- Understanding Agile Methodologies and Principles | A Complete Tutorial
- What is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)? | Learn Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Traditional Project Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Complete Guide [STEP-IN]
- Total Productive Maintenance Tutorial | Get an Overview
- Virtual Team Tutorial – Learn Origin, Definition and its Scope
- The Rule of Seven in Project Management – Tutorial
- Make or Buy Decision – A Derivative Tutorial for Beginners
- What is Halo Effect? | Learn More through Tutorial
- Balanced Score Card Tutorial | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Supply Chain Management? | Tutorial with Examples
- Succession Planning Tutorial | A Complete Guide with Definitions
- What is Structured Brainstorming? | Quickstart & Learn the Tutorial
- Stress Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- What is a Statement of Work? | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Stakeholder Management? – The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- How to Create a Staffing Management Plan? | Learn from Tutorial
- What is Resource Leveling? | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Requirements Collection Tutorial: Gather Project Needs
- What Is a RACI Chart? | Learn with Example & Definitions
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control: Tutorial with Definitions & Differences
- Project Workforce Management Tutorial | A Definitive Guide
- Project Time Management Tutorial: Strategies, Tips & Tools
- Project Management Success Criteria Tutorial | Understand and Know More
- Identify Risk Categories in Project Management | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Project Records Management Tutorial | Quickstart -MUST READ
- Project Quality Plan (PQP) Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Project Portfolio Management | A Defined Tutorial for Beginners
- Goals of a Project Manager Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Project Management Triangle Tutorial: What It Is and How to Use
- Project Management Tools Tutorial | Learn Tools & Techniques
- What is PMO (project management office)? | A Complete Tutorial from Scratch
- Project Management Lessons | Learn in 1 Day [ STEP-IN ]
- What is a Project Kickoff Meeting? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Project Cost Management Tutorial | Steps, Basics, and Benefits
- Types of Contracts in Project Management | Learn with Examples
- Project Activity Diagram | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- What is Project Procurement Management? | Tutorial Explained
- Procurement Documents Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Process-Based Project Management Tutorial: A Beginner’s Guide
- What Is PRINCE2 Project Management? | A Definitive Tutorial for Beginners
- Effective Presentation Skills – Learn More through Tutorial
- Powerful Leadership Skills Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- PERT Estimation Technique Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Pareto Chart Tool Tutorial | Learn Analysis, Diagram
- Organizational Structure Tutorial: Definition and Types
- Negotiation Skills for Project Management | Learn from the Basics
- Monte Carlo Analysis in Project Management Tutorial | A Perfect Guide to Refer
- Effective Management Styles Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Management by Objectives (MBO) Tutorial | Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Leads, Lags & Float – Understand the Difference through Tutorial
- What is Knowledge Management? – Tutorial Explained
- What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT)? | Know More through Tutorial
- Gantt Chart Tool Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Extreme Project Management Tutorial – Methodology & Examples
- Introduction for Event Chain Methodology Tutorial | Guide For Beginners
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | A Complete Tutorial for Beginners
- What Is Design of Experiments (DOE)? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Decision Making Tutorial – Know about Meaning, Nature, Characteristics
- Critical Path Method Tutorial | How to use CPM for project management
- What is Critical Chain Project Management? | A Complete Tutorial
- What is Conflict Management? | Learn the Definition, styles, strategies through Tutorial
- Effective Communication Skills Tutorial – Definitions and Examples
- Communication Models Tutorial – Project Management
- Methods of Communication Tutorial | A Complete Learning Path
- Communication Management Tutorial | Know more about Plans & Process
- What are Communication Channels? | Learn Now Tutorial
- Communication Blocker Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Cause and Effect Diagrams Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- What is Benchmarking? | Technical & Competitive Tutorial
