- Most Popular SAP SuccessFactors Interview Questions and Answers
- [BEST & NEW] Business Management Interview Questions and Answers
- [ STEP-IN ] SAP BusinessObjects Cloud Interview Questions and Answers
- 80+ [REAL-TIME] Base Sas Interview Questions
- 100+ SAP Bodi Interview Questions & Answers
- [ TO GET HIRED ] PowerApps Interview Questions and Answers
- Must-Know [LATEST] Denodo Interview Questions and Answers
- [BEST & NEW] SAP Business One Interview Questions and Answers
- [FREQUENTLY ASK] SAP BI ABAP Interview Questions and Answers
- [BEST & NEW] Hyperion Planning Interview Questions and Answers
- 50+ Best SAP CS Interview Questions and Answers
- Get [LATEST] Boxi Interview Questions and Answers
- 50+ Best SAP E-Recruitment Interview Questions and Answers
- Get [LATEST] SAP SuccessFactors LMS Interview Questions and Answers
- 50+ Best SAP EHS Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP ECM Interview Questions and Answers [ TOP & MOST ASKED ]
- SAP FSCM Interview Questions and Answers [ FRESHERS ]
- Must-Know [LATEST] SIEBEL Business Analyst Interview Questions and Answers
- [FREQUENTLY ASK] Looker Interview Questions and Answers
- [BEST & NEW] SAP GTS Interview Questions and Answers
- 40+ REAL-TIME Anaplan Interview Questions and Answers
- [BEST & NEW] SAP BPC Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Adobe Forms Interview Questions and Answers [SCENARIO-BASED ]
- Most Popular Alteryx Interview Questions and Answers [ SOLVED ]
- 50+ REAL-TIME SAP GRC Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP APO Interview Questions and Answers [ STEP-IN ]
- [FREQUENTLY ASK] SAP PM Interview Questions and Answers
- Top 30+ Splunk Admin Interview Questions and Answers
- 50+ Best Hyperion Financial Management Interview Questions and Answers
- Get SAP QM Interview Questions and Answers [BEST & NEW]
- Best SAS BI Interview Questions and Answers [LEARN NOW]
- [ TOP & MOST ASKED ] SAP ABAP on HANA Interview Questions and Answers
- Top SAP FIORI Interview Questions and Answers
- [50+] SAP FICA Interview Questions and Answers [ TO GET HIRED ]
- 30+ REAL-TIME Crystal Reports Interview Questions and Answers
- Browse [LATEST] SAP PI Interview Questions and Answers
- [ TOP & MOST ASKED ] SAP UI5 Interview Questions and Answers
- 30+ Best Jaspersoft Interview Questions [FREQUENTLY ASK]
- Business Objects Interview Questions and Answers
- SAS Interview Questions and Answers
- Splunk Interview Questions and Answers
- MSBI Developer Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP FICO Interview Questions and Answers
- SSAS Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP CRM Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP HR Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Workflow Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP PP Interview Questions and Answers
- Dimensional Data Modeling Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Bank Analyzer Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP ESS MSS Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP BI Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP WM Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP BI/BO Interview Questions and Answers
- Advanced SAS Interview Questions and Answers
- Appian Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP AFS Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Retail Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Security Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP COPA Interview Questions and Answers
- Pentaho Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Material Management Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP BI/BW Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP SD Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP HANA Interview Questions and Answers
- Cognos Interview Questions and Answers
- QlikView Interview Questions and Answers
- MicroStrategy Interview Questions and Answers
- Business Analyst Interview Questions and Answers
- Qlik Sense Interview Questions and Answers
- Talend Interview Questions and Answers
- ETL Testing Interview Questions
- SSRS Interview Questions and Answers
- Tally Interview Questions and Answers
- OBIEE Interview Questions and Answer
- MSBI Interview Questions and Answers
- Power BI Interview Questions and Answers
- Tableau Interview Questions and Answers
- Most Popular SAP SuccessFactors Interview Questions and Answers
- [BEST & NEW] Business Management Interview Questions and Answers
- [ STEP-IN ] SAP BusinessObjects Cloud Interview Questions and Answers
- 80+ [REAL-TIME] Base Sas Interview Questions
- 100+ SAP Bodi Interview Questions & Answers
- [ TO GET HIRED ] PowerApps Interview Questions and Answers
- Must-Know [LATEST] Denodo Interview Questions and Answers
- [BEST & NEW] SAP Business One Interview Questions and Answers
- [FREQUENTLY ASK] SAP BI ABAP Interview Questions and Answers
- [BEST & NEW] Hyperion Planning Interview Questions and Answers
- 50+ Best SAP CS Interview Questions and Answers
- Get [LATEST] Boxi Interview Questions and Answers
- 50+ Best SAP E-Recruitment Interview Questions and Answers
- Get [LATEST] SAP SuccessFactors LMS Interview Questions and Answers
- 50+ Best SAP EHS Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP ECM Interview Questions and Answers [ TOP & MOST ASKED ]
- SAP FSCM Interview Questions and Answers [ FRESHERS ]
- Must-Know [LATEST] SIEBEL Business Analyst Interview Questions and Answers
- [FREQUENTLY ASK] Looker Interview Questions and Answers
- [BEST & NEW] SAP GTS Interview Questions and Answers
- 40+ REAL-TIME Anaplan Interview Questions and Answers
- [BEST & NEW] SAP BPC Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Adobe Forms Interview Questions and Answers [SCENARIO-BASED ]
- Most Popular Alteryx Interview Questions and Answers [ SOLVED ]
- 50+ REAL-TIME SAP GRC Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP APO Interview Questions and Answers [ STEP-IN ]
- [FREQUENTLY ASK] SAP PM Interview Questions and Answers
- Top 30+ Splunk Admin Interview Questions and Answers
- 50+ Best Hyperion Financial Management Interview Questions and Answers
- Get SAP QM Interview Questions and Answers [BEST & NEW]
- Best SAS BI Interview Questions and Answers [LEARN NOW]
- [ TOP & MOST ASKED ] SAP ABAP on HANA Interview Questions and Answers
- Top SAP FIORI Interview Questions and Answers
- [50+] SAP FICA Interview Questions and Answers [ TO GET HIRED ]
- 30+ REAL-TIME Crystal Reports Interview Questions and Answers
- Browse [LATEST] SAP PI Interview Questions and Answers
- [ TOP & MOST ASKED ] SAP UI5 Interview Questions and Answers
- 30+ Best Jaspersoft Interview Questions [FREQUENTLY ASK]
- Business Objects Interview Questions and Answers
- SAS Interview Questions and Answers
- Splunk Interview Questions and Answers
- MSBI Developer Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP FICO Interview Questions and Answers
