeling, application development, and data warehousing. It provides a point-and-click graphical user interface for non-technical users and more advanced options through the SAS language. This is a helpful tool through which you can use qualitative techniques and procedures that allow you to increase employee productivity and business profit.
In SAS, data is extracted and categorized in tables which helps you to identify and analyze data patterns. This is a software suite that allows you to manage the advanced analysis, business intelligence, predictive analysis, and data to work effectively in competing and changing business situations. Besides, SAS is a platform independent software, which means that you can run SAS on any operating system like Linux, Windows, Mac, Ubuntu etc.

What is SAS?
SAS or Statistical Analysis Software is a software suite developed by the SAS Institute. It is used for data analytics and helps you with various qualitative techniques and processes to enhance the overall productivity of employees and business profits too. SAS should not be misunderstood with SAAS, which means the software as a service.
SAS helps in extracting data and categorize it that helps you in identifying patterns further. It can be used to perform advanced analysis, predictive analysis, business intelligence, data management, etc. to operate effectively in the competitive world. Moreover, SAS is platform-independent, and it can be used with different platforms like Linux, Windows, etc.
When compared to other BI tools, SAS gives extensive support to transform and analyze data programmatically. It provides granular control for data manipulation and analyzes its USP.
Why SAS is popular in job market?
SAS has over 40,000 customers worldwide and holds largest market share in advanced analytics. It has been tagged ‘leader’ consistently for last 6 consecutive years in advanced analytics platforms. In finance (BFSI) industry, SAS retains No. 1 spot and is being used as a primary tool for data manipulation and predictive modeling.
- Data Security – Because of unparalleled data security provided by SAS software, it is leading the analytics software industry in BFSI sector.
- Tech Customer Support – SAS provides one of the best tech support. If you are stuck in anything related to SAS whether it is installation related issue or clarity in any of SAS functions and procedures, they have both online and offline community to support you.
- Detailed Documentation – SAS documentation is very detailed as compared to open source software like R and Python.
- Memory Management – SAS can store datasets on hard drive and process bigger data set than size of your RAM.
- Stable Software more important than cost of software license – All the functions and procedures of previous software version are supported in new SAS versions. Cost of software license is a peanut to a bank or pharmaceutical company.
- Legacy System – Many banks have been using SAS for last 20-30 years and they have automated the whole process of analysis and have written millions of lines of working code. To convert all the stable reporting system from SAS to R/Python, it may require significant additional cost.
- SAS Applications
- Advanced Analytics
- Multivariate Analytics
- Predictive Analytics
- Business Intelligence
- Data Management
Learn the concepts of SQL Server with our online training program and become the most demanded SQL professional today!
Quick Introduction to Data Analytics
Analytics is a technical term quite trendy these days, yet there is no single definition for this term. Let us understand this with the help of a simple example. Imagine you want to buy a t-shirt. So, what possible questions can strike your mind? Let me help you with a few suggestions.
- When to buy a T-shirt?
- What should be the maximum cost for the T-shirt?
- Can I buy it online or I need to visit a store?
- For online shopping, which site should I prefer?
- If I want to buy it from a store then which store should I visit?
Here, your final decision depends on multiple factors like budget, preferences, and past experiences, etc. let us continue with the problem.
- You can choose the weekend as you are usually free on Saturday or Sunday.
- Your maximum budget is $300, not higher.
- You love buying t-shirts from the store because it helps you in making a quick decision.
- It is better to visit a store where you have gone earlier, too; it will not disappoint you.
With these facts, finally, you decided to buy a t-shirt from your favorite store that costs you around $280. In simple words, you did perform a simple analysis here that helped in buying a t-shirt of your choice. Let me explain to you in two simple steps:
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
- 1.You just collected information based on your requirements.
- 2.You understood the data based on facts and information that helped you in buying your favorite T-shirt quickly.
So, it must be clear now how the data analytics process can help you. You can collect data, analyze the data, and make a decision based on your analysis. There are plenty of tools to perform analysis and to simplify these problems. One such prominent tool in SAS let us understand what SAS is and why it is necessary with the help of this SAS Tutorial.
Why do we need SAS?
Given example was simpler, so you could make a decision here based on a few assumptions only. What to do if the decision making is not that much simpler? Think again from a business point of view where an e-commerce website wants to study the buying patterns of customers based on historical data. The company has to study thousands of records for this purpose. Also, the Company may have to use the permutation combination technique here to record different preferences of people.
Sometimes, the Company may not have all the data. For example, if a customer has not purchased a T-shirt from your site, you simply ignore this data. This missing data may create problems later. So, how to work out with these problems? How to handle this type of data? Well, these problems become easier with analytics where we can use different techniques to find the relevant data that further helps in finding patterns to help you in making better decisions.