- Seven Processes of Prince2 Tutorial | Everything you Need to Know
- Design Thinking Tutorial – Quick Guide For Beginners
- What is Performance Testing | A Complete Testing Guide With Real-Time Examples Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Agile Scrum Tutorial
- PMI-RMP Plan Risk Management Tutorial
- Designing the Blueprint Delivery Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Program Benefits Management Tutorial
- Continuous Improvement – Agile Value Stream Mapping
- Program Organization Tutorial
- Risk and Issue Management Tutorial
- Project Integration Management Tutorial
- Planning and Control Tutorial
- Program Management Principles Tutorial
- program strategy Alignment Tutorial
- PMP Tutorial
- Program Governance Tutorial
- Program Life Cycle Management Tutorial
- PMP Exam Preparation Tutorial
- PMI-PgMP Tutorial
- Agile Methodologies and Frameworks- Kanban and Lean Management Tutorial
- JIRA Tutorial
- Primavera P6 Tutorial
- Understanding Agile Methodologies and Principles | A Complete Tutorial
- What is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)? | Learn Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Traditional Project Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Complete Guide [STEP-IN]
- Total Productive Maintenance Tutorial | Get an Overview
- Virtual Team Tutorial – Learn Origin, Definition and its Scope
- The Rule of Seven in Project Management – Tutorial
- Make or Buy Decision – A Derivative Tutorial for Beginners
- What is Halo Effect? | Learn More through Tutorial
- Balanced Score Card Tutorial | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Supply Chain Management? | Tutorial with Examples
- Succession Planning Tutorial | A Complete Guide with Definitions
- What is Structured Brainstorming? | Quickstart & Learn the Tutorial
- Stress Management Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- What is a Statement of Work? | Learn with Definition & Examples
- What is Stakeholder Management? – The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- How to Create a Staffing Management Plan? | Learn from Tutorial
- What is Resource Leveling? | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Requirements Collection Tutorial: Gather Project Needs
- What Is a RACI Chart? | Learn with Example & Definitions
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control: Tutorial with Definitions & Differences
- Project Workforce Management Tutorial | A Definitive Guide
- Project Time Management Tutorial: Strategies, Tips & Tools
- Project Management Success Criteria Tutorial | Understand and Know More
- Identify Risk Categories in Project Management | A Comprehensive Tutorial
- Project Records Management Tutorial | Quickstart -MUST READ
- Project Quality Plan (PQP) Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- Project Portfolio Management | A Defined Tutorial for Beginners
- Goals of a Project Manager Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Project Management Triangle Tutorial: What It Is and How to Use
- Project Management Tools Tutorial | Learn Tools & Techniques
- What is PMO (project management office)? | A Complete Tutorial from Scratch
- Project Management Lessons | Learn in 1 Day [ STEP-IN ]
- What is a Project Kickoff Meeting? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Project Cost Management Tutorial | Steps, Basics, and Benefits
- Types of Contracts in Project Management | Learn with Examples
- Project Activity Diagram | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- What is Project Procurement Management? | Tutorial Explained
- Procurement Documents Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Process-Based Project Management Tutorial: A Beginner’s Guide
- What Is PRINCE2 Project Management? | A Definitive Tutorial for Beginners
- Effective Presentation Skills – Learn More through Tutorial
- Powerful Leadership Skills Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- PERT Estimation Technique Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Pareto Chart Tool Tutorial | Learn Analysis, Diagram
- Organizational Structure Tutorial: Definition and Types
- Negotiation Skills for Project Management | Learn from the Basics
- Monte Carlo Analysis in Project Management Tutorial | A Perfect Guide to Refer
- Effective Management Styles Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- Management by Objectives (MBO) Tutorial | Overview, Steps, Benefits
- Leads, Lags & Float – Understand the Difference through Tutorial
- What is Knowledge Management? – Tutorial Explained
- What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT)? | Know More through Tutorial
- Gantt Chart Tool Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide
- Extreme Project Management Tutorial – Methodology & Examples
- Introduction for Event Chain Methodology Tutorial | Guide For Beginners
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | A Complete Tutorial for Beginners
- What Is Design of Experiments (DOE)? | Learn Now – A Definitve Tutorial
