- Financial Performance – A Complete Tutorial
- How Six Sigma Principles Can Progress Your Productivity – Tutorial
- Google Analytics Pro Tutorial | Fast Track your Career
- Activity-Based Costing Tutorial | Know about Definition, Process, & Example
- Create a workbook in Excel Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Excel ROUNDUP Formula Tutorial | Learn with Functions & Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Tutorial | Learn In 1 Day
- SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- IBM SPSS Statistics Tutorial: Getting Started with SPSS
- SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [Updated]
- SAP FIORI Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Introduction to Business Analytics with R Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Tableau Desktop Tutorial | Step by Step resource guide to learn Tableau
- Implementing SAP BW on SAP HANA | A Complete Guide
- SAP HANA Administration | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau API Tutorial | Get Started with Tools, REST Basics
- SAP FICO ( Financial Accounting and Controlling ) Tutorial | Complete Guide
- Alteryx Tutorial | Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- Getting started with Amazon Athena Tutorial – Serverless Interactive | The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction to Looker Tutorial – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Sitecore Tutorials | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE |Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Adobe Analytics Tutorial – The Ultimate Student Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- Pentaho Tutorial – Best Resources To Learn in 1 Day | CHECK OUT
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Spotfire Tutorial for Beginners | Quickstart – MUST- READ
- JasperReports Tutorial: Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Charts and Tables – Qlikview Tutorial – Complete Guide
- TIBCO Business Works | Tutorial for Beginners – Learn From Home
- Cognos TM1 Tutorial : Learn Cognos from Experts
- Kibana
- Power BI Desktop Tutorial
- Tableau Tutorial
- SSAS Tutorial
- Creating Tableau Dashboards
- MDX Tutorial
- Tableau Cheat Sheet
- Analytics Tutorial
- Lean Maturity Matrix Tutorial
- MS Excel Tutorial
- Business Analysis Certification Levels & Their Requirements Tutorial
- Solution Assessment and Validation Tutorial
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Enterprise Analysis Tutorial
- Create Charts and Objects in Excel 2013 Tutorial
- Msbi Tutorial
- MicroStrategy Tutorial
- Advanced SAS Tutorial
- OBIEE Tutorial
- Tableau Server Tutorial
- OBIA Tutorial
- Business Analyst Tutorial
- Cognos Tutorial
- Qlik Sense Tutorial
- SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
- SAS Tutorial
- PowerApps Tutorial
- Financial Performance – A Complete Tutorial
- How Six Sigma Principles Can Progress Your Productivity – Tutorial
- Google Analytics Pro Tutorial | Fast Track your Career
- Activity-Based Costing Tutorial | Know about Definition, Process, & Example
- Create a workbook in Excel Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day
- Excel ROUNDUP Formula Tutorial | Learn with Functions & Examples
- Business Analytics with Excel Tutorial | Learn In 1 Day
- SAP Tutorial – Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- IBM SPSS Statistics Tutorial: Getting Started with SPSS
- SAP Security Tutorial | Basics & Definition for Beginners
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [Updated]
- SAP FIORI Tutorial | Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Introduction to Business Analytics with R Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- Tableau Desktop Tutorial | Step by Step resource guide to learn Tableau
- Implementing SAP BW on SAP HANA | A Complete Guide
- SAP HANA Administration | Free Guide Tutorial & REAL-TIME Examples
- Tableau API Tutorial | Get Started with Tools, REST Basics
- SAP FICO ( Financial Accounting and Controlling ) Tutorial | Complete Guide
- Alteryx Tutorial | Step by Step Guide for Beginners
- Getting started with Amazon Athena Tutorial – Serverless Interactive | The Ultimate Guide
- Introduction to Looker Tutorial – A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Sitecore Tutorials | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE |Ultimate Guide to Learn [UPDATED]
- Adobe Analytics Tutorial – The Ultimate Student Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Splunk For Beginners – Learn Everything About Splunk with Free Online Tutorial
