- ITIL Tutorial – Incident & amp Problem Management | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- ITIL4 Service Value Chain Model Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- The ITIL 4 Service Value System | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- What are the ITIL 4 Management Practices? | Tutorial for Learning Path
- Guiding Principles of ITIL 4 | Learn Now Tutorial
- Four Dimensions of Service Management in ITIL 4 | A Definitive Guide
- What is the Continual Improvement Model? ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL4 Tutorial | A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI)Tutorial | Learn the Methods and Techniques
- Service Transition Overview – ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL® 4 Foundation Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Design an Effective IT Service with ITIL® v3 Tutorial
- Nagios Tutorial
- ITIL – Service management lifecycle Tutorial
- Service Validation and Testing Tutorial
- Service Operation Processes Tutorial
- ITIL Turtorial
- Services Strategy Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate SOA – Demand Management Tutorial
- Availability Management Tutorial
- ITIL Key Concepts of the Service Lifecycle Tutorial
- ITIL Change Evaluation Tutorial
- The principles of COBIT® 5 Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate CSI – Continual Service Improvement Processes Tutorial
- ITIL-Service Level Management Tutorial
- ServiceNow Tutorial
- SCCM Tutorial
- ITIL Tutorial – Incident & amp Problem Management | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- ITIL4 Service Value Chain Model Tutorial | Everything You Need to Know
- The ITIL 4 Service Value System | The BEST Step-By-Step Guide
- What are the ITIL 4 Management Practices? | Tutorial for Learning Path
- Guiding Principles of ITIL 4 | Learn Now Tutorial
- Four Dimensions of Service Management in ITIL 4 | A Definitive Guide
- What is the Continual Improvement Model? ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL4 Tutorial | A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI)Tutorial | Learn the Methods and Techniques
- Service Transition Overview – ITIL Tutorial
- ITIL® 4 Foundation Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Design an Effective IT Service with ITIL® v3 Tutorial
- Nagios Tutorial
- ITIL – Service management lifecycle Tutorial
- Service Validation and Testing Tutorial
- Service Operation Processes Tutorial
- ITIL Turtorial
- Services Strategy Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate SOA – Demand Management Tutorial
- Availability Management Tutorial
- ITIL Key Concepts of the Service Lifecycle Tutorial
- ITIL Change Evaluation Tutorial
- The principles of COBIT® 5 Tutorial
- ITIL Intermediate CSI – Continual Service Improvement Processes Tutorial
- ITIL-Service Level Management Tutorial
- ServiceNow Tutorial
- SCCM Tutorial

SCCM Tutorial
Last updated on 19th Sep 2020, Blog, IT service and Architecture, Tutorials
Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) is a Windows product that enables administrators to manage the deployment and security of devices and applications across an enterprise. Administrators also commonly use SCCM for endpoint protection. SCCM is part of the Microsoft System Center systems management suite.
The SCCM integrated console enables management of Microsoft Application Virtualization (App-V), Microsoft Enterprise Desktop Virtualization (Med-V), Citrix XenApp, Microsoft Forefront and Windows Phone applications from a single location.
System Center Configuration Manager relies on a single infrastructure, unifying physical and virtual clients under one umbrella. SCCM also adds tools to help IT administrators with access control. SCCM discovers servers, desktops and mobile devices connected to a network through Active Directory and installs client software on each node. It then manages application deployments and updates on a device or group basis, allowing for automated patching with Windows Server Update Services and policy enforcement with Network Access Protection. System Center Endpoint Protection Manager is built into System Center Configuration Manager to secure data stored on those devices.
What is the use of SCCM?
- 1.One Client:
The ConfigMgr client controlling all installations on a computer, both software updates and application installations. No more “Another installation is already running errors”. When ConfigMgr installs a software update to a c client Software distribution is paused to avoid these situations. When using a standalone WSUS the ConfigMgr client and WSUS client often tries to install software updates at the same time, which results in an error which is a hazard both for the end user and to the IT department. This is the one thing that many don’t think about but I think is one of the most important once. - 2.Reporting:
There are many built-in reports for Software Update Compliance, troubleshooting and details. The reports combined with all the other information ConfigMgr holds about your clients in your environment you can easily create really powerful and customized reports that you need in your environment. - 3.Unified Management / One console to rule them all:
When using Configuration Manager 2012 for Software Updates as well as all other features in Configuration Manager 2012 like Application Management, OSD, Settings Management, inventory and now also Endpoint Protection you will have a single management console for your environment. - 4.Maintenance Windows:
Maintenance Windows can be used to control when changes are allowed to be made to a specific system. This means that you deploy the update once and then based on Maintenance Windows the updates are installed and the servers are rebooted according to the deployment. More information about - 5.Scheduling:
In Configuration Manager 2012 we have much more available options when it comes to scheduling an update and in combination with Maintenance Windows, it is truly powerful. - 6.One Infrastructure:
The actual software update files are downloaded from the local DP and not the WSUS/SUP server. This means that you will not need a separate WSUS infrastructure and the updates are downloaded from the DP which minimizes the WAN impact for remote sites. - 7.Automatic deployment rules:
This isn’t really a benefit compared to WSUS, but as it is a new feature of Configuration Manager 2012 I will still add it to the list. It is possible to automatically approve updates, download them and distribute them to the DP’s automatically, just as you would in WSUS. - 8.System Center Updates Publisher:
You can use System Center Updates Publisher to both download vendors catalog’s with updates like Adobe, HP and Dell and to publish your own updates into the WSUS DB and deploy them as updates in Configuration Manager 2012. - 9.OS deployment integration:
A built-in task is available and can be used to deploy software updates from Configuration Manager during the OS deployment in the Task Sequence. - 10.End-user experience:
Software center is used for all end-user interaction, dialogs shown to the user all have the same look, making it easier for the end user to understand what is happening. - 11.Targeting:
Using query based collections we get really powerful options for targeting. We can dynamically create a collection based on any value that exists in the database, for instance, divide all clients based on the last number in the computer name, and deploy software updates to computers with odd computers on one day and all with even numbers the day after. Spreading the load and the risk automatically. - 12.Offline Servicing of Images:
If you use ConfigMgr 2012 for managing your Software Updates you can use the built-in feature to do offline servicing on you OS Images, which means that you can install OS related Software Updates in the image without rebuilding the image. This will reduce the number of times you have to rebuild the image.
