- An Overview of AWS Machine Learning Tutorial
- Mapplet In Informatica | Purpose and Implementation of Mapplets | Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Spring Cloud Tutorial
- Azure IoT Hub Integration Tutorial | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Cloud Native Microservices Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- Azure Stream Analytics | Learn in 1 Day FREE Tutorial
- Azure Data Warehouse | Learn in 1 Day FREE Tutorial
- AWS Lambda Tutorial | A Guide to Creating Your First Function
- Azure Logic Apps Tutorial – A beginners Guide & its Complete Overview
- Azure Service Bus Tutorial | Complete Overview – Just An Hour for FREE
- Introduction to Azure Service Fabric Tutorial | Learn from Scratch
- Amazon CloudWatch Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- AWS Data Pipeline Documentation Tutorial | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE
- What is Azure App Service? | A Complete Guide for Beginners
- AWS Key Management Service | All You Need to Know
- Apigee Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- Kubernetes Tutorial | Step by Step Guide to Basic
- AWS SQS – Simple Queue Service Tutorial | Quickstart – MUST READ
- AWS Glue Tutorial
- MuleSoft
- Cloud Computing Tutorial
- AWS CloudFormation tutorial
- AWS Amazon S3 Bucket Tutorial
- Kubernetes Cheat Sheet Tutorial
- AWS IAM Tutorial
- Cloud Concepts And Models Tutorial
- Cloud Network Security Tutorial
- Azure Active Directory Tutorial
- NetApp Tutorial
- OpenStack tutorial
- AWS Cheat Sheet Tutorial
- Informatica Transformations Tutorial
- AWS vs AZURE Who is The Right Cloud Platform?
- How to Host your Static Website with AWS Tutorial
- VMware Tutorial
- Edge Computing Tutorial
- Cognitive Cloud Computing Tutorial
- Serverless Computing Tutorial
- Sharepoint Tutorial
- AWS Tutorial
- Microsoft Azure Tutorial
- IOT Tutorial
- An Overview of AWS Machine Learning Tutorial
- Mapplet In Informatica | Purpose and Implementation of Mapplets | Expert’s Top Picks | Free Guide Tutorial
- Spring Cloud Tutorial
- Azure IoT Hub Integration Tutorial | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE
- Cloud Native Microservices Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide
- Azure Stream Analytics | Learn in 1 Day FREE Tutorial
- Azure Data Warehouse | Learn in 1 Day FREE Tutorial
- AWS Lambda Tutorial | A Guide to Creating Your First Function
- Azure Logic Apps Tutorial – A beginners Guide & its Complete Overview
- Azure Service Bus Tutorial | Complete Overview – Just An Hour for FREE
- Introduction to Azure Service Fabric Tutorial | Learn from Scratch
- Amazon CloudWatch Tutorial | Ultimate Guide to Learn [BEST & NEW]
- AWS Data Pipeline Documentation Tutorial | For Beginners Learn in 1 Day FREE
- What is Azure App Service? | A Complete Guide for Beginners
- AWS Key Management Service | All You Need to Know
- Apigee Tutorial | A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- Kubernetes Tutorial | Step by Step Guide to Basic
- AWS SQS – Simple Queue Service Tutorial | Quickstart – MUST READ
- AWS Glue Tutorial
- MuleSoft
- Cloud Computing Tutorial
- AWS CloudFormation tutorial
- AWS Amazon S3 Bucket Tutorial
- Kubernetes Cheat Sheet Tutorial
- AWS IAM Tutorial
- Cloud Concepts And Models Tutorial
- Cloud Network Security Tutorial
- Azure Active Directory Tutorial
- NetApp Tutorial
- OpenStack tutorial
- AWS Cheat Sheet Tutorial
- Informatica Transformations Tutorial
- AWS vs AZURE Who is The Right Cloud Platform?