- Pentaho Tutorial – Best Resources To Learn in 1 Day | CHECK OUT
- Statistical Package for the Social Sciences – SPSS Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- An Overview of SAP HANA Tutorial: Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Spotfire Tutorial for Beginners | Quickstart – MUST- READ
- JasperReports Tutorial: Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Charts and Tables – Qlikview Tutorial – Complete Guide
- TIBCO Business Works | Tutorial for Beginners – Learn From Home
- Cognos TM1 Tutorial : Learn Cognos from Experts
- Kibana
- Power BI Desktop Tutorial
- Tableau Tutorial
- SSAS Tutorial
- Creating Tableau Dashboards
- MDX Tutorial
- Tableau Cheat Sheet
- Analytics Tutorial
- Lean Maturity Matrix Tutorial
- MS Excel Tutorial
- Business Analysis Certification Levels & Their Requirements Tutorial
- Solution Assessment and Validation Tutorial
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Enterprise Analysis Tutorial
- Create Charts and Objects in Excel 2013 Tutorial
- Msbi Tutorial
- MicroStrategy Tutorial
- Advanced SAS Tutorial
- OBIEE Tutorial
- Tableau Server Tutorial
- OBIA Tutorial
- Business Analyst Tutorial
- Cognos Tutorial
- Qlik Sense Tutorial
- SAP-Bussiness Objects Tutorial
- SAS Tutorial
- PowerApps Tutorial

OBIEE Tutorial
Last updated on 29th Sep 2020, Blog, Business Analytics, Tutorials
Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition (OBIEE) is a Business Intelligence (BI) tool by Oracle Corporation. Its proven architecture and common infrastructure producing and delivering enterprise reports, scorecards, dashboards, ad-hoc analysis, and OLAP analysis provides a rich end-user experience. This tutorial explains all the fundamental aspects of OBIEE.
In today’s competitive market, most successful companies respond quickly to market changes and opportunities. The requirement to respond quickly is by effective and efficient use of data and information. “Data Warehouse” is a central repository of data that is organized by category to support the organization’s decision makers. Once data is stored in a data warehouse, it can be accessed for analysis.
The term “Data Warehouse” was first invented by Bill Inmon in 1990. According to him, “Data warehouse is a subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant and non-volatile collection of data in support of management’s decision making process.”
Ralph Kimball provided a definition of data warehouse based on its functionality. He said, “Data warehouse is a copy of transaction data specifically structured for query and analysis.”
Data Warehouse (DW or DWH) is a system used for analysis of data and reporting purposes. They are repositories that saves data from one or more heterogeneous data sources. They store both current and historical data and are used for creating analytical reports. DW can be used to create interactive dashboards for the senior management.
For example, analytic reports can contain data for quarterly comparisons or for annual comparison of sales report for a company.
Data in DW comes from multiple operational systems like sales, human resource, marketing, warehouse management, etc. It contains historical data from different transaction systems but it can also include data from other sources. DW is used to separate data processing and analysis workload from transaction workload and enables to consolidate the data from several data sources.
OBIEE Architecture
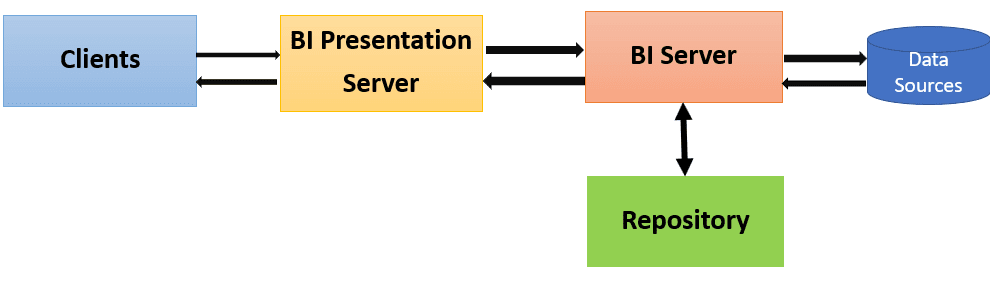
OBIEE Architecture Diagram
Oracle Bl Server is a central component in the suite. It is a query engine which converts the logical requests to a physical SQL statement to execute data sources. It also generates optimized queries, which depends on business rules that are defined in the Bl server repository.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Oracle Bl Architecture Components
Following architecture components and their relationships:
- Clients
- Oracle Bl Presentation Services
- Oracle Bl Server
- Oracle Bl repository
- Data sources
Clients:
It provides access to business intelligence information
Oracle Bl Answers:
It is a set of graphical tools used to build, view, and modify Oracle Bl requests
- Oracle Bl Interactive Dashboards
- Display the results of answers and requests and other items
- Oracle Bl Administration Tool: It is used to build an Oracle Bl repository:
BI Presentation Server
- BI presentation server offers processing to visualize the information for client consumption. It is implemented as an extension to a Web server.