- Decision Making Tutorial – Know about Meaning, Nature, Characteristics
- Critical Path Method Tutorial | How to use CPM for project management
- What is Critical Chain Project Management? | A Complete Tutorial
- What is Conflict Management? | Learn the Definition, styles, strategies through Tutorial
- Effective Communication Skills Tutorial – Definitions and Examples
- Communication Models Tutorial – Project Management
- Methods of Communication Tutorial | A Complete Learning Path
- Communication Management Tutorial | Know more about Plans & Process
- What are Communication Channels? | Learn Now Tutorial
- Communication Blocker Tutorial | Explained with Examples
- Cause and Effect Diagrams Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- What is Benchmarking? | Technical & Competitive Tutorial
- Seven Processes of Prince2 Tutorial | Everything you Need to Know
- Design Thinking Tutorial – Quick Guide For Beginners
- What is Performance Testing | A Complete Testing Guide With Real-Time Examples Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Lean Six Sigma Tutorial
- Agile Scrum Tutorial
- PMI-RMP Plan Risk Management Tutorial
- Designing the Blueprint Delivery Tutorial
- What is Confluence? : Tutorial For Beginners | A Complete Guide
- Program Benefits Management Tutorial
- Continuous Improvement – Agile Value Stream Mapping
- Program Organization Tutorial
- Risk and Issue Management Tutorial
- Project Integration Management Tutorial
- Planning and Control Tutorial
- Program Management Principles Tutorial
- program strategy Alignment Tutorial
- PMP Tutorial
- Program Governance Tutorial
- Program Life Cycle Management Tutorial
- PMP Exam Preparation Tutorial
- PMI-PgMP Tutorial
- Agile Methodologies and Frameworks- Kanban and Lean Management Tutorial
- JIRA Tutorial
- Primavera P6 Tutorial

PMP Tutorial
Last updated on 29th Sep 2020, Blog, Project Management, Tutorials
What is Project?
A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service or result. A project is defined as temporary because it has a defined beginning and end time, and it is unique because it has a particular set of operations designed to accomplish a goal
The primary characteristics of a project are
- It has a definite start and end point
- Once the end point is reached, the project is over
- It is attempting to achieve something new
- Project must meet the customer or stakeholder requirements
What is Project Management?
The project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, motivating and controlling resources to achieve specific goals. The main challenge of project management is to achieve project goals and objectives while keeping in mind the project scope, time, quality and cost.
Project management actually began in the early 1950s. The need for project management arised observing the benefit of organizing work within the project and critical need to co-ordinate across different departments and professionals.
Project management mainly deals with these ten areas
- 1. Integration
- 2. Cost
- 3. Human resources
- 4. Stakeholder management
- 5. Scope
- 6. Quality
- 7. Communications
- 8. Time
- 9. Procurement
- 10. Risk Management
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Project Management Objectives
While preparing project, look project into these three perspectives, it helps to give much better understanding of the whole process
- How does project fit into the organization?
- How the project will evolve over time?
- What skills are required to manage the project successfully?
Project Management Methodologies
There are various methodologies that are available for project management.
- 1. Prince2
- 2. Agile
- 3. Six Sigma
- 4. Scrum
- 5. Kanban
- 6. Lean
- 7. Waterfall
We will look each of this into in a later part of the tutorial. Various tools are available to track project tasks and measure accomplishments during the project. These includes Gantt charts, PERT charts and Work down structures.
Stages of Project Management:
Apart from the cohesive team effort in the successful completion of any project, the one person on whose shoulders the entire project rests is the Project Manager. They have a profound knowledge of all the intricacies of the project to steer it efficiently towards the desired goal. There are five common stages to the project management cycle developed by the Project Management Institute – PMI®. These are Conception or the initial stage, planning, execution, performance monitoring and the closure or the concluding stage.
A team of more than 80 PMI® members developed the guide to Project Management Book of Knowledge – PMBOK® Guide. This guide book encapsulates the fundamental principles of project management to achieve the best results that have become a benchmark for project management studies worldwide. Acknowledging that each project is different, the guide details some of the process standards that can be applied to any project.
