- Difference between Waterfall approach and Agile approach
- CCIE Certification Cost in India
- What is IOT? | Know about IOT Application
- How to install Jenkins on Ubuntu? : A Complete Guide
- What is AWS Instance Types? : A Complete Guide
- VMware Site Recovery Manager : Know all about it
- What is Big Engineering? | Know about the salary
- What is Data Model in Salesforce ?
- Splunk architecture| Know from the basics [ OverView ]
- What is Azure Arc? | Integration Guide | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Introduction To Docker Networking: Advantages and Working | Everything You Need to Know
- Introduction to Azure ASR-enabled servers | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Create Alarms in Amazon CloudWatch | Integration Guide | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What’s AWS VPC? Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Explained | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What Makes the Difference between Containers Vs Virtual Machines | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is a CDN? | How Do Content Delivery Networks Work | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Top Real World Applications of Cloud Computing | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What to Expect AWS Reinvent Reinforces the Growth of Cloud Computing|All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Cloud Computing Technology with SalesForce Integration | How its Work [ OverView ]
- Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm | What’s the Difference and Which Should You Learn?
- Big Data vs Data Warehouse | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Public Cloud vs Private Cloud | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Red Hat Certification Path: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- An Overview of AWS SDK and Toolkit | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- An Overview of MuleSoft Anypoint | Benefits and Special Features | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What is Amazon Elastic Load Balancer? : Benefits and Special Features with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is AWS Console ? : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Microsoft Azure Application Gateway | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- A Definitive Guide for Azure Automation | Benefits and Special Features
- Azure ExpressRoute | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- What is Hybrid Cloud? | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- A Complete Citrix Certification Path | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Azure Active Directory B2C ? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Azure DNS ? Azure DNS – Azure Domain Name System | REAL-TIME Examples
- Top AWS Statistics | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Docker Swarm Architecture | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- What is Dell Boomi? | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- Cloud Architect Salary in India | All you need to know [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What Is Multitenancy ? : Characteristics , Features , Benefits | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What Is the Recommended List of AWS Whitepapers? | Expert’s Top Picks
- OSCP vs CEH | Difference You Should Know
- Openshift vs Kubernetes | Difference You Should Know
- AWS Cloud Practitioner and Required Skills | Expert’s Top Picks
- CRISC Certification and Benefits | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Kali vs Parrot | Difference You Should Know
- How to Install Docker on Ubuntu | Comprehensive Guide
- AWS Certification Cost and Types of Exams [ Job & Future ]
- What is the Average AWS Solutions Architect Salary?
- Reasons to Take up A Cloud Computing Certification
- What is Cloud Databases
- What is Cloud Computing Architecture?
- AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
- Top AWS Services
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing 2020: An Analysis Of Cisco’s Cloud Index Survey, 2016
- What Are The Fundamental Microsoft Cloud Services That Are In Demand?
- What are the Issues in cloud computing?
- Top Important Cloud Computing Terms
- From Developer to AWS Cloud Specialist – The AWS Certification Learning Paths
- Why and How to Pursue a Career in AWS?
- The Top In-demand cloud skills for 2020
- Edge Computing Vs. Cloud Computing
- Top 10 Reasons to Learn AWS
- Cloud Computing Career Guide
- What does a AWS solution architect do?
- AWS Career Guide
- VMware vSphere best practices
- The AWS Engineer: Job Roles, Salaries And the Career Path
- What Is Microsoft Azure in Cloud Computing?
- How to Become an Azure Developer?
- Citrix Xenserver Vs Vmware vSphere
- Microsoft’s Project Olympus Delivers Cloud Hardware
- The Future of Cloud Computing
- Why Cloud Computing Is Essential to Your Organization?
- Amazon Web Services – WorkMail
- What is AWS?
- AWS Vs OpenStack
- AWS Certification Path
- AWS ElasticSearch
- AWS EC2 Instance Types
- Microsoft Azure Portal
- AWS Vs Azure
- Amazon Web Services WorkSpaces
- What is AWS Management Console?
- Difference between Waterfall approach and Agile approach
- CCIE Certification Cost in India
- What is IOT? | Know about IOT Application
- How to install Jenkins on Ubuntu? : A Complete Guide
- What is AWS Instance Types? : A Complete Guide
- VMware Site Recovery Manager : Know all about it
- What is Big Engineering? | Know about the salary
- What is Data Model in Salesforce ?