- Uses a catalog to store saved content
- Receives data from Oracle Bl Server and provides it to the client that requested it
- Gives access to Business Intelligence information
- Oracle Bl Answers – a set of tools for creating, viewing, and modifying applications
- Oracle Bl Interactive Dashboards – visualizing the results of inquiries made with Bl Answers
- Oracle Bl Administration Tool: It provides the processing to visualize the information for client consumption.
- It is implemented as an extension to a Web server.
- Uses a catalog to store saved content
- Receives data from Oracle Bl Server and provides it to the client that requested it
Oracle BI server
- The Server for Oracle Business Intelligence
- It uses a meta database directly.
- Generate Dynamic SQL requests to the physical data sources
- Structure the results to Bl Presentation Server
Repository
- Stores Metadatabase used by Bl Server.
- It is Generated by the Oracle Bl Administration Tool
- Imports meta base from data sources
- Structure and organize metadata into your business models
- Structures the business model for presentation to users who want the information
Data Sources
Oracle Bl Server accesses the business data which users want to analyze which can be in any format, such as:
- Relational databases
- Online analytical processing (OLAP) databases
- Flat files
- Spreadsheets
- XML for Analysis (XMLA)
Features of OBIEE
- RPD Presentation layer allows for creating this object
- Fully implemented interface in WEB; Rich interactive boards
- Support for Level based hierarchy and ragged hierarchy
- OBIEE provides a feature of Enterprise Reporting
- Easy Microsoft Office Integration
- OBIEE allows a user to create their reports from the scratch
- Integration with MS Office and Multilingual support
- The tool offers a real time alert engine which is based on the business Events
OBIEE vs. Tableau
Here, are some significant differences between OBIEE and Tableau:
| Parameters | OBIEE | Tableau |
| Use for | OBIEE is a multifaceted network of tools which can create a more fluid and better-integrated data flow for your business. | Tableau BI allows people and organizations to become more data-driven as the trusted leader in analytics. |
| Stability | More Stable | Less Stable |
| Type of solution | Offers enterprise-wide solution | Point solution |
| Support for writeback feature | Writeback feature supported | Writeback feature not supported |
| Process of report | Auditing done on reports | Trail and testing done on reports |
Advantages of using OBIEE
- Real time data updating within third-party vendors such as Microsoft applications
- It helps you to create new deductions or altering existing ones without any IT assistance.
- Maps and spatial visualizations help you to monitor the analytics.
- This analytical tool helps users to view and analyze data.
- Offers metrics to measure the state of the data
- Shows present key indicators of changes in the market trends etc.
- You do not require deep level technical skills to run this BI tool.
- Offers robust Customizations
- Multilanguage reports can be created with data.
- Report creation from Scratch
- Integration with major data sources
Disadvantages of using OBIEE
- This solution is not ideal for data science perspective
- It is not a useful tool for data visualization.
- It lacks lots of functionality.
- When large numbers of queries are running parallelly, the report fails.
- It tends to crash when many people login simultaneously.
Best Practices of using Oracle Business Intelligence
- Use only logical links in the Business Model Mapping layer.
- Rename the logical columns.
- Remove unwanted objects to simplify the model
- Use short names to save space in the references.
- Use names corresponding to the organization, which is easily understandable for customers.
- Do not use the same name with the name of the logical table in the BMM.
- You should avoid using quotation marks (‘) in the names and double quotes (“).
- Make the names of the object unique.
What are the different layers of the OBIEE 11g Repository?
