- TypeScript Vs JavaScript Tutorial | Learn the Difference
- Web Components in Ionic Framework Tutorial – A Perfect Guide to Refer
- TypeScript Tutorial | A Step-By-Step Guide to Learn
- Creating and Publishing an Android Library | A Concise Tutorial
- How to Link a Style Sheet (CSS) File to Your HTML File | A Defined Tutorial
- HTML Video Tag Tutorial | Learn to Embed Video in Your HTML
- How To Create a Header – HTML Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- HTML Lists Tag Tutorial : Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- HTML Entity Tutorial | Learn Complete list of HTML Entities
- HTML Input Tutorial | Learn the Forms & Input Tags
- HTML Textbox Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- HTML vs HTML5 Tutorial | Know the Difference
- Know the Difference between HTML vs CSS Tutorial | Complete Guide [STEP-IN]
- Create a Top Navigation Bar using HTML Tutorial | Learning Path – Complete Guide
- HTML – Image Tag Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- HTML iframe Tutorial | Learn All about Tags and Element
- HTML Semantics – Free Tutorial to learn HTML
- HTML Mailto Attribute Tutorial | A Complete Guide
- Angular Tutorial | A Complete Guide To HTTP & Routing In Angular
- Introduction to HTML Line Breaks Tutorial | Complete Guide
- How to Redirect a Web Page in HTML | Learn in 1 Day FREE Tutorial
- Introduction To HTML Games | Build a Game with HTML Tutorial
- How to Create a Dropdown in Html | The Complete Guide Tutorial For Free
- Creating HTML Table Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- How to Create Image Slider in HTML Tutorial | Ultimate Guide
- HTML Symbols Tutorial | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE
- HTML Canvas Tutorial – Learn the Shape, Circle, Gradients
- A Complete Guide | UI Developer (Skills & Resources)
- jQuery Tutorial
- Advanced JavaScript Tutorial
- Angular Js Dom Tutorial
- Angular 7 Tutorial
- AngularJS Installation
- JavaScript Tutorial
- React Redux Tutorial
- AngularJS – Custom Directives Tutorial
- REACT JS Tutorial
- ANGULAR Tutorial
- Augmented Reality And Virtual Reality Tutorial
- Full Stack Development Tutorial
- ANGULAR 8 Tutorial
- TypeScript Vs JavaScript Tutorial | Learn the Difference
- Web Components in Ionic Framework Tutorial – A Perfect Guide to Refer
- TypeScript Tutorial | A Step-By-Step Guide to Learn
- Creating and Publishing an Android Library | A Concise Tutorial
- How to Link a Style Sheet (CSS) File to Your HTML File | A Defined Tutorial
- HTML Video Tag Tutorial | Learn to Embed Video in Your HTML
- How To Create a Header – HTML Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
- HTML Lists Tag Tutorial : Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- HTML Entity Tutorial | Learn Complete list of HTML Entities
- HTML Input Tutorial | Learn the Forms & Input Tags
- HTML Textbox Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- HTML vs HTML5 Tutorial | Know the Difference
- Know the Difference between HTML vs CSS Tutorial | Complete Guide [STEP-IN]
- Create a Top Navigation Bar using HTML Tutorial | Learning Path – Complete Guide
- HTML – Image Tag Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- HTML iframe Tutorial | Learn All about Tags and Element
- HTML Semantics – Free Tutorial to learn HTML
- HTML Mailto Attribute Tutorial | A Complete Guide
- Angular Tutorial | A Complete Guide To HTTP & Routing In Angular
- Introduction to HTML Line Breaks Tutorial | Complete Guide
- How to Redirect a Web Page in HTML | Learn in 1 Day FREE Tutorial
- Introduction To HTML Games | Build a Game with HTML Tutorial
- How to Create a Dropdown in Html | The Complete Guide Tutorial For Free
- Creating HTML Table Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn
- How to Create Image Slider in HTML Tutorial | Ultimate Guide
- HTML Symbols Tutorial | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE
- HTML Canvas Tutorial – Learn the Shape, Circle, Gradients
- A Complete Guide | UI Developer (Skills & Resources)
- jQuery Tutorial
- Advanced JavaScript Tutorial
- Angular Js Dom Tutorial
- Angular 7 Tutorial
- AngularJS Installation
- JavaScript Tutorial
- React Redux Tutorial
- AngularJS – Custom Directives Tutorial
- REACT JS Tutorial
- ANGULAR Tutorial
- Augmented Reality And Virtual Reality Tutorial
- Full Stack Development Tutorial
- ANGULAR 8 Tutorial

Full Stack Development Tutorial
Last updated on 19th Sep 2020, Blog, Tutorials, Website Development
Modern web development is both an exciting & tiring field. Javascript standards, frontend frameworks, backend frameworks, and deployment solutions are constantly evolving in the never ending battle to augment web software engineering.