Core features of Microsoft SCCM
Some core features in Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager include:
- Windows management- To keep pace with updates to Windows 10.
- Endpoint protection- To provide identification and malware protection.
- Reporting- To present information on users, hardware, software, applications and software updates.
- Operating system (OS) deployment- To distribute operating systems to devices in an enterprise.
- Software update management- Which allows users administrators to deliver and manage updates to devices across an enterprise.
- Application delivery- Which allows administrators to deliver an application to all devices across an enterprise.
- Health monitoring- Which shows client health and activities in the console, and can alert users if health statistics decrease past a specified level.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Several key features of System Center Configuration Manager help administrators address the bring-your-own-device (BYOD) trend in the enterprise, including user-centric management. End users can search for applications with a self-service software center and specify times when installations and upgrades take place. IT administrators can install applications in different ways on different devices. For example, as a native application on a primary device or as a Remote Desktop Services app or App-V program on a tablet. SCCM also includes role-based access control (RBAC), which enhances system security by only showing end users the interface elements that apply to their specific roles as defined by Active Directory.
SCCM Vs. SCOM
Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager is similar to, and can be confused with, Microsoft System Center Operations Manager (SCOM). SCOM allows system and application administrators to deploy, configure, manage and monitor the operations, services and applications of many devices within an enterprise through a management console.