- SSAS Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP CRM Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP HR Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Workflow Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP PP Interview Questions and Answers
- Dimensional Data Modeling Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Bank Analyzer Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP ESS MSS Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP BI Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP WM Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP BI/BO Interview Questions and Answers
- Advanced SAS Interview Questions and Answers
- Appian Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP AFS Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Retail Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Security Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP COPA Interview Questions and Answers
- Pentaho Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP Material Management Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP BI/BW Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP SD Interview Questions and Answers
- SAP HANA Interview Questions and Answers
- Cognos Interview Questions and Answers
- QlikView Interview Questions and Answers
- MicroStrategy Interview Questions and Answers
- Business Analyst Interview Questions and Answers
- Qlik Sense Interview Questions and Answers
- Talend Interview Questions and Answers
- ETL Testing Interview Questions
- SSRS Interview Questions and Answers
- Tally Interview Questions and Answers
- OBIEE Interview Questions and Answer
- MSBI Interview Questions and Answers
- Power BI Interview Questions and Answers
- Tableau Interview Questions and Answers

Business Analyst Interview Questions and Answers
Last updated on 05th Oct 2020, Blog, Business Analytics, Interview Question
A business analyst works as a bridge between different stakeholders in an organization. He connects with the different stakeholders of an organization to clarify and finalize the requirements, helps the project team in project planning, designing and finally validating the developed components. He is the person who possesses adequate domain knowledge and can sort the business needs amongst the stakeholders who belong to different domains.
1. Name some of the documents that a business analyst uses to handle?
Ans:
Following are some of the common documents that a business analyst use to handle:
- Project vision document
- Use cases
- Requirement Management Plan
- User stories
- Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- Business Requirement Document
- System Requirement Specification (SRS)/ System Requirement Document (SRD)
- Test case
- Functional Requirement Specification (FRS)/ Functional Specification Document (FSD)
2. What is SRS and what are its key elements?
Ans:
A System Requirements Specification (SRS) or a Software Requirements Specification is a document or set of documents that describe the features of a system or software application. It includes a variety of elements which define the intended functionality required by the stakeholders and customer to satisfy the end users.
In addition to that, an SRS provides a high-level idea of the system and its behavior, the main supported business processes, the assumptions and the key performance parameters for the system. The key elements of an SRS are:
- Scope of Work
- Functional Requirements
- Non-Functional Requirements
- Dependencies
- Data Model
- Assumptions
- Constraints
- Acceptance Criteria
3. What is a requirement?
Ans:
A requirement is a targeted solution to achieve specific business goals or objectives. It is an input to various stages of SDLC. This is a basis of a project which must be validated by the stakeholders and business users before implementation. Besides that, every requirement needs to be properly documented for future reference purposes.
4. What is a Use case?
Ans:
A use case is a diagrammatic representation of a system which describes how a user uses a system to accomplish a goal. It is an integral part of software engineering and software modelling technique which defines the targeted features and the resolution of any possible errors which a user may encounter.
5. What are the steps that you need to follow to design a use case?
Ans:
The steps in designing use cases are:
- Identify the users of the system
- Creating a user profile for each category of users. This includes all roles that the users may play and are relevant to the system.
- Identify essential goals associated with each role. Also, identifying the significant roles.
- Creating use cases for every goal associated for a use case template. This also includes maintaining the same abstraction level for the entire use case. Higher level use case steps are considered as goals for the lower level.
- Structuring the use cases
- Reviewing and validating the users
6. What is Scope creep and how can you avoid scope creep?
Ans:
Scope creep, or requirement creep is a term that relates to the uncontrolled changes or deviation in the project’s scope within the same resource range for example within same schedule and budget of the project. It’s an indication of poor project management and a viable risk to a project. Some of the possible causes of scope creep are:
- Poor communication between the project’s stakeholders
- Improper documentation of the project’s requirements
Scope creep could be avoided by:
- Clear documentation about the project scope
- Following proper change management
- Prior intimation about the effects of the changes to the associated parties
- Proper documentation of the new requirements in the project log
- Refrain from Gold Plating which means adding extra features to the existing functionalities
7. What is BRD? How is it different from SRS?
Ans:
A Business Requirements Document (BRD) is a formal contract between the customer and the organization for a product.
The difference between BRD and SRS are as follows:
| BRD | SRS |
|---|---|
| It is a high-level functional specification of the software. | It is a high level functional and technical specification of the software |
| It is a formal document to describe the requirement provided by the client (written, verbal) | It describes the functional and non-functional requirements of the software to be developed |
| The Business Analyst creates it after their direct interaction with the clients | The System Architect creates it as it needs technical expertise. Though sometimes Bas too can create it. |
| It is derived based on the requirements and client interaction | It is derived from the BRS |
8. What is Gap Analysis?
Ans:
Gap Analysis is a technique to analyze the gap between the existing system and functionalities, and the targeted system. Here gap means the amount of task or change that may be required to get the intended result. It’s a performance level comparison between the present and the proposed functionalities.
