- Financial Performance – A Complete Tutorial
- How Six Sigma Principles Can Progress Your Productivity – Tutorial
- Google Analytics Pro Tutorial | Fast Track your Career
- Activity-Based Costing Tutorial | Know about Definition, Process, & Example
- Create a workbook in Excel Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Excel ROUNDUP Formula Tutorial | Learn with Functions & Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Tutorial | Learn In 1 Day
- SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- IBM SPSS Statistics Tutorial: Getting Started with SPSS
- SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [Updated]
- SAP FIORI Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Introduction to Business Analytics with R Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Tableau Desktop Tutorial | Step by Step resource guide to learn Tableau
- Implementing SAP BW on SAP HANA | A Complete Guide
- SAP HANA Administration | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau API Tutorial | Get Started with Tools, REST Basics
- SAP FICO ( Financial Accounting and Controlling ) Tutorial | Complete Guide
- Alteryx Tutorial | Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- Getting started with Amazon Athena Tutorial – Serverless Interactive | The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction to Looker Tutorial – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Sitecore Tutorials | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE |Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Adobe Analytics Tutorial – The Ultimate Student Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- Pentaho Tutorial – Best Resources To Learn in 1 Day | CHECK OUT
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Spotfire Tutorial for Beginners | Quickstart – MUST- READ
- JasperReports Tutorial: Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Charts and Tables – Qlikview Tutorial – Complete Guide
- TIBCO Business Works | Tutorial for Beginners – Learn From Home
- Cognos TM1 Tutorial : Learn Cognos from Experts
- Kibana
- Power BI Desktop Tutorial
- Tableau Tutorial
- SSAS Tutorial
- Creating Tableau Dashboards
- MDX Tutorial
- Tableau Cheat Sheet
- Analytics Tutorial
- Lean Maturity Matrix Tutorial
- MS Excel Tutorial
- Business Analysis Certification Levels & Their Requirements Tutorial
- Solution Assessment and Validation Tutorial
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Enterprise Analysis Tutorial
- Create Charts and Objects in Excel 2013 Tutorial
- Msbi Tutorial
- MicroStrategy Tutorial
- Advanced SAS Tutorial
- OBIEE Tutorial
- Tableau Server Tutorial
- OBIA Tutorial
- Business Analyst Tutorial
- Cognos Tutorial
- Qlik Sense Tutorial
- SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
- SAS Tutorial
- PowerApps Tutorial
- Financial Performance – A Complete Tutorial
- How Six Sigma Principles Can Progress Your Productivity – Tutorial
- Google Analytics Pro Tutorial | Fast Track your Career
- Activity-Based Costing Tutorial | Know about Definition, Process, & Example
- Create a workbook in Excel Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Excel ROUNDUP Formula Tutorial | Learn with Functions & Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Tutorial | Learn In 1 Day
- SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- IBM SPSS Statistics Tutorial: Getting Started with SPSS
- SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [Updated]
- SAP FIORI Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Introduction to Business Analytics with R Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Tableau Desktop Tutorial | Step by Step resource guide to learn Tableau
- Implementing SAP BW on SAP HANA | A Complete Guide
- SAP HANA Administration | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau API Tutorial | Get Started with Tools, REST Basics
- SAP FICO ( Financial Accounting and Controlling ) Tutorial | Complete Guide
- Alteryx Tutorial | Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- Getting started with Amazon Athena Tutorial – Serverless Interactive | The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction to Looker Tutorial – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Sitecore Tutorials | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE |Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Adobe Analytics Tutorial – The Ultimate Student Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- Pentaho Tutorial – Best Resources To Learn in 1 Day | CHECK OUT
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Spotfire Tutorial for Beginners | Quickstart – MUST- READ
- JasperReports Tutorial: Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Charts and Tables – Qlikview Tutorial – Complete Guide
- TIBCO Business Works | Tutorial for Beginners – Learn From Home
- Cognos TM1 Tutorial : Learn Cognos from Experts
- Kibana
- Power BI Desktop Tutorial
- Tableau Tutorial
- SSAS Tutorial
- Creating Tableau Dashboards
- MDX Tutorial
- Tableau Cheat Sheet
- Analytics Tutorial
- Lean Maturity Matrix Tutorial
- MS Excel Tutorial
- Business Analysis Certification Levels & Their Requirements Tutorial
- Solution Assessment and Validation Tutorial
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Enterprise Analysis Tutorial
- Create Charts and Objects in Excel 2013 Tutorial
- Msbi Tutorial
- MicroStrategy Tutorial
- Advanced SAS Tutorial
- OBIEE Tutorial
- Tableau Server Tutorial
- OBIA Tutorial
- Business Analyst Tutorial
- Cognos Tutorial
- Qlik Sense Tutorial
- SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
- SAS Tutorial
- PowerApps Tutorial

SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
Last updated on 27th Sep 2020, Blog, Business Analytics, Tutorials
SAP Business Objects is an enterprise software company, specializing in business intelligence. Business Objects was acquired in 2007 by SAP AG a German company. SAP Business Objects software helps organizations gain better insight into their business, improving decision-making and enterprise performance. SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence (BI) platform supports the entire range of end-user reporting, query, and analysis, and performance management uses.