The 5 stages of Project Management:
1. Conception or the Initial Stage:
The project is analysed in a comprehensive manner including its feasibility, scope, timelines, cost and so on with a bit of research on the related subject. This stage will help you decide whether you want to go ahead with the project considering all aspects including its stakeholders and the successful completion of the project on time. A Project Initiation Document (PID) is developed that summarises the scope and requirements of the project.
2. The Planning Stage:
The success of the project depends on planning. It develops a blueprint that everyone can follow. One of the key components in the planning stage is goal setting and elements to measure the progress and success of the project. Goals must be realistic and achievable within the timelines with the resources allocated for it. The planning stage also defines the roles and responsibilities for each and every team member involved in the project with a clear definition of what is expected from them. One must also take into consideration the drawbacks and shortcomings at this stage that could create snags in the project. During the planning stage, measures must be outlined to steer clear of such situations.
There are two popular methods adapted for Goal Setting during the planning stage. They are SMART Goals and CLEAR Goals.
A) SMART is an acronym for:
- Specific – specific goals are set that have answers to who, what, where, why, when and which.
- Measurable – yardsticks are developed to measure the success of the goals set.
- Attainable – distinguishes the most crucial goals and the strategy to achieve them.
- Realistic – A goal must be realistic to the extent that everyone identifies with it and agrees to achieve it.
- Timely – Create the timeframe within which you can achieve the goal.
B) CLEAR is an acronym for:
- Collaborative – The goal must be such that all the team members get motivated to work together towards it.
- Limited – The scope must be limited to ensure it is managed effectively.
- Emotional – There must be an emotional connect towards achieving the goal such that it inspires them to do so.
- Appreciable – Big tasks are fragmented to make it convenient to achieve.
- Refinable – Goals must be refined according to incidents and situations during the process.
3. Project Launch / Execution Stage:
The project kick starts at this stage. It almost feels like the crux of the project since deliverables are defined. During the execution stage, the teams are declared, and resources are allocated. The project management plans are rolled out with procurements and supplies. Since the ball gets rolling, the Project Manager keeps an eye to guide the team in managing the project effectively. Project tracking is put in place. Tasks are assigned and executed while meetings are scheduled, and plans are altered to suit the requirements.
4. Performance Monitoring:
From the execution stage, the progress of the project is measured, which is a continuous process till the end of the project. Project tracking is done to ensure tasks are being completed as per schedule. Any deviations or shortcomings are immediately addressed with alternative measures. The smooth functioning of the project is determined through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Usually, a Project Manager selects two to five of these KPIs to measure the project performance.
- Objectives – Tracking the schedule and examining the progress made to ensure it matches with stakeholders’ interest.
- Quality – Completion and delivery of each task or module on time with no errors.
- Budget Tracking – The Project Manager will check to ensure the project task has not exceeded the allocated budget. Based on the progression and the time taken, it is also estimated whether the project will be completed on time.
- Performance – Issues that may arise are tackled efficiently and addressed to ensure smooth functioning. Alternative plans are made to handle such hitches.
5. The Concluding or Delivery Stage:
This is when the project is completed and ready for handover. All members and team leaders are recognised and acknowledged. A concluding meeting is usually held with all the key stakeholders and team members to look back at what was done well and where were the pitfalls. This contributes to a learning experience that can be taken care of during the next project. A final project report is prepared including the final project budget, after approval from all stakeholders.
Project Management Principles
Project Management is an intricate and an essential part of any venture you start. It involves the development of a detailed strategy of the proposed initiative clearly defining its purpose, goals, budget, timelines, resources and so on. While explaining the scope of your project, you will also have to take into consideration the aspects that could slip or cause interruptions in order to be ready with alternative plans to achieve your concluding objective within the specified timeframe. Let’s look at some of the fundamental principles of Project Management that govern the success of the whole initiative. These basic principles are useful while starting a new program or introducing learning and development modules, especially if you’re collaborating on the HR, quality and operational enhancement processes.