Read: Difference Between SQLite and MySQL
If the analysis is performed manually, then this task may take hundreds of hours. With the help of analytics tools like SAS, the same task can be completed within a few hours only. It helps in eliminating waste data and optimize the available data. It helps you to workout with missing data too. Finally, SAS enables you to make a better decision than usual. In the next section, we will discuss popular analysis tools and how they can be compared together.
SAS vs. R vs. Python
During the last few years, data analytics has grown immensely. It results in an increase in the number of tools day by day. All of them are beneficial in one or another way. Moving ahead, let us discuss a few popular tools that are used frequently in the analytics market.
- SAS (Statistical Analysis Software): It is the most powerful tool in the commercial analytics market. With an interactive GUI and a plethora of statistical benefits, it certainly leads the market.
- R language: It is a well-documented, open-source, and easy to use programming language. It is a cost-effective programming language with plenty of statistical benefits.
- Python: It is a popular open-source scripting language that has grown over time. It supports several libraries like NumPy, Scipy, MatPlotLib, etc. To check on Python libraries in detail.
Let us compare these three tools based on these four parameters. These are Jobs, Flexibility, fourth-generation language, and Easy to learn, etc.
- Jobs: The vast usage of analytics tools generated a lot of positions for skilled SAS resources. SAS holds more than 70 percent of the market share. R holds 15 %, and Python holds the least market share.
- Flexibility: It is a highly flexible tool that can be quickly integrated with third-party tools or platforms. In brief, it amalgamates well with other technologies.
- Fourth Generation Language: SAS is a 4th generation programming language designed with a specific purpose in mind like the development of commercial enterprise software. It reduces the overall programming efforts, time, or costs, etc. at the same time, R and Python are not 4th generation programming languages.
- Easy to Learn: SAS programming language can be learned quickly. Python and R are not so much convenient for data analysis like SAS. R results in lengthy and boring code hence giving SAS an edge.
Brief History and Evolution of SAS
- It was discovered by Jim Goodnight and John Shall in 1970 at N.C. University.
- It was primarily designed for agricultural research.
- It was clubbed with other tools to perform predictive analysis, BI, data management, etc.
- Today, top Companies in fortune 400 using SAS for effective and quick data analysis.
Key Features of SAS
- It helps in accessing raw data quickly from an external database. It accesses data written in almost any format.
- It helps in data management for data entry, data formatting, data conversions, or data edition, etc.
- It analyzes data using modeling techniques, Forecasting, linear programming, descriptive techniques, statistical techniques, etc.
- It helps in performing advanced analytics to make improvements in business decisions.
- It helps in report generation with the help of graphs.
- It helps in data updates and necessary modifications.
- It helps in project management and operations research.
- It supports a powerful data handling language.
- It has excellent data cleansing functions.
- It can interact with multiple host systems together.
SAS Product Suite or SAS Components
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Base SAS | It promotes hardware agility and can be integrated with all types of cloud environments. |
| SAS / Graph | It helps in you representing structured data into meaningful graphs. |
| SAS / STAT | It helps you to perform a different type of analysis like regression analysis, statistical analysis, psychometric analysis, and more. |
| SAS / ETS | It can be used for forecasting and helps you in performing series analysis. |
| SAS EBI | It is a popular tool for business intelligence apps. |
| SAS Grid Manager | It is an important component that allows data management feature and a programming language for data analysis too. |
| SAS / OR | It is a tool for operational research. |
| SAS / QC | It is a component for quality control. |
| SAS / Enterprise Miner | It is generally required for data mining. |
| SAS / PH | It is used for clinical trial analysis. |
| SAS / AF | It is needed for applications facility. |
| SAS / IML | IML means Interactive Matric Language. It is used for translating mathematical functions into innovative programs. |
| Enterprise Guide | It is a GUI-based code editor and project manager. |
SAS Intelligence Platform Architecture
SAS Intelligence Platform Architecture is designed to access large numbers of data efficiently, as well as provides timely intelligence to a great number of users simultaneously.
The platform follows a three-tier architecture that enables you to distribute functionality in computer resources so that each type of work can be done by those resources that are most suitable for the job.
You can easily examine the architecture to determine whether it meets the demands of your workload or not. For a large company, tiers can be installed in several machines with different operating systems, and for demonstrations, prototyping or very small enterprises, all the tires can be installed on a single machine.
As shown in the following SAS Architecture Diagram, the SAS Information Delivery Portal is implemented using a three-tier architecture. This architecture has proved to be highly effective for developing and deploying enterprise applications.