Understanding this infrastructure will help you successfully administer the SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence (BI) platform.
By understanding Business Intelligence (BI), you will better comprehend how SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence (BI) solutions address the BI product spectrum.
Gartner Inc., a research and advisory firm that helps clients leverage technology, coined the term “Business Intelligence” in the late 1980s.
Business Intelligence, as defined by Gartner, is an iterative user-centred process that includes accessing and exploring information, analyzing this information, and developing insights and understanding that lead to improved and informed decision making.
BI usage crosses the spectrum of users, both internally and externally throughout any enterprise, and includes rank-and-file workers, executives, analysts, and knowledge workers.
Examples of internal and external BI applications include
- Generating a class list for a training session
- Creating an employee performance review
- Scheduling in a health care setting
- Manufacturing computer parts
SAP BODS Architecture
Here, are some basic components of SAP BODS architecture:
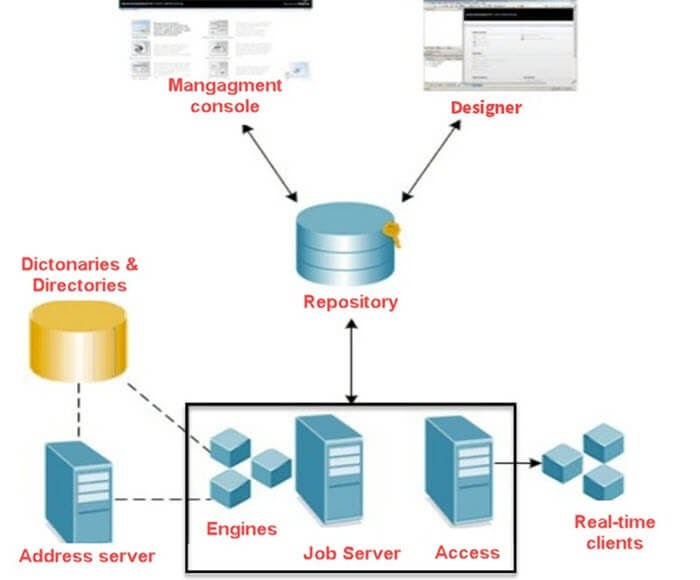
SAP BODS Architecture Diagram
Repository:
A repository is a set of a table which holds user-created and predefined system object, source, target metadata, and transformation rules. It allows you to set up repositories on an open client/server platform. This helps you for sharing metadata with other enterprise tools. Each local repository is connected with one or more job server which runs the job you have created.
Management Console
SAP BOD Data Services Management Console is the web-based application with the following features.
- Impact and Linear Analysis
- Administration
- Auto Documentation
- Operational Dashboard
- Data Validation
- Data Quality Data Reports.
Job server:
The Job Server component helps you to starts the data movement engine. It allows you to integrate data from multiple sources. It helps you to perform complex data transformations and manages transactions and extractions from ERP systems and other sources.
The Data integration Job server tool allows you to move in data in either batch or real-time mode. It delivers high data throughput and scalability. Moreover, while designing a job, you can also run it from the Designer which tells the Job Server to run the job. The Job Server also allows you to get the job from its associated bods repository.
Data Services Designer
The Data services Designer tool offers an easy-to-use graphical user interface that helps you define transformations, data mappings, and control logic.
This component helps you to build applications containing data and workflows. This component also allows you to manage metadata stored in a repository.