There are three layers in OBIEE
11g Repository Physical Layer : This layer is used for
1. Importing data
2. Creating Aliases
3. Building physical joins
4. Setting up the connection pool and its properties
5. Enabling/ Disabling cache for individual table
BMM(Business Model & Mapping) Layer : This layer is used for
1. Writing the business logic
2. Creating Logical columns and tables
3. Creating hierarchy
4. Creating LBM (level based measures)
5. Creating shares
6. Creating Time series functions
7. Creating Fragmentation on tables
8. Creating filters on repository
Presentation Layer : This layer is used for
1. Arranging the data for users view (Folder Structure)
2. Creating Presentation hierarchy
3. Creating Implicit Fact column
4. Implementing Column level security
Oracle Business Intelligence System Logical Architecture
The below diagram describes the standard logical architecture of Oracle business intelligence 11g system
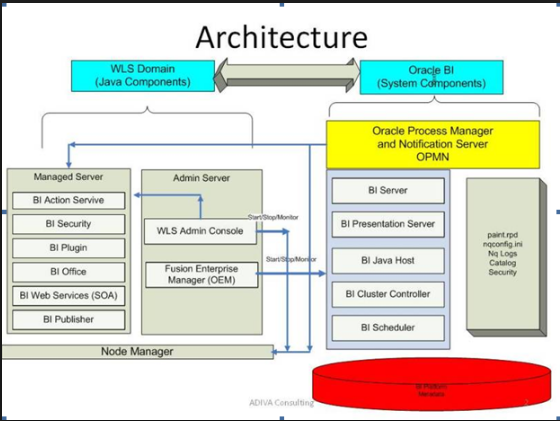
The entire system architecture is called BI Domain, this BI Domain divided into Java components and non-Java components. Java components are WebLogic server Domain components and non-java components are Oracle BI system components.
Weblogic Server Domain
This domain consists of a Managed server and Admin Server. These services comprise mainly with all the java modules to trigger the java services.
Admin Server: A JEE container that runs in a dedicated Java virtual machine that contains Java components for administering the system. It typically triggers the start, stops kind of admin activity for his peer Manager server processes.
Managed Server: A JEE container that runs in a dedicated Java virtual machine that provides the run-time environment for the Java-based services and applications within the system. The services comprise of BI plug-in, Security, publisher, SOA, BI Office services, etc
Node Manager: Node Manager is a separate java utility run to trigger the auto start, stop, restart activities and it provides process management services for the Admin Server and Managed Server.
Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server (OPMN): By using this OPMN services we can stop and start all system components of BI. It is monitored, managed, and controlled by Fusion Middleware Controller.
Oracle Weblogic Server (Console):
It is a Java EE application server that supports the deployment of Oracle Business Intelligence Java components. Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console access has been provided by Fusion Middleware Control. Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console enables to monitor and manage a WebLogic Server domain. Its capabilities include the following:
- Monitoring health and performance of JEE servers· Configuring WebLogic domains· Stopping and starting JEE servers· Viewing JEE server logs
Fusion Middleware Control:
Fusion Middleware Control is a browser-based tool and the recommended method for monitoring, managing, and configuring Oracle Business Intelligence components.
Starting, stopping, and restarting all system components (BI Server, BI Presentation Server) and Managed Servers
Configuring preferences and defaults : Starting, stopping, and restarting all system components (BI Server,BI Presentation Server) and Managed Servers – Managing performance and monitoring system metrics(DMS-Dynamic Monitoring System) – Performing diagnostics and logging (ODL-Oracle Diagnostic Logging)Fusion Middleware Control also provides access to Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, where you monitor and manage Oracle Business Intelligence Java components.
Java components:
Deployed as one or more Java EE applications:
1.Administrative Components — Enterprise Management applications and JMX MBeans for managing all configuration and run-time settings for Oracle Business Intelligence.
2.Oracle BI Publisher — This component provides an enterprise reporting solution for authoring, managing, and delivering all types of highly formatted documents to employees, customers, and suppliers.
3.Oracle BI Office — This component provides the integration between Oracle Business Intelligence and Microsoft Office products.
4.Oracle BI Action Services — This component provides the dedicated Web services that are required by the Action Framework and that enables an administrator to manually configure which Web service directories can be browsed by users when they create actions.