9. What is requirement prioritization? What are the different techniques used for it?
Ans:
Requirements prioritization is the process to allocate requirements based on the business urgency to different phases, schedule, cost, etc.
There are various techniques which are used for requirements prioritization:
- MoSCoW Technique
- Requirements Ranking Method
- 100-dollar method
- Kano Analysis & More
- Five Whys
10. What is the fundamental difference between a requirement and need in a business analysis perspective?
Ans:
Needs are high-level definitions of the future goals of a business. Whereas, Requirements are the representation of the detailed description of that business needs.
11. What are non-functional requirements and how do you capture them?
Ans:
Non-functional requirements represent the performance level characteristics like how fast it can respond, how smooth is a user interface, security, etc. of the application under development (AUD).
No functional requirements are captured in the SRS document in its designated section.
12. What are the skills that a business analyst must possess?
Ans:
We can broadly categorize the skills of a business analyst in three types:
- Fundamental skills
- Technical skills
- Business Analysis skills
For each of the above categories a business analyst should possess some skills as mentioned below:
| Skill category | Skills |
|---|---|
| Fundamental skills | Problem Solving CommunicationManagement skillsResearch |
| Technical skills | IT skills like MS Office, Operating systems, Programming languages, Knowledge of database, SDLC knowledge, Domain knowledge |
| Business Analysis skills | Requirement ElicitationDocumentation Decision makingCreativity Analytical skills |
Subscribe For Free Demo
Error: Contact form not found.
13. How will you define a good quality requirement as a business analyst?
Ans:
We can measure the quality of a requirement using the SMART rule. As per this rule, a good quality requirement should be:
Specific: The requirement should be specific and could be documented properly
Measurable: Different parameters can measure the success criteria of the requirement
Attainable: The requirement should be feasible within the scope of the given resources
Relevant: The requirement must be in line with the project’s business case
Timely: The requirement should be communicated early in the project lifecycle
14. Which documents are used to capture non-functional requirements?
Ans:
There are two documents that are used to capture non-functional requirements, and they are:
- SDD (System Design Document)
- FRD (Functional Requirement Document)
15. What is alternate flow in use case diagrams?
Ans:
It is an alternative solution or activity in a use case that should be followed in case of any failure in the system.
16. Define Personas?
Ans:
Personas represents User-Centered Design methodologies. To enable an application capable of performing on a demographic basis, fictional characters are conceptualized by the business analysts and based on their possible demographic specific behavior scenarios are created during design.
17. What is an activity diagram and what are the important elements of it?
Ans:
An activity diagram is a visual representation of the workflow of a business use case. This diagram shows various activities that take place in an organization in different departments like HR, Sales, Accounts, etc. The activity diagram highlights the differences in the departments. The important elements in the Activity diagram are initial nodes, activities, control flows, decisions, a fork, guard conditions, join and end nodes.
18. What is UML modelling?
Ans:
UML stands for Unified Modelling Language. It is a standard that the industry uses for documenting, constructing and visualizing various components of a system. This modelling standard is primarily used for software development. However, it is also used for describing job roles, organizational functions, and business processes. Some of the important diagrams that BAs use as part of UML are the class diagram, state diagrams and use cases.
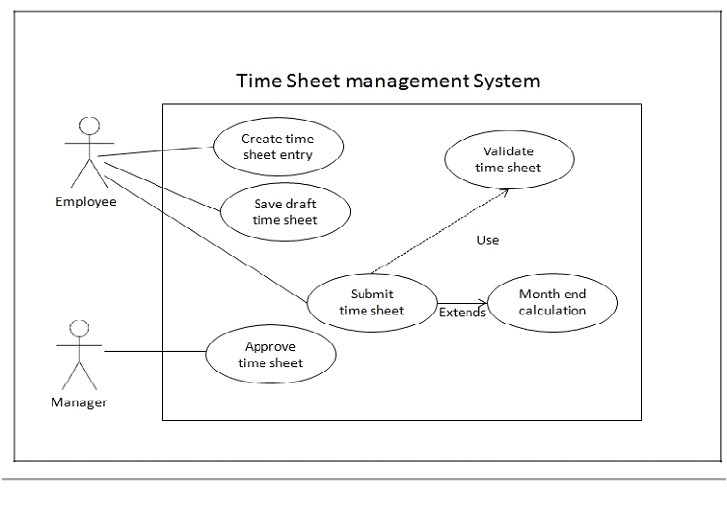
19. What are the best practices to follow while writing a use case?
Ans:
Some of the best practices to write a use case are as follows:
- To become a valid use case, the use case must provide some value back to the actor or stakeholder.
- The functional and non-functional requirements must be captured appropriately in the use case.
- The use case must have one or more alternate flow along with the main flow.
- The use case should only describe what the system does and not how it is done which means it will not describe the design. It will act as a black box from the viewpoint of an actor.
- The use case should not have any, i.e. it should be stand alone.
20. What is the difference between exception flow and alternate flow?
Ans:
Alternate flow are the alternative actions that can be performed apart for the main flow and can be considered as an optional flow.
Exception flow is the path traversed in case of any exception or error.
21. Do you think a business analyst should be involved in testing?
Ans:
Yes. Because a business analyst understands the overall system requirements and challenges associated with it very well. Hence, he can be instrumental during the testing phase to run it appropriately and resolve any system related query.