Engines:
After SAP BusinessObjects Data Services job are executed, the Job Server starts the engine to perform data extraction, transformation, and movement. The engine uses parallel processing and in-memory data transformation to offer high data connectivity, quality, and scalability.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Access server:
Access server offers real time request-reply message that collects message request routes them to a real-time service and delivers a message reply in a specific duration. The Acess Server queries message and sends them to the next available real-time service across numerous computing resources.
Address Server:
The next component is the Address Server. It offers address validation and corrections. The Address Server must be started before processing data flows which contain the Global address Cleanse or Global Suggestion list transform with the EMEA engine enabled.
Business Intelligence can help organizations to
- Identify and track key performance metrics against their direct competitors and the overall market
- Improve customer service and target high yield accounts
- Streamline operations and improve supplier and warehouse operations
- Identify successful marketing campaigns
- Improve response time to market trends and customer requests
- Decrease query and reporting time
- Reduce cost and anxiety over compliance
- Deliver true cost of goods and services
- Reduce strain on IT departments
Business Intelligence provides insights that enable business managers to make tactical decisions, as well as to establish, modify, or tune business strategies and processes in order to gain competitive advantage and improve business operations and profitability.
SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence platform supports a range of performance management (Dashboard and Analytics), reporting, querying, and analysis applications.
- It also provides an industry-standard, proven architecture and platform-support for semantic layers, data integration, and security.
- SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence platform provides for web-based administration and configuration of the entire system.
Benefits of Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence can help organizations to:
- Identify and track key performance metrics against their direct competitors and the overall market Improve customer service and target high yield accounts
- Streamline operations and improve supplier and warehouse operations
- Identify successful marketing campaigns
- Improve response time to market trends and customer requests
- Decrease query and reporting time
- Reduce cost and anxiety over compliance
- Deliver true cost of goods and services
- Reduce strain on IT departments
Business Intelligence provides insights that enable business managers to make tactical decisions, as well as to establish, modify, or tune business strategies and processes in order to gain competitive advantage and improve business operations and profitability.
Business Objects
- A business object (BO) is a container for application data, such as a customer or an invoice. Data is exchanged between components by business objects. The underlying structure of a business object is an XML schema definition (XSD).
- Service Component Architecture (SCA) provides the framework for defining an application module, the services it provides, the services it consumes, and the composition of components that provide the business logic of the application module. Business objects play an important role in the application, defining the business data that is used to describe the service and component contracts and the business data that the components manipulate.
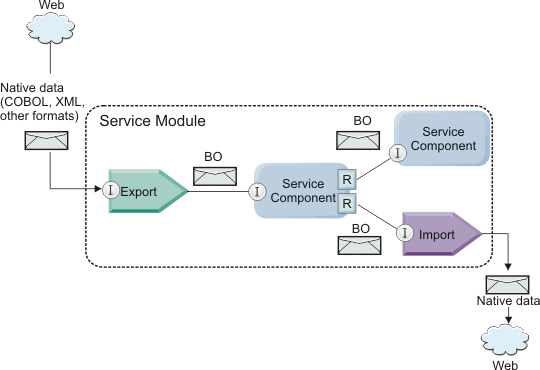
- A business object contains fields that have a name, a type (scalar type or another business object), a default value (for scalar types) and cardinality. Business objects can extend (define a superset of fields) other business objects through parent/child relationships; however, a business object can only inherit from a single parent. These objects can also be used in conjunction with each other to perform a task.
WORKS
- Using the interface in the SAP BusinessObjects BI OnDemand solution, you can follow an intuitive process to upload a spreadsheet, bring in different data sources, and explore your data with the software’s unique search and browse functionality. The integrated solution lets you create accurate, timely dashboards and reports. That means you no longer need to pull together sales reports from various sources or manually create pivot tables, charts, and graphs. You can also perform ad hoc “what-if” analyses. And there’s no need to share spreadsheets and reports via e-mail or paper – instead, you can share the information online. Partner offerings for industry and business-specific uses are available.
STRUCTURE
- To achieve this encapsulation, the SAP Business Objects are constructed as entities with multiple layers:
- At the core of an SAP Business Object is the kernel, which represents the object’s inherent data.
- The second layer, the integrity layer, represents the business logic of the object. It comprises the business rules and constraints that apply to the Business Object.
- The third layer, the interface layer, describes the implementation and structure of the SAP Business Object, and defines the object’s interface to the outside world.