- Splunk architecture| Know from the basics [ OverView ]
- What is Azure Arc? | Integration Guide | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Introduction To Docker Networking: Advantages and Working | Everything You Need to Know
- Introduction to Azure ASR-enabled servers | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- Create Alarms in Amazon CloudWatch | Integration Guide | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What’s AWS VPC? Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Explained | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What Makes the Difference between Containers Vs Virtual Machines | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is a CDN? | How Do Content Delivery Networks Work | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Top Real World Applications of Cloud Computing | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- What to Expect AWS Reinvent Reinforces the Growth of Cloud Computing|All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What is Cloud Computing Technology with SalesForce Integration | How its Work [ OverView ]
- Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm | What’s the Difference and Which Should You Learn?
- Big Data vs Data Warehouse | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Public Cloud vs Private Cloud | Know Their Differences and Which Should You Learn?
- Red Hat Certification Path: A Complete Guide For Beginners with Best Practices
- An Overview of AWS SDK and Toolkit | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- An Overview of MuleSoft Anypoint | Benefits and Special Features | A Definitive Guide with Best Practices
- What is Amazon Elastic Load Balancer? : Benefits and Special Features with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is AWS Console ? : A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Microsoft Azure Application Gateway | Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- A Definitive Guide for Azure Automation | Benefits and Special Features
- Azure ExpressRoute | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- What is Hybrid Cloud? | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- A Complete Citrix Certification Path | A Complete Guide For Beginners [ OverView ]
- What is Azure Active Directory B2C ? : Step-By-Step Process with REAL-TIME Examples
- What is Azure DNS ? Azure DNS – Azure Domain Name System | REAL-TIME Examples
- Top AWS Statistics | Everything You Need to Know | Expert’s Top Picks
- Docker Swarm Architecture | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- What is Dell Boomi? | Everything You Need to Know [ OverView ]
- Cloud Architect Salary in India | All you need to know [ For Freshers and Experience ]
- What Is Multitenancy ? : Characteristics , Features , Benefits | All you need to know [ OverView ]
- What Is the Recommended List of AWS Whitepapers? | Expert’s Top Picks
- OSCP vs CEH | Difference You Should Know
- Openshift vs Kubernetes | Difference You Should Know
- AWS Cloud Practitioner and Required Skills | Expert’s Top Picks
- CRISC Certification and Benefits | A Complete Guide with Best Practices
- Kali vs Parrot | Difference You Should Know
- How to Install Docker on Ubuntu | Comprehensive Guide
- AWS Certification Cost and Types of Exams [ Job & Future ]
- What is the Average AWS Solutions Architect Salary?
- Reasons to Take up A Cloud Computing Certification
- What is Cloud Databases
- What is Cloud Computing Architecture?
- AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
- Top AWS Services
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing 2020: An Analysis Of Cisco’s Cloud Index Survey, 2016
- What Are The Fundamental Microsoft Cloud Services That Are In Demand?
- What are the Issues in cloud computing?
- Top Important Cloud Computing Terms
- From Developer to AWS Cloud Specialist – The AWS Certification Learning Paths
- Why and How to Pursue a Career in AWS?
- The Top In-demand cloud skills for 2020
- Edge Computing Vs. Cloud Computing
- Top 10 Reasons to Learn AWS
- Cloud Computing Career Guide
- What does a AWS solution architect do?
- AWS Career Guide
- VMware vSphere best practices
- The AWS Engineer: Job Roles, Salaries And the Career Path
- What Is Microsoft Azure in Cloud Computing?
- How to Become an Azure Developer?
- Citrix Xenserver Vs Vmware vSphere
- Microsoft’s Project Olympus Delivers Cloud Hardware
- The Future of Cloud Computing
- Why Cloud Computing Is Essential to Your Organization?
- Amazon Web Services – WorkMail
- What is AWS?
- AWS Vs OpenStack
- AWS Certification Path
- AWS ElasticSearch
- AWS EC2 Instance Types
- Microsoft Azure Portal
- AWS Vs Azure
- Amazon Web Services WorkSpaces
- What is AWS Management Console?

What is Cloud Databases
Last updated on 14th Oct 2020, Artciles, Blog, Cloud Computing
Now a day, data has been specifically getting stored over clouds also known as a virtual environment, either in a hybrid cloud, public or private cloud. A cloud database is a database that has been optimized or built for such a virtualized environment. There are various benefits of a cloud database, some of which are the ability to pay for storage capacity and bandwidth on a per-user basis, and they provide scalability on demand, along with high availability.