SCCM and SCOM are both Microsoft enterprise applications. SCOM, however, focuses on enterprise monitoring on the server-side. SCCM, instead, is not considered a monitoring application and focuses on the client side.
Business Solutions addressed by SCCM
System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) helps an organization maintain consistency in the system configuration and management across all the systems. Rather than having to build a workstation or a server manually and individually, SCCM makes use of the templates to build these systems pretty quick. IT personnel can create these templates based on the guidelines outlaid and also to meet the requirements of the organization. In the case of template-based installation, organizations can very well depend on the consistency in the build configuration for all the hardware systems throughout the enterprise.
SCCM in conjunction with other components ensures achieving different functionalities. One of the best examples of such a component is System Center Operations Manager (SCOM). System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) along with System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) helps an organization stay ahead and proactive to identify issues, faults on time and helps take necessary actions to minimize the downtime on any issues. These tools also help recover systems that have failed for various other reasons with the help of a tool called Data Protection Manager (DPM). It also enables monitoring of the normal operations of the available set of servers, workstations, and applications.
There are policies that are established to update systems of a specific functional role be updated or patched at the same time. This is a feature that is provided by one of the SCCM components called the Desired Configuration Management (DCM). It ensures specific updates are pushed to systems that meet a functional role. This further helps in ensuring all the audit requirements, and also in maintaining compliance at an organization level. This helps in answering all the questions related to audits and compliance requirements with just reports and nothing at all.