- The fourth and outermost layer of a Business Object is the access layer, which defines the technologies that can be used to obtain external access to the object’s data, for example COM/DCOM (Component Object Model/Distributed Component Object Model).
Business object programming model
- The business object programming model consists of a set of Java interfaces that represent:
- The business object definition and instance data
- A set of services that support the operations on the business objects
- Business object type definitions are represented by the commonj.sdo.Type and commonj.sdo.Property interfaces. The business object programming model provides a set of rules for mapping the XML schema complex type information to the Type interface and each of the elements in the complex type definition to the Property interface.
- Business object instances are represented by the commonj.sdo.DataObject interface. The business object programming model is untyped, which means that the same commonj.sdo.DataObject interface can be used to represent different business object definitions, such as Customer and Order. The definition of which properties can be set and retrieved from each business object is determined by type information defined in the XML schema associated with each business object.
- The business object programming model behavior is based on the Service Data Object 2.1 specification. For additional information, see the SDO 2.1 for Java specification, tutorials and javadocs on the web: http://www.oasis-opencsa.org/.
- Business object services support various lifecycle operations (such as creation, equality, parsing, and serialization) on business objects.
- For specifics on the business object programming model, see the Generated API and SPI documentation on business objects.
SAP BO
- SAP BO (Business Objects) is a financial application of enterprise data warehouse (DWH) reporting tool for SAP system and non SAP systems. SAP BO is basically used to create higher level reports based on the interaction (Interactive reports) generated by using dash boards and score cards. Dashboards and score cards are used to take corporation level online.
- BO provides the following solutions
- 1.Solutions for large enterprises
- 2.Solutions for small and medium business organizations
- 3.On-demand solutions
- 4.SAP-BO rapid development solutions
SAP Business Objects has the following technologies.
- 1.Enterprise Performance Management (EPM).
- 2.Business Intelligence (BI)
- 3.Enterprise Information Management)
- 4.Governance, Compliance, Resource (GRS)
Installing
Step 1: Register with SAP in order to receive your trial license key via email (required for installation)
Step 2: Download the Business Objects Server (SAP BO BI 4.2 SP5 versions) and Client software
Step 3: Once the files are downloaded, please extract the ZIP file.
- You cannot install the SAP BO BI 4.2 SP5 server into your personal machine which runs on windows clients like Windows 7/8/10 and you will thrown the below error message and you cannot continue further for the installation.
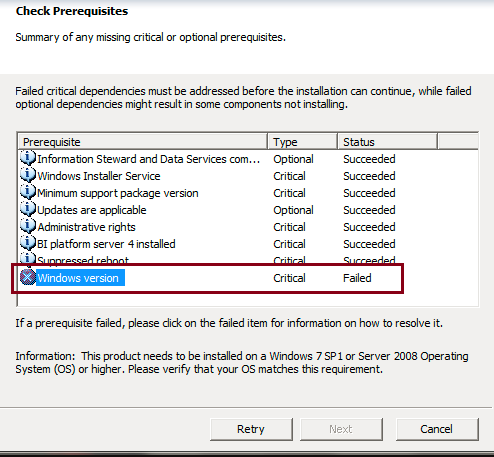
- By default, SAP BO BI 4.2 server cannot be installed in personal PC which uses Windows 7 / 8 /10 OS rather it will work only on server-based OS like windows Server 2012, etc.
- There is a work around to change the installation file to convert the Server to compatible to install in personal PC OS (Windows 7 /8 / 10)
- Before we start our installation process, in order to install it in our desktop, unzip the compressed file and go to the file: product.seed.XML (Path: DATA_UNITS\BusinessObjectsServer_win\dunit\product.businessobjects64-4.0-core-32)
- Edit the file with AllowedSuffix value from “Server to Workstation”.
- Once you updated the above file, please click the setup.exe and then the installation will start.