While much of the innovation in the field has been groundbreaking, it has come with the expense of significant time up front to learn & master the necessary tooling and paradigms. This is especially true for junior engineers just entering the world of modern web development.
At Thinkster, we saw this happening first hand with the developers learning on our site. The most common question we are asked is “how do I use {X} frontend framework with {Y} backend framework to create a fullstack app?”. Indeed, if you search how to build fullstack apps on Google, you’ll find hundreds of different recommendations that are all specific to one set of technologies (React+Node, Angular+Rails, etc) — none let you choose your ideal frontend and backend.
This came as no surprise to us — we know first hand that creating a single fullstack tutorial is a lot of work, much less creating a tutorial for every possible frontend & backend combo out there. But then we had an idea:
What if we created a fullstack tutorial series where every frontend & every backend built the exact same app & API endpoints?
That would allow learners to mix & match any frontend tutorial with any backend tutorial and learn how to to build a fullstack app with them.
These aren’t the only benefits we discovered to this approach though — having the same project specifications across all tutorials also makes the process of learning new frontends & backends substantially faster.
What you will learn?
We feel that learning is best accomplished by “doing”, and as such, throughout this tutorial series we will be creating a production ready Medium.com clone called “Conduit” powered by your choice of our supported frontend & backend frameworks.
You can view a live demo of the application here. Conduit is a fully featured social blogging site including:
- Authentication with JWT
- Profiles with images
- Write/edit/read articles
- Comments on articles
- Ability to “favorite” articles
- Ability to follow other users & have their articles show up in your feed
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Building Conduit covers most of the advanced use cases and best practices of each framework. Every frontend and backend was created & vetted by the open source community via the RealWorld Github project — a project we created (and maintain) specifically for this tutorial series.
Supported frontends & backends
We’re always working on adding more frontend & backend stacks to this tutorial series. We also keep all of our existing stacks up-to-date with the latest framework versions & updates.
We currently support the latest versions of any combination of the following frontends & backends:
FRONTENDS
- React / Redux — tutorial, github repo
- AngularJS — tutorial, github repo
- Angular 2+ — tutorial, github repo
BACKENDS
- Node.js — tutorial, github repo
- Django — tutorial, github repo
- Rails — tutorial, github repo
Who this is for
This tutorial series was made to accomodate both junior and senior developers looking to master fullstack development. While the step-by-step instructions are particularly useful for junior developers just starting to learn fullstack development, the advanced use cases & best practices covered in each tutorial provide a birds-eye view for senior devs looking to keep their skills sharp and up-to-date.
Types of web developers
There are different types of web developers who focus on different areas. These include:
- Frontend developers:
Frontend developers implement web page designs using HTML and CSS. They make sure the website looks pretty on different devices, and that the forms and buttons work.
- Backend developers:
Backend developers create the backbone of the web application. They write code logic that handles a user’s input (for example, what should happen when you click the signup button after filling in a form).
- Full stack developers:
Full stack developers do bits of both backend and frontend. Depending on the problem at hand, they can switch capes to move stacks. You can learn more about the differences between frontend and backend development in this guide.
There are many other specific roles in web development, like system architects, AI, machine learning and security engineers. These roles require more specialized knowledge of one or more of the above types of development, so many professionals in these roles will start by gaining some general web development experience.