22. What does INVEST stand for?
Ans:
INVEST stands for –
- Independent
- Negotiable
- Valuable
- Estimable
- Sized Appropriately
- Testable
It can assist project managers and technical team to deliver quality products/services.
23. What is Pareto Analysis?
Ans:
Pareto Analysis which is also known as 80/20 rule is a decision-making technique. It is a useful technique for defect resolution and quality control. As per this analysis rule, 20 % causes 80 % effects in a system, which is why it is named as 80/20 rule.
24. What is BPMN and what are its basic elements?
Ans:
BPMN is the Business Process Model and Notation. It is a graphical representation of business processes.
There are five basic elements of BPMN, and they are –
- Flow Objects
- Data
- Connecting Objects
- Swimlanes
- Artifacts
25. What is Kano analysis?
Ans:
Kano Analysis is used to analyze a system regarding its requirements to identify its impact on customers’ satisfaction.
26. What are the different types of actors you know in use case diagrams?
Ans:
There are mainly two types of actors can be depicted in a Use case-
- Primary actors – It starts the process
- Secondary actors – It assists the primary actor
Moreover, we can categorized actors into four types :
- Human
- System
- Hardware
- Timer
27. What are the different types of the gap that a business analyst can encounter during gap analysis?
Ans:
There are mainly four types of gap –
Performance Gap – The difference between expected performance and the actual performance
Product/Market Gap – The gap between budgeted sales and actual sales is termed as product/market gap
Profit Gap – The variance between a targeted and actual profit of the company.
Manpower Gap – The gap between the required number and quality of workforce and actual strength in the organization
28. What is Benchmarking?
Ans:
Benchmarking is about measuring the performance of an organization to compete in the industry. In this process, a company may measure its policies, performance, rules and other measures.
29. How do you decide that as a business analyst you have gathered all the requirements?
Ans:
We can conclude that all the requirements are gathered only when –
- It is validated and approved by the business users.
- The requirements are appropriately aligned with the project’s business requirements.
- The requirements can be implemented with the available resources.
- All the key business stakeholders are aligned with the elicited requirements.
30. How do you perform requirement gathering?
Ans:
The requirement gathering process is generally divided into multiple steps which are agnostic to the SDLC cycle. Each step involves:
- specific tasks to perform
- principles to follow
- documents to produce
The steps are as follows:
Step 1: Gather Background Information – This may include collecting background information about the project, analyzing any potential risk associated with the project. Techniques like PESTLE analysis, Porter’s Five forces framework could be used for this purpose.
Step 2: Identify Stakeholders – They are the decision makers of a project and approver for requirements and priorities. Stakeholders may range from project owners to senior managers, end users, and even competitors.
Step 3: Discover Business Objectives – This is to understand the business needs of the project before going deep into the project. SWOT analysis, Benchmarking, analyzing business objectives SMART and listing business objectives are some of the techniques used for this purpose.
Step 4: Evaluate Options – This is to identify the options to achieve business objectives. Impact analysis, Risk analysis, Cost-benefit analysis are some of the methods which are used for this purpose.
Step 5: Scope Definition – A scope is a project development goal which is set based on the business objectives. A scope definition document is used to detail the goals for each phase of a project.
Step 6: Business Analyst Delivery Plan – Based on the project scope, stakeholders availability and project methodology a document called business analyst is created at this step. The document provides information on deliverables with their timeline.
Step 7: Define Project Requirements – In this step, two types of documents are used – Functional requirement document and Non-functional requirement document. Based on the development methodology to be used in the project the business analyst needs to clarify the requirements with the stakeholders by interviewing them on the requirements and get the sign off on the same.
Step 8: Support Implementation through SDLC – This is the technical implementation step of the requirements where a business analyst gets involved with different teams. This includes coordinating with the development team and testing team to ensure requirements are implemented as expected and appropriately tested against all the possible business scenarios. They also need to handle the change request which may arise from the stakeholders at the later point of time.
Step 9: Evaluate Value Added By Project – This is the continuous evaluation of the project to evaluate whether the business objectives implementation correctly meets the business needs outcome and timeline.
31. Why is it necessary for a business analyst to get involved during the implementation of requirements?
Ans:
Gaining domain knowledge and providing an analytical solution are the two major criteria of a business analyst. Hence, during actual implementation of a requirement or use case a business analyst can help to resolve many business strategies related problems that may arise during the implementation stage. On the contrary, they can learn from the problems which may help them to provide the solution in similar scenarios and also help to gain their domain knowledge.
32. What are the problems that a business analyst may face?
Ans:
From the initiation to post implementation of a project a business analyst may face the following problems –
- Employees related issues
- Technology related problems
- Access related
- Business policies related issues
- Business model errors
33. Explain requirement elicitation strategy?
Ans:
Requirement elicitation is the process to collect all the requirements related to a system from the end users, customers, and stakeholders. As per the BABOK guide, there are nine methods which can be used as part of requirement elicitation process, and these are:
- Brainstorming
- Interviews
- Observation
- Document Analysis
Focus Groups - Requirements Workshops
- Interface Analysis
- Survey or Questionnaire
- Prototyping
34. What is Business Model Analysis?
Ans:
Business Model Analysis is a technique to analyze whether a business is viable and valuable regarding social, economic and other perspectives. The business model analysis provides the foundation for any required business model change and innovation for an organization.
35. Do you think the role of a Business Analyst is a need for a project?
Ans:
Yes, because the role of a Business analyst is extremely beneficial from the kick-off to the implementation of a project. Here are the top 5 reasons:
- During the project kick-off session, there are high possibilities that some technical queries come up from stakeholder and clients. As we don’t involve the technical project team during this phase and immediate answering is essential, a business analyst may play a pivotal role to answer those queries.