- How to Host your Static Website with AWS Tutorial
- VMware Tutorial
- Edge Computing Tutorial
- Cognitive Cloud Computing Tutorial
- Serverless Computing Tutorial
- Sharepoint Tutorial
- AWS Tutorial
- Microsoft Azure Tutorial
- IOT Tutorial

IOT Tutorial
Last updated on 18th Sep 2020, Blog, Cloud Computing, Tutorials
The Internet-of-Things (IoT) is gradually becoming one of the most prominent ICT technologies that underpin our society, through enabling the orchestration and coordination of a large number of physical and virtual Internet-Connected-Objects (ICO) towards human-centric services in a variety of sectors including logistics, trade, industry, smart cities and ambient assisted living. In a series of posts, I will be presenting a set of internet-of-things technologies and applications in the form of a series of tutorial nature posts. The present post is the first introductory one.
For over a decade after the introduction of the term Internet-of-Things, different organizations and working groups have been providing various definitions. For example:
- 1.ITU-T (as part of ITU-T Y.2060) defines IoT as: “A global infrastructure for the Information Society, enabling advanced services by interconnecting (physical and virtual) things based on, existing and evolving, interoperable information and communication technologies.”
- 2.The EU and more specifically the EU Projects Research Cluster in the Internet of Things (IERC) gives the following definition: “A dynamic global network infrastructure with self-configuring capabilities based on standard and interoperable communication protocols where physical and virtual “things” have identities, physical attributes, and virtual personalities and use intelligent interfaces, and are seamlessly integrated into the information network.”
Independently of the defintion, the exploitation and coordination of ICOs data and services is enabling a large number of novel human centric applications (e.g., Smart Cities & Communities, IoT in Healthcare, IoT in Manufacturing & Logistics, IoT Platforms & Ecosystems).
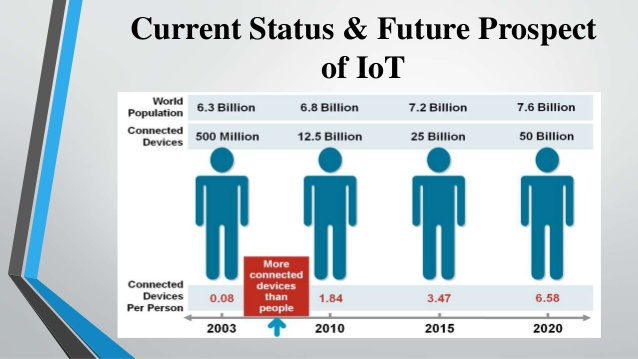
The IoT paradigm is enabling the vision of pervasive & ubiquitous computing, which was back in the 90’s envisaged to be a direct consequence of the rapid prolifration of computing devices. Indeed, following the era of super-computing (where a few fat computing systems served many users (many-to-one)) and the era of personal-computing (where each user had its own personal device (one-to-one), we are already in the era where each human individual enjoys services based on multiple internet-connected computing devices (such as laptops, mobile devices, multi-purpose sensors, home gateways). Hence, the IoT revolution is indeed propelled by the exponential increase of the number of connected devices, which is (according to CISCO) estimated to reach 50 billion devices in 2020. This will mean that each of the estimated 7.8 billion people on the planet will use on average more than six devices. Nowadays, we have already crossed the point (back in 2005) where the number of people around the globe was equal to the number of internet connected devices.
The proliferation of internet-connected-objects, empowers interactions both between devices and things, but also between things and people, thus providing unprecedented application opportunities. Indeed, people can directly connect to things (such as mobile phones, electronic health records etc..) via wearable sensors such as motion sensors, ECG (electrocardiogram) sensor and smart textiles. Likewise, things connect to each other e.g., as part wireless sensors networks (WSN), but also as part of a WSN’s interaction with other devices (gateways, mobile devices etc.). As another example car sensors, connect to intelligent transport systems and with sensors from other vehicles. These interactions are in most cases empowered by heterogeneous networking infrastructures, which provide ubiquitous high-quality connectivity, such as 4G/5G infrastructures.
How IoT Works?
The entire process starts with the devices themselves, such as smartphones, digital watches, electronic appliances which securely communicate with an internet of things platform. IoT platform collects and combines data from multiple devices and platforms and applies analytics to share the most valuable data with applications to address industry-specific needs.