Why Do We Need Websites?
Websites primarily act as a bridge between one who wants to share information and those who want to consume it. If you are running a business, then it is almost imperative for you to have a website to broadcast your offerings and reach out to potential clients at a global stage.
The following points explain why it is important to have a website −
- A website is an online brochure where you can advertise your business offers.
- It gives you a platform to reach out to a far-and-wide global customer base.
- If you are a blogger, you have the possibility to influence your readers.
- You can show all your ideas and publish them on a website.
- If you have a business idea, then you don’t have to wait. You can straightaway open an online shop and sell your products or services online. An added advantage is that the online shop will be open 24/7 for your clients, throughout the year.
- You can communicate with your customers, giving them an opportunity to express themselves.
- You can provide valuable customer support by having a trouble-ticket system.
- If you have an official website with a domain, then you can have your personalized email. For example, info@tutorialspoint.com (it is much better than florjan.llapi@yahoo.com).
What are the skills required to become a web developer?
What does it take to become a web developer? Essentially, just three things: HTML, CSS and JavaScript—the three pillars of the web, which we’ll be learning about over the next few days. Together, these three pillars make every website work, defining the content to be displayed (HTML), telling a browser how to display that content (CSS), and making the content interactive (JavaScript), respectively.
A web developer is well versed in these three technologies. They can read other people’s code and make changes to it. They can find and debug bugs (shortcomings in existing code). A web developer might, at times, work on a new project (a new website) from scratch, or may have to work on an existing website and make it better. A typical day in the life of a web developer involves fixing bugs, developing new features (that is, enhancements) and webpages, and working with other developers to discuss ways to solve problems.
Don’t be overwhelmed by all of these details. You’ll soon see that they’re all very connected, and learning one of these automatically makes you good at a few others!
What’s the job outlook like for web developers?
In short, very good. Employment of web developers is projected to grow 13 percent from 2018 to 2028, much faster than the average for all occupations. Demand will be driven by the growing popularity of mobile devices and ecommerce (Bureau of Labor Statistics). It is a great time to be a web developer as startups are flourishing, which results in above average salaries for web developers in most parts of the world.
Also given the nature of the job, finding a remote job as a web developer is easier than many other domains. As a result, it opens up the entire world’s job market to everyone irrespective of where they’re physically located.
How to Setup a Website?
A website is composed of several elements and while setting up a website, you would have to take care of each of them.
- To set up a website and make it live, you should first purchase a hosting plan.
- Select a domain name for this website.
- Point the DNS records to the server or the hosting provider.
- Develop the content that you want to publish on the website.
- Check if you need to purchase a public certificate and install it.
- Publish the webpage on the Internet.
After understanding most of the important factors of Website Development, it is now time to set up a webpage. For setting up a webpage, we should adhere to all the steps given below.
Step 1 − Firstly, we purchased a domain name at GODADDY.
Step 2 − We chose the hosting provider based on the analysis of the hosting plans that we needed.
Step 3 − We configured the DNS records and the DNS servers of the registrar that in our case was GODADDY again.
Step 4 − Now that we are done with all the above-mentioned steps, it is time to upload the files of the webpage through CPanel → File Manager.
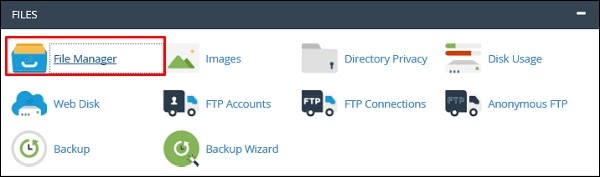
Step 5 − After opening it, upload the files in the folder named public_html as shown in the following screenshot.
Step 6 − If you have a dynamic website, then you must configure the database too. To do it, go to MySQL Databases.