A cloud database also gives enterprises the opportunity to support business applications in a software-as-a-service deployment.
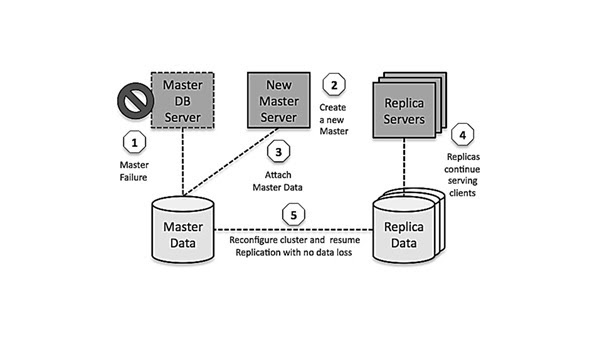
What are Cloud Databases?
- 1. First, let’s look into what a cloud database software is and how it can be beneficial for your startup. A cloud database is a storage system that lets you save files and data on a server that is connected to the internet. With a cloud database service provider, all the info stored in your company’s computers is transferred to the database that you access through the internet.
- 2. You no longer have to worry about running out of storage space, or hiring a technician every time your computer conks out, or when there is intermittent weather that can cause damage to your machines. All your data is stored in the “clouds” somewhere in the wide, wide world of the internet.
- 3. As a startup, getting a cloud database service provider can be costly, but there is free software that you can get that is free or almost free. There are databases that come with free use for a limited time that will allow you to choose the best one for your startup. Here are the top ten best and free cloud-based database software:
- 4. A cloud database is a scalable content database running on a cloud computing platform that could be private, public or hybrid.
- 5. There are two cloud database environment models, namely, Traditional cloud model and Database-as-a-service (DBaaS).
- 6. In the Traditional cloud model, the content database will be run on the particular enterprise’s infrastructure and any oversight will fall into the shoulders of IT staffers of the company.
- 7. On the other hand, DBaaS runs on the service provider’s infrastructure and they (the vendor) would be responsible for any hitches or glitches should they occur.
- 8. The service provider assumes the full responsibility of handling the client database leaving them to focus on operations and business goals.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Features:
- A database service built and accessed through a cloud platform
- Enables enterprise users to host databases without buying dedicated hardware
- Can be managed by the user or offered as a service and managed by a provider
- Can support relational databases (including MySQL and PostgreSQL) and NoSQL databases (including MongoDB and Apache CouchDB)
- Accessed through a web interface or vendor-provided API
Why cloud databases
1. Ease of access : Users can access cloud databases from virtually anywhere, using a vendor’s API or web interface.
2. Scalability : Cloud databases can expand their storage capacities on run-time to accommodate changing needs. Organizations only pay for what they use.
3. Disaster recovery : In the event of a natural disaster, equipment failure or power outage, data is kept secure through backups on remote servers.
Considerations for cloud databases
- Control options :
Users can opt for a virtual machine image managed like a traditional database or a provider’s database as a service (DBaaS). - Database technology :
SQL databases are difficult to scale but very common. NoSQL databases scale more easily but do not work with some applications. - Security :
Most cloud database providers encrypt data and provide other security measures; organizations should research their options. - Maintenance :
When using a virtual machine image, one should ensure that IT staffers can maintain the underlying infrastructure.
Advantages of Working with Cloud Databases
Shifting to the cloud can be extremely beneficial today due to the wide range of inherited advantages it brings with it. Some of them include:
- 1. Less Dependence on Hardware – With the cloud service provider covering the maintenance and infrastructure aspects, companies can now invest less in hardware and resources, as well as IT expenditure. There are also fewer complications and conflicts that often hinder development.
- 2. Enhanced Scalability – Working with a DBaaS allows for seamless and smooth scalability during peak times or ahead of big releases with tight deadlines. This is a huge benefit for growing companies that may not possess the budget and resources for on-premise infrastructure.
- 3. Value for Money - Not worrying about operational costs or costly upgrades is only the tip of the iceberg when it comes to cloud databases. Most DBaaS solutions are available in multiple configurations today, something that makes it easier for companies to pay for only what they actually use.