5.Oracle Real-Time Decisions (Oracle RTD) — This component provides enterprise analytics software solutions that enable companies to make better decisions in real-time at key, high-value points in operational business processes.
6.Oracle BI Security Services — This component provides dedicated Web services that enable the integration of the Oracle BI Server with the Oracle Fusion Middleware security platform i.e JPS (Java Platform Security) , CSF (Credential Store Framework), and users and groups managed by BI LDAP security.
7.Oracle BI SOA Services — This component provides dedicated Web services for objects in the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog, to invoke analyses, agents, and conditions. They make it easy to invoke Oracle Business Intelligence functionality from the Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) processes.
8.Oracle BI Plug-in — A JEE application that routes HTTP and SOAP requests to Oracle BI Presentation Services.
System components:
Deployed as non-JEE components, such as processes and services written in C++ and J2SE:
1.Oracle BI Server — This component provides the query and data access capabilities at the heart of Oracle Business Intelligence and provides services for accessing and managing the enterprise semantic model (stored in a file with a .RPD extension).
2.Oracle BI Presentation Services — This component provides the framework and interfaces for the presentation of business intelligence data to Web clients. It maintains an Oracle BI Presentation Catalog service on the file system for the customization of this presentation framework.
Oracle BI Scheduler — This component provides extensible scheduling for analyses to be delivered to users at specified times. (Oracle BI Publisher has its own scheduler)
3.Oracle BI JavaHost — This component provides component services that enable Oracle BI Presentation Services to support various components such as Java tasks for Oracle BI Scheduler, Oracle BI Publisher, and graph generation.
4.Oracle BI Cluster Controller — This component distributes requests to the BI Server, ensuring requests are evenly load-balanced across all BI Server process instances in the BI domain.
The Need for Data Warehouse
For example − You have a home loan agency, where data comes from multiple SAP/non-SAP applications such as marketing, sales, ERP, HRM, etc. This data is extracted, transformed and loaded into DW. If you have to do quarterly/annual sales comparison of a product, you cannot use an operational database as this will hang the transaction system. This is where the need for using DW arises.
Characteristics of a Data Warehouse
Some of the key characteristics of DW are −
- It is used for reporting and data analysis.
- It provides a central repository with data integrated from one or more sources.
- It stores current and historical data.
Data Warehouse vs. Transactional System
Following are few differences between Data Warehouse and Operational Database (Transaction System) −
- Transactional system is designed for known workloads and transactions like updating a user record, searching a record, etc. However, DW transactions are more complex and present a general form of data.
- Transactional system contains the current data of an organization whereas DW normally contains historical data.
- Transactional system supports parallel processing of multiple transactions. Concurrency control and recovery mechanisms are required to maintain consistency of the database.
- Operational database query allows to read and modify operations (delete and update), while an OLAP query needs only read-only access of stored data (select statement).
- DW involves data cleaning, data integration, and data consolidations.
DW has a three-layer architecture − Data Source Layer, Integration Layer, and Presentation Layer. The following diagram shows the common architecture of a Data Warehouse system.
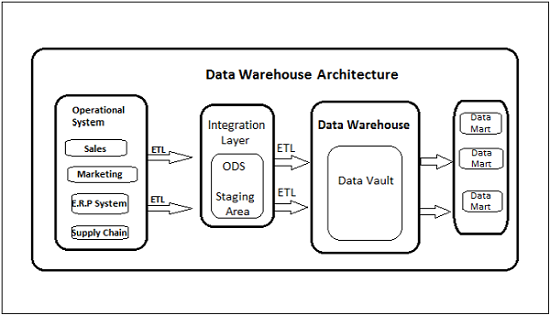
Types of Data Warehouse System
Following are the types of DW system −
- Data Mart
- Online Analytical Processing (OLAP)
- Online Transaction Processing (OLTP)
- Predictive Analysis
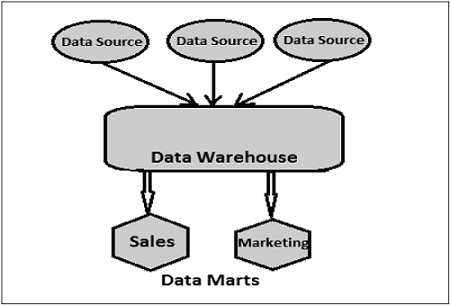
Data Mart
Data Mart is the simplest form of DW and it normally focuses on a single functional area, such as sales, finance or marketing. Hence, data mart usually gets data only from few data sources.