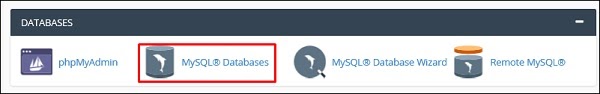
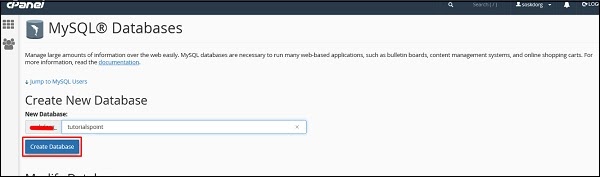
Step 7 − Click on Create New Database and then write the database name that your website will have and then click on Create Database as shown in the screenshot given below.
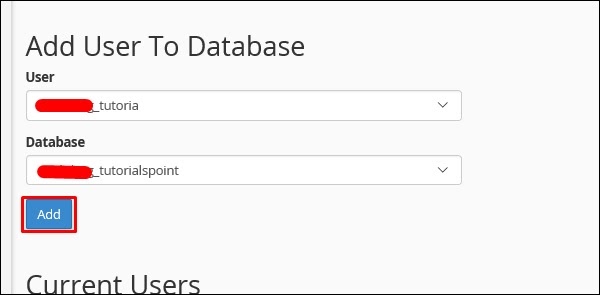
Step 8 − In the Add New User section type the Username and the password and then click on Create User.
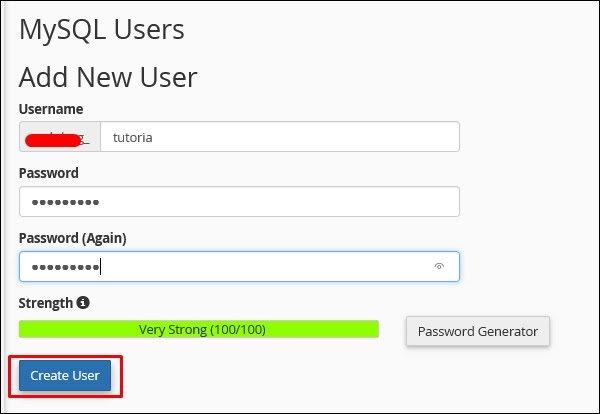
Step 9 − We must add the user that we created for this database to give rights or permissions to manage it.
Types of Validations
There are three types of validations, which are as follows −
- Domain validation SSL Certificate.
- Organization Validated SSL Certificates.
- Extended Validation SSL Certificates.
Let us now discuss each of them in detail.
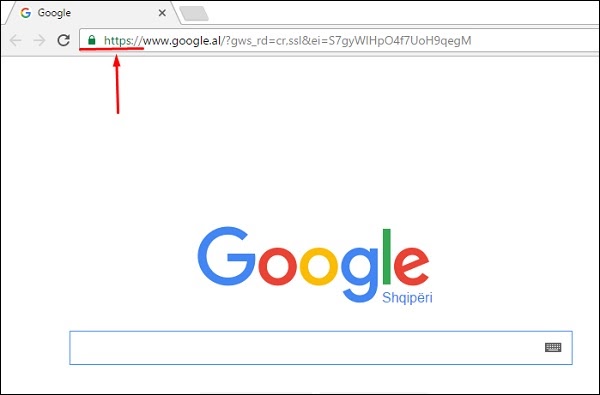
Domain validation SSL certificate
It validates the domain that is registered by a system administrator and he has the administrator rights (authorization or permission) to approve the certificate request. This validation is generally done by an email request or by DNS record.