NEW SCCM INSTALLATION
We are finally ready to launch the setup. First, reboot the server. This will make sure that the machine is not in a Reboot pending state.
- Mount and open the SCCM ISO that was previously downloaded from the Microsoft Volume Licensing Site
- Run Splash.hta
- Select Install
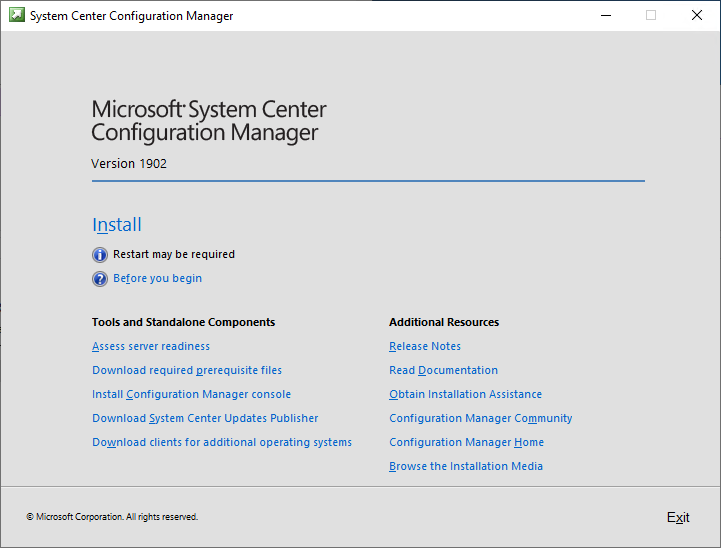
- On the first screen, Click Next
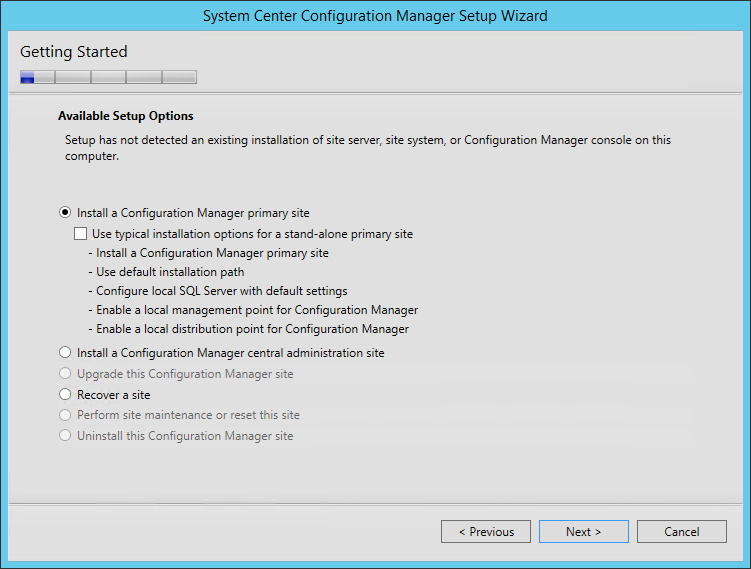
- On the Getting Started screen, Select Install a Configuration Manager Primary Site and click Next
- On the Product Key screen, enter it and click Next
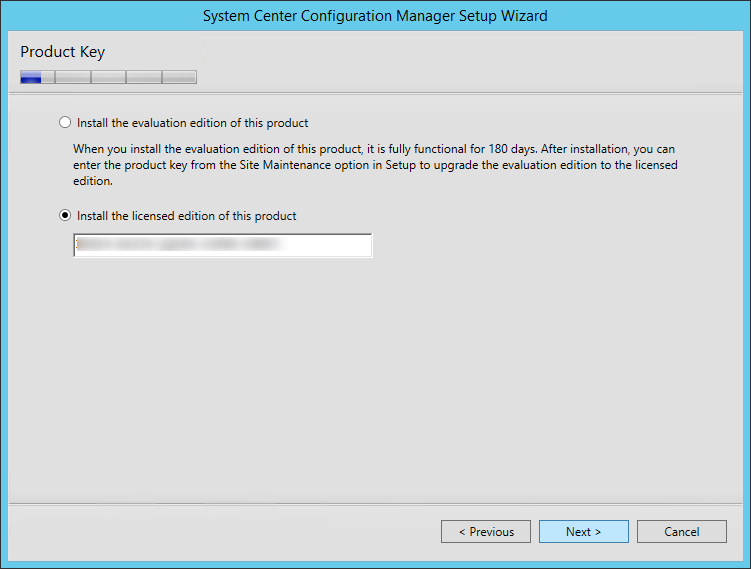
- On the Microsoft Software License Terms screen, accept the terms and click Next
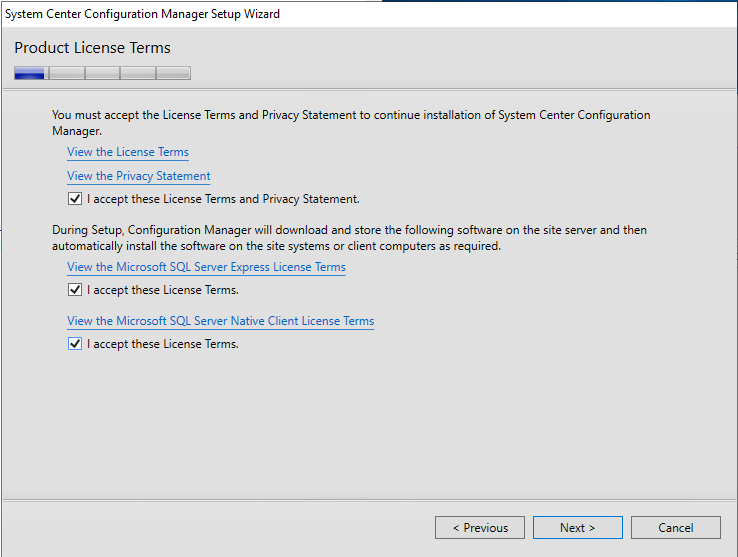
- On the Product License Terms screen, accept the License Terms and click Next
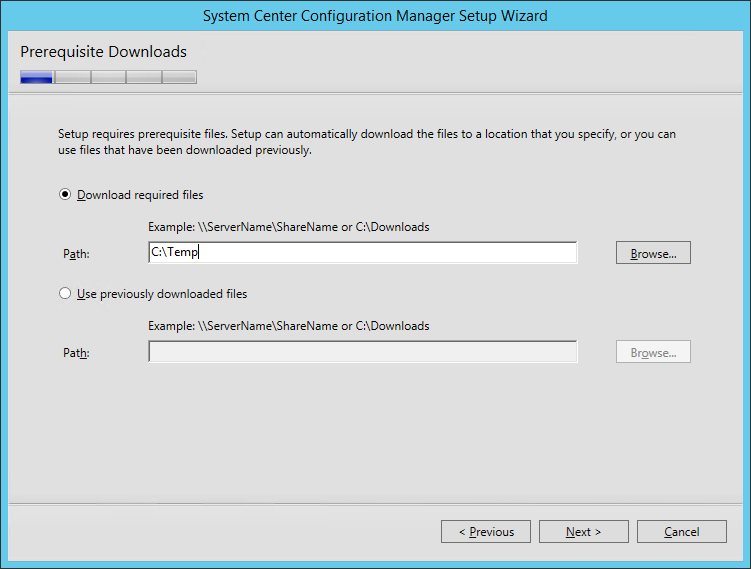
- On the Prerequisite Downloads screen, specify a location to download the prerequisite file. This folder can be deleted after setup
- On the Server Language Selection screen, select the language you want to display in the SCCM Console and Reports. You can modify language later by running setup again and select the Site Maintenance option
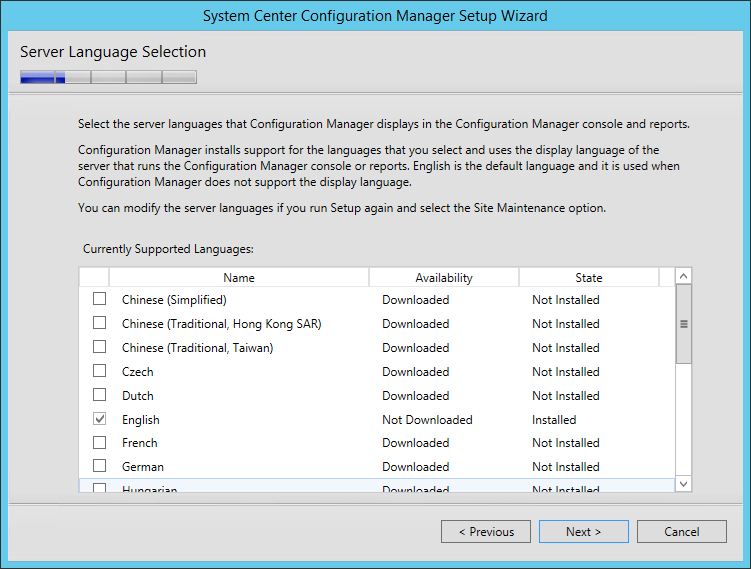
- On the Client Language Selection screen, select the Client language to support. You can modify languages later by running setup again and select the Site Maintenance option
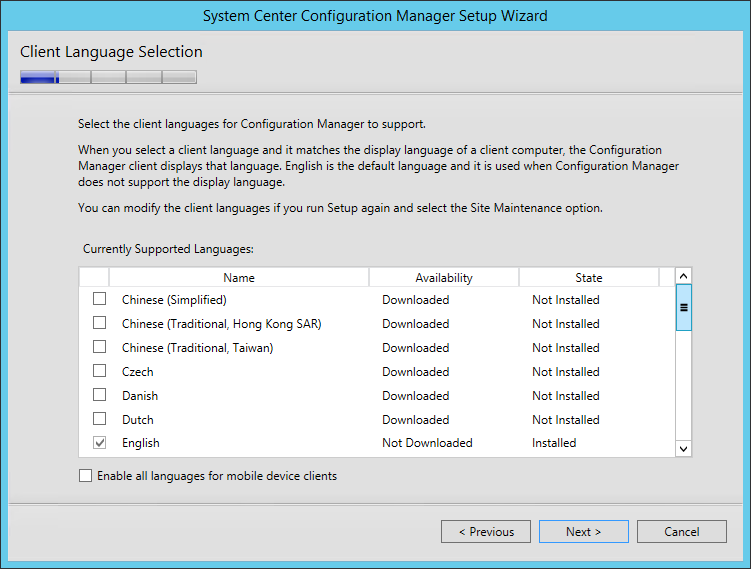
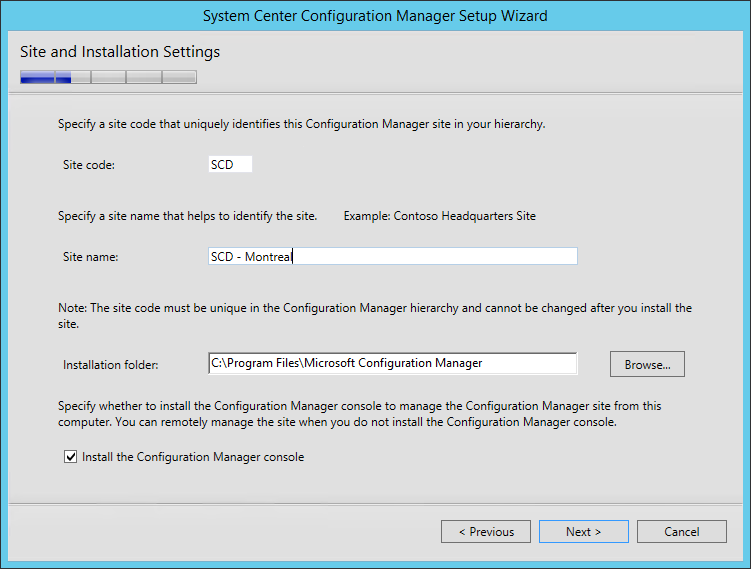
- On the Site and Installation Settings screen, enter your Site Code. Use the same Site Code as you specified when creating your Database
- Note : Site codes cannot be used more than one time in a Configuration Manager hierarchy for a central administration site or primary sites. If you reuse a site code, you run the risk of having object ID conflicts in your Configuration Manager hierarchy. This applies also if you’re doing a migration from an earlier version.