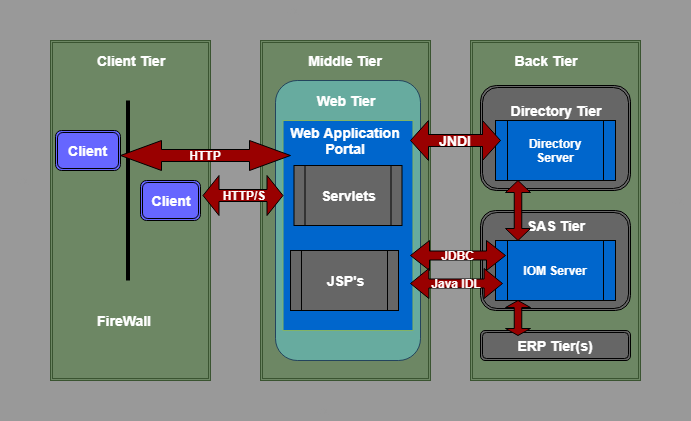
Architecture Components of SAS software are listed below.
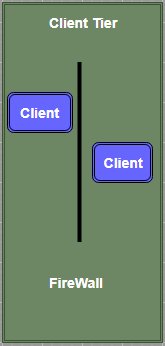
Client Tier
The client tier is used to view the portal and its content. It includes all the components that are used to view the portal and content. The client tier includes a web browser that is used to interact with the portal over HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) OR HTTP/S (HyperText Transmission Protocol, Secure). These HTTP or HTTP/S protocols makes the SAS Information Delivery Portal “firewall friendly.” The portal can be deployed anywhere on the network and users can access it from any internet connectivity like corporate intranet, extranet, or public internet.
Depending on the content, the client can also use one or more standard desktop applications such as Adobe Acrobat Reader or Microsoft Excel. These applications are used in the process of view content. The content is streamed by the servlets in the middle tier of the portal.
When the web browser receives such content that it does not know how to present it, it looks at the mime-type of content and tries to find a viewer that knows how to display it. Standard Web browser functionality redirects the stream of content to the appropriate viewer for displaying. Once the content comes under one of these applications, the user can process it locally or save it to disk.
There is also another optional client application that is the SAS Package Reader. SAS Package Reader is part of the SAS Publishing Framework. The Package Reader enables the user to view and manage the contents of a SAS package off-line, independent of the portal Web application.
Middle Tier
The middle tier is a center of SAS architecture which provides a centralized access point for enterprise information. All direct access to content is processed by the components that are operating in this tier. This design point offers several advantages.
By separating business logic from display logic, you can use different clients to take advantage of logic at the middle tier. One more advantage is that the centralized point of access makes it easy to implement security rules, administer the portal and manage code changes.
The following functions are hosted by the middle tier:

Web Tier
The first part of the middle tier is the web tier that contain Web Application Portal for SAS Information Delivery.
Web Application Portal
SAS Information Delivery Portal is a collection of web applications, Java Servlets, JSP, JavaBinx and other sections and resources. These components work together to access the information stored in the Enterprise Directory and present a customizable interface for the user.
Servlet container
The servlet container or servlet engine is responsible for the management of the SAS Information Distribution Portal web application. Servlet Container or engine provides a runtime environment that supports deployment, concurrency, life-cycle management, and other services for Java components.
Web server
The web server provides services for the servlet engine. For example, the servlet engine depends on the HTTP server so that it can provide HTTP message handling. Web servers can also be used to host web sites that can be accessed through the portal.
Back Tier
The back tier is the third and last part of SAS architecture. This tier provides run time environment to Data Servers and Compute Servers. A compute server can also have business objects. For example, SAS IOM servers contain SAS stored processes that analyze the data and summarize the results. As shown in the above figure, the SAS Information Delivery Portal uses standard interfaces like JDBC and Java IDL to communicate and access data from IOM servers.
Back tier contains two servers one is IOM Server that we have explained above, and another is the Enterprise Directory Server. According to the description of the Single Access Point for Enterprise Information, the Enterprise Directory Server stores metadata about the content that is located in the entire enterprise. The directory does not have content, and it contains only metadata that describes it. It contains the location of the information and how to access it, and how it relates to other content items. Web application portal uses JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface) to access the enterprise directory server.
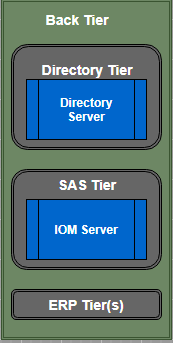
Back Tier does not necessarily translate into additional hardware platforms. For small implementation, these servers can run on a machine similar to a web server. On the other hand, a large enterprise can have many compute and data servers and can be an enterprise directory that is distributed on many platforms. The architecture of the SAS Information Delivery Portal gives you the flexibility to distribute these functions as per the need.