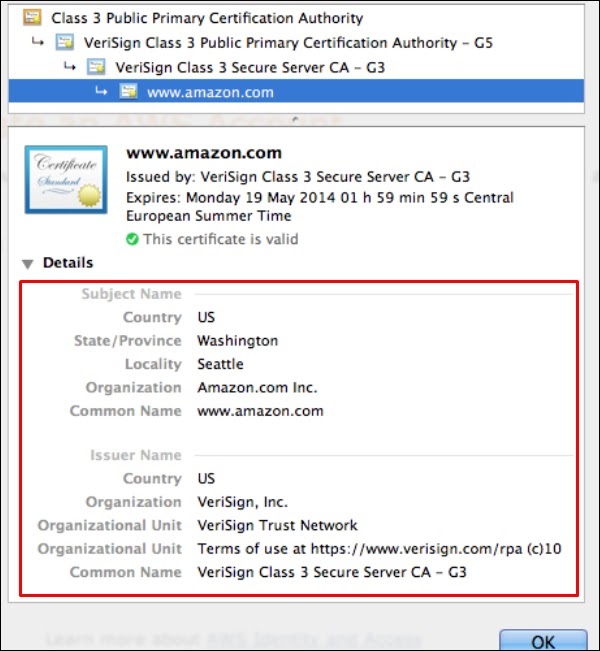
Organization Validated SSL Certificates
It validates the domain ownership and business information like the official name, City, Country. Validation is done also by email or DNS record entering. The certificate authority also needs some genuine documents to verify your Identity. The Organization Validated SSL Certificates display the company information in the certificate details as shown in the following screenshot.
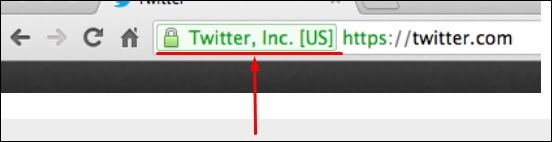
Extended Validation SSL Certificates
It validates the domain ownership, organization information and the legal existence of the organization. It also validates that the organization is aware of the SSL certificate request and approves it. The validation requires documentation to certify the company identity plus a set of additional steps and checks. The Extended Validation SSL Certificates are generally identified with a green address bar in the browser containing the company name like the one shown in screenshot below.
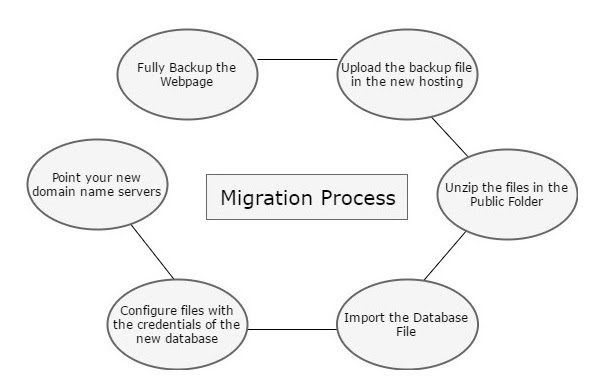
Web Page Migration
Webpage Migration is a process of moving a webpage from one host to another. This process is done for various reasons, some of which are −
- You are not satisfied anymore with the support of the Hosting Company
- Prices are cheaper to another hosting
- Your actual hosting plan doesn’t fulfill your needs anymore
- Technology offered is not competitive anymore, etc.
As migration is a process, the following steps are needed to complete it in a minimal downtime of your webpage.
- We must fully backup our webpage as discussed in the previous chapters.
- Upload the backup file in the new hosting.
- Unzip files in the Public folder.
- Import the database file.
- Configure files with the credentials of the new database.
- Point your new domain name servers with your current registrar and wait for the new records to be propagated.
Web Development Security
Securing your web pages is as important as developing it, because any threat which can compromise the security can harm your business reputation, damage you financially (by stealing your online deposits), damage your clients that visit your website, etc.
As per security experts, they will suggest doing the website security check based on the OWASP TOP 10, which is a powerful awareness document for web application security. The OWASP Top 10 represents a broad consensus about what the most critical web application security flaws are.
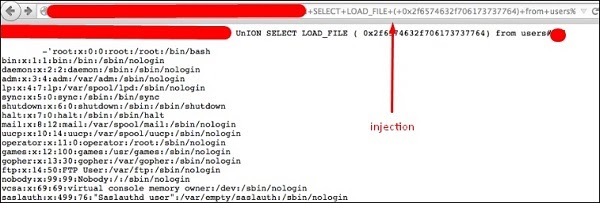
SQL Injections
Injection flaws, such as SQL, OS and LDAP injection occur when untrusted data is sent to an interpreter as part of a command or a query. The attacker’s hostile data can trick the interpreter into executing unintended commands or accessing data without proper authorization.