- The next phase after the kick-off session essentially involves some gap analysis, business process analysis, documentation, SOW review, project scheduling and of course preparing requirement specification documents.
- During the development and testing phase, a business analyst can play a significant role to resolve any requirement related queries from the project teams. Besides that, he can validate whether the requirements are correctly implemented and tested considering different functional and non-functional scenarios.
- In a waterfall model, new requirements or modification of requirements can be asked from stakeholders considering changing business needs. In this case a business analyst is the person who can handle this change request with proper validation and analysis.
36. What is the difference between Business analysis and Business Analytics?
Ans:
The key difference between Business analysis and Business analytics is the first one is more functions and process related whereas the second one is data related.
Business analysis – recognizes business needs and determines the solutions to those problems. Tools and techniques like SWOT, PESTLE, CATWOE, MOST, FIVE WHY, etc. are used for business analysis.
Business analytics – handles data and analyze data to get insights into a business. Finally, it generates reports. Mainly four types of business analytics are used, and they are – descriptive analytics, decisive analytics, prescriptive analytics, and predictive analytics Tools and technologies like Big data, BI is used for this purpose.
37. What is process design?
Ans:
Process design is a way that helps a business to analyze the challenges in business and to find an effective solution for those. Through Process design workflows are created to get the best possible outcome in the shortest time.
38. What are the effective skills to solve any problem as a business analyst?
Ans:
- Leadership skill
- Excellent communication skill
- Problem analysis skill
- Technical knowledge
- Domain knowledge
39. What is the Agile Manifesto?
Ans:
Agile Manifesto is a software guide about the Agile development principles which ensure iterative solutions.
40. What are the essential qualities of an Agile BA?
Ans:
An Agile BA must be able to:
- The BA is expected to collaborate with product owners and developers to elicit requirements. The BA also must work to develop realistic functional requirements.
- The BA must do requirement elicitation in an iterative way
- The BA must make requirement specifications, data models and business rules as much lightweight as possible.
- The BA must be technically sound so that he can understand how the components of the system interact with each other. Besides that, he must understand the agile terminologies as he acts as the middleman between the customer and the project team.
- The BA must concentrate on the just-enough requirement and test criteria to meet the just in time delivery goal of an agile project.
41. When should you use the Waterfall model instead of Scrum?
Ans:
If the requirement is simple and specific, we should go for Waterfall model instead of Scrum.
42. What are the four key phases of business development?
Ans:
The four key phases of business development:
- Forming
- Storming
- Norming
- Performing
43. What do you know about Kanban?
Ans:
Kanban is a tool which helps the agile team to visually guide and manage the work as it progresses through the process. Besides, it works as a scheduling system in Agile just-in-time production. The Kanban board is used to describe the current development status.
44. Mention about some of the most important agile metrics
Ans:
The following are some important agile Matrices
- Velocity – This is used to track the progress of a project
- The sprint burndown matric – This helps to track the work done with the sprint.
- The priority of the work
- Work category allocation – This metric helps to get an idea about the priority of the work and work category allocation.
- The cumulative flow diagram – the uniform flow of work can be checked through this diagram of cumulative flow. Here the x-axis represents time and the y-axis stands for the number of efforts.
- Defect removal awareness – This helps to produce quality products.
- Business value delivered – This is used to estimate the work efficiency of the team. It associates 100 points for measurement.
- Time coverage – It estimates the amount of time invested in coding during testing. It is the ratio of the number of lines of code called by the test suite to the number of relative lines of codes.
- Defect resolution time – This is the turnaround time for detecting and fixing bugs. There processes involved in for this purpose are:
-
- bug fixing
- eliminating the bug
- Scheduling a fix
- Defect fixation
- Handover of the resolution report
45. Explain the term ‘increment’?
Ans:
Increment refers to the sum of all the product backlog items completed in a sprint. The new increment value also includes the increment of the previous sprints.
46. What are the different types of Agile methodologies?
Ans:
Some of the well-known agile methodologies are:
- Scrum
- Lean software development and Extreme Programming (XP)
- Feature-driven development (FDD)
- Crystal Methodology
- DSDM (Dynamic Software Development Method)
47. Is there any difference between incremental and iterative development?
Ans:
Yes.
In an iterative development software development happens without any interruption. Here the software development cycles which typically consist of sprint and release are repeated till the final product is obtained. Whereas, in an incremental model, software development follows the product design, implementation, and testing incrementally until the product is finished. Hence, it involves development and maintenance.
48. Difference between extreme programming and scrum?
Ans:
Scrum and extreme programming both follow iterations which are known as sprints. However, the sprints in a Scrum process last up to two weeks to one month long whereas in extreme programming (XP) teams the iteration lasts for one or two weeks. Extreme programming is more flexible than Scrum as Scrum does not allow any change in during iterations. Though we have categorized the above business analyst interview questions based on the experience levels, however, it could be a mixed and match for any career level depending on the organization and their requirement.
49. How will you be able to handle the changes to requirements?
Ans:
This is a logical question asked in an interview. As a Business Analyst, the first task will be to get a signature on a document by the user which states that after a point of time no changes to the requirements are accepted.
In a few cases, if the changes to the requirements are accepted then:
- Firstly, I will note down the changes made to the requirements and will prioritize them.
- I will also go through those changes and find out the impact of them on the project.
- I will calculate the cost, timeline, and resources required to cover the impact of change requirements on the project.
- And will make sure that whether those changes affect or create gaps to functional design documents, testing or coding.
50. Can you name the tools that are helpful for business analysis?
Ans:
The process performed by a Business Analyst is termed as Business Analysis. The tools used include Rational tools, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft Word, PowerPoint, MS Project, ERP systems.