Advantages of SAS
There are several advantages of SAS Programming Language:
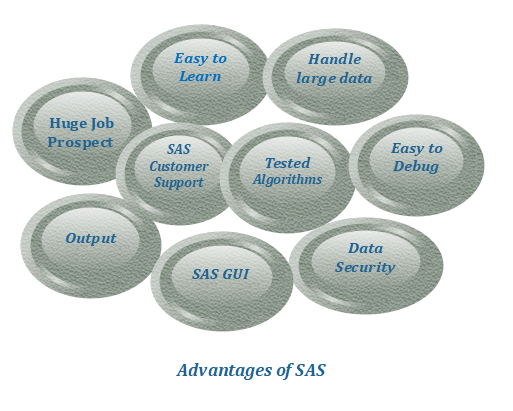
1. Easy to learn
SAS is very easy to learn syntax. It can be learned easily without any programming skill so that anyone can learn it. Coding of SAS is in the form of simple statements. It is like giving instructions to the machine what to do.
2. Ability to handle Large Database
SAS is strongly capable of handling large database very easily.
3. Easy to Debug
SAS is a very comprehensible language. The process of debugging is very easy. It is easy to understand and correct the error because the log window states it clearly.
4. Tested Algorithms
The algorithm implemented in the SAS program is fully tested and analyzed by developers. Every version of SAS is tested in a controlled environment, before its release. Testing is possible because SAS is a closed source language.
5. SAS Customer Support
The organization of SAS maintains proper monitoring, as it is like a complete organization to analyze SAS. It has intuitive customer support. SAS customer support handles all kind of problems.
6. Data Security
SAS software is a primary tool for many large scale companies. Company’s data is confidential here that’s why it is a close source of companies.
No external tincture is possible. Because SAS is a closed source tool, it can only be edited by the SAS organization.
In the extension of the above point, the data in SAS is completely secure. In the case of office use, without license we cannot extract data. Manipulation is not possible because of Data security, and this is the reason behind its popularity in the corporate world.
SAS is preferred over R and any other language used for analysis. R is open source; therefore, data security is not guaranteed. Only freelancer uses the R.
7. SAS GUI
SAS is a language that has made statistical computing easier for non-programming users. It has an amazing GUI (Graphical User Interface). Its user interface has various tools like plots, graphs, and highly versatile libraries.
8. Output
SAS has been developed in a long period of time. That’s why it provides a well formatted and absolutely correct output, which is easy to understand.
9. Huge Job Prospects
Due to the fact that SAS has been used in the industry for a very long time, there are huge employment potentials. Professionals learn SAS as a condition so that they can enter in the analytics industry. The person who commands the SAS can easily learn R and Python. This is a market leader in the Analytics industry.
Disadvantages of SAS
Some major disadvantages of SAS programming are as follows
1. Cost
The cost of SAS software is one of its major disadvantages. We cannot use all its functions without a license, which is very expensive.It is a complete software due to being in a closed environment, so there is no facility for the license of any single function that we need. All these prerequisite makes it very expensive.
2. SAS is Not Open Source
R is always quicker than SAS in implementing an algorithm related to machine learning. The reason behind this, R is an open source so that anyone can operate it, but this is unfavorable for SAS. SAS is a closed environment software, and it doesn’t support open source so, the algorithm of SAS procedures is not for the use of public. SAS is available only in the licensed version. Algorithms are not openly available for public research.
3. Lack of Graphic Representation
There is more availability of R for advanced graphics. Its graphics presentation is much more vivid and consistent than SAS. It has a more descriptive plot, diagram, and graph.
4. Difficult Text Mining
- Text mining in R is free, but in SAS, it uses SAS Enterprise. Text mining means extracting information from text. This is used to decrypt a written code. It tells us what the written text can decide in terms of decision making. This is the process in which the text converts data into decision making and analysis.
5. Difficult than R
SAS is more procedural language than R. There are more lines of code in SAS than R.
We can quickly apply new innovations such as statistical learning and machine learning in R in comparison to SAS.
Many packages which are free in R, are chargeable in SAS. For example, Text Mining, Time Series Forecasting (SAS / ETS), etc.
We studied SAS programming which is a statistical language for mining and converting raw data into a legible and interpretable format. We use it in business analytics to make strategic decisions. SAS program is sequential statements, that we write in an orderly manner. We can write SAS statements easily in English statements to instruct the system. In short, we studied a complete guide or a cheat sheet for the SAS Programming Tutorial.