- 4. Enjoy the Latest Technology - Companies no longer need to worry about shelling money on buying new technologies because updated infrastructure is the headache (and sole responsibility) of the cloud vendor. Companies also don’t need to hire dedicated staff for training and onboarding purposes.
- 5. Security – Just like the previous advantages, all top vendors today take care of the security aspect and invest in the best available solutions to keep the databases safe. No solution is bullet-proof, but it is definitely proving to be a safer way to protect sensitive data and information with less margin for error.
Top 7 Cloud Databases for 2020
1 – Amazon Web Service (AWS)
Amazon has become the market leader in the DBaaS space. It offers supplementary data-management services such as Redshift, a data warehouse and Data Pipeline, which is a data integrating service for easier data management. Amazon’s current offerings include:
- Amazon RDS – Amazon’s Relational Database Service runs on either Oracle, SQL or MySQL server instances.
- Amazon SimpleDB – This is primarily a schema-less database that is meant to handle smaller workloads.
- Amazon DynamoDB – This falls on the NoSQL databases (SSD), capable of automatically replicating workloads across three availability zones.
Strengths: Lots of Features, Easy to Use, Good Support and Documentation Weaknesses: Not Too Customizable, Downtimes as per Amazon’s Schedule
2 – Oracle Database
Oracle Database provides companies with enterprise-scale database technology stored in the cloud. Despite its first offering being quite comprehensive, the Generation 2 offering has consistently higher performance with extensive governance and security controls.
Data migration is also covered with a dedicated solution and tight customer support in case any technical issues or questions arise.
Strengths: Intuitive Interface, Easy to Use, Solid Customer Support
Weaknesses: No Free Version, No Mobile Access, Pricey for Small Companies
3 – Microsoft Azure
In a nutshell, Azure is a cloud computing platform for VM creation, building and running web-based applications, smart client applications, and XML web services. It currently boasts the biggest and strongest global infrastructure, with 55 regions, more than any other cloud provider.
A big point that needs to be considered is that Microsoft arguable offers the biggest range of software that a modern company needs today. This can allow you to create a huge ecosystem that has the same roots, with just one place to go with your questions or issues, if any may arise.
Strengths: Comprehensive Solution, Good Security, Strong Ecosystem
Weaknesses: Iffy Customer Service, Not User Friendly
4 – Google Cloud Platform
Surprisingly, Google is still playing catch-up with the big players in the market. But its solutions are being adopted by more and more businesses of different sizes, thanks to its no-nonsense approach and comprehensive documentation which reduces stress on developers, IT professionals, and other stakeholders.
The broad open-source compatibility also has its fair share of benefits, allowing you to scale while doing more with analytics and integrations.
Strengths: Comprehensive Documentation, Good for Small and Big Businesses
Weaknesses: Not Yet at the Level of the Big Three (AWS, Oracle, Azure)
5 – IBM DB2
This is a relational database that delivers advanced data management and analytics capabilities for transactional and warehousing workloads. IBM DB2 is designed to deliver high performance, actionable insights, data availability and reliability, and it is supported across Linux, Unix, and Windows.
However, it has fewer regional options, which may impact performance and compliance requirements depending on your development project/s.
Strengths: Well Designed Product, Easy Migration Process
Weaknesses: Average Customer Service, Pricey, Mediocre Functionality
6 – MongoDB Atlas
MongoDB Atlas is a popular open-source NoSQL database that offers powerful scaling, sharding, and automation capabilities. Another advantage is that most developers using this can speed through continuous delivery models without any database administrator (DBA) hand holding.
On the negative side, some applications require SQL databases to function, which automatically eliminates MongoDB Atlas from consideration.
Strengths: Strong Support Community, Quick Installation, Flexibility
Weaknesses: NoSQL Only, Can be Challenging for New/Inexperienced Devs
7 – OpenStack
Another interesting open-source rival for Google is OpenStack. These databases come in managed or hosted cloud databases. Rackspace is highly customizable and its architecture is easy to understand and implement. Many reviews have complimented the scaling capabilities of this solution.
The OpenStack community collaborates around a six-month, time-based release cycle with frequent development milestones.
Strengths: Good Value for Money, Easy to Use
Weaknesses: Cumbersome Interface, Some Stability Issues
Conclusion:
Armed with effective cloud database infrastructure, you can potentially scale up your development cycle while saving valuable money and resources. That being said, this solution list is not exhaustive in any way or form. Feel free to suggest cloud databases that we may have missed out or overlooked.