51. What makes you unique from others?
Ans:
The answer to this question will test your experience, skills, and individuality. You can answer like, “I am technically sound and can make a strong relationship with the customer. With this unique combination, I can use my knowledge and information to build a user-friendly environment”.
52. What are the tasks that are not part of a Business Analyst’s job?
Ans:
Business Analyst is not part of the enlisted tasks:
- Should not intend to organize the project team meetings.
- Should not bother regarding the risks and issues tracker of a project.
- Should not perform activities like testing (executing the TC’s), coding or programming.
53. Differentiate between a Risk and an Issue?
Ans:
‘Risk’ is nothing but a problem or something that can be predicted earlier so that some improvement plans are used to handle them. Whereas, an ‘Issue’ means the risk that had happened or occurred.
The role of a BA is not to solve the issue instead should suggest some plans to control the loss/damage caused. And this should be marked as a precautionary measure for other projects.
Example: On some roads, few caution boards are stating that “Road under repair, take diversion”. This is called Risk.
If we travel through the same route which is under construction, then this may cause some damage to the vehicle. This is called an issue.
54. List out the documents that are used by a BA in a Project?
Ans:
As a Business Analyst we deal with various documents like Functional Specification document, Technical Specification document, Business Requirement document, Use Case diagram, Requirement Traceability Matrix, etc.
55. What is a misuse case?
Ans:
Misuse case is defined as an activity performed by a user which in turn causes system failure. It may be malicious activity. As it is misguiding the system function flow, it is termed as a misuse case.
56. How can you handle and manage the difficult stakeholders?
Ans:
Dealing with difficult stakeholders is a major task for a BA. There are many ways to handle such situations.
Important points to be noted among them are listed below:
- Identify that difficult stakeholder among the group of stakeholders, listen and concentrate on their point of view with patience. Be polite to them and do not close off the conversation immediately with such people.
- Generally, a stakeholder will be difficult because they are not comfortable with a few things in the project. So listen to them and diplomatically answer such difficult stakeholders.
- Find out a way to meet them personally and have a one on one discussion. By this, you can show your commitment to them.
- Try to find out and resolve their motivations like are they worried about the budget of the project or Curious about the project whether it is turning exactly as per their vision etc.
- Continuously engage such difficult stakeholders and make them understand that their contribution is much value for the project.
57. When can a BA say that the requirements are done?
Ans:
Requirements are considered as complete when they satisfy the below criteria:
- Requirements should be aligned with the objectives of a business. It means that the views of business stakeholders should align with the needs to be built for the project.
- All the possible views and ideas of key stakeholders are to be extracted.
- The quality of the requirements should meet/satisfy the organization’s set of criteria through which the quality of the requirements is tested.
- One can say that the requirements are complete when they could be done within the possible available resources.
- All the stakeholders of the project should be in consent with the gathered requirements.
58. What are the various diagrams that a BA should know about?
Ans:
There are various types of diagrams that BA’s use in their work.
Few important diagrams among them are,
Activity Diagram: This represents the flow from one activity to the other activity. Activity refers to the operation of the system.
Data Flow Diagram – Graphical representation of the flow of data into and out of the system. This diagram represents how data is shared between organizations.
Use case Diagram: This diagram describes the set of actions that systems perform with one or more actors (users) of the systems. Use Case diagram is also called as a Behavioral diagram.
Class Diagram: This is the structural diagram that represents the structure of the system by showing its classes, objects, methods or operations, attributes, etc. A class diagram is the main building block for detailed modeling which is used for programming.
Entity Relationship Diagram – ER Diagram is the graphical representation of entities and the relationships between them. This is a data modeling technique.
Sequence Diagram: Sequence diagram describes the interaction between the objects like how they operate and in what time sequence the messages flow from one object to the other.
Collaboration Diagram – Collaboration diagram represents the communication that occurs between the objects by showing the messages flow among them.
59. Brief the difference between the Fish model and V model?
Ans:
The fish model consumes more time in dealing with requirements when compared to the V model. Even the Fish model is a bit more expensive than the V model. Generally, a Fish model is preferred when there are no uncertainties in the requirements.
60. Which model is better than the Waterfall model and Spiral Model?
Ans:
Selecting the life cycle model for a project is based on its type, scope, and limitations. It is solely dependent on the culture of the organization, its terms, and conditions, policies, a process of developing the system, etc.
61. Differentiate an alternate flow and exception flow of a use case diagram?
Ans:
Basic flow represents the activities carrying out in order as required by the business. Alternate flow represents actions that are performed apart from the basic flow and also be considered as an optional flow. Whereas Exception flow is executed in a case or any errors.
Example: When we open a login page of any website, there is a link “forgot password” to retrieve the password. This is called an alternate flow.
In the same login page if we enter the correct username and password, sometimes we get an error message stating “404 error”. This is called the exception flow.
62. What does INVEST mean?
Ans:
INVEST means Independent, Negotiable, Valuable, Estimable, Sized Appropriately, Testable. With this INVEST process, the project managers and technical teams can deliver the good quality of the product and can provide quality service.
63. What all steps are included in developing a product from a basic idea?
Ans:
In the process of developing a product from an idea, there are many steps to be followed as enlisted below,
Market Analysis: This is a business plan through which the characteristics of a market have been studied, like how the market changes and behaves dynamically.
SWOT Analysis: This is a process through which the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of an organization are identified.
Personas: These are typical users of websites or intranet who represent the goals and characteristics of various large groups of users. Personas replicate the real users in functional design.
Competitor Analysis: Evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of outside competitors.
Strategic Vision and Feature set: The process of developing the goals in present and planning to achieve the same in the future by moving towards the vision.