Sources could be an internal transaction system, a central data warehouse, or an external data source application. De-normalization is the norm for data modeling techniques in this system.
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP)
An OLAP system contains less number of transactions but involves complex calculations like use of Aggregations − Sum, Count, Average, etc.
What is Aggregation?
We save tables with aggregated data like yearly (1 row), quarterly (4 rows), monthly (12 rows) and now we want to compare data, like Yearly only 1 row will be processed. However, in an un-aggregated data, all the rows will be processed.
OLAP system normally stores data in multidimensional schemas like Star Schema, Galaxy schemas (with Fact and Dimensional tables are joined in logical manner).
In an OLAP system, response time to execute a query is an effectiveness measure. OLAP applications are widely used by Data Mining techniques to get data from OLAP systems. OLAP databases store aggregated historical data in multi-dimensional schemas. OLAP systems have data latency of a few hours as compared to Data Marts where latency is normally closer to few days.
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP)
An OLTP system is known for large number of short online transactions like insert, update, delete, etc. OLTP systems provide fast query processing and also responsible to provide data integrity in multi-access environment.
For an OLTP systems, effectiveness is measured by the number of transactions processed per second. OLTP systems normally contain only current data. The schema used to store transactional databases is the entity model. Normalization is used for data modeling techniques in OLTP system.
OLTP vs OLAP
The following illustration shows the key differences between an OLTP and OLAP system.
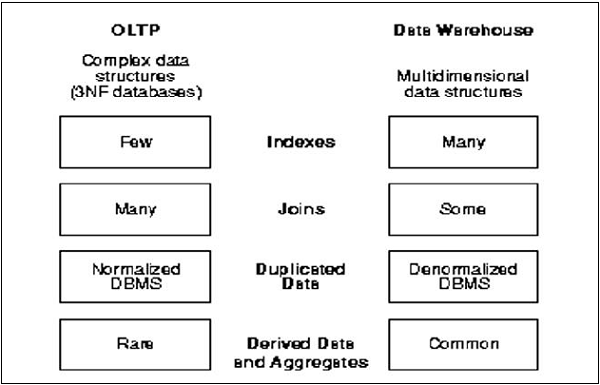
1.Indexes − In an OLTP system, there are only few indexes while in an OLAP system there are many indexes for performance optimization.
2.Joins − In an OLTP system, large number of joins and data is normalized; however, in an OLAP system there are less joins and de-normalized.
3.Aggregation − In an OLTP system, data is not aggregated while in an OLAP database more aggregations are used.
OBIEE Architecture involves various BI system components which are required to process the end user’s request.
How OBIEE System Actually Works?
The initial request from the end user is sent to the Presentation server. The Presentation server converts this request in logical SQL and forwards it to BI server component. BI server converts this into physical SQL and sends it to database to get the required result. This result is presented to the end user through the same way.
The following diagram shows detailed OBIEE Architecture −
OBIEE Architecture contains Java and non-Java components. Java components are Web Logic Server components and non-Java components are called Oracle BI system component.
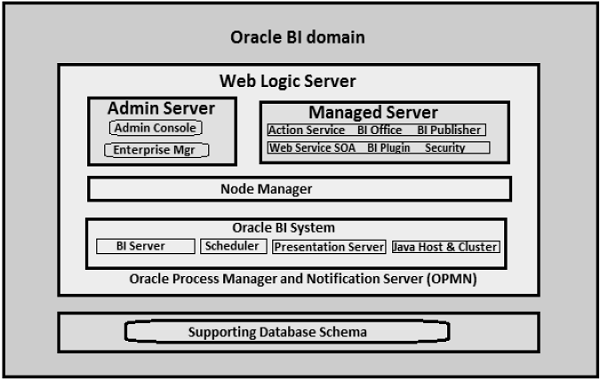
Web Logic Server
This part of OBIEE system contains Admin Server and Managed Server. Admin server is responsible for managing the start and stop processes for Managed server. Managed Server comprises of BI Plugin, Security, Publisher, SOA, BI Office, etc.