Let’s start with a simple real-life example- Rajesh, in between his road trip notices some problem with the check engine light, however, he doesn’t know the intensity of the problem. The good part is that the sensor that triggers the check engine light monitors the pressure in the inner brake line. This sensor is one of the many sensors present in the car which constantly communicate with each other. A component called the diagnostic bus gathers the data from all these sensors and then passes it to the gateway in the car. The gateway collects and sorts the data from different sensors.
Before this connection to happen, the car’s gateway and platform must register with each other and confirm a secure communication. The platform keeps on constantly gathering and storing information from hundreds of cars worldwide, building a record in a database. The manufacturer has added rules and logic to the platform. The platform triggers an alert in his car, after sensing the brake fluid has dropped below the recommended level. The manufacturer then sends him an appointment for servicing of his car, and the car’s problem is rectified.
Prerequisites for learning IoT
Some basic knowledge of networking, databases, programming, and related technology and you are good to go.
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
Features of IoT
Here, in this part of IoT Tutorial, we will discuss the most important features of IoT in areas of artificial intelligence, sensors, connectivity. A brief review of these features is given below:
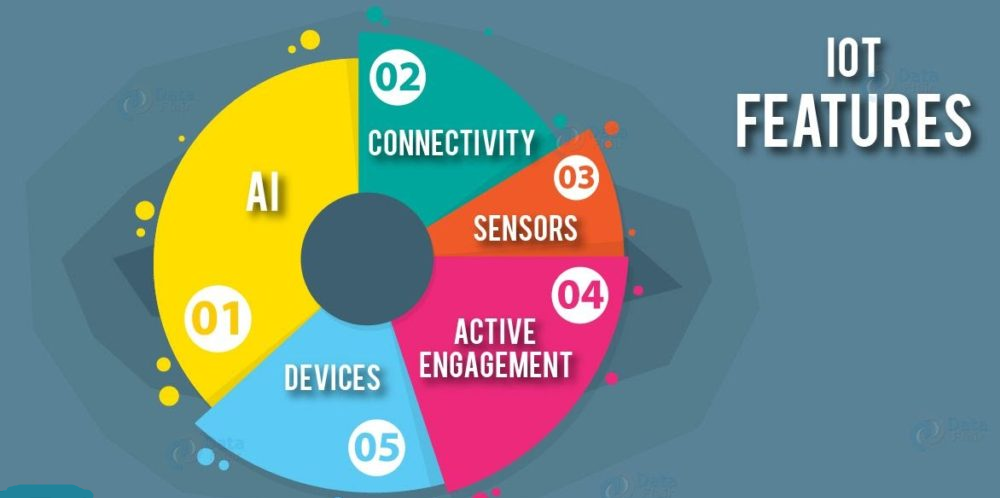
- AI– IoT technically makes things smart, meaning that it enhances different aspects of life through proper usage of that data, networks, and algorithms. This can range from something as simple as improving or enhancing your refrigerator by embedding it with sensors that automatically detect when milk and eggs run low, to placing an order with your choice of the grocer.
- Connectivity–The notion of networking doesn’t always have to restrict to large networks, it can also exist on a smaller and cheaper scale without compromising its efficiency. IoT comes into the picture and creates these small networks between its system devices.
- Sensors–The true essence of IoT would not hold effective without sensors. They are basically the reason and the crux of why this technology stands out. They play a major role in defining boundaries of IOT by converting it from a passive to an active network.
- Active Engagement–Today’s interaction between different connected technologies happens through passive engagement. IoT has set an example by bringing in active content, product, or service engagement.
- Devices–Devices are more powerful, cheaper and smaller over time, Internet of Things purposely makes use of small devices to deliver its scalability, versatility, and accuracy.
IoT Applications
In this IoT Tutorial, we learn Applications of Internet of Things. Let’s discuss them one by one:
- Healthcare Application: These days we have digital watches and fitness monitoring devices that have changed the ways of healthcare monitoring. People can now monitor their own health at regular intervals of time. These days if a person is being rushed to the hospital by an ambulance, his/her healthcare statistics are already given to the doctor, and the treatment gets started well in time. Also, data collected from different patients are now being put to use for the cure.