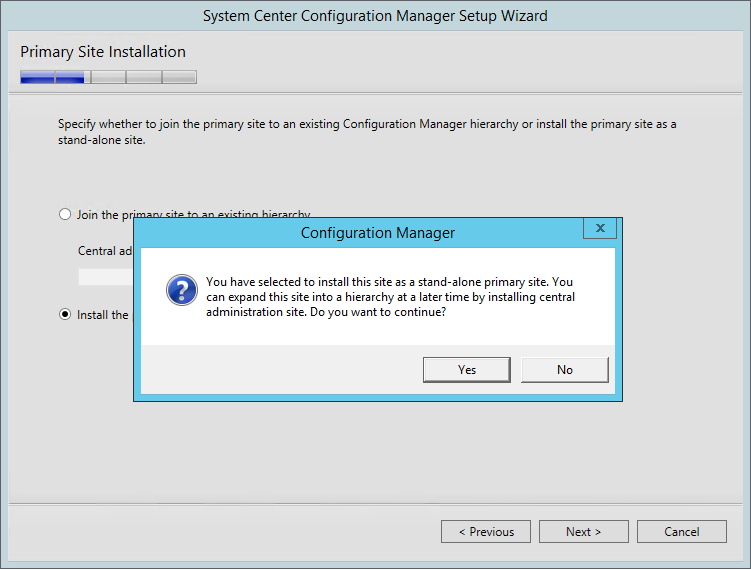
- On the Primary Site Installation screen, select Install the primary site as a stand-alone site. If you have a Central Administration site, this is where you would join the Primary Site to the existing hierarchy
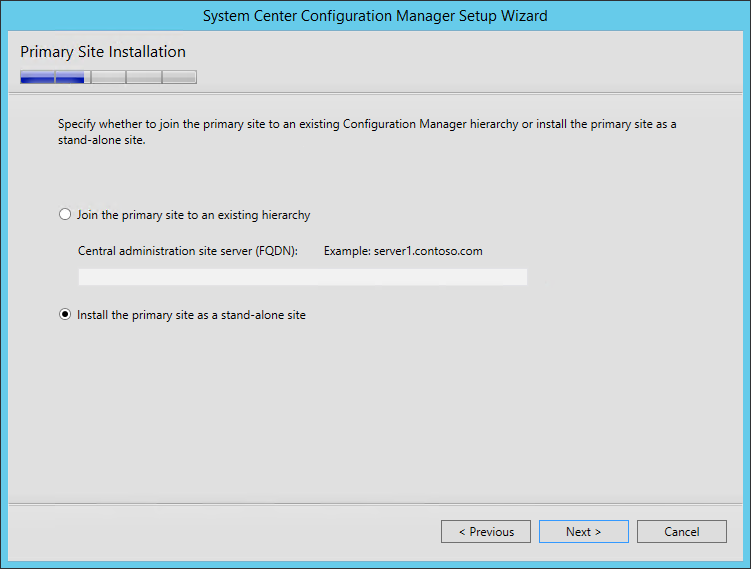
- On the warning, click Yes
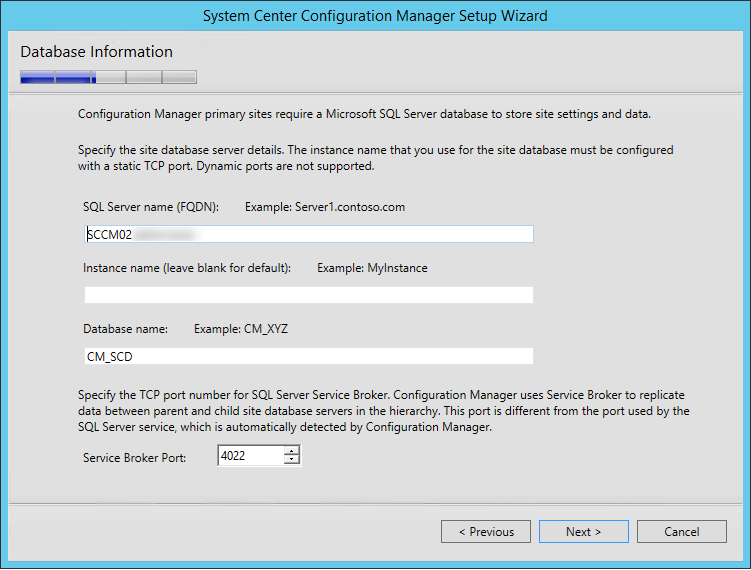
- li>On the Database Information screen
- Enter your SQL Server Name. In our case the SQL server is the same box as SCCM
- Leave the Instance Blank
- Enter your Database name. Once again, this must match the previously created Database in part 2
- Leave the Service Broker Port to 4022
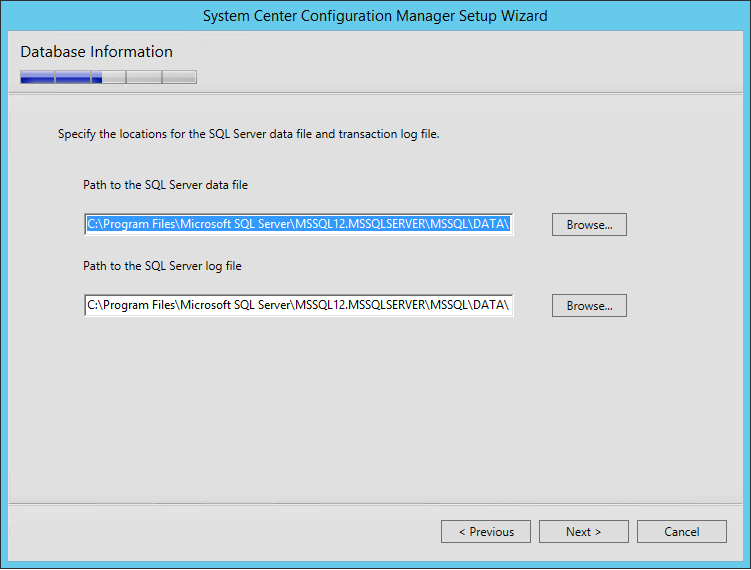
- On the Database Information screen :
- Enter the path to the SQL Server data file. Locate this on the SQL Volume
- Enter the path to the SQL Server log file. Locate this on the SQL Logs Volume.