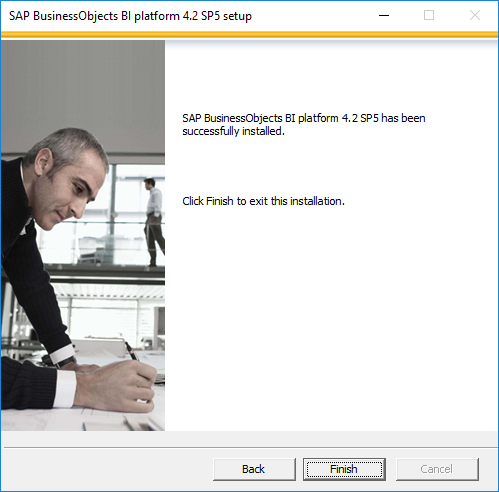
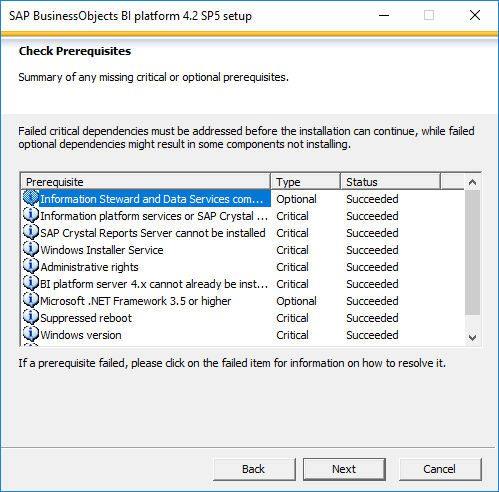
- Now you can see the updates as the windows client version is compatible to install the SAP BO BI 4.2 server.
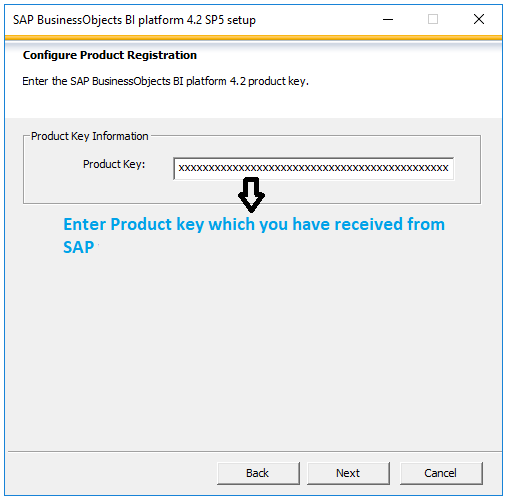
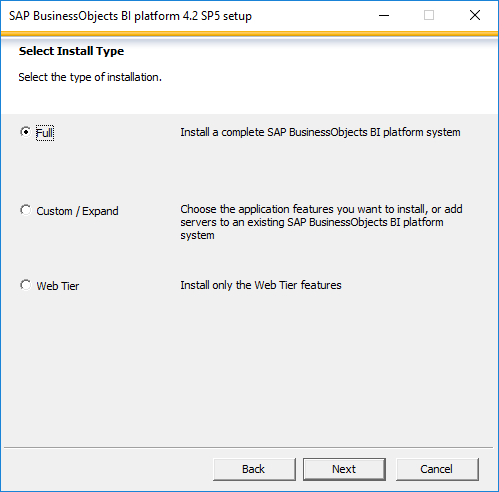
- Once you selected the Install type, setup will continue the remaining installation.
- You can also download the client tools from the above mentioned link and install in your machine and enjoy your new leanings.
- Please feel free to post your comments and I am happy to assist your queries.
Login:
- Click on start menu.
- Go to this path: start –> All Programs –> Business Objects XI Release 2 –> Business Objects Enterprise –> Designer.
- Enter system, user name, password and authentication: Enterprise (by default)
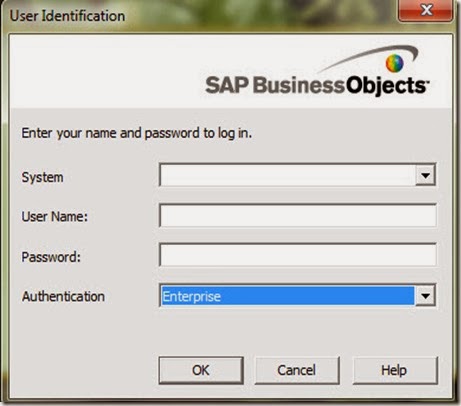
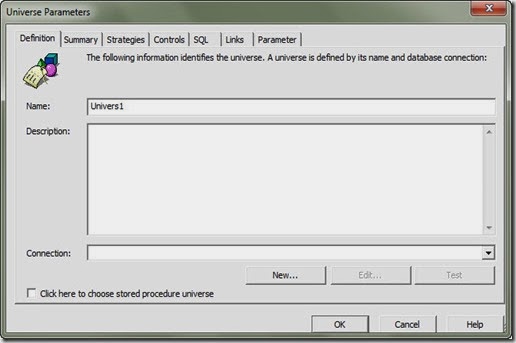
Create new universe wizard:
- When you login in to the first time the create wizard will start automatically and the welcome screen will displayed.