1. Project with a vision
The most important vision for a Project Manager is to successfully complete the project within time with all its deliverables. It must clearly define your goals and objectives. This will need to prepare a roadmap to achieve the set objectives. The goals and objectives you set must be measurable, relevant and realistic that can be achieved within the scheduled time frame. The appropriate resources and tools must be provided to achieve the goal. A cohesive approach bringing all the team members on to the same page with a single vision is critical to the success of any project.
2. The Key Role of a Project Manager
A Project Manager works along with his/her team to develop a project plan with risk assessment and clarity on goals and objectives. They manage and guide the team throughout the project phase taking it to its desired closure. The Project Manager also takes inputs, feedback and approval from clients and other stakeholders for each of the task components of the project. Communication, documentation, risk management, reporting, scheduling and escalating issues are some of the important attributes that a Project Manager dwells with. Some of the skill sets mandatory for a Project Manager includes:
- Technical knowledge with regard to the project elements
- Comprehending management principles
- Effective communication with teamwork and interpersonal skills
- Ability to envision the project wholly being aware of all its intricacies
3. Accountability and Commitment
Once the responsibilities are taken, it is important to stay committed and be accountable for the project at every stage. Everyone in the project team must unanimously agree to the principles, goals, scope, quality and schedule of the project. Communication plays an important role in bridging the gaps. Sharing information and feedback will contribute to the smooth flow of the project.
4. Creating a structure with estimated timelines
The milestones are defined using this principle with a planner that indicates work schedules, estimates and timelines for each task or module. The detailed schedule will specify the man-hours at your disposal and the bandwidth you have to complete the project. It cautions you not to make unrealistic commitments that cannot be achieved in the given timeframe.
5. Have a defined framework
A clearly defined framework that has been agreed upon by all stakeholders and teammates will ensure smooth completion of the project. As opinions and views differ from people to people, the Project Manager must bring everyone on the same page with clearly defined objectives of the project to set expectations right. Each of the team members also must know their individual responsibilities and deliverables. Documenting the same using a Gantt chart, a project management software or even an excel sheet will help in mapping the tasks to get a bird’s eye view of the project. Monitoring the tasks closely will help in taking corrective action as and when required.
6. Clear Goals and Milestones
Clearly defining goals and milestones before the commencement of the project will bring clarity on expectations. Milestones indicate the successful completion of significant portions of the project. They would also boost the team’s morale and acknowledge them for their commitment.
7. Measuring Progress and Success
Managing the scope of the project in order to maintain quality, time schedule and cost estimates with well-defined objectives is crucial to the success of any project. A timely review is part of the mandate to understand the shortcomings and take remedial measures after discussing with respective team members. This helps in consistent process improvement.
8. Being aware of Risks
Being aware of risks and managing them effectively is part of the Project Manager’s role. One needs to be cautious about the potential risk factors during project execution, which could also be gathered using previous project experiences, data and knowledge from other members involved in the project. Remedial measures to encounter such risks is also essential. This is not a one-time activity; risk evaluation is a consistent exercise that must be taken up during various stages of the project. Understanding risks helps you navigate through it and emerge as a winner.
For more information about the principles of Project Management, look for a Project Management Professional(PMP)® Certification Training Institute near you.
Benefits of using Project Management principles
Project Management seems complicated; however, it is easy to comprehend. The significant aspect is to know the benefits or advantages of Project Management. You ought to be a pro with basic organisational skills to manage any type of project effectively – it could be a wedding or the construction of a sea-link. Knowledge comes from playing the right chords to get the desired tune. It is the effective utilisation of resources and knowing how and when to use them appropriately.
Let’s look at the value addition given by Project Managers that will clarify why project management by a professional is so important. For starters, they hold the team and the client or stakeholders together. They are like a compass that shows the direction and guides you to your desired destination. They deliver whatever is required to keep the project on track through all ups and downs, managing conflicts and challenges, risks and team spirits that keep the project rolling. When a project is executed efficiently and managed well, it resonates beyond completion and handover. It leaves a trail of success.