Solution − To secure your webpage from iSQL, you must validate inputs and filtering symbols.
Broken Authentication and Session Management
Application functions related to authentication and session management are often not implemented correctly, which allows attackers to compromise passwords, keys, session tokens or even to exploit other implementation flaws to assume other users’ identities.
Solution − To secure your site from this flaw, you must make cookies and sessions with expiration time.
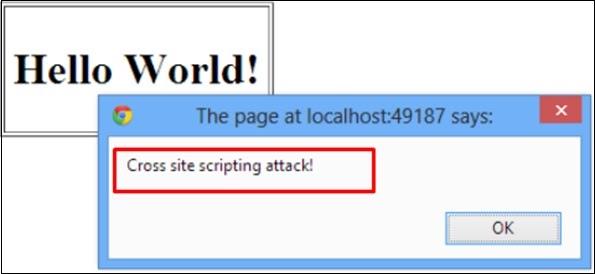
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
XSS flaws occur whenever an application takes untrusted data and sends it to a web browser without proper validation or escaping. XSS allows attackers to execute scripts in the victim’s browser, which can then hijack user sessions, deface websites or redirect the user to malicious sites.
Solution − Protection from this is on the same lines as it is for iSQL.
Insecure Direct Object Reference
A direct object reference occurs when a developer exposes a reference to an internal implementation object, such as a file, directory or a database key. Without an access control check or other protection, attackers can manipulate these references to access unauthorized data.
Solution − You should implement specific protection mechanisms such as passwords to safeguard such files.
Security Misconfiguration
Good security requires having a secure configuration defined and deployed for the application, frameworks, application server, web server, database server and the platform. Secure settings should be defined, implemented and maintained, as the defaults are often insecure.
Solution − Software should be kept up to date.
Sensitive Data Exposure
Many web applications do not properly protect sensitive data, such as credit cards, tax IDs and authentication credentials. Attackers may steal or modify such weakly protected data to conduct credit card fraud, identity theft or other crimes.
Solution − Sensitive data deserves extra protection such as encryption at rest or in transit, as well as special precautions when exchanged with the browser.
Missing Function Level Access Control
Most web applications verify function level access rights before making that functionality visible in the UI. However, applications need to perform the same access control checks on the server when each function is accessed. If requests are not verified, attackers will be able to forge requests to access functionality without proper authorization.
Solution − You should check the levels of authentication.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
A CSRF attack forces a logged-on victim’s browser to send a forged HTTP request, including the victim’s session cookie and any other automatically included authentication information, to a vulnerable web application. This allows the attacker to force the victim’s browser to generate requests which the vulnerable application thinks are legitimate requests from the victim.
Solution − The most commonly used prevention is to attach some unpredictable challenge based tokens to each request that comes from a website and associate them with the user’s session.
Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
Components, such as libraries, frameworks and other software modules almost always run with full privileges. If a vulnerable component is exploited, such an attack can facilitate serious data loss or server takeover. Applications using components with known vulnerabilities may undermine application defenses and enable a range of possible attacks and impacts.
Solution − Check if that component version has vulnerabilities and try to avoid or change with another version.
Invalidated Redirects and Forwards
Web applications frequently redirect and forward users to other pages and websites. These applications use untrusted data to determine the destination pages. Without proper validation, attackers can redirect victims to phishing or malware sites or use forwards to access unauthorized pages.
Solution − Always validate a URL.
Secure Used Protocols
This is the case where you have a VPS plan and you manage everything on your own. When the services are installed they use default ports. This makes the job easier to a hacker because he knows where to look at.
Some of the main service ports which are used in hosting of websites are given below −
- SSH – port 22
- FTP – port 21
- MySQL – port 3306
- DNS – port 53
- SMTP – port 25
The port changing of those services varies depending on the Operating System and its different versions. In addition to this, you have to install a firewall. If it is a Linux OS, we will recommend IPtables and block all the other unneeded ports. In case your OS is Windows, you can use its incorporated firewall.