- Universe Name: Ejada
- Connection: create a new connection of use an already exists one.
- In the “create initial classes and objects” screen start by select tables form the left pan and add them by clicking the add button to the right pan. You even can select a specific column. Just expand the + beside table and select column or multiple by holding the CTRL button while you selecting.
- In the “Create measure objects” start selecting your measure column (column that contains numbers and you will not use it in aggregation, like profit, cost, balance etc.) and the function that you want to apply to that measure (count, sum, max, min etc.)
- In the congratulation screen click finish.
- Note: you can just cancel the wizard and do all this steps manually.
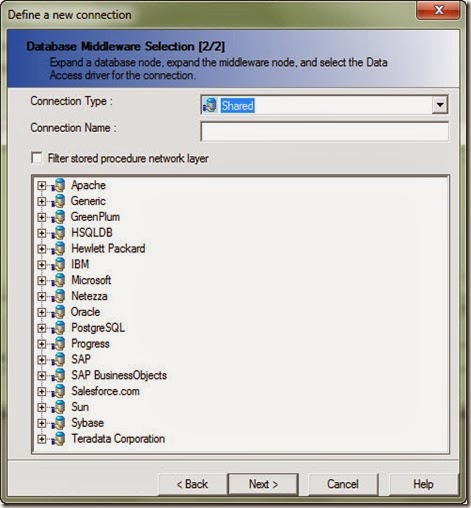
Note(s):
- There are 3 types of connection:
- Personal
- shared
- secured.
- There are many connection type. you can connect to different types of databases [Oracle – Teradata – DB2 – MYSQL..etc]
- There are many native connection types to other SAP products like SAP Strategy management & SAP ERP.
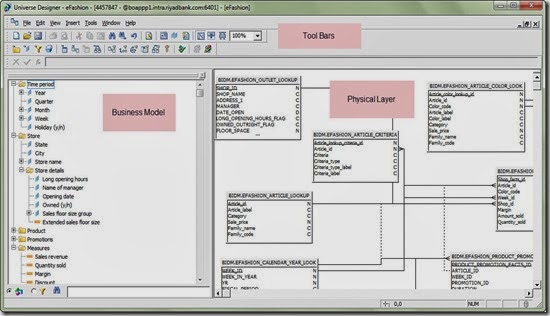
Tool interface description:
- After define the universe name and connection you should be ready to start working in your model. The universe designer interface can be categorized into 3 main panels.
- 1.Physical Panel:Here you will create your data foundation model by adding tables. Then create the required joins. create alias & derived tables as per your need. There are some advanced topics related to context & loops that we will talk in details about in another post.
- 2.Business Model: This is the right panel as shown in the figure below. This should be the end result that will be displayed to the end user. the end user should be able to drag the required objects from this panel and the query behind will be generated automatically so the end user should not worry anymore about technical staff. The objects names should be business wise and in business term and you need also to add description to make your business model more user friendly .
- 3.Tool bars area:This should contains icons to access many functionalities and features provided by SAP BO universe designer.
Physical Layer [Data Foundation]:
Insert new Table:
- After finishing the wizard you can add any tables that you want to use in this universe. Let’s say that we want to add some lookups tables (tables contains descriptions for some cods stored in the fact table)
- Right click anywhere in the designer windows in the area that contains the previously added table. [You can also do the same from the insert menu]
- Select insert Tables… from the drop down menu.
- Navigate to the required schema & a list with all tables names in your database will be displayed, just select a table and click on the insert button.
- Click refresh button if you don’t see the table that you want. This may happen if the tables added while you just open the insert table window
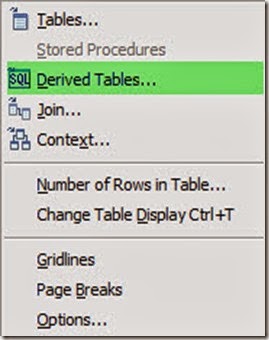
Joins:
- To insert a join you may just drag a column from the first table and drop it on the referenced column in the target table. A black line will join between the 2 columns. Double click on this black line and the join window will open:
- Table1: primary table with the key column.