1. Delivering Value
Project Management ensures that each of the segments in the project development phase are aligned to its business objectives, complementing the client’s perspective in a broader sense. It aims to deliver value through return on investment. Facing risks and challenges is part of any project. The effectiveness of a Project Manager is when they are able to realign their strategy to achieve business objectives.
2. Ensuring Customer Delight
Any project that’s completed on time within the budget pleases the client and the stakeholders. And, when a client is happy, your work is appreciated and recommended to others. Smart Project Management ensures a healthy client-manager relationship.
3. Leadership Skills
A Project Manager is the leader of the project. They give direction and are in command. Without them, the project lacks alignment and pace. They motivate the teams to bring out the best in them and provide the route map in achieving the project goal. Project Managers ensure the teams work within the given framework and follow set guidelines. They follow processes and protocols and carry the responsibility of the entire project till its completion.
4. Timely accomplishment of tasks
Without a leader, the teams lack direction and focus. They need clear briefs and a proper outlook. Their roles and responsibilities are clearly outlined by the Project Manager to ensure there are no conflicts. The project is executed in a systematic manner. Tasks are accomplished on time. The tasks are given in smaller portions that help the teams to focus better, complete on time and take corrective measures quickly whenever necessary,
5. Accuracy in Project Planning and Execution
A Project Manager estimates the budget, sets the objectives, evaluates timelines and allocates resources. Without the Project Manager, goals and objectives could be over-ambitious or illogical. The timelines may not be realistic and the resources and tools may not be adequate. A Project Manager is able to take into consideration all the risks involved and substitutes to manage unexpected outcomes. A Project Manager understands the scope of the project and delegates work in a manner that doesn’t feel overburdened to the teams.
6. Quality and Consistency
A dedicated Project Manager for every project – large or small ensures timely delivery, proper utilisation of resources and quality output. With Project Management skills, the quality and consistency of the project segments are screened, tested and evaluated for quality assurance.
7. Risk Assessment
A Project Manager is trained in risk management. The anticipated risk factors are analysed to find a resolution that would not lose focus on the project deliverables and timelines. They will be ready with alternative plans in the event of any such eventuality.
8. Proactive Approach
There have been situations that in spite of proper planning, things go wrong, and people tend to take a reactive approach compromising on quality, cost, time and resources. A Project Manager knows his team members and through effective communication, they are able to bridge the gaps as they know the tasks given to each member of the team, their deadlines and resources allocated to each of them. They constantly monitor the progress to ensure the project is on track. Without a systematic proactive approach to Project Management, companies and clients take the risk of project delays or failure, lack of people management, wastage of resources and overall unpleasant experiences.
9. Consistent Tracking and Monitoring
A project needs to be monitored regularly to ensure tasks are completed on time and eventualities are addressed effectively. Project Managers review the project at every stage. It is like a diagnostic tool to take corrective action as and when required instead of waiting till the end and doing a post-mortem. They provide regular status reports with details of tasks completed, work in progress, time spent, resources utilised and so on. These reports are evaluated by the teams as well as the stakeholders, which helps in patching the differences in any and ensuring work flows smoothly.
10. Learnings and Takeaways
Project Management enriches your experience with each project based on its success and shortfalls. After the completion of each project, Project Managers look back to analyse and review the aspects that went well and the challenges they faced in order to find ways of implementing a different approach to the next project. Each project cycle gets documented, which is a rich source of information for reference to other Project Managers.
Project Management strategies drive organisational success. Project Managers invest in time, project planning and due diligence contributing to the success of the business in the larger context. They conduct frequent reviews, risk assessment, measure success and ensure qualitative output. Organisations must define ROI, manage what’s measured, use analytical tools to align projects with strategy and implement strong project management practices that will determine the growth of the organisation.