- Energy Applications: The energy rates have become paramount. All Individuals and organizations, both are searching for ways to reduce and control the consumption of energy. IoT provides a way to monitor energy usages not only at the appliance-level but also at the grid level, house-level or even at the distribution level. Smart systems such as Meters & Smart Grids are installed at various organizations to monitor energy consumption.
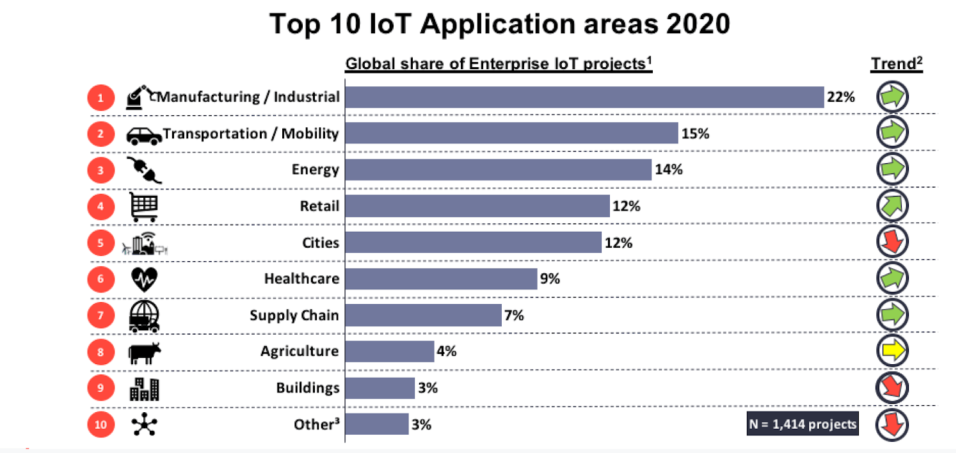
- Education Applications: IoT’s yet another great application lies in the field of education. IoT helps in fulfilling the gaps and loopholes in the education industry. It improves the quality of education being offered to students by optimizing the cost. It also improves administration and management by taking into consideration students’ response and performance.
- Government Applications: The smart city initiative by our government is an example of how efficient and big this technology is. Its incorporation in sectors like transportation, healthcare, armed forces, and security is commendable.
IoT − Advantages
The advantages of IoT span across every area of lifestyle and business. Here is a list of some of the advantages that IoT has to offer −
- Improved Customer Engagement − Current analytics suffer from blind-spots and significant flaws in accuracy; and as noted, engagement remains passive. IoT completely transforms this to achieve richer and more effective engagement with audiences.
- Technology Optimization − The same technologies and data which improve the customer experience also improve device use, and aid in more potent improvements to technology. IoT unlocks a world of critical functional and field data.
- Reduced Waste − IoT makes areas of improvement clear. Current analytics give us superficial insight, but IoT provides real-world information leading to more effective management of resources.
- Enhanced Data Collection − Modern data collection suffers from its limitations and its design for passive use. IoT breaks it out of those spaces, and places it exactly where humans really want to go to analyze our world. It allows an accurate picture of everything.
IoT − Disadvantages
Though IoT delivers an impressive set of benefits, it also presents a significant set of challenges. Here is a list of some its major issues −
- Security − IoT creates an ecosystem of constantly connected devices communicating over networks. The system offers little control despite any security measures. This leaves users exposed to various kinds of attackers.
- Privacy − The sophistication of IoT provides substantial personal data in extreme detail without the user’s active participation.
- Complexity − Some find IoT systems complicated in terms of design, deployment, and maintenance given their use of multiple technologies and a large set of new enabling technologies.
- Flexibility − Many are concerned about the flexibility of an IoT system to integrate easily with another. They worry about finding themselves with several conflicting or locked systems.
- Compliance − IoT, like any other technology in the realm of business, must comply with regulations. Its complexity makes the issue of compliance seem incredibly challenging when many consider standard software compliance a battle
Professional IoT Projects
- Guide to Help Support Urban Open Data Projects by Adi Gaskell. Smart cities thrive on open data, and now there is a guide available to help initiatives be successful with a focus on user engagement and data use.