To block brute force logins in your services, you can use Fail2ban, which is a Linux based software and block all the IP addresses which makes many failed login attempts.
What is a Full Stack developer?
FULL STACK DEVELOPER is an engineer who works on both client-side and server-side software. This type of software developer works on the Full Stack of an application meaning Front End Technology, Back End Development Languages, Database, Server, API, and version Controlling Systems. Hence, the name “Full Stack” Developer.
Full stack developer translates user requirements into the overall architecture and implement the new systems. A Full-Stack Developer doesn’t necessarily master all technologies. However, the professional is expected to work on the client as well as server sides and understand what is going on when developing an application. He or she should have a genuine interest in all software technologies.
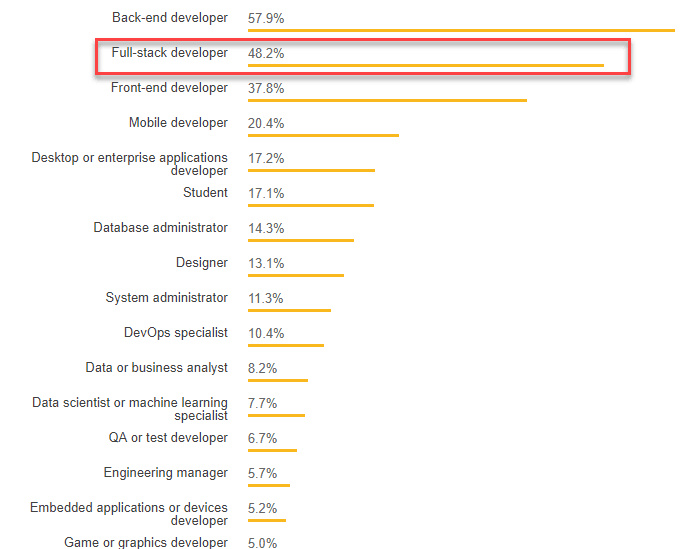
Stackoverflow Survey of Developer profiles
Why do you need a Full-Stack Developer?
Here are some prominent reasons why you should hire a full stack development professional:
Skip Ad
- Full stack developer helps you to keep every part of the system running smoothly
- Full stack developer can provide help to everyone in the team and greatly reduce the time and technical costs of team communication
- If one person plays different roles, it saves your company’s personnel, infrastructure and operational cost
Skill sets required to become a Full Stack Developer
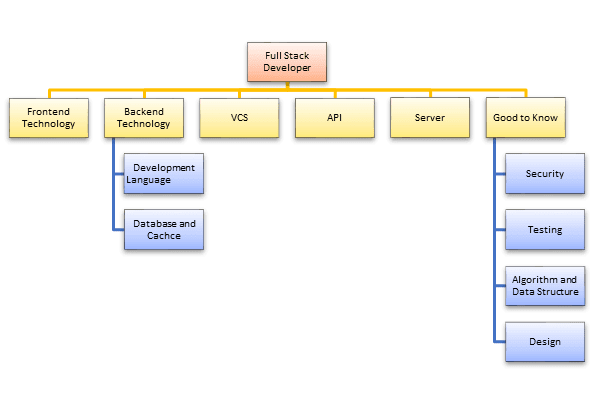
Full Stack Developer Skill Set
1) Front-end technology
Full stack developer should be master of essential front-end technologies like HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript. Knowledge of third-party libraries like jQuery, LESS, Angular and React JS is desirable
2) Development Languages
Full stack engineer should know at least one server-side programming languages like Java, Python, Ruby, .Net etc.
3) Database and cache
Knowledge of various DBMS technology is another important need of full stack developer. MySQL, MongoDB, Oracle, SQLServer are widely used for this purpose. Knowledge of caching mechanisms like varnish, Memcached, Redis is a plus.
4) Basic design ability
In order to become a successful full stack developer, the knowledge of designing is also recommended. Moreover, the person should know the principle of basic prototype design and UI /UX design.