What is a Project? A Quick Look at Project Characteristics

A project is a practice that is undertaken by experts together to form a unique product, service, or result. It may include a new product development, building construction, planning industrial plant infrastructure, implementation of the project, enhancing or improving business procedures and its processes.
A project is started by a group of experts, constrained by limited resources, deployed to the client when finished. A project is temporary in nature that is planned, controlled, and executed as per the requirements. The different operations of a project are the primary focus and they continue on the repetitive basis that contains a set of repetitive elements and it will not change the unique characteristics of a project.
So, would you like to explore the characteristics of a project ahead?
- A project is always unique in terms of its characteristics. Although it is temporary in nature, it can be extended anytime based on Company needs. However, each project starts with a plan and there is one ending date too. It will not go indefinitely.
- Each project is started to deliver a unique product in the end. The final output could be a product, service or result etc. Many times, plenty of activities are common between projects but they are always unique in one or the other.
- The project is declared closed when all objectives are met and it is ready to deploy to the client. There is one more reason for closing the project that the final output does not exist anymore. Keep in mind that project work is always different from the regular operational work.
What is Project Management? Understanding the Project Methodology
The next important term to discuss here is project management that is taken as the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques applied to different activities or operations of a project to meet varied needs of a complex project. The project management can be achieved by the integration of 49 processes and they should always be executed in a proper manner and follow the right order too.
Here is one example of project management methodology that is defined by the project management institute (PMI). PMI is a non-profit organization that offers certification to project practitioners for their knowledge and skills set.
- Each project follows 5 process group, 49 processes, and the 10 knowledge areas.
- The documentation should always be proper with standard processes or approaches.
- The process can be applied to a wide range of industries like healthcare, life sciences, IT, oil & gas, petrochemical, or telecom industries etc.
- It should be tailored perfectly to meet the complex needs of a business.
You must be wondering why project management is necessary and its value for businesses.

The project management contributes majorly to the organizational success within a fixed time frame and budgeted costs. The chances of project success get higher and it is quickly accepted by the users or Companies etc.
It can define the project scope clearly without disturbing the main workflow and culture of the organization. The project management incorporates innovative thinking and advanced planning too.
What is PMP and PMI?
PMP or Project Management Professional is one of popular certification awarded by PMI to skilled project practitioners. The PMP certification is highly recognized by industries and demanded worldwide. For the project manager role or to become a successful project management professional, this qualification is mandatory. Here is a list of most coveted project management certificates for your reference. With this graph, you can realize yourself why PMP is so popular and most suitable career choice for learners.
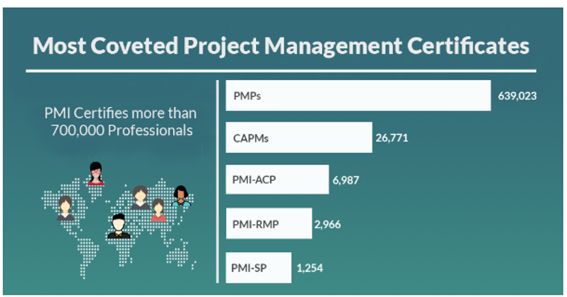
PMP certification is not limited to a particular domain but a project manager could work almost any industry either it is retail, banking, defense, IT, or manufacturing industries. Once the PMP certification exam is completed successfully and you can add to your project a PMP® certified professional.

So, PMI is an institute and the PMP is a credential. PMI helps you in writing or supervising the PMP exams successfully. If you need still more detail on PMP then you can browse the official website right away – www.pmi.org.
To sum up, PMI is an organization, and PMP® is a credential. PMI therefore writes and supervises the PMP® examinations. If you need more information on PMI, you can visit their website, www.pmi.org.
Prerequisites or application requirements for the PMP Exam
Before you appear for the PMP certification then don’t forget to check the latest version of the exam. The PMP certification is valid for three years and there are chances that you will get your dream job quickly with fat salary packages.