Node Manager
Node Manager triggers the auto start, stop, restart activities and provides process management activities for Admin and Managed server.
Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server (OPMN)
OPMN is used to start and stop all components of BI system. It is managed and controlled by Fusion Middleware Controller.
Oracle BI System Components
These are non-Java components in an OBIEE system.
1.Oracle BI Server
This is the heart of Oracle BI system and is responsible for providing data and query access capabilities.
2.BI Presentation Server
It is responsible to present data from BI server to web clients which is requested by the end users.
3.Scheduler
This component provides scheduling capability in BI system and it has its own scheduler to schedule jobs in OBIEE system.
4.Oracle BI Java Host
This is responsible for enabling BI Presentation server to support various Java tasks for BI Scheduler, Publisher and graphs.
5.BI Cluster Controller
This is used for load balancing purposes to ensure that the load is evenly assigned to all BI server processes.
Job Responsibilities Of A OBIEE Administrator
Install OBIEE 11g setup in the Unix Environment.Create/Modify Metadata repository suiting to data requirements by using OBIEE Administration tool.Migration from UAT Environment to Production Environment.Server and memory upgrade activities & Deploy patches in a server.Maintain the Platform Availability.Resolve Data Quality, Security issue and Report performance issue.Software installation in a server.Provide access to the end user and maintaining the entire applicationAssign Data Security, RPD level & UI level security to the Users.
1. Business Intelligence
Provides data and tools required by users to answer questions that are important for running a part of the business for which they are responsible:Determine if the business is on trackIdentify where things are going wrongTake and monitor corrective actionsSpot trends
Examples:
Show me the most effective promotionsShow me customers most likely to switchShow me products that are not profitableCompare sales this quarter with sales a year agoShow me sales for each district by month
2. Oracle BI Products
Oracle Business Intelligence is sold in two varieties:
- Oracle BI Enterprise Edition
- Oracle BI Applications
Oracle BI Enterprise Edition:
- Is a comprehensive suite of enterprise BI products that delivers a full range of analysis and reporting capabilities
- It has the following components:
- Oracle BI Server – Common enterprise business model and abstraction layer
- Oracle BI Answers – Ad-hoc query and reporting
- Oracle BI Interactive Dashboards – Highly interactive dashboards for accessing business intelligence and applications content
- Oracle BI Delivers – Proactive business activity monitoring and alerting
- Oracle BI Disconnected Analytics – Full analytical functionality for the mobile professionals
- Oracle BI Publisher – Enterprise reporting and distribution of “pixel-perfect” reports
- Oracle BI Briefing Books – Snapshots of dashboard pages to view and share in offline mode
Oracle BI Applications:
- Are complete, prebuilt BI solutions that deliver intuitive, role-based intelligence for everyone in an organization
- Oracle BI Applications are built on the Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition
Provides all that the standalone application does, plus:
1.Applications for common industry analytical processing such as Service Analytics, Sales Analytics, Marketing Analytics, and so on
2. Prebuilt role-based dashboards to support the needs of line managers to chief executive officers
3. A prebuilt database (Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse) designed for analytical processing with prebuilt routines to extract, load, and transform data from the transactional databases.