- Table2: secondary table with the referenced column.
- Operation: operation that will be used in join (example: table1.user_id = table2.user_id)
- Cardinality: use the detect button to detect the join cardinality or set it manually. (1- many, many-1, many – many)
- If you need to specify an outer join just select the box under the table that you want to outer join.
- For complex joins use the expression text area below.
Notes:
- Take care from loops and resolve it before you finalize your physical layer development.
- Take care from the following traps and fix them before you move forward:
- Fan trap.
- Chasm trap.
- You need to start looking fro context after you complete your joins.
- Derived table:
- To create a derived table, right click in the designer window and select derived tables from the drop down menu.
- Derived table name:type the descriptive name for your derived table.
- Type the SQL select statement that will define you derived table
- Click on check syntax button and close.
- A new table with the specified columns in the select statement will be displayed in the table’s area in the designer window.
- Business Model:
- In business model you define your objects and group them in a meaningful folders (Classes). You may also create condition which will act like a pre-defined filters ready to be used by end user in their reports and on the fly analysis. There are 4 types of the objects that you can create in the business model:
- Dimensions:
- Measures
- Detail
- Condition.
- Class:
- class is a business grouping of some objects. Class act like a folder & To create a new class click on the insert class button from the tool bar or select insert–>class. Then type the class name and description.
- Dimension:
- Dimensions are the angle that you can look at the date from. Most likely it will be string or date type. like Region, Product, Customer sector …etc. to create a dimension Select the class that you want to create the dimension in:
- Name: dimension name
- Type: character, number, date, long text.
- Description: write description for this dimension.
- Select: select the column that associated with that dimension. May be also being complex and having some logic.
- Where: type the filter that you want to use while displaying this dimension.
- Measure:
- Measure is a number represent the value, amount, volume, rate or benchmark data. to create a measure you need to identify the following
- Name: name for the measure.
- Function: function that will be used when aggregating (sum, count, max, min)
- Select: data base column or any calculated numeric value.
- Condition:
- Condition is a pre-defined filter ready to be used by the end user by drag and drop in their Webi report to filter or restrict the data based on business rule.
- Name: condition name.
- Condition: expression that define the condition.
Benefits of using SAP Business Objects:
- Optimize and automate business processes
- Reduce costs and mitigate risks
- Full control of the company
- Improve cash flow and financial management
- Accuracy of information, more informed decisions
- Mobile access in real-time
- Tracking critical processes
- Reducing decision cycle
- Qualifications of staff involved in the preparation of reports do not require knowledge of IT.
Advantages
- Easy visualization of the accounting information
- Personalization
- Ease of scaling
- Automatic generation and sending the report by email to schedule a convenient
- Quick filtering, sorting data, DrillDown
- Using reports Web- interfaces
- Export to PDF, MS Word, MS Excel, HTML and other documents
- Integration with MS Office
FEATURES
- Complete solution: Explore, report, and share all in a single, integrated offering
- Powerful search and browse functionality: Supercharge searching and browsing to find the information you need
- Combined data: Bring together data from several sources to create a single report for a complete view
- Preconfigured, customizable templates: Create interactive visualizations, data sets, charts, and graphs
- Ad hoc reporting: Perform what-if analysis
- On-time reporting: Schedule and share data, reports, or dashboards online securely, inside or outside the organization
- Intuitive interface: Accelerate learning and ramp up quickly
- Free trial: Try it for free, then get the scalable, subscription-based solution
- Security: Use folder-level security to limit access and help ensure data security
- SaaS offering: Be up and running quickly without software or hardware installation
- Streamline operations: Leverage a hosted data warehouse and development environment
- Industry and business-specific offerings: Get solutions for industry and specific line-of-business uses through partners.
Where can I work with SAP Business Objects (SAP BO), what can I earn?
SAP BO is used in a variety of industries. The job offers for specialists in this area are accordingly large. The tasks are primarily in the reporting and decision making of the management. Entry-level salaries range from EUR 60,000 to EUR 80,000 annually, depending on the industry and company size.
Conclusion
SAP Business Objects is a powerful tool for data analysis and preparation. The various components of the BI suite enable data access on a variety of different platforms and the extensive and at the same time intuitive design of queries, analyzes and reports. In the area of business intelligence, SAP BO is the standard in many companies and offers a corresponding number of job offers.