5) Server
Exposure to handling Apache or nginx servers is desirable. A good background in Linux helps tremendously in administering servers.
6) Version control system (VCS)
A version control system allows full stack developers to keep track of all the changes made in the codebase. The knowledge of Git helps full stack developers to understand how to get the latest code, update parts of the code, make changes in other developer’s code without breaking things.
7) Working with API (REST & SOAP):
Knowledge of web services or API is also important for full stack developers. Knowledge of creations and consumption of REST and SOAP services is desirable.
Other Pieces of the Puzzle:
- 1.Ability to write quality unit tests
- 2.He or she should have a complete understanding of automated processes for building testing, document, and deploying it at scale
- 3.An awareness of security concerns is important, as each layer has its own vulnerabilities
- 4.Knowledge of Algorithms and data structures is also an essential need for professional full stack developers
What is a Software Stack? Which Stack should I learn?
Software stack is a collection of the programs which are used together to produce a specific result. It includes an operating system and its application. For example, a smartphone software stack includes OS along with the phone app, web browsers, and default applications.
The above list of skill sets for a full stack engineer could be daunting. You need to master a software stack based on your career goals, project and company requirement. Following is a list of popular software stacks.
Irrespective of the stack you choose, you will find similarities in the architecture and design patters across different stacks
LAMP stack
LAMP is a widely used model for web service stacks. Its name “LAMP” is an acronym of four open-source components.
- L= Linux: An open source operating system
- A= Apache: Widely used web server software
- M= MySQL: Popular open source database
- P=PHP: Server-side open source scripting language
These above-discussed components, supporting one another. Many popular websites and web applications run on LAMP stack, Example: Facebook.
MERN stack
MERN is a collection of JavaScript-based technologies:
- M=MongoDB: Popular NoSQL database
- E=Express: Light and portable web program framework
- R=React: A javascript library for building user interfaces
- N=Node.js: A server-side JavaScript run time
This stack currently in the huge demand as it is widely used to develop web applications.
MEAN stack
MEAN Stack Application Development is witnessing a growing trend in usage. MEAN is an abbreviation of:
- M = MongoDB: nosql Database
- E = Express: Easy to use light and portable web program framework
- A = Angular.js: Robust framework for developing HTML5 and JavaScript- web programs
- N = Node.is: a server-side JavaScript run time
What does a Full Stack Developer do?
As a full stack developer, you may be involved in following activities:
- Translate user requirements into the overall architecture and implementation of new systems
- Manage Project and coordinate with the Client
- Write backend code in Ruby, Python, Java, PHP languages
- Writing optimized front end code HTML and JavaScript
- Understand, create and debug database related queries
- Create test code to validate the applicaition against client requirement.
- Monitor the performance of web applications & infrastructure
- Troubleshooting web application with a fast and accurate a resolution
Full Stack Developer Salary
As a FULL STACK DEVELOPER, you are likely to earn$112000 per year.
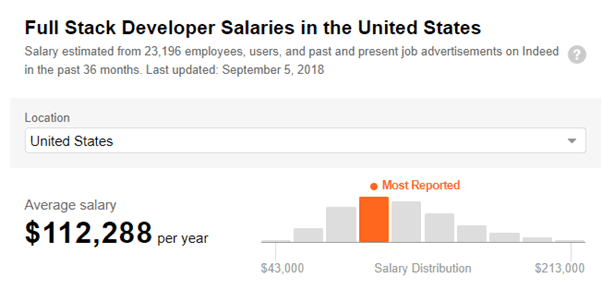
Full Stack Developer Salary
In this UK, the salary range is £40,000 – £70,000
What is the Market Trend happening in the arena of Full Stack Web Development?
The Full Stack Tutorial provides time to time updates regarding changes happening with the full stack technology. Here is the list of trends in full-stack web development.
- There is an increase in numbers of real-time web apps, progressive apps, mobile web development, and Vue JS functionality.
- JavaScript is coming up with many improvements
- Compatible extensions are emerging in the industry.