OBIEE Architecture
Is made up of five main components:
- Web Clients
- Oracle BI Presentation Server
- Oracle BI Server
- Oracle BI Scheduler
- Data Sources
Web Clients: Provide access to bi information
- Web browser
- Enterprise application
- Corporate portals
Oracle BI Presentation Server
Provides the processing to visualize the information for client consumption
1. Is implemented as an extension to a web server
2. Uses the presentation catalog to store aspects of the application
Receives data from the Oracle BI Server and provides it to the client that requested it
Oracle BI Presentation Catalog
- Stores the application dashboards request definitions and information about scheduling reports
- Contains information regarding permissions and accessibility of the dashboards by groups and users
- Is created when the Oracle BI Presentation Server starts
- Is administered using Oracle BI Catalog Manager
Oracle BI Delivers
Client application that:
1. Is used to create iBots
2. Deliver alerts to subscribed users
3. Is integrated with Dashboards and Answers
4. Job identifies what information to filter when it should run, and who to send alerts to
Oracle BI Presentation Services Administration
Is used to access administrative functions of Oracle BI presentation services and view information about the currently installed system
Oracle BI Server :
1. Provides efficient processing to intelligently access the physical data sources and structures the information
- Uses metadata to direct processing
- Generates dynamic SQL to query data in the data sources
- Connects natively or via ODBC to the RDBMS
- Structures results to satisfy requests
2. Provides the data to the Oracle BI Presentation Server
Several important components are used by the Oracle BI Server:
1. Repository file (.rpd)
2. Cache
3. NQSConfig.ini
4. DBFeatures.ini
5. Log files
1. Repository file (.rpd)
- Contains metadata that represents the analytical mode
- Is created using the Oracle BI Administration Tool
It Is divided into three layers:
- Physical layer – represents the data sources
- Business and Mapping layer – models the data sources into facts and dimensions
- Presentation layer – specifies the users view of the model; rendered in Oracle BI Answers
2.CACHE :
- Contains results of queries
- Is used to eliminate redundant queries to the database:
3. NQSConfig.INI :
- Is a configuration file used by the Oracle BI Server at startup
- Specifies values that control processing such as, Defining the repository (.rpd) to load and Enabling or disabling caching of results
4. DBFeatures.INI
- Is a configuration file used by the Oracle BI Server
- Specifies values that control SQL generation
5. Log Files
- NQServer.log records Oracle BI Server messages
- NQQuery.log records information about query requests
Oracle BI Scheduler:
- Manages and executes jobs requesting data analytics
- Schedules reports being delivered to users at specified times
- In windows, the scheduler runs as a service
Data Sources:
1. Contain the business data users want to analyze
2. Are accessed by the Oracle BI Server
3. Can be in any format, such as:
- Relational databases
- Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) databases
- Flat files
- Spreadsheets
Oracle Business Analytics Warehouse
It is a predefined data source to support the analytical requirements of Oracle Business Intelligence Applications. Relevant data structures support Oracle BI Applications
- Is in a star schema format
- Is included with Oracle BI Applications (not available with standalone OBIEE purchases)
Data Warehouse Administration Console
Data Warehouse Application Console (DAC) Client:
- Used to schedule, monitor, configure, and customize OBAW extraction, transformation, and load
- Accesses metadata about ETL mappings and dependencies in the DAC repository
DAC Server:
1.Organizes ETL requests for processing
2.Third-party Informatica Server : populates the OBAW from the transactional Database (PeopleSoft database) .Uses extract, transform, and load (ETL) routines
Sample Request Processing
1. User views a Dashboard or submits an Answers request
2. The Oracle BI Presentation Server makes a request to the Oracle BI Server to retrieve the requested data
3. The Oracle BI Server, using the repository file, optimizes functions to request the data from the data sources
4. The Oracle BI Server receives the data from the data sources and processes as necessary
5. The Oracle BI Server passes the data to the Oracle BI Presentation Server
6. The Oracle BI Presentation Server formats the data and sends it to the client
REAL-TIME Implementation :
Oracle BI components are often implemented across several computers on the network. Example:
Clustering Oracle BI Servers
Cluster Server Feature:
- Allows up to 16 Oracle BI Servers in a network domain to act as a single server
- Servers in cluster share requests from multiple Oracle BI clients, including Oracle BI Answers and Oracle BI Delivers
Cluster Controller is a primary component of the Cluster Server feature:
1. Monitors status of resources in a cluster and performs session assignment as resources change
2. Supports detection of server failures and failover for ODBC clients of failed servers
3. OBIEE Repository Basics
- Stores the metadata used by the OBIEE Server in a file format with.RPD as an extension
- Is accessed and exposed using the Administration Tool
- Is created by the server architect who:
- Imports – metadata from databases and other data sources
- Simplifies and reorganizes the metadata into business models
- Structures the business model for presentation to users for requesting information
- Exposes the Oracle BI repository in three separate panes, called layers
- Physical layer
- Business Model and Mapping layer
- Presentation layer