PMP exam Pre-requisites
- You should have a four years bachelor degree
- And a minimum experience of 4500 hours in project management
OR
- You could start with a secondary degree like a diploma or any other associated degree.
- And a minimum experience of 7500 hours in project management.
AND
- 35 to 40 hours of education from a registered education provider like JanBask Training.
Guidelines for the PMP Certification Exam
Let us have a quick discussion on a few guidelines that would help you in completing your application successfully.
- You should join the PMP membership first before you apply for the PMP examination. The members will get a flat discount of $150 for the PMP certification that is actually higher than the registration costs. So, this would be a smart decision to help you in saving money during the first process only. Becoming a member is quite an easy process and easy to complete by the official PMP site in a few steps.

- Open the site, click on join PMI button and enter the necessary details. Make sure that the details are correct because the same will be published on your PMP certification too.
- You have to cautious when adding the project experience because it will be verified later and add details that are handled during the project only. Focus on things minutely and the work done by you.
- Now had a look at the primary contacts given in your application before you submit it. These contacts will be the witnesses for the project experience during the verification process. If you are not sure how to complete this step then don’t forget to take help from experts.
- In case, your application is selected for the audit then a list of instructions will be given on your email id. You should follow the instructions wisely and be prepared in advance.
In the next section, we will focus on the exam outline for PMP tutorial guide blog.
PMP Exam Outline
The PMP exam will be conducted for a total of four hours that contains 200 questions in total and 25 questions are fixed for the future tests and they will not be scored. These 25 questions will be picked randomly by the team and you should answer all 200 questions seriously.
All 200 questions are multiple-choice questions and there is no negative marking scheme for the wrong replies. You should answer all the questions in the given time only and you can answer all questions together even if you are unsure. There are grades given for all participants instead of rating like –
In this section, we will discuss the topics to be covered in the PMP exam and their weightage too. The percentage of questions from different chapters is given below that would help you in preparing for the exam accordingly.
| Project Management Process Group | Percentage of Questions | Number of Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Initiating | 13 | 26 |
| Planning | 24 | 48 |
| Executing | 31 | 62 |
| Monitoring and Controlling | 25 | 50 |
| Closing | 7 | 14 |
The Role of a Project Manager
Moving ahead, let us discuss the common roles of a project manager for different domains –
A project manager is a dominant role for a project and he is entirely responsible for the organizational success too. The position is directly associated with the tremendous accountability, responsibility, ownership, and the authority. Here are the popular roles and responsibilities of a project manager that are listed after a proper research only –
He is completely responsible for the accountability of a project and applies concepts that are learned from the recent similar projects. He needs to understand the project needs deeply and plan the activities accordingly. He also performs the project tracking and updates for project status regularly.
He always adopts best practices for project management and manages project priorities too. He works on project risks and issues carefully and promotes client involvement too. He encourages and support the escalations and enforces effective change controls or management. PMP focuses more on agile practices and minimizes the role of a PM as a controller. Further, he is responsible to monitor and manage project risks, stakeholders, and communications.
Project management skills requirements by professionals
| Technical Skills | Strategic and Business Management | Leadership Skills |
| PMBOK ® Guide | Business acumen Basic management Vision Strategic alignment | Motivational teams Communication Emotional Intelligence Critical Thinking |
What is difference between Portfolio, Program management, and Projects?
- A “Portfolio” is a collection of other projects or programs. The components could or could not be interdependent.
- The “program management” is the centralized and coordinated management of program to achieve the strategic benefits or objectives. Here, multiple projects can be aligned in such way that it could help in achieving the program goals and optimizing the overall project costs, schedules, and efforts too.
- On the other hand, “Project” is an independent delivery in a program that has loose association with a portfolio of projects.
- A “Stakeholder” is the person who could be positively or negatively affected by the outcome of a project.
With this discussion, we come to an end for the blog PMP Tutorial Guide. I hope this blog is 100 percent suitable and will help you in starting with PMP certification training and how to prepare for PMP exams.