- I like to use the same directory where I created my database and logs (E:\SCCMDB, G:\SCCMLogs)
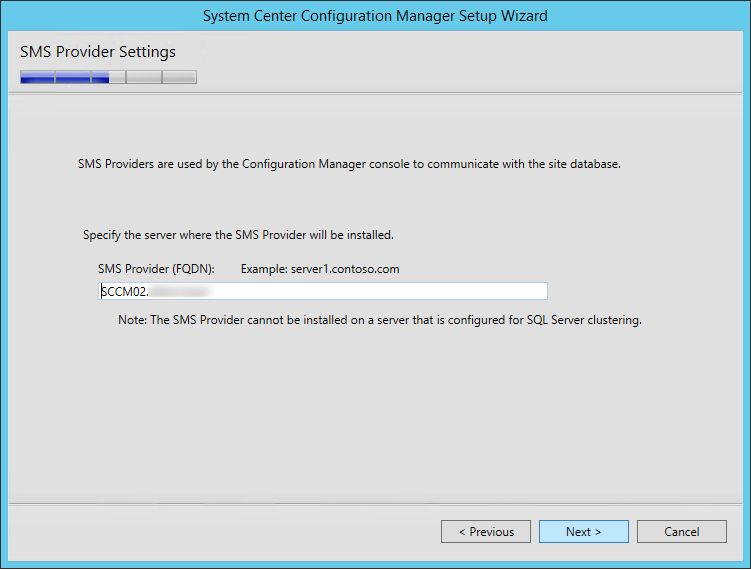
- On the SMS Provider Settings screen, leave the SMS Provider to the default value which is the local server. Refer to the following Technet article to read about the SMS Provider.
- On the Client Computer Communication Settings screen, select Configure the communication method on each site system role. This is where you select to have HTTPS or not on your initial Management Point and Distribution Point. This setting can be changed later
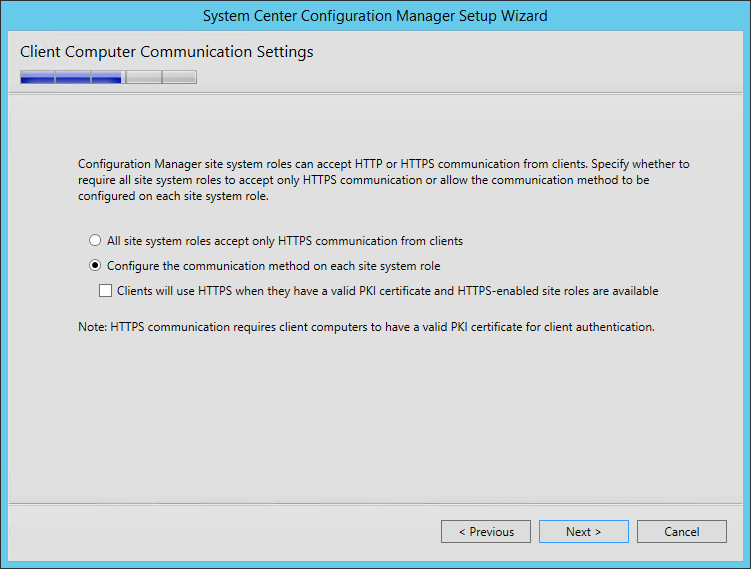
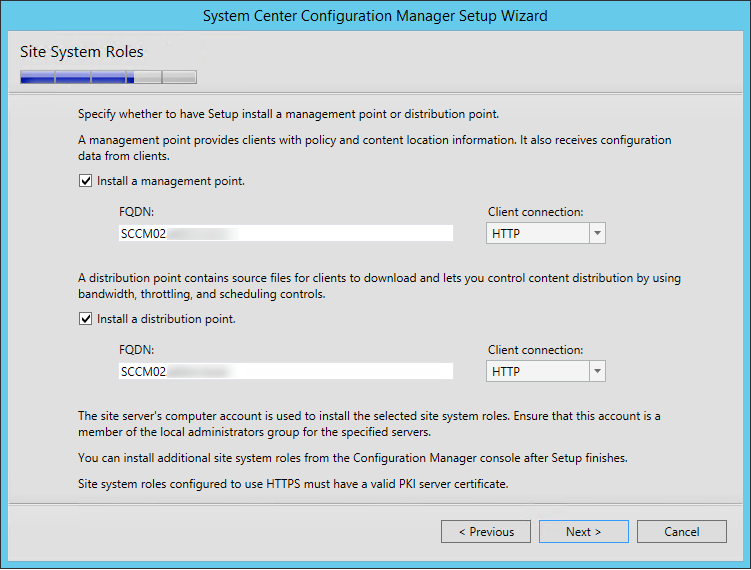
- On the Site System Roles screen :
- Check Install a Management Point
- Check Install a Distribution Point
- We will install both MP and DP on the same box so leave the FQDN as is
- The Client connection drop-down is unavailable due to our previous selection