Prioritize Features: All the features of the product that is to be developed are prioritized by the product management to help the development team.
Apart from the above-mentioned steps, there are furthermore terms involved in the process of developing a product. They are Use case, SDLC, Storyboards, Test Cases, Monitoring, and Scalability.
64. What is the purpose of the Requirement Traceability Matrix?
Ans:
Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) is used to record all the requirements given by a client, so the purpose of RTM is to ensure that all of the mentioned requirements are met.
65. What is business process modeling?
Ans:
Business process modeling is a part of business process management, which is used to improve the business process. It is the representation of an organization’s business process.
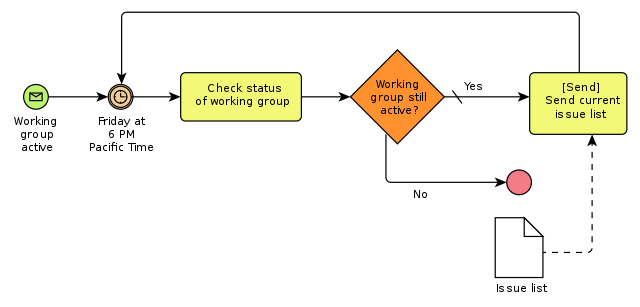
66. List the benefits of business process modeling.
Ans:
- It is used to picture a clear understanding of the business processes.
- It provides consistency and control over the processes of the project.
- It is used to identify and eliminate errors and bottlenecks.
- It gives a pathway for clear start and end for the process without hassles.
67. What is the use of UML?
Ans:
Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental modeling language that provides a standard way to visualize the system. It is used to:
- Reason the system behavior
- Detect and eliminate errors
- Propose design plans to stakeholders
68. How do you analyze performance metrics?
Ans:
- Make sure that your key deliverables are met.
- The budget and time for the project should not be extended.
- Quality deliverables are maintained.
69. What do you think is the scope of Business Analysts in the Agile methodology perspective?
Ans:
With Agile methodology, Business Analysts act as a bridge between the development team and stakeholders. They act on key deliverables to prioritize and deliver the project in the stipulated time and budget.
70. What is meant by scope creep?
Ans:
Scope creep is defined as the uncontrolled or sudden changes or deviations in the project’s scope without changes in other resources of the project. It is due to the failure in proper monitoring, miscommunication, etc.
71. List the elicitation techniques in Business Analytics.
Ans:
Elicitation is a practice of collecting requirements from end customers and stakeholders; it is a requirement-gathering process. Various techniques involved in this are:
- Brainstorming
- Document analysis
- Focus group
- Interface analysis
- Interview
- Observation
- Prototyping
- Requirements workshop
- Reverse engineering
- Survey
72. What are the initial steps involved in product development?
Ans:
- Market analysis
- SWOT analysis
- Personas
- Competitor analysis
- Identifying the strategic vision
73. What are some of the steps that you can take to avoid scope creep?
Ans:
Following steps can be very useful in avoiding scope creep:
- Highly readable documentation about the project scope
- Defining proper change management schemas
- Accurate documentation of new requirements in logs
- Avoiding the addition of a lot of extra features to existing entities
74. Differentiate between BRD and SRS in Business Analysis.
Ans:
| BRD | SRS |
|---|---|
| High-level functional specification of software | Technical specification of software |
| Created by Business Analysts after client | Created by System Architects with technical expertise |
| Derived from the client requirement | Derived from BRS after client engagement. |
75. What is requirement prioritization in Business Analysis?
Ans:
Requirement prioritization, as the name suggests, is a structured process that is used to allocate the requirements based on the urgency with respect to many factors such as:
- Project phase
- Delivery schedule
- Cost capping
76. What are the techniques used for requirement prioritization?
Ans:
There are a variety of techniques used for requirement prioritization, and following are some of the widely used ones:
- MoSCoW technique
- 100-dollar method
- Five whys
- Kano analysis
- Requirement ranking method
77. What is the FRD and the SRD?
Ans:
Both FRD and SRD are forms of documents that are related to a use case. The FRD is an acronym for Functional Requirement Document while the SDD is an acronym for System Design Document.
78. What are the personal skills that make a Business Analyst different from all others?
Ans:
Any successful Business Analyst has the following set of soft skills that makes him/her stand apart from the rest of the crowd:
- Strong analytical skills to perform their job well.
- Problem-Solving skills:They need to have the ability to create a workable solution, find ways to resolve the problem and move forward towards successful completion of the project.
- Excellent Communication skills:To communicate with clients, developers, testers, etc. about project requirement, changes required.
- Technical Skills:Business analyst needs to have knowledge about a few testing, designing, reporting software. They need to know what technology tools are being used and what do they have to offer.
- Customer focused:Should be able to understand and get client’s requirements fulfilled.
- Decision- Making Skills:As an analyst, you should be able to assess the situation and select the best course of action. You need to be able to understand the viability of the solution.
- Managerial Skills:A business analyst needs to plan the project scope, he/she needs to direct the team members, forecast budget, handle change requests, etc. He/she needs to have the ability to manage the project.
79. Do you know anything about a database transaction?
Ans:
Any activity performed on a database is called as database transaction. The various activities that can be carried out in a database are addition, deletion, modification, searching etc.
80. Do you know anything about the OLTP systems?
Ans:
OLTP is the acronym for On-Line Transaction Processing. These systems can carry out the transactions from any kind of database at a remarkable speed. They are used for data entry and data retrieval from database.
81. What is the SWOT Analysis?
Ans:
SWOT is an acronym for Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is a technique popularly used for analyzing and assessing the organization for these things. It helps in any decision making process when there is a change or improvement required in the organization.