- Pitfalls for Industrial IoT Projects by Sri Kanth. This post assesses potential pitfalls in Industrial IoT, including companies with high capacities, holdup in support, integration concerns, and cybersecurity.
- How to Start an Enterprise IoT Project by Jeffrey Lee. Understanding how IoT works and what it can do for your business is essential to starting an enterprise IoT project. Let’s look at everything you need to know!
- Who’s Really Running Your Industrial IoT Project by Marc Phillips. Who’s really in charge here? And how can we use accountability to drive success? Check out this post where we evaluate the key to Industrial IoT projects.
- 5 Reasons to Choose ASP.NET Core 3.0 for Your IoT Projects by Vivek Bagdai. Check out this post to learn more about the top five reasons why you should choose ASP.NET Core 3.0 for your next IoT project, including cross-platform support and a large and helpful community.
- Four Keys to Successful IoT Projects by Danielle Goodman. As IoT is a young field, it’s key to plan ahead when developing solutions. Keep your business case in mind, know your components, and plan ahead.
- 7 Common IoT Mistakes and How to Avoid Them by Jessica Califano. When it comes to adopting new IoT implementations in your business, it is best to learn from other’s mistakes and avoid these common flaws in IoT projects.
- Four Steps for Building a Profitable IoT Product by Dan Jamieson and Jeffrey Lee. Check out this post to learn the best practices for building a profitable IoT product, addressing business problems and challenges, the right team, and more.
- The Best IoT Platforms in 2019 – Based on Customer Reviews by Knud Lasse Lueth. In a new report, the top platforms for IoT projects were ranked based on customer reviews, with AWS, Microsoft, Oracle, Google, and Cisco IoT platforms ranking at the top.
- The Best IoT Platforms Today by Raj Ven. We explore the top platforms for professional IoT projects, as well as potential use cases and example products to help guide you through selecting the platform that’s right for you.
- Tips for Developing Successful IoT Applications by Arpita Sharma. A look at the top tips for developing successful IoT projects, focusing on proper planning, security, scalability options, and more.
- Learnovita Research: IoT and Devs by Tom Smith. A DZone Research Analyst sat down to talk with IoT experts about the role developers must play in the future of IoT, looking beyond programming languages.
- Ultimate List of 30 IoT Platforms You Must Try by Maryna Prokopets. This post takes a look at the top 30 IoT platforms for developing your projects, focusing on scalability, security, M2M connectivity, cloud, data, and more.
- Learnovita Research: IoT Use Cases by Tom Smith. Check out the best use cases for IoT and the future of connected devices, focusing on smart homes, agriculture, automation, and more.
- IoT Platform Selection Guide by Victor Polyakov. Need help selecting the IoT platform that’s right for you? We’ve got you covered by focusing on platforms from a technical, business, and partnership standpoint.
Customer Engagement Enhancement
IoT improves customer experience by automatically detecting problems and providing solutions. For e.g. as we discussed above, how an issue in Rajesh’s car was automatically detected by the sensors. The driver and the manufacturer will get notified about it. Till the time driver reaches the service station or a mechanic, the manufacturer will make sure that the faulty part is available at the service station and the problem is rectified.
Technical Optimization
If the technology is great, the experience is bound to be great. IoT has played a major part in improving technologies and making them better. Like in the above example, the manufacturer collected the data from different car sensors and analyzed it to improve its design.
Reduced Waste
With the latest technology, IoT provides real-time insights on crucial problems leading to effective decision making & management of resources. For example, if a manufacturer finds fault in engines of multiple cars, it might give him an insight on major fault and he can track the manufacturing plant of those engines and can rectify the issue with manufacturing belts.
Conclusion
This IoT tutorial has covered every detail that a beginner needs to know. This IoT tutorial covered all the fundamentals of IoT to get a solid grasp of the topic. It’s now time to take one step ahead: Learn about the working of IoT and amaze yourself with its operational procedure.