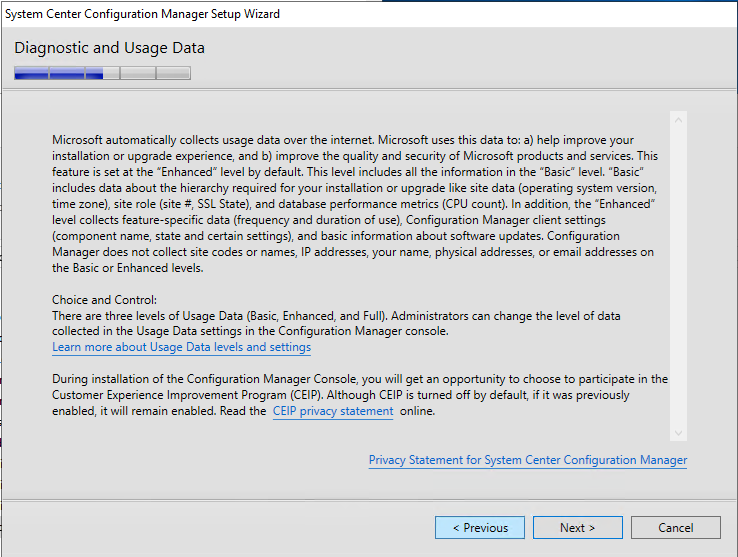
- On the Usage Data screen, click Next. This new screen basically tells that you accept that you will send some telemetry data to Microsoft
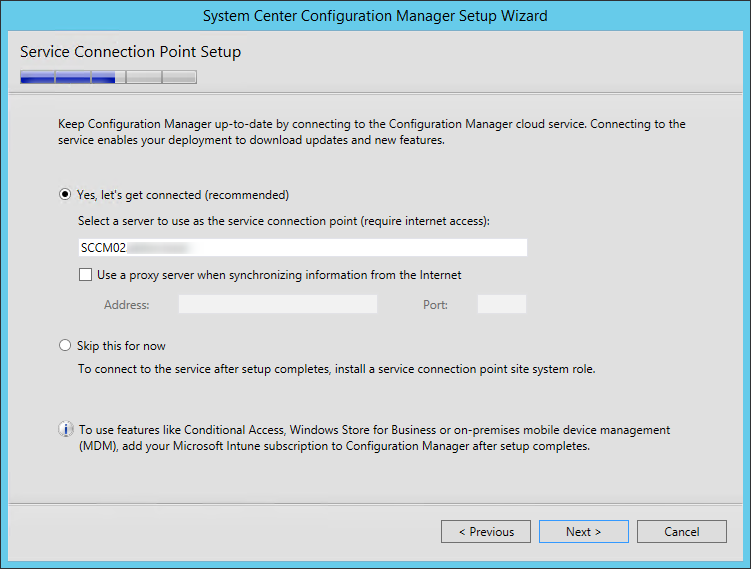
- On the Service Connection Point screen, click Next. This new role enables your deployment to download updates and new features
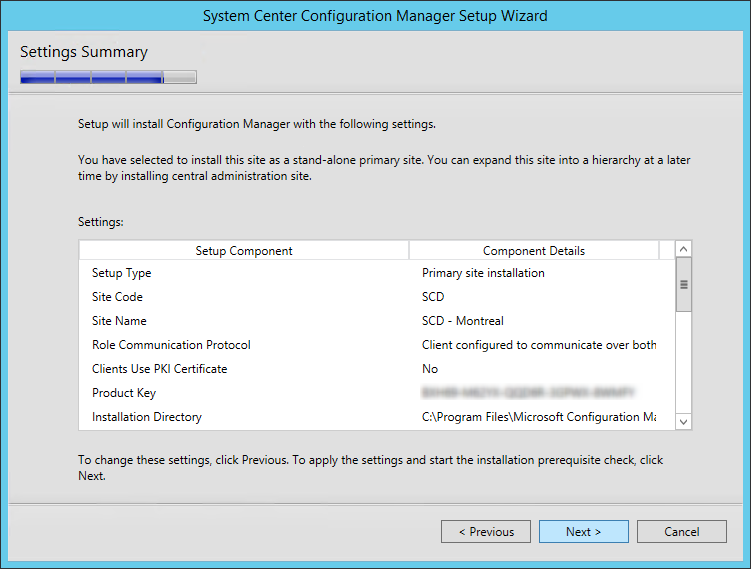
- On the Settings Summary Screen, review your options and click Next
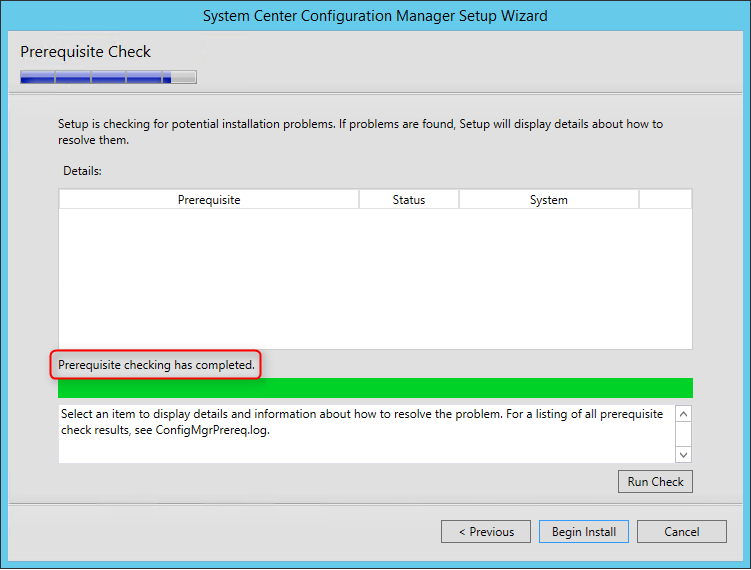
- On the Prerequisite Check screen, you should have no error since you’ve run it before setup, click Next
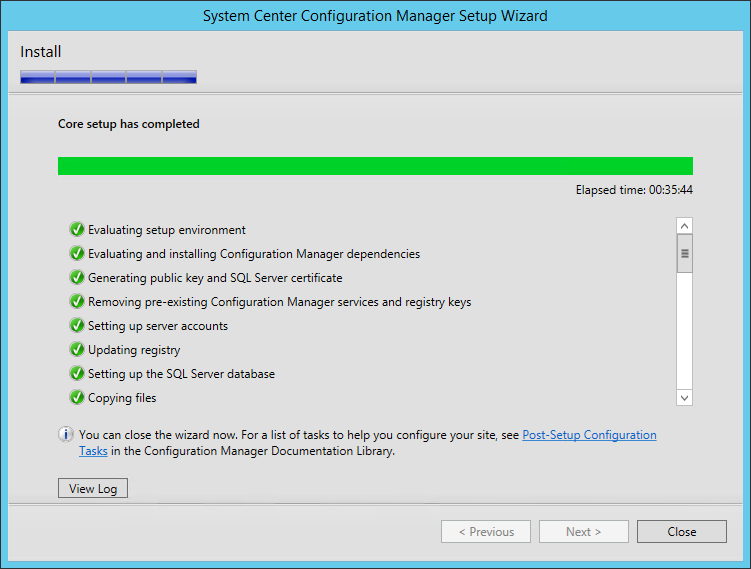
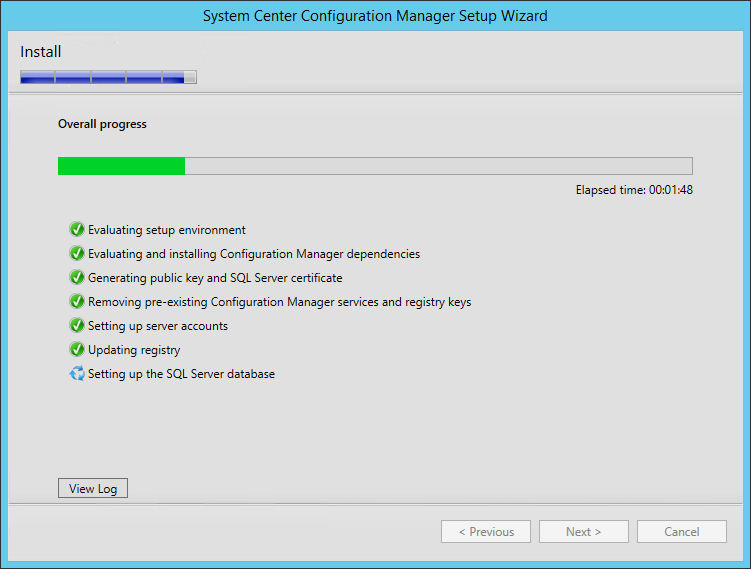
- The installation is in progress. You can count between 15 and 30 minutes depending of your server specifications
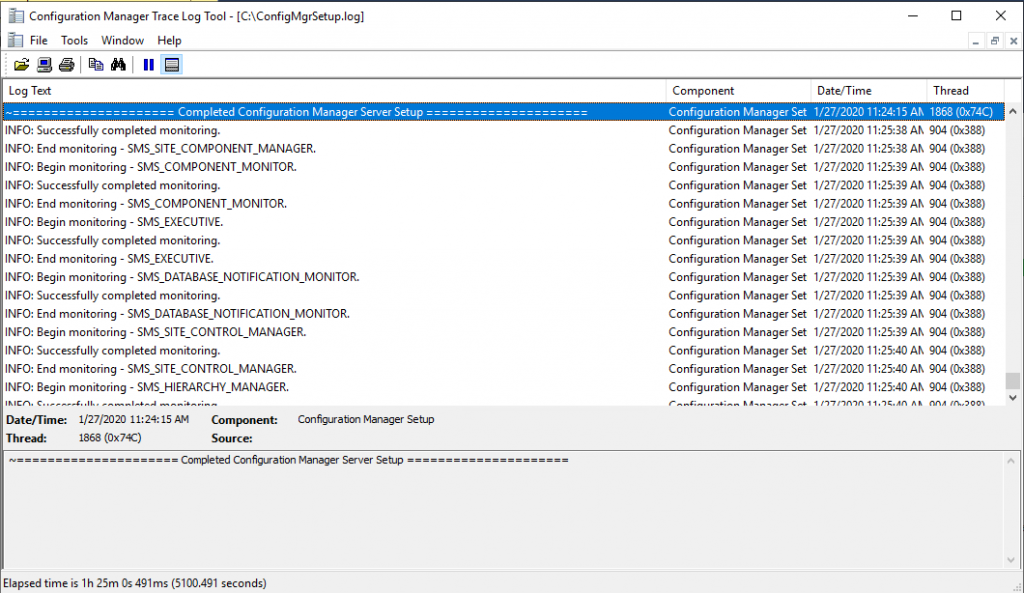
- You can follow the progress by clicking the View Log button or open the ConfigMgrSetup.log file on the C: drive
- aiWt for Core setup has completed and close the wizard
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have tried to understand the business problem that Software Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) tries to resolve. We have understood the systems management in an enterprise and how SCCM resolves this problem with the features that it provides. We have then discussed the System Center suite of products and its features, along with it, we have also taken a closer look at the major features provided by SCCM. We have also seen the business use cases where SCCM finds its usage. We have also discussed the new features that are provided in the latest releases of SCCM. Hope you have found all the details that you were looking for, in this tutorial.