82. Elaborate on the BCG Matrix.
Ans:
BCG matrix is an acronym for Boston Consulting Group matrix. It helps to analyze the various business processes and products from a company. It plays a significant role in the following areas:
- Portfolio analysis
- Strategic management
- Product management
- Brand marketing
83. Elaborate on the PUGH Matrix.
Ans:
The PUGH matrix is also referred to as the Problem/ Design matrix. It helps in deciding the most optimal and alternate solution and is now a major part of Six Sigma technique.
84. What do you know about FMEA?
Ans:
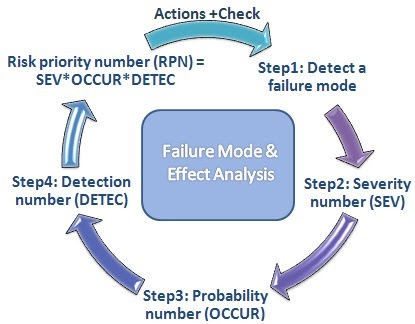
FMEA is an acronym for Failure Mode and Effects Analysis. It is used in product development, system engineering, and operations management to identify various failure modes and how severe can their effect be on the system.
85. Differentiate between the BPMN and the Gateway of BPMN.
Ans:
BPMN is the acronym for Business Process Model and Notation. It provides a graphical representation of the various processes that need to be carried out in a business.
The BPMN Gateway is a processing modeling component. It is used to control the sequence of processes to be followed and flow of interaction.
86. Who are the actors in a use-case?
Ans:
In the use-case, there are four types of actors- Human, hardware, System and Timer. Usually there can be two types of actors in a Use case- the Primary Actor and the Secondary Actor. While Primary actors initiate the process, the Secondary actors are given the function of assisting them.
87. Explain the 100-point method.
Ans:
The 100 -point method is used to set up the priority for different steps in a process. In this method, all the group members are required to assign points to every step in the process individually. The points earned by each step are then calculated and the step with highest points is awarded the highest priority.
88. What do you know about SQUARE?
Ans:
SQUARE is an acronym for Security Quality Requirements Engineering. It is a software engineering step that deals with documenting the security requirements of the system.
89. Explain the 8-Omega.
Ans:
The 8 -omega is a business framework used by business houses to improve their business. The key factors associated with it are:
- Strategy
- People
- Process
- Technology
90. What is a user-centered design methodology?
Ans:
In the user-centered design methodology, everything is done to make the end users comfortable and happy with the final product. The system is developed keeping in mind the end users and their requirements etc. The effectiveness of a system is judged by its “Application Usability”.
91. What do you know about Extends?
Ans:
Extends are relationships that are shown by dotted line. It is usually used to specify optional behavior which has no independent meaning. For example, the Help on “Sign on” extends use case “Sign on”.
92. Do you know anything about SaaS?
Ans:
SaaS is the acronym for Software as a Service. It is related to cloud computing. It is different from other software bundles as one doesn’t need this type of software to be installed on the machine. All that is needed is an Internet connection and a Web Browser to use it.
93. What is Application Usability?
Ans:
Application usability is the quality of the system that makes the system useful for its end users. System’s usability is good if it is capable of achieving users’ goals.
94. What is the Pair-Choice Technique?
Ans:
The Pair-Choice Technique is used to give priority to various items in a process. It is mainly used when distinctive stakeholders are involved in the project. This technique asks the group to compare each item with the other and select the one having the highest priority.
95. What is the difference between a Swimlane and a Pool?
Ans:
A Swimlane is related to a group of activities on an activity diagram while a pool is dedicated to only the activity of a single person.
96. What are the four important phases of business development?
Ans:
The four key phases of business development are
- Forming
- Storming
- Norming
- Performing
97. What is Agile?
Ans:
Agile is a technique that uses several light-weight methodologies such as Rapid Application Development (RAD), Extreme Programming (XP) and SCRUM. All these methodologies focus on the development of iterative solutions.
98. What do you know about the Scrum Method?
Ans:
The Scrum Method is one of the agile methods that is used to develop iterative information systems. In this method, a small team works on the assigned tasks for a time period of 30 days usually.
99. Elaborate the terms JAD and SWEBOK.
Ans:
JAD is the acronym for Joint Application Development while SWEBOK stands for Software Engineering Body of Knowledge.
100. What are the different steps that a business analyst must follow while benchmarking?
Ans:
In order to perform a foolproof benchmarking process, any business analyst needs to take the following steps while benchmarking:
- Identify the problem to benchmark in order define the scope of the work to be done.
- Decide and prioritize the processes that need to be benchmarked.
- Identify the different companies that have a similar product and specifically note down the leaders of the industries as well as the concerned companies.
- Do proper research on which process or practice can be favorable and if they are feasible enough to be adopted by your organization.
- After researching, identify the practice that can be implemented in your company.
- Finally, make a proper plan for improvements.
101. What is the requirement elicitation technique?
Ans:
Requirement elicitation is the process of requirement gathering from stakeholders, users, and customers by conducting meetings, questionnaires, interviews, brainstorming prototyping, sessions, etc.
Conclusion
Every organization hiring a Business Analyst wants to make sure that the hired professional should start contributing his valuable thoughts and ideas from the first day. The output of a BA’s work is utilized by IT people for developing the product and by the non-IT people to see the model of their application product.
102. How is a product developed from an idea?
Ans:
In order to develop a product from an idea, one needs to follow the given steps. The business analyst needs to perform, Market Analysis, Competitor Analysis, SWOT Analysis, Personas, Strategic Vision and Feature Set, Prioritize Features, Use Cases, SDLC, Storyboards, Test Cases, and Monitoring, Scalability